生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 2339-2350.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.12.009
冉晓追1( ), 刘鸿雁1,3,*(
), 刘鸿雁1,3,*( ), 涂宇1, 顾小凤1, 于恩江2
), 涂宇1, 顾小凤1, 于恩江2
收稿日期:2021-06-17
出版日期:2021-12-18
发布日期:2022-01-04
通讯作者:
*刘鸿雁(1969年生),女,教授,博士,主要从事土壤环境与污染修复研究。E-mail: hyliu@gzu.edu.cn作者简介:冉晓追(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事土壤重金属污染与修复方向研究。E-mail: 1347135148@qq.com
基金资助:
RAN Xiaozhui1( ), LIU Hongyan1,3,*(
), LIU Hongyan1,3,*( ), TU Yu1, GU Xiaofeng1, YU Enjiang2
), TU Yu1, GU Xiaofeng1, YU Enjiang2
Received:2021-06-17
Online:2021-12-18
Published:2022-01-04
摘要:
为探究黔西北地质高背景区,工业污染小流域(MS)的大气TSP微观形貌及其载带重金属(Cd、As、Pb、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn)的质量浓度、季度分布特征和健康风险,以没有明显污染源的小流域(HS)为对照,于2018年5月—2020年11月分四季采集大气TSP样品,使用ICP-MS测定TSP的重金属(Cd、As、Pb、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn)质量分数,SEM-EDS对TSP的微观形貌以及能谱进行分析;并采用US EPA推荐的人体暴露健康风险评价模型对TSP重金属健康风险进行评价。结果表明,污染区TSP微观形貌主要为规则的“块状”、“片状”和“层状”,以及不规则的“球状”和“蓬松状”,O、Si、Ca、C、Zn为特征元素,呈现扬尘和工业源污染特征;对照区TSP为“片状”、“层状”、“块状”和“类球状”,以O、Si、Ca为特征元素,呈现矿物源和土壤源的特征。对照和污染区的TSP质量浓度范围分别为55.69—84.52 μg∙m-3和130.27—218.22 μg∙m-3,均呈现冬>春>秋>夏的趋势;污染区的TSP中Cd、As、Pb、Zn的质量浓度显著大于对照区,其中,Pb和Zn的质量浓度分别是对照区的10.12倍和14.43倍。健康风险评价结果表明,两个区的重金属非致癌风险总值(HI)均小于1,没有非致癌健康风险;两个区的Cd、Cr和Ni的致癌风险值(R)均处于10-7—10-4之间,其Cd、As的R值远高于非地质高背景区,As的R值都达到10-4以上,存在As的潜在健康风险,在黔西北地质高背景区需注意防范大气TSP中 As的潜在致癌风险。
中图分类号:
冉晓追, 刘鸿雁, 涂宇, 顾小凤, 于恩江. 大气TSP微观形貌、重金属分布特征及健康风险评价——以黔西北地质高背景与污染叠加区典型小流域为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2339-2350.
RAN Xiaozhui, LIU Hongyan, TU Yu, GU Xiaofeng, YU Enjiang. Micro-morphology, Heavy Metal Distribution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of TSP: A Case Study in Typical Watershed with Superposition of Industry Pollution under High Geological Background in Northwest Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2339-2350.
| 元素 Element | Cd | As | Pb | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准物质测定值 Measured value of reference material/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.50±0.02 | 350.74±15.54 | 493.16±13.42 | 104.70±3.16 | 138.95±4.19 | 45.01±2.18 | 427.51±19.67 |
| 标准物质标准值 Standard value of reference material/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.45±0.06 | 412.00±16.00 | 552.00±29.00 | 118.00±7.00 | 144.00±6.00 | 40.00±4.00 | 494.00±25.00 |
| 回收率 Recovery rate/% | 111.11 | 85.13 | 89.34 | 88.73 | 96.49 | 112.53 | 86.54 |
表1 7种重金属元素测定标准物质值及回收率
Table 1 Measured values and recovery rates of 7 heavy metal elements in reference materials
| 元素 Element | Cd | As | Pb | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标准物质测定值 Measured value of reference material/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.50±0.02 | 350.74±15.54 | 493.16±13.42 | 104.70±3.16 | 138.95±4.19 | 45.01±2.18 | 427.51±19.67 |
| 标准物质标准值 Standard value of reference material/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.45±0.06 | 412.00±16.00 | 552.00±29.00 | 118.00±7.00 | 144.00±6.00 | 40.00±4.00 | 494.00±25.00 |
| 回收率 Recovery rate/% | 111.11 | 85.13 | 89.34 | 88.73 | 96.49 | 112.53 | 86.54 |
| 参数 Parameter | 含义 Meaning | 单位 Unit | 成年男性 Adult male | 成年女性 Adult female | 儿童 (1—6岁) Children | 文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR | 呼吸速率 Breathing rate | m3∙d-1 | 19.02 | 14.17 | 5 | DB 11/T656—2009; 王宗爽等, |
| EF | 暴露频率 Exposure frequency | d∙a-1 | 350 | 350 | 350 | DB 11/T656—2009 |
| ED | 暴露持续时间Exposure duration | a | 30 | 30 | 6 | DB 11/T656—2009 |
| BW | 体重 Weight | kg | 62.7 | 54.4 | 15 | DB 11/T656—2009; 王宗爽等, |
| AT (致癌Carcinogenic) | 平均暴露时间 Average exposure time | d | 70×365 | 70×365 | 70×365 | 杜金花等, (Du et al., |
| AT (非致癌Non-carcinogenic) | 30×365 | 30×365 | 6×365 | DB 11/T656—2009; 杜金花等, |
表2 经呼吸进入人体的暴露应用参数
Table 2 Application parameters of exposure to human body through breathing
| 参数 Parameter | 含义 Meaning | 单位 Unit | 成年男性 Adult male | 成年女性 Adult female | 儿童 (1—6岁) Children | 文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR | 呼吸速率 Breathing rate | m3∙d-1 | 19.02 | 14.17 | 5 | DB 11/T656—2009; 王宗爽等, |
| EF | 暴露频率 Exposure frequency | d∙a-1 | 350 | 350 | 350 | DB 11/T656—2009 |
| ED | 暴露持续时间Exposure duration | a | 30 | 30 | 6 | DB 11/T656—2009 |
| BW | 体重 Weight | kg | 62.7 | 54.4 | 15 | DB 11/T656—2009; 王宗爽等, |
| AT (致癌Carcinogenic) | 平均暴露时间 Average exposure time | d | 70×365 | 70×365 | 70×365 | 杜金花等, (Du et al., |
| AT (非致癌Non-carcinogenic) | 30×365 | 30×365 | 6×365 | DB 11/T656—2009; 杜金花等, |

图2 两个小流域TSP微观形貌季节分布特征及能谱图(×4000倍) MS:工业污染小流域;HS:无明显污染源小流域;n=36
Fig. 2 Seasonal distribution characteristics and energy spectrum of TSP micro-morphology in two small watersheds (×4000 times) MS: Small watershed polluted by industry; HS: Small watershed without obvious pollution source; n=36
| 元素Element | MS | HS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 质量分数 Mass fraction/% | 原子百分比 Atomic percentage/% | 质量分数 Mass fraction/% | 原子百分比 Atomic percentage/% | ||
| C | 34.37±19.52 | 43.49±19.68 | 18.34±2.17 | 26.97±3.19 | |
| O | 43.72±6.64 | 44.90±12.31 | 50.53±2.72 | 55.81±3.02 | |
| Mg | 0.36±0.15 | 0.24±0.09 | 2.50±0.78 | 1.81±0.55 | |
| Al | 3.72±5.55 | 2.39±3.74 | 0.53±0.15 | 0.35±0.10 | |
| Si | 9.23±7.35 | 5.36±4.65 | 14.86±12.02 | 9.28±7.44 | |
| Cl | 0.50±0.24 | 0.22±0.11 | 0.96±0.71 | 0.47±0.36 | |
| K | 0.29±0.06 | 0.11±0.01 | 0.31±0.08 | 0.15±0.03 | |
| Ca | 8.07±14.43 | 3.70±6.89 | 15.09±10.27 | 6.73±4.68 | |
| Fe | 2.49±1.94 | 0.77±0.66 | 0.63±0.36 | 0.20±0.11 | |
| Zn | 15.56±10.29 | 8.55±6.18 | 0.58±0.49 | 0.17±0.14 | |
表3 两个小流域TSP各元素质量分数和原子百分比
Table 3 Mass fraction and atomic percentage of each element in TSP of the two small watersheds
| 元素Element | MS | HS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 质量分数 Mass fraction/% | 原子百分比 Atomic percentage/% | 质量分数 Mass fraction/% | 原子百分比 Atomic percentage/% | ||
| C | 34.37±19.52 | 43.49±19.68 | 18.34±2.17 | 26.97±3.19 | |
| O | 43.72±6.64 | 44.90±12.31 | 50.53±2.72 | 55.81±3.02 | |
| Mg | 0.36±0.15 | 0.24±0.09 | 2.50±0.78 | 1.81±0.55 | |
| Al | 3.72±5.55 | 2.39±3.74 | 0.53±0.15 | 0.35±0.10 | |
| Si | 9.23±7.35 | 5.36±4.65 | 14.86±12.02 | 9.28±7.44 | |
| Cl | 0.50±0.24 | 0.22±0.11 | 0.96±0.71 | 0.47±0.36 | |
| K | 0.29±0.06 | 0.11±0.01 | 0.31±0.08 | 0.15±0.03 | |
| Ca | 8.07±14.43 | 3.70±6.89 | 15.09±10.27 | 6.73±4.68 | |
| Fe | 2.49±1.94 | 0.77±0.66 | 0.63±0.36 | 0.20±0.11 | |
| Zn | 15.56±10.29 | 8.55±6.18 | 0.58±0.49 | 0.17±0.14 | |
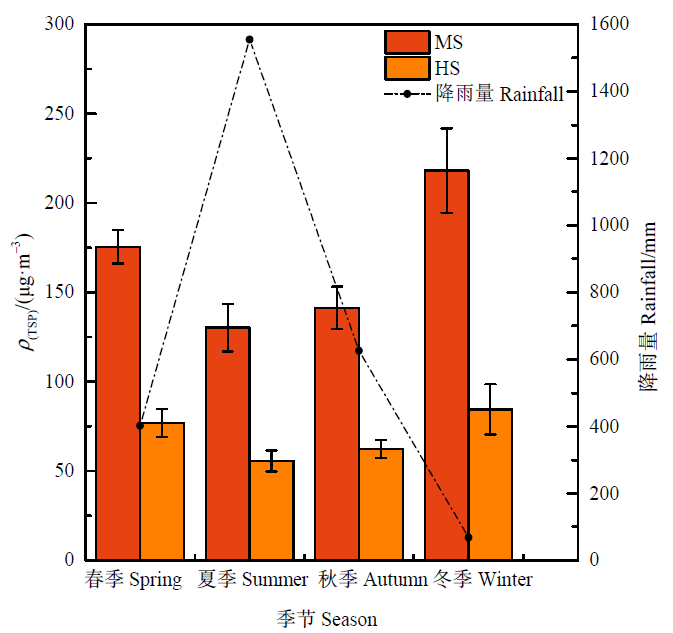
图3 两个小流域TSP的质量浓度以及降雨总量季节分布 MS:工业污染小流域;HS:无明显污染源小流域;n=113。下同
Fig. 3 Seasonal distribution of TSP mass concentration and total rainfall in two small watersheds MS: Small watershed polluted by industry; HS: Small watershed without obvious pollution source; n=113. The same below
| 致癌元素Carcinogenic element | 项目Project | ILCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | As | Cr | Ni | |||
| MS | 成年男性 Adult male | 6.23×10-5 | 1.91×10-4 | 5.66×10-5 | 6.25×10-7 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 5.35×10-5 | 1.64×10-4 | 4.86×10-5 | 5.37×10-7 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 6.85×10-5 | 2.10×10-4 | 6.22×10-5 | 6.87×10-7 | ||
| HS | 成年男性 Adult male | 2.23×10-5 | 1.22×10-4 | 3.88×10-5 | 2.41×10-6 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 1.92×10-5 | 1.04×10-4 | 3.34×10-5 | 2.07×10-6 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 2.45×10-5 | 1.34×10-4 | 4.27×10-5 | 2.64×10-6 | ||
| 非致癌元素Non-carcinogenic element | HQ | HI | ||||
| Pb | Cu | Zn | ||||
| MS | 成年男性 Adult male | 8.19×10-2 | 5.57×10-5 | 1.63×10-3 | 8.36×10-2 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 7.03×10-2 | 4.79×10-5 | 1.40×10-3 | 7.18×10-2 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 9.00×10-2 | 6.12×10-5 | 1.79×10-3 | 9.19×10-2 | ||
| HS | 成年男性 Adult male | 8.10×10-3 | 2.50×10-5 | 1.13×10-4 | 8.24×10-3 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 6.95×10-3 | 2.14×10-5 | 9.67×10-5 | 7.07×10-3 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 8.90×10-3 | 2.74×10-5 | 1.24×10-4 | 9.05×10-3 | ||
表4 两个小流域大气TSP重金属健康风险值
Table 4 Health risk values of heavy metal in atmospheric TSP in two small watersheds
| 致癌元素Carcinogenic element | 项目Project | ILCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | As | Cr | Ni | |||
| MS | 成年男性 Adult male | 6.23×10-5 | 1.91×10-4 | 5.66×10-5 | 6.25×10-7 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 5.35×10-5 | 1.64×10-4 | 4.86×10-5 | 5.37×10-7 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 6.85×10-5 | 2.10×10-4 | 6.22×10-5 | 6.87×10-7 | ||
| HS | 成年男性 Adult male | 2.23×10-5 | 1.22×10-4 | 3.88×10-5 | 2.41×10-6 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 1.92×10-5 | 1.04×10-4 | 3.34×10-5 | 2.07×10-6 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 2.45×10-5 | 1.34×10-4 | 4.27×10-5 | 2.64×10-6 | ||
| 非致癌元素Non-carcinogenic element | HQ | HI | ||||
| Pb | Cu | Zn | ||||
| MS | 成年男性 Adult male | 8.19×10-2 | 5.57×10-5 | 1.63×10-3 | 8.36×10-2 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 7.03×10-2 | 4.79×10-5 | 1.40×10-3 | 7.18×10-2 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 9.00×10-2 | 6.12×10-5 | 1.79×10-3 | 9.19×10-2 | ||
| HS | 成年男性 Adult male | 8.10×10-3 | 2.50×10-5 | 1.13×10-4 | 8.24×10-3 | |
| 成年女性 Adult female | 6.95×10-3 | 2.14×10-5 | 9.67×10-5 | 7.07×10-3 | ||
| 儿童 Children | 8.90×10-3 | 2.74×10-5 | 1.24×10-4 | 9.05×10-3 | ||
| [1] |
CHIN Y H, HUNG C C, SHENG L L, et al., 2016. Elemental characterization and source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in the western coastal area of central Taiwan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 541: 1139-1150.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CUSACK M, ARRIETA J M, DUARTE C M, 2020. Source Apportionment and Elemental Composition of Atmospheric Total Suspended Particulates (TSP) Over the Red Sea Coast of Saudi Arabia[J]. Earth Systems and Environment, 4(4): 777-788.
DOI URL |
| [3] | DAVID A E, INENGITE A K, UZOEKWE S, et al., 2017. Measurement of total suspended particulate matter (TSP) in an urban environment: Yenagoa and its environs[J]. Journal of Geography Environment and Earth Science International, 11(3): 1-8. |
| [4] |
EMOHAMMED G, KARANI G, MITCHELL D, 2017. Trace elemental composition in PM10 and PM2.5 collected in Cardiff, Wales[J]. Energy Procedia, 111: 540-547.
DOI URL |
| [5] | EPA, 1991. Risk assessment guidance for super fund volume I: human health evaluation manual. Supplemental guidance. “standard default exposure fators”interim final [S]. Ethernet for Plant Automation. |
| [6] |
JIANG S, YANG F, CHAN K L, et al., 2014. Water solubility of metals in coarse PM and PM2.5 in typical urban environment in Hong Kong[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 5(2): 236-244.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KONG S F, LU B, JI Y Q, et al., 2012. Risk assessment of heavy metals in road and soil dusts within PM2.5, PM10 and PM100 fractions in Dongying city, Shandong Province, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring: JEM, 14(3):791-803.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
KURNIAWAN S, HUBOYO H S, SAMADIKUN B P, 2021. Prediction of coal dust dispersion to total suspended particulate (TSP) concentration in ambient air quality, case study: PLTU Tanjung Jati B[J]. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/623/1/012035.
DOI |
| [9] |
LI H M, WANG J H, WANG Q G, et al., 2015. Chemical fractionation of arsenic and heavy metals in fine particle matter and its implications for risk assessment: A case study in Nanjing, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 103: 339-346.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI P H, KONG S F, GENG C M, et al., 2013. Assessing the hazardous risks of vehicle inspection workers' exposure to particulate heavy metals in their work places[J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 13(1): 255-265.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI Y G, HUANG H, GRIFFITH S M, et al., 2017. Quantifying the relationship between visibility degradation and PM2.5 constituents at a suburban site in Hong Kong: Differentiating contributions from hydrophilic and hydrophobic organic compounds[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 575: 1571-1581.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LV J S, LIU Y, ZHANG Z L, et al., 2013. Factorial kriging and stepwise regression approach to identify environmental factors influencing spatial multi-scale variability of heavy metals in soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 261: 387-397.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MA J, SINGHIRUNNUSORN W, 2012. Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface dusts of Maha Sarakham Municipality[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 50(1): 280-293.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
EMBIALE A, ZEWGE F, CHANDRAVANSHI B S, et al., 2019. Short-term exposure assessment to particulate matter and total volatile organic compounds in indoor air during cooking ethiopian sauces (Wot) using electricity, kerosene and charcoal fuels[J]. Indoor and Built Environment, 28(8): 1140-1154.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
NA Z, LIU J S, WANG Q C, et al., 2010. Heavy metals exposure of children from stairway and sidewalk dust in the smelting district, northeast of China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 44(27): 3239-3245.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
TAO W, JOAQUIM R, JORDI S, et al., 2019. Characterization and risk assessment of total suspended particles (TSP) and fine particles (PM2.5) in a rural transformational e-waste recycling region of southern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 692:432-440.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Environmental Protection Agency, 2013. Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) [EB/OL] http://www.epa.gov/iris/ , 2013-10-14. |
| [18] | WHO, 2018. Global Health Observatory Data Repository [Z]. World Health Organizations: 2018-07-06. |
| [19] |
ZHANG Z, LIU J, SHEN F H, et al., 2020. Temporal influence of reaction atmosphere and chlorine on arsenic release in combustion, gasification and pyrolysis of sawdust[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121047.
DOI |
| [20] |
ZHOU C J, WEI G, XIANG J, et al., 2018. Effects of synoptic circulation patterns on air quality in Nanjing and its surrounding areas during 2013-2015 [J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 9(4): 723-734.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SUN Z Y, 2017. Study on environmental chemical behavior and dust control of lead and cadmium in atmosphere[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions (CET Journal), DOI: 10.3303/CET1759156.
DOI |
| [22] | 艾建超, 王宁, 杨净, 2014. 基于UNMIX模型的夹皮沟金矿区土壤重金属源解析[J]. 环境科学, 35(9): 3530-3536. |
| AI J C, WANG N, YANG J, 2014. Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in Jiapigou goldmine based on the UNMIX model[J]. Environmental Science, 35(9): 3530-3536. | |
| [23] | 北京市环境保护科学研究院, 2009. 场地环境评价导则: DB11/T 656-2009 [S]. 北京: 北京市质量技术监督局. |
| Beijing Municipal Research Institute of Environmental Protection, 2009. Environmental site assessment guideline: DB 11/T656-2009 [S]. Beijing: Beijing Municipal Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. | |
| [24] | 邓文叶, 贾尔恒∙阿哈提, 杨静, 等, 2017. 乌鲁木齐PM10和PM2.5的形貌特征与来源解析[J]. 环境工程, 35(8): 96-101. |
| DENG W Y, JIA E H·A H T, YANG J, et al., 2017. Morphology characteristics and source of PM10 and PM2.5 in Urumqi[J]. Environmental Engineering, 35(8): 96-101. | |
| [25] | 杜金花, 张宜升, 何凌燕, 等, 2012. 深圳某地区大气PM2.5中重金属的污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 29(9): 838-840. |
| DU J H, ZHANG Y S, HE L Y, et al., 2012. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric PM2.5 in a certain area of Shenzhen[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 29(9): 838-840. | |
| [26] | 段菁春, 谭吉华, 王淑兰, 等, 2012. 兰州市大气单颗粒来源识别及应用[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2(3): 234-239. |
| DUAN J C, TAN J H, YU S L, et al., 2012. Source identification of individual particles and its application to air quality management in Lanzhou, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2(3): 234-239. | |
| [27] | 冯利红, 赵岩, 李建平, 等, 2018. 天津市大气重污染天气下细颗粒物中重金属污染特征及健康风险评估[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 22(11): 116-1167, 1172. |
| FENG L H, ZHAO Y, LI J P, et al., 2018. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in fine particles with different levels of air pollution in Tianjin[J]. Chinese Journal of Disease Control, 22(11): 116-1167, 1172. | |
| [28] | 冯茜丹, 明彩兵, 刘晖, 等, 2015. 2011年秋季广州城区大气PM2.5微观形貌和粒度分布[J]. 中国环境科学, 35(4): 1013-1018. |
| FENG X D, MING C B, LIU H, et al., 2015. Microscopic morphology and size distribution of PM2.5 in Guangzhou urban area in fall 2011 [J]. China Environmental Science, 35(4): 1013-1018. | |
| [29] | 符传博, 丹利, 2014. 重污染下我国中东部地区1960-2010年霾日数的时空变化特征[J]. 气候与环境研究, 19(2): 219-226. |
| FU C B, DAN L, 2014. Spatiotemporal characteristics of haze days under heavy pollution over central and eastern China during 1960-2010 [J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 19(2): 219-226. | |
| [30] | 郭家瑜, 张英杰, 郑海涛, 等, 2017. 北京2015年大气细颗粒物的空间分布特征及变化规律[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(7): 2409-2419. |
| GUO J Y, ZHANG Y J, ZHENG H T, et al., 2017. Characteristics of spatial distribution and variations of atmospheric fine particles in Beijing in 2015[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(7): 2409-2419. | |
| [31] | 韩玉丽, 邱尔发, 王亚飞, 等, 2015. 北京市土壤和TSP中重金属分布特征及相关性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(1): 146-155. |
| HAN Y L, QIU E F, WANG Y F, et al., 2015. Study on heavy metals distribution and correlation in soil and TSP of Beijing[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(1): 146-155. | |
| [32] | 何瑞东, 张轶舜, 陈永阳, 等, 2019. 郑州市某生活区大气PM2.5中重金属污染特征及生态、健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 40(11): 4774-4782. |
| HE R D, ZHANG Y S, CHEN Y Y, et al., 2019. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological and health risk assessment of atmospheric PM2.5 in a living area of Zhengzhou City[J]. Environmental Science, 40(11): 4774-4782. | |
| [33] | 雷文凯, 李杏茹, 张兰, 等, 2021. 保定地区PM2.5中重金属元素的污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 42(1): 38-44. |
| LEI W K, LI X R, ZHANG L, et al., 2021. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5 collected in Baoding[J]. Environmental Science, 42(1): 38-44. | |
| [34] | 李萍, 薛粟尹, 王胜利, 等, 2014. 兰州市大气降尘重金属污染评价及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 35(3): 1021-1028. |
| LI P, XUE L Y, WANG S L, et al., 2014. Pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition in Lanzhou[J]. Environmental Science, 35(3): 1021-1028. | |
| [35] | 李友平, 刘慧芳, 周洪, 等, 2015. 成都市PM2.5中有毒重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 35(7): 2225-2232. |
| LI Y P, LIU H F, ZHOU H, et al., 2015. Contamination characteristics and health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in PM2.5 in Chengdu[J]. China Environmental Science, 35(7): 2225-2232. | |
| [36] | 刘爱霞, 韩素芹, 蔡子颖, 等, 2012. 天津地区能见度变化特征及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(11): 1847-1850. |
| LIU A X, HAN S Q, CAI Z Y, et al., 2012. Variation trends and affect factors of visibility in Tianjin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(11): 1847-1850. | |
| [37] | 刘宝林, 刘珈鹭, 窦文爽, 等, 2017. 长春市初冬季节大气PM10的微观形貌特征与来源分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 17(36): 248-252. |
| LIU B L, LIU J L, DOU W S, et al., 2017. Investigations of microscopic morphology and sources of ambient air PM10 in the early winter of Changchun[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 17(36): 248-252. | |
| [38] | 刘新春, 钟玉婷, 何清, 等, 2012. 乌鲁木齐市TSP微观形貌特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 6(2): 44-48. |
| LIU X C, ZHONG Y T, HE Q, et al., 2012. Seasonal characteristic analysis of TSP micro-morphology in Urumqi[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 6(2): 44-48. | |
| [39] | 刘新会, 牛军峰, 史江红, 2009. 环境与健康[M]. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社: 335-361. |
| LIU X H, NIU J F, SHI J H, 2009. Environment and Health[M]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Press: 335-361. | |
| [40] | 刘彦飞, 邵龙义, 王彦彪, 等, 2010. 哈尔滨春季大气PM2.5物理化学特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 33(2):131-134, 149. |
| LIU Y F, SHAO L Y, WANG Y B, et al., 2010. Physico-chemical characteristics and source identification of atmospheric PM2.5 in Harbin during spring season[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 33(2): 131-134, 149. | |
| [41] | 鲁斯唯, 林婷, 李森琳, 等, 2015. 厦门城区秋季不同粒径大气颗粒物的微观形貌分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 54(2): 216-223. |
| LU S W, LIN T, LI S L, et al., 2015. Morphological characteristics of atmospheric aerosols with different sizes in Xiamen during autumn[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 54(2): 216-223. | |
| [42] | 吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等, 2012. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 67(7): 971-984. |
| LV J S, ZHANG Z L, LIU Y, et al., 2012. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao City[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67(7): 971-984. | |
| [43] | 马先杰, 陆凤, 陈兰兰, 等, 2019. 贵州水城典型铅锌矿区土壤和蔬菜中重金属累积特征及风险评价[J]. 环境污染与防治, 41(10): 1227-1232. |
| MA X J, LU F, CHEN L L, et al., 2019. Accumulation characteristics and risk assessment for heavy metals in soil and vegetables in typical lead-zinc mining region of Shuicheng, Guizhou[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 41(10): 1227-1232. | |
| [44] | 阮玉龙, 李向东, 黎廷宇, 等, 2015. 喀斯特地区农田土壤重金属污染及其对人体健康的危害[J]. 地球与环境, 43(1): 92-97. |
| RUAN Y L, LI X D, LI T Y, et al., 2015. Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of the Karst areas and its harm to human health[J]. Earth and Environment, 43(1): 92-97. | |
| [45] | 宋晓焱, 魏思民, 邵龙义, 等, 2013. 扫描电镜下煤矿区大气PM10微观形貌识别[J]. 湖南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 28(4): 118-122. |
| SONG X Y, WEI S M, SHAO L Y, et al., 2013. Micro-morphology of PM10 collected in coal- mine cities under FESEM[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 28(4): 118-122. | |
| [46] | 唐荣莉, 马克明, 张育新, 等, 2012. 北京城市道路灰尘重金属污染的健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 32(8): 2006-2015. |
| TANG R L, MA K M, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2012. Health risk assessment of heavy metals of street dust in Beijing[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 32(8): 2006-2015. | |
| [47] | 王慧, 刘庆倩, 安海龙, 等, 2016. 城市环境中毛白杨和油松叶片表面颗粒污染物的观察[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 38(8): 28-35. |
| WANG H, LIU Q Q, AN H L, et al., 2016. Observation of particulate pollutants retained on populus tomentosa and pinus tabulaeformis leaves in urban environment[J]. Journal of Beijing University, 38(8): 28-35. | |
| [48] | 王永晓, 曹红英, 邓雅佳, 等, 2017. 大气颗粒物及降尘中重金属的分布特征与人体健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 38(9): 3575-3584. |
| WANG Y X, CAO H Y, DENG Y J, et al., 2017. Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric particulate matter and dust[J]. Environmental Science, 38(9): 3575-3584. | |
| [49] | 王钊, 韩斌, 倪天茹, 等, 2013. 天津市某社区老年人PM2.5暴露痕量元素健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究, 26(8): 913-918. |
| WANG Z, HAN B, NI T R, et al., 2013. Health risk assessment of trace elements of PM2.5 exposure for the elderly subpopulation in Tianjin, China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 26(8): 913-918. | |
| [50] | 王宗爽, 段小丽, 刘平, 等, 2009. 环境健康风险评价中我国居民暴露参数探讨[J]. 环境科学研究, 22(10): 1164-1170. |
| WANG Z S, DUAN X L, LIU P, et al., 2009. Human exposure factors of Chinese people in environmental health risk assessment[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(10): 1164-1170. | |
| [51] | 邢丹, 刘鸿雁, 于萍萍, 等, 2012. 黔西北铅锌矿区植物群落分布及其对重金属的迁移特征[J]. 生态学报, 32(3): 796-804. |
|
XING D, LIU H Y, YU P P, et al., 2012. The plant community distribution and migration characteristics of heavy metals in tolerance dominant species in lead/zinc mine areas in Northwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(3): 796-804.
DOI URL |
|
| [52] | 徐宗泽, 代群威, 王岩, 等, 2019. 大气颗粒物中颗粒微观形貌特征及其矿物组成分析[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 48(9): 55-58. |
| XU Z Z, DAI Q W, WANG Y, et al., 2019. Morphology and mineral composition of atmosphere particulates[J]. Chemical Minerals and Processing, 48(9): 55-58. | |
| [53] | 许栩楠, 曾立民, 张远航, 等, 2016. 北京市怀柔区冬季大气重金属污染状况分析[J]. 环境化学, 35(12): 2460-2468. |
| XU X N, ZENG L M, ZHANG Y H, et al., 2016. The pollution status analysis of atmospheric heavy metal elements during winter in Huairou District of Beijing[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 35(12): 2460-2468. | |
| [54] | 许云海, 刘亚宾, 伍钢, 等, 2019. 湖南某铅锌锰冶炼区总悬浮颗粒物重金属来源及健康风险评价[J]. 环境污染与防治, 41(7): 803-808. |
| XU Y H, LIU Y B, WU G, et al., 2019. Source and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the TSP around a Pb-Zn-Mn smelting area in Hunan[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 41(7): 803-808. | |
| [55] | 杨浩, 2011. 乌鲁木齐市TSP浓度、形貌及水溶性离子特性分析[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学. |
| YANG H, 2011. Analysis of TSP concentration, morphology and water-soluble ion characteristics in Urumqi City[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University. | |
| [56] | 杨鹏月, 帕丽达∙牙合甫, 2019. 乌鲁木齐市大气颗粒物中重金属的污染特征及风险水平评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 32(12): 2084-2090. |
| YANG P Y, PA L D·Y H F,, 2019. Pollution Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy Metals in atmospheric particulates in Urumqi City[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32(12): 2084-2090. | |
| [57] | 杨永兴, 包良满, 雷前涛, 2013. 地铁颗粒物PM2.5的SEM和微束XRF分析[J]. 电子显微学报, 32(1): 47-53. |
| YANG Y X, BAO L M, LEI Q T, 2013. SEM and microbeam XRF analysis of PM2.5 in metro particulate matter[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 32(1): 47-53. | |
| [58] | 游超, 2018. 乌鲁木齐市PM2.5、PM10浓度时空变化特征[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学. |
| YOU C, 2018. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations in Urumqi City[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University. | |
| [59] | 于扬, 岑况, STEFAN N, 等, 2012. 北京市PM2.5中主要重金属元素污染特征及季节变化分析[J]. 现代地质, 26(5): 975-982. |
| YU Y, CEN K, STEFAN N, et al., 2012. Concentration characteristics and seasonal trend of main heavy metal elements of PM2.5 in Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 26(5): 975-982. | |
| [60] | 张松, 郑刘根, 陈永春, 等, 2020. 淮南矿区道路环境大气颗粒物重金属污染特征及来源解析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 42(7): 912-916, 928. |
| ZHANG S, ZHNEG L G, CHEN Y C, et al., 2020. Characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in atmospheric particles at the roadside of Huainan mining area[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 42(7): 912-916, 928. | |
| [61] | 张鑫, 赵小曼, 孟雪洁, 等, 2018. 北京、新乡夏季大气颗粒物中重金属的粒径分布及人体健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 39(3): 997-1003. |
| ZHANG X, ZHAO X M, ZHANG X J, et al., 2018. Particle size distribution and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric particles from Beijing and Xinxiang during summer[J]. Environmental Science, 39(3): 997-1003. | |
| [62] | 赵晨曦, 王云琦, 王玉杰, 等, 2014. 北京地区冬春PM2.5和PM10污染水平时空分布及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 环境科学, 35(2): 418-427. |
| ZHAO C X, WANG Y Y, WANG Y J, et al., 2014. Temporal and spatial distribution of PM2.5 and PM10 pollution status and the correlation of particulate matters and meteorological factors during winter and Spring in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 35(2): 418-427. | |
| [63] | 赵承美, 2016. 燃煤排放PM2.5单颗粒特征及其在大气环境中的变化[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学 (北京). |
| ZHAO C M, 2016. Characterisation of individual particles in PM2.5 from coal combustion and their behaviour in atmosphere environment[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing). | |
| [64] | 赵长盛, 司国瑞, 王春燕, 等, 2018. 济南春季颗粒态汞污染特征及健康评估研究[J]. 环境保护科学, 44(6): 112-116. |
| ZHAO C S, SI G R, WANG C Y, et al., 2018. Pollution characteristics and health assessment of particulate mercury in spring of Jinan City[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 44(6): 112-116. | |
| [65] | 赵珍丽, 赵委托, 黄庭, 等, 2018. 电镀厂周边大气PM10中重金属季节性分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 39(1): 18-26. |
| ZHAO Z L, ZHAO W T, HUANG T, et al., 2018. Seasonal characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in PM10 around electroplating plants[J]. Environmental Science, 39(1):18-26. | |
| [66] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2012. 环境空气质量标准 (GB 309-2012) [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2021. Ambient air quality standards (GB 3095-2012) [S]. China Environmental Press. | |
| [67] | 钟宇红, 房春生, 邱立民, 等, 2008. 扫描电镜分析在大气颗粒物源解析中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 38(3): 473-478. |
| ZHONG Y H, FANG C S, QIU L M, et al., 2008. Application of electron microscopic analysis for the sources apportionment of atmospheric particles[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 38(3): 473-478. | |
| [68] | 周安琪, 刘建伟, 周旭, 等, 2021. 北京大气PM2.5载带金属浓度、来源及健康风险的城郊差异[J]. 环境科学, 31(2): 56-64. |
| ZHOU A Q, LIU J W, ZHOU X, et al., 2021. Concentration, source, and health risk of PM2.5 carrier metal in Beijing urbanarea and suburb[J]. Environmental Science, 31(2): 56-64. | |
| [69] | 朱恒亮, 刘鸿雁, 何天容, 等, 2014. 贵州省典型污染区土壤重金属的污染特征分析[J]. 地球与环境, 42(4): 505-512. |
| ZHU H L, LIU H Y, HE T R, et al., 2014. Analysis of pollution characteristics of soil heavy metals in typical polluted areas in Guizhou Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 42(4): 505-512. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [3] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [4] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [5] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [6] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [7] | 石文静, 周翰鹏, 孙涛, 黄金涛, 杨文焕, 李卫平. 矿区周边土壤重金属污染优先控制因子及健康风险评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1616-1628. |
| [8] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [9] | 李莹, 张洲, 杨高明, 祖艳群, 李博, 陈建军. 湿地植物根系泌氧能力和根表铁膜与根系吸收重金属的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [10] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [11] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [12] | 彭红丽, 谭海霞, 王颖, 魏建梅, 冯阳. 不同种植模式下土壤重金属形态分布差异与生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [13] | 黄敏, 赵晓峰, 梁荣祥, 王鹏忠, 戴安然, 何晓曼. 3种螯合剂对Cd、Cu复合污染土壤淋洗修复的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [14] | 朱立安, 张会化, 程炯, 李婷, 林梓, 李俊杰. 珠江三角洲林业用地土壤重金属潜在生态风险格局分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [15] | 施建飞, 靳正忠, 周智彬, 王鑫. 额尔齐斯河流域典型尾矿库区周边土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 187
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
