生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 2234-2241.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.11.015
收稿日期:2022-07-20
出版日期:2022-11-18
发布日期:2022-12-22
通讯作者:
*杨洪杏(1986年生),女,讲师,博士,主要从事土壤微生物研究。E-mail: yanghx@ahstu.edu.cn作者简介:周椿富(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事土壤微生物研究。
基金资助:
ZHOU Chunfu, YU Rui, WANG Xiang, CHUANG Shaochuang, YANG Hongxing*( ), XIE Yue
), XIE Yue
Received:2022-07-20
Online:2022-11-18
Published:2022-12-22
摘要:
农田土壤抗生素累积产生的生态风险已成为目前国内外研究的热点,土壤酶活性的变化对于研究抗生素影响下的农田土壤生态系统养分循环,具有重要的生态学意义。分别以酸性、中性和碱性农田土壤为研究对象,添加畜禽养殖业中常用的3种抗生素--土霉素(Oxytetracycline,OTC)、恩诺沙星(Enrofloxacin,ENR)和磺胺二甲嘧啶(Sulfamethazine,SM2)进行处理,分析了土壤中脲酶、过氧化氢酶和磷酸酶对抗生素的敏感性。结果表明,在添加抗生素处理的0-28 d过程中,脲酶活性整体呈现抑制趋势,过氧化氢酶活性整体呈现促进趋势,磷酸酶活性随着添加抗生素的不同呈现不同的变化趋势。在28 d时,与对照组相比,脲酶活性在添加3种抗生素的酸性、中性土壤中及添加ENR与SM2的碱性土壤中均显著受到抑制,抑制率为38.03%-96.08%,而在添加OTC的碱性土壤中受到促进,促进率为28.43%;过氧化氢酶活性在添加3种抗生素的酸性土壤中及添加OTC与SM2的中性、碱性土壤中均受到促进,促进率为24.88%-268.25%,而在添加ENR的中性、碱性土壤中受到抑制,抑制率为18.42%和29.04%;磷酸酶活性在添加OTC的3种土壤中均受到促进,促进率为14.73%-101.26%,而在添加ENR的3种土壤中均无显著变化,在添加SM2的3种土壤中均受到抑制,抑制率为61.83%-70.54%。该研究表明抗生素对土壤酶活性影响复杂,尤其是对脲酶活性的抑制,减弱了土壤氮循环相关酶的代谢功能及其稳定性,进而影响土壤生态系统的功能稳定性。
中图分类号:
周椿富, 于锐, 王翔, 闯绍闯, 杨洪杏, 谢越. 抗生素对不同土壤中酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2234-2241.
ZHOU Chunfu, YU Rui, WANG Xiang, CHUANG Shaochuang, YANG Hongxing, XIE Yue. Effects of Antibiotics on Soil Enzyme Activities in Different Soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2234-2241.
| 组别 Test group | 供试土壤类型 Test soil | 抗生素 Antibiotic |
|---|---|---|
| CKAc | 酸性 | 0 |
| OTCAc | 酸性 | 20 mg·kg-1 OTC |
| ENRAc | 酸性 | 20 mg·kg-1 ENR |
| SM2Ac | 酸性 | 150 mg·kg-1 SM2 |
| CKNe | 中性 | 0 |
| OTCNe | 中性 | 20 mg·kg-1 OTC |
| ENRNe | 中性 | 20 mg·kg-1 ENR |
| SM2Ne | 中性 | 150 mg·kg-1 SM2 |
| CKAl | 碱性 | 0 |
| OTCAl | 碱性 | 20 mg·kg-1 OTC |
| ENRAl | 碱性 | 20 mg·kg-1 ENR |
| SM2Al | 碱性 | 150 mg·kg-1 SM2 |
表1 不同土壤处理下的抗生素添加量
Table 1 Antibiotic addition under different soil treatments
| 组别 Test group | 供试土壤类型 Test soil | 抗生素 Antibiotic |
|---|---|---|
| CKAc | 酸性 | 0 |
| OTCAc | 酸性 | 20 mg·kg-1 OTC |
| ENRAc | 酸性 | 20 mg·kg-1 ENR |
| SM2Ac | 酸性 | 150 mg·kg-1 SM2 |
| CKNe | 中性 | 0 |
| OTCNe | 中性 | 20 mg·kg-1 OTC |
| ENRNe | 中性 | 20 mg·kg-1 ENR |
| SM2Ne | 中性 | 150 mg·kg-1 SM2 |
| CKAl | 碱性 | 0 |
| OTCAl | 碱性 | 20 mg·kg-1 OTC |
| ENRAl | 碱性 | 20 mg·kg-1 ENR |
| SM2Al | 碱性 | 150 mg·kg-1 SM2 |
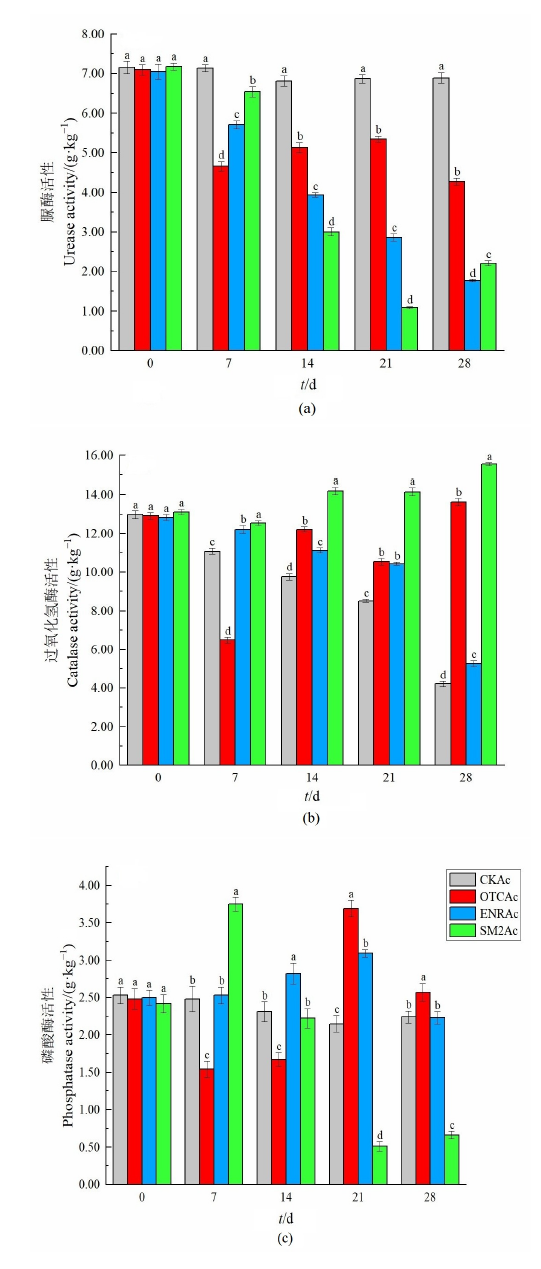
图1 抗生素对酸性土壤中酶活性的影响 CKAc:酸性土壤不添加抗生素;OTCAc:酸性土壤添加土霉素;ENRAc:酸性土壤添加恩诺沙星;SM2Ac:酸性土壤添加磺胺二甲嘧啶。柱上不同小写字母表示差异达到显著水平(P<0.05),下同
Figure 1 Effect of antibiotics on enzyme activity in acid soil CKAc: Acid soil without antibiotics; OTCAc: Acid soil supplemented with oxytetracycline; ENRAc: Acid soil supplemented with enrofloxacin; SM2Ac: Acid soil supplemented with sulfamethazine. Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate the significantly different at 5% level, the same as below
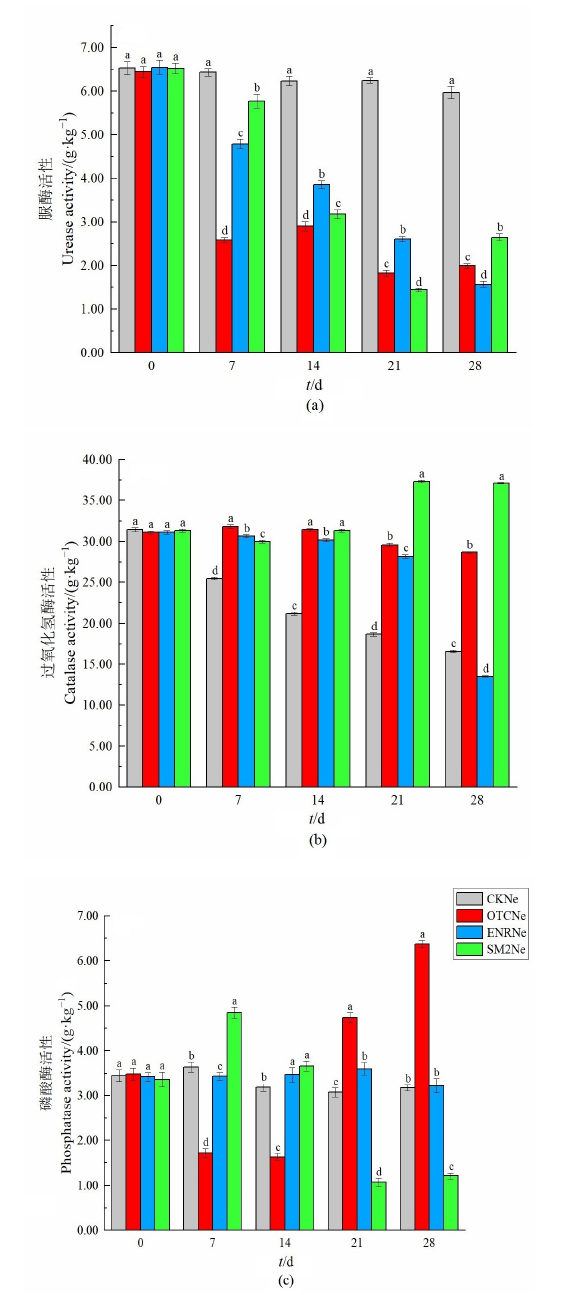
图2 抗生素对中性土壤中酶活性的影响 CKNe:中性土壤不添加抗生素;OTCNe:中性土壤添加土霉素;ENRNe:中性土壤添加恩诺沙星;SM2Ne:中性土壤添加磺胺二甲嘧啶
Figure 2 Effect of antibiotics on enzyme activity in neutral soil CKNe: Neutral soil without antibiotics; OTCNe: Neutral soil supplemented with oxytetracycline; ENRNe: Neutral soil supplemented with enrofloxacin; SM2Ne: Neutral soil supplemented with sulfamethazine
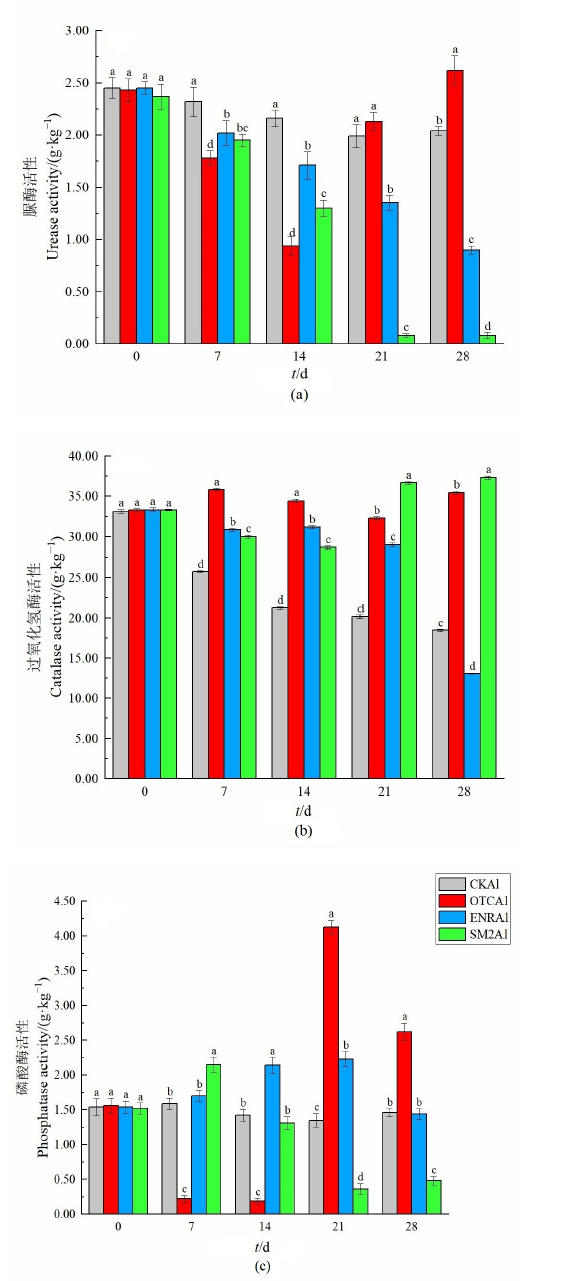
图3 抗生素对碱性土壤中酶活性的影响 CKAl:碱性土壤不添加抗生素;OTCAl:碱性土壤添加土霉素;ENRAl:碱性土壤添加恩诺沙星;SM2Al:碱性土壤添加磺胺二甲嘧啶
Figure 3 Effect of antibiotics on enzyme activity in alkaline soil CKAl: Alkaline soil without antibiotics; OTCAl: Alkaline soil supplemented with oxytetracycline; ENRAl: Alkaline soil supplemented with enrofloxacin; SM2Al: Alkaline soil supplemented with sulfamethazine
| [1] |
AMORIM C L, MOREIRA I S, MAIA A S, et al., 2014. Biodegradation of ofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin as single and mixed substrates by Labrys portucalensis F11[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(7): 3181-3190.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BARAN W, ADAMEK E, ZIEMIANSKA J, et al., 2011. Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 196: 1-15.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
CHEN J L, MOORHEAD D L, 2021. Progressively decreased nitrogen-stimulation of soil phosphatase activity with long-term nitrogen addition[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 169: 104213.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DONNELLY K C, CLAXTON L D, HUEBNER H J, et al., 1998. Mutagenic interactions of model chemical mixtures[J]. Chemosphere, 37(7): 1253-1261.
PMID |
| [5] |
ENSENBACH U, NAGEL R, 1997. Toxicity of binary chemical mixtures: effects on reproduction of zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio)[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 32(2): 204-210.
PMID |
| [6] |
JABBOROVA D, SAYYED R Z, AZIMOV A, et al., 2021. Impact of mineral fertilizers on mineral nutrients in the ginger rhizome and on soil enzymes activities and soil properties[J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(9): 5268-5274.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
LAHR J, MOREAU C, FABER J H, 2005. Do veterinary pharmaceuticals affect soil functioning at environmentally relevant concentrations?[J]. PloS One, 9(11): e107723.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIAO X, LI B, ZOU R, et al., 2016. Antibiotic sulfanilamide biodegradation by acclimated microbial populations[J]. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 100(5): 2439-2447.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
LIU F, YING G G, TAO R, et al., 2009. Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities[J]. Environmental Pollution, 157(5): 1636-1642.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
MA Q Y, LI J W, AAMER M, et al., 2020. Effect of Chinese Milk Vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) and rice straw incorporated in paddy soil on greenhouse gas emission and soil properties[J]. Agronomy, 10(5): 717.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
QIN J M, XIONG H Y, MA H T, et al., 2019. Effects of different fertilizers on residues of oxytetracycline and microbial activity in soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(1): 161-170.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
QIAN X, GU J, SUN W, et al., 2017. Diversity, abundance, and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in various types of animal manure following industrial composting[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 344: 716-722.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SIWACH A, KAUSHAL S, BAISHYA R, 2021. Terricolous mosses impact soil microbial biomass carbon and enzymatic activity under temperate forest types of the Garhwal Himalayas[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(8): 516-516.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
TOPAL M, SENEL G U, OEBEK E, et al., 2016. Investigation of relationships between removals of tetracycline and degradation products and physicochemical parameters in municipal wastewater treatment plant[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 173: 1-9.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
VAN BOECKEL T P, BROWER C, GILBERT M, et al., 2015. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(18): 5649-5654.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YANG J F, YING G G, ZHAO J L, et al., 2010. Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC-MS/MS[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 408(16): 3424-3432.
DOI URL |
| [17] | ZHANG Y, SNOW D D, PARKER D, et al., 2013. Intracellular and extracellular antimicrobial resistance genes in the sludge of livestock waste management structures[J]. Environmental Science&Technology, 47(18): 10206-10213. |
| [18] |
ZHU Y G, JOHNSON T A, SU J Q, et al., 2013. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(9): 3435-3440.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 鲍艳宇, 2008. 四环素类抗生素在土壤中的环境行为及生态毒性研究[D]. 天津: 南开大学: 18-72. |
| BAO Y Y, 2008. Environmental behavior and eco-toxicity of tetracycline antibiotics in soils[D]. Tianjin: Nankai University: 18-72. | |
| [20] | 陈俊辉, 2010. 抗生素类污染物在土壤含水氧化物中吸附行为的研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学: 6-35. |
| CHEN J H, 2010. Study on adsorption of antibiotic contaminants to hydrous oxidexidess in soil matrix[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University: 6-35. | |
| [21] | 陈智学, 2013. 土霉素对酶活性及微生物群落代谢的影响[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学: 9-27. |
| CHEN X Z, 2013. Effects of OTC on enzyme acticities and microbial community metabolic profiles[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University: 9-27. | |
| [22] | 程章, 2009. 诺氟沙星对阿部鲻鰕鯱细胞色素P450 1A1和P-gp基因诱导和表达的影响[D]. 广州: 暨南大学: 49-56. |
| CHENG Z, 2009. Two biomarker cytochrome P450 1A1 and P-glycoprotein in Mugilogobius abei: cDNA clone expression induced by Norfloxacin[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University: 49-56. | |
| [23] | 杜黎明, 吴昊, 陈彩萍, 2006. 喹诺酮类药物的分析方法与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:8-36. |
| DU L M, WU H, CHEN C P, 2006. Analysis method and application of quinolones[M]. Beijing: Science Press:8-36. | |
| [24] | 范菲菲, 朱健, 闫献芳, 等, 2013. 兽药土霉素在土壤环境中的行为[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 49(8): 58-59. |
| FAN F F, ZHU J, YAN X F, et al., 2013. Behavior of veterinary drug oxytetracycline in soil environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 49(8): 58-59. | |
| [25] | 顾觉奋, 2002. 合理应用青霉素类和头孢菌素类抗生素[J]. 药学与临床研究, 10(3): 49-54. |
| GU J F, 2002. Rational application of penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics[J]. Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 10(3): 49-54. | |
| [26] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社: 260-339. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzymes and the research methods[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 260-339. | |
| [27] | 金彩霞, 刘军军, 鲍林林, 等, 2010. 磺胺间甲氧嘧啶-镉复合污染对作物种子发芽的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 30(6): 839-844. |
| JIN C X, LIU J J, BAO L L, et al., 2010. Joint toxicity of sulfamonomethoxine and Cd on seed germination and root elongation of crops in soil[J]. China Environmental Science, 30(6): 839-844. | |
| [28] | 金兰淑, 申龙, 刘艳茹, 等, 2013. 鸡粪与四环素对土壤脲酶和磷酸酶活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 32(5): 986-990. |
| JIN L S, SHEN L, LIU Y R, et al., 2013. Effect of chicken manure and tetracycline on soil urease and phosphatase activity[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 32(5): 986-990. | |
| [29] | 刘超, 赵光影, 宋艳宇, 等, 2019. 气候变化背景下湿地土壤酶活性研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 35(33): 91-97. |
| LIU C, ZHAO G Y, SONG Y Y, et al., 2019. Soil enzyme activity in wetland under the background of climate change: Research progress[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 35(33): 91-97. | |
| [30] | 李凯旋, 2018. 三氯生和克拉霉素复合污染对土壤酶活性及微生物群落结构的影响[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学: 11-35. |
| LI K X, 2018. The combined contamination of triclosan and clarithromycin on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University: 11-35. | |
| [31] | 刘莉莉, 林匡飞, 苏爱华, 等, 2008. 四溴双酚A对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 30(6): 5. |
| LIU L L, LIN K F, SU A H, et al., 2008. Effects of tetrabromobisphenol A on soil enzyme activities[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 30(6): 5. | |
| [32] | 刘文英, 2003. 药物分析[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社: 10-66. |
| LIU W Y, 2003. Pharmaceutical analysis[M]. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House: 10-66. | |
| [33] | 陆琴, 李冬琴, 2020. 土壤酶及其生态指示作用研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 48(18): 14-17. |
| LU Q, LI D Q, 2020. Research progress on soil enzymes and their functioning as ecosystem indicators[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 48(18): 14-17. | |
| [34] | 李鑫, 2015. 四环素类抗生素在不同质地土壤中迁移模拟研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学: 10-39. |
| LI X, 2015. The study on environmental behavior of tetracycline antibiotics in different texture soils[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University: 10-39. | |
| [35] | 毛书帅, 2016. 三种抗生素和铜单一及复合污染对土壤酶和微生物群落功能多样性的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学: 14-60. |
| MAO S S, 2016. Single and joint toxicity of three typical antibiotics and Cu on soil microbial community function diversity and soil enzyme activity[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University: 14-60. | |
| [36] | 隋倩雯, 张俊亚, 魏源送, 等, 2015. 畜禽养殖过程抗生素使用与耐药病原菌及其抗性基因赋存的研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 10(5): 20-34. |
| SUI Q W, ZHANG J Y, WEI Y S, et al., 2015. Veterinary antibiotics use, occurrence of antibiotic resistance pathogen and its antibiotic resistance genes in animal production: An overview[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 10(5): 20-34. | |
| [37] | 汪杏, 沈根祥, 胡双庆, 等, 2016. 铬(Ⅵ)和菲单一及复合污染对土壤微生物酶活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(7): 8. |
| WANG X, SHEN G X, HU S Q, et al., 2016. Effects of single and joint pollution of chromium (Ⅵ) and phenanthrene on microbiological enzyme activities in soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(7): 8. | |
| [38] | 王冉, 刘铁铮, 王恬, 2006. 抗生素在环境中的转归及其生态毒性[J]. 生态学报, 26(1): 265-270. |
| WANG R, LIU T Z, WANG T, 2006. The fate of antibiotics in environment and its ecotoxicology: A review[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(1): 265-270. | |
| [39] | 吴杰, 李志琳, 徐佳迎, 等, 2019. 兽用抗生素磺胺二甲嘧啶对稻田N2O排放的影响及其微生物机制[J]. 环境科学, 40(6): 2847-2857. |
| WU J, LI Z L, XU J Y, et al., 2019. Effects of the veterinary antibiotic sulfamethazine on N2O emissions and the associated microbiological mechanism in a rice field[J]. Environmental Science, 40(6): 2847-2857. | |
| [40] | 魏子艳, 王金花, 夏晓明, 等, 2014. 三种抗生素对蔬菜种子芽与根伸长的生态毒性效应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(2): 237-242. |
| WEI Z X, WANG J H, XIA X M, et al., 2014. Ecotoxicity of three antibiotics to shoots and root elongation of cucumber, rape and chinese cabbage[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(2): 237-242. | |
| [41] | 徐东峰, 2000. 恩诺沙星的作用机理与妙用[J]. 湖北畜牧兽医 (5): 31-32. |
| XU D F, 2000. Action mechanism and wonderful use of enrofloxacin[J]. Hubei Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences (5): 31-32. | |
| [42] | 杨玖, 2014. 磺胺类抗生素与锌对堆肥过程中酶活性及微生物群落结构多样性的影响[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学: 28-36. |
| YANG J, 2014. Effects of sulfonamides and znic on enzymeactivity and microbial community diversity during composting[D]. Xianyang: Northwest Normal University: 28-36. | |
| [43] | 闫赛红, 2015. 恩诺沙星与镉单一及复合污染对土壤微生物群落结构和功能的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学: 18-66. |
| YAN S H, 2015. Single and joint toxicity of enrofloxacin and Cd on soil microbial community structure and function[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University: 18-66. | |
| [44] | 张晨, 张丽红, 李亚宁, 等, 2018. 典型磺胺类抗生素对土壤脱氢酶和过氧化氢酶活性的影响[J]. 安全与环境学报, 18(6): 2379-2382. |
| ZHANG C, ZHANG L H, LI Y N, et al., 2018. Impact of the typical sulfonamides on the enzyme activities of the soil[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 18(6): 2379-2382. | |
| [45] | 张昊, 张利兰, 王佳, 等, 2012. 土霉素暴露对小麦根际抗生素抗性细菌及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(2): 508-516. |
|
ZHANG H, ZHANG L L, WNAG J, et al., 2012. Influence of oxytetracycline exposure on antibiotic resistant bacteria and enzyme activities in wheat rhizosphere soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(2): 508-516.
DOI URL |
|
| [46] | 张书菡, 2019. 环境抗生素抑制土壤脲酶的毒性效应与机制研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学: 19-39. |
| ZHANG S H, 2019. Study on toxicity and mechanism of environmental antibiotics inhibited soil urease[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Normal University: 19-39. | |
| [47] | 张文婕, 杨莉莉, 王金花, 等, 2020. 三种抗生素与铜复合污染对土壤过氧化氢酶活性的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(1): 135-143. |
| ZHANG W J, YANG L L, WANG J H, et al., 2020. Effect of combined pollution of three antibiotics and Cu on soil catalase activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 37(1): 135-143. |
| [1] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [2] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [3] | 孙建波, 畅文军, 李文彬, 张世清, 李春强, 彭明. 香蕉不同生育期根际微生物生物量及土壤酶活的变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1169-1174. |
| [4] | 刘畅, 罗艳丽, 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐. 奎屯河下游区域地下水和农田土壤砷的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078. |
| [5] | 王飞, 赵颖. 太原市污灌区农田土壤中多环芳烃污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 160-169. |
| [6] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [7] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [8] | 李欣, 陈小华, 顾海蓉, 钱晓雍, 沈根祥, 赵庆节, 白玉杰. 典型农田土壤酶活性分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1634-1641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
