生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 918-930.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.007
陈金凤1,2( ), 余世钦1,2, 符加方3, 徐国良1,2,*(
), 余世钦1,2, 符加方3, 徐国良1,2,*( ), 于波4, 赖晓群1, 胡思源1, 张开渠1, 刘家华1
), 于波4, 赖晓群1, 胡思源1, 张开渠1, 刘家华1
收稿日期:2022-01-06
出版日期:2022-05-18
发布日期:2022-07-12
通讯作者:
* 徐国良(1975年生),男,博士,主要研究方向为区域环境变化与土壤生态学。E-mail: xugl@gzhu.edu.cn作者简介:陈金凤(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为土壤生态修复。E-mail: 2112001033@e.gzhu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Jinfeng1,2( ), YU Shiqin1,2, FU Jiafang3, XU Guoliang1,2,*(
), YU Shiqin1,2, FU Jiafang3, XU Guoliang1,2,*( ), YU Bo4, LAI Xiaoqun1, HU Siyuan1, ZHANG Kaiqu1, LIU Jiahua1
), YU Bo4, LAI Xiaoqun1, HU Siyuan1, ZHANG Kaiqu1, LIU Jiahua1
Received:2022-01-06
Online:2022-05-18
Published:2022-07-12
摘要:
红层地貌在中国,乃至世界,都有广泛的分布。以往对红层的研究主要集中在成因、分布和地貌特征等方面,但对于红层区土壤在不同土地利用下的质量变化缺乏了解。为了研究华南典型红层地貌区不同土地利用类型土壤质量特征及其影响因素,在粤北韶关南雄红层盆地,选择红层强蚀岗地、红层裸岩岗地、草丛地、灌木地、乔木地、农用地6种土地利用类型,采集94个土壤样品并测试pH、有机质、碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾和微量元素有效铜、有效锌、有效铁、有效锰等土壤指标,通过主成分分析,计算不同土地利用类型的土壤质量综合指数及土壤退化指数。研究结果表明,南雄盆地红层区不同土地利用类型土壤质量差异显著,受自然和人为因素共同影响。(1)南雄红层区土壤质量特征明显受到红层母岩的影响。由于红层区土壤主要是由紫红色砾岩、砂岩和泥质岩等发育而成,土壤总体上呈中性或弱碱性,土壤速效钾含量较高。(2)植被覆盖差异对土壤质量有显著影响。红层强蚀岗地是研究区土壤退化的极端表现,其表层缺乏植被覆盖,土壤质量综合指数最低;乔木地土壤综合质量最高,有效锌、有效铁和有效锰的含量最多,但pH值最低,可能是受到凋落物分解酸化和南方暴雨淋洗等的作用。不同乔木林地土壤质量的差异可能与凋落物类型、产生和分解能力的差异有关。(3)人类活动对红层区土壤质量具有深远影响,历史上人类开荒和农耕活动造成连片的红层荒漠化;近年农户的拾薪、踩踏和收胶也使马尾松林地出现大面积的地表裸露,导致土壤质量退化;农用地人为输入养分一定程度也可以明显提升土壤质量。
中图分类号:
陈金凤, 余世钦, 符加方, 徐国良, 于波, 赖晓群, 胡思源, 张开渠, 刘家华. 华南红层地貌区不同利用方式土壤质量特征及其影响因素——以南雄盆地为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 918-930.
CHEN Jinfeng, YU Shiqin, FU Jiafang, XU Guoliang, YU Bo, LAI Xiaoqun, HU Siyuan, ZHANG Kaiqu, LIU Jiahua. Soil Quality Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Different Land Use in the Red Bed Landform Region of South China: Taking Nanxiong Basin as An Example[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 918-930.
| 样地类型 Land use types | 主要植物种类 Vegetation properties | 样地特征 Landform properties |
|---|---|---|
| 红层蚀地 Red bed erosion hillock | 表层几乎没有植被覆盖 | 红层蚀地是红层区土地退化的极端性表现 |
| 裸岩地 Red bed bare rock hillock | 有少数先锋植被覆盖,如兰香草 (Caryopteris incana)、鼠尾草 (Setaria viridis)、黄细 心 (Boerhavia diffusa) 等,无乔木 | 裸岩地是自然演替初始阶段 |
| 草丛地 Grassland | 草丛地物种较丰富,草本植物有狗尾草 (Setaria viridis)、细柄草 (Capillipedium parviflorum)、兰香草 (Caryopteris incana)、小蓬草 (Conyza canadensis)、鸡眼草 (Kummerowia striata)、扭黄茅 (Heteropogon contortus)、香茅 (Cymbopogon citratus) 等 | 植物生长较茂盛,依地势高低呈多种斑块状 |
| 灌木地 Shrubland | 主要有牡荆 (Vitex negundo)、糯米条 (Abelia chinensis)、了哥王 (Wikstroemia indica)、紫葳 (Lagerstroemia indica)、雀梅滕 (Sageretia thea)、金丝桃 (Hypericum monogynum)、榔榆 (Ulmus parvifolia)、中华绣线菊 (Spiraea chinensis)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa) 等 | 灌木地分布在红层荒漠地的周围,有些存在人为破坏的迹象 |
| 乔木地 Arbor woodland | 主要有马尾松林 (Pinus massoniana)、台湾相思林 (Acacia confusa)和新银合欢林 (Leucaena leucocephala) 3种乔木林地,林下灌木层主要有牡荆 (Vitex negundo)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、了哥王 (Wikstroemia indica)、小果蔷薇 (Rosa cymosa)等;草本层主要有狗尾草 (Setaria viridis)、鸭嘴草 (Ischaemum aristatum)、毛秆野古草 (Arundinella hirta)、升马唐 (Digitaria ciliaris) 等 | 乔木林为人工林,3种乔木林地的土壤质量因人为影响有一定的差异 |
| 农用地 Farmland | 农作物包括烟草 (Nicotiana tabacum)、花生 (Arachis hypogaea)、脐橙 (Citrus sinensis) | 农作物均在红层发育的土壤上人为管理种植 |
表1 样地基本情况
Table 1 Vegetation and landform properties in different land use types
| 样地类型 Land use types | 主要植物种类 Vegetation properties | 样地特征 Landform properties |
|---|---|---|
| 红层蚀地 Red bed erosion hillock | 表层几乎没有植被覆盖 | 红层蚀地是红层区土地退化的极端性表现 |
| 裸岩地 Red bed bare rock hillock | 有少数先锋植被覆盖,如兰香草 (Caryopteris incana)、鼠尾草 (Setaria viridis)、黄细 心 (Boerhavia diffusa) 等,无乔木 | 裸岩地是自然演替初始阶段 |
| 草丛地 Grassland | 草丛地物种较丰富,草本植物有狗尾草 (Setaria viridis)、细柄草 (Capillipedium parviflorum)、兰香草 (Caryopteris incana)、小蓬草 (Conyza canadensis)、鸡眼草 (Kummerowia striata)、扭黄茅 (Heteropogon contortus)、香茅 (Cymbopogon citratus) 等 | 植物生长较茂盛,依地势高低呈多种斑块状 |
| 灌木地 Shrubland | 主要有牡荆 (Vitex negundo)、糯米条 (Abelia chinensis)、了哥王 (Wikstroemia indica)、紫葳 (Lagerstroemia indica)、雀梅滕 (Sageretia thea)、金丝桃 (Hypericum monogynum)、榔榆 (Ulmus parvifolia)、中华绣线菊 (Spiraea chinensis)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa) 等 | 灌木地分布在红层荒漠地的周围,有些存在人为破坏的迹象 |
| 乔木地 Arbor woodland | 主要有马尾松林 (Pinus massoniana)、台湾相思林 (Acacia confusa)和新银合欢林 (Leucaena leucocephala) 3种乔木林地,林下灌木层主要有牡荆 (Vitex negundo)、桃金娘 (Rhodomyrtus tomentosa)、了哥王 (Wikstroemia indica)、小果蔷薇 (Rosa cymosa)等;草本层主要有狗尾草 (Setaria viridis)、鸭嘴草 (Ischaemum aristatum)、毛秆野古草 (Arundinella hirta)、升马唐 (Digitaria ciliaris) 等 | 乔木林为人工林,3种乔木林地的土壤质量因人为影响有一定的差异 |
| 农用地 Farmland | 农作物包括烟草 (Nicotiana tabacum)、花生 (Arachis hypogaea)、脐橙 (Citrus sinensis) | 农作物均在红层发育的土壤上人为管理种植 |
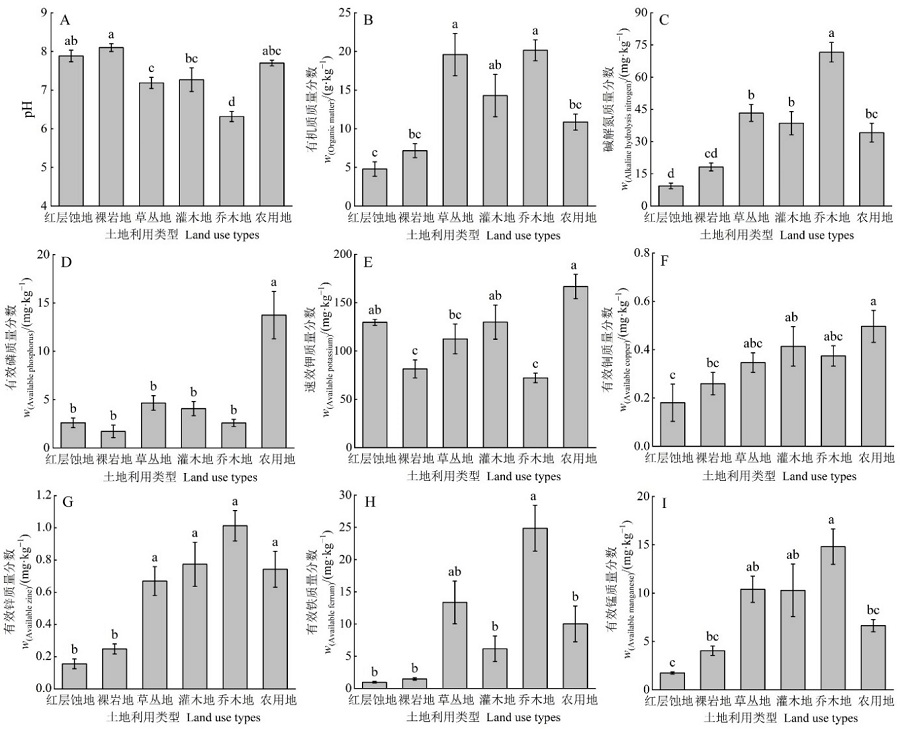
图3 不同土地利用类型下土壤理化性质 图中,小写字母表示不同土地利用类型间差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 3 Soil physical and chemical properties in different land use types In the figure, different small letters meant significant difference among different land use types (P<0.05)
| 用地类型 Land use types | pH | w(organic matter)/ (g·kg-1) | w(alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available phosphorus)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available potassium)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available copper)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available zine)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available ferrum)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available manganese)/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新银合欢林地 Leucaena leucocephala plantation | 7.04± 0.22a | 17.37± 1.98b | 73.00± 16.62ab | 4.74± 1.57a | 85.31± 21.61a | 0.60± 0.28a | 1.08± 0.45ab | 14.20± 11.41a | 14.24± 9.26a |
| 台湾相思林地 Acacia confuse plantation | 6.27± 0.41b | 25.44± 7.42a | 88.89± 16.79a | 2.78± 1.21b | 87.82± 25.92a | 0.31± 0.11b | 1.45± 0.46a | 30.25± 20.82a | 16.10± 7.42a |
| 马尾松林地 Pinus massoniana plantation | 5.81± 0.70b | 18.25± 7.99ab | 57.61± 27.33b | 0.81± 0.69c | 50.44± 14.79b | 0.25± 0.09b | 0.63± 0.27b | 28.81± 19.98a | 14.26± 12.03a |
表2 不同乔木地的土壤理化性质
Table 2 Soil physical and chemical properties in different woodlands
| 用地类型 Land use types | pH | w(organic matter)/ (g·kg-1) | w(alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available phosphorus)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available potassium)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available copper)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available zine)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available ferrum)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(available manganese)/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新银合欢林地 Leucaena leucocephala plantation | 7.04± 0.22a | 17.37± 1.98b | 73.00± 16.62ab | 4.74± 1.57a | 85.31± 21.61a | 0.60± 0.28a | 1.08± 0.45ab | 14.20± 11.41a | 14.24± 9.26a |
| 台湾相思林地 Acacia confuse plantation | 6.27± 0.41b | 25.44± 7.42a | 88.89± 16.79a | 2.78± 1.21b | 87.82± 25.92a | 0.31± 0.11b | 1.45± 0.46a | 30.25± 20.82a | 16.10± 7.42a |
| 马尾松林地 Pinus massoniana plantation | 5.81± 0.70b | 18.25± 7.99ab | 57.61± 27.33b | 0.81± 0.69c | 50.44± 14.79b | 0.25± 0.09b | 0.63± 0.27b | 28.81± 19.98a | 14.26± 12.03a |
| 指标 Index | pH | 有机质OM | 碱解氮AN | 有效磷AP | 速效钾AK | 有效铜AC | 有效锌AZ | 有效铁AF | 有效锰AM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||
| 有机质OM | -0.356** | 1 | |||||||
| 碱解氮AN | -0.571** | 0.736** | 1 | ||||||
| 有效磷AP | 0.253* | 0.049 | 0.027 | 1 | |||||
| 速效钾AK | 0.565** | -0.008 | -0.341** | 0.536** | 1 | ||||
| 有效铜AC | -0.069 | 0.162 | 0.336** | 0.392** | 0.076 | 1 | |||
| 有效锌AZ | -0.422** | 0.602** | 0.706** | 0.180 | -0.027 | 0.416** | 1 | ||
| 有效铁AF | -0.492** | 0.535** | 0.679** | 0.001 | -0.375** | 0.197 | 0.344** | 1 | |
| 有效锰AM | -0.654** | 0.260* | 0.594** | -0.058 | -0.424** | 0.312** | 0.578** | 0.422** | 1 |
表3 土壤质量指标的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlationship analysis of soil properties
| 指标 Index | pH | 有机质OM | 碱解氮AN | 有效磷AP | 速效钾AK | 有效铜AC | 有效锌AZ | 有效铁AF | 有效锰AM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||
| 有机质OM | -0.356** | 1 | |||||||
| 碱解氮AN | -0.571** | 0.736** | 1 | ||||||
| 有效磷AP | 0.253* | 0.049 | 0.027 | 1 | |||||
| 速效钾AK | 0.565** | -0.008 | -0.341** | 0.536** | 1 | ||||
| 有效铜AC | -0.069 | 0.162 | 0.336** | 0.392** | 0.076 | 1 | |||
| 有效锌AZ | -0.422** | 0.602** | 0.706** | 0.180 | -0.027 | 0.416** | 1 | ||
| 有效铁AF | -0.492** | 0.535** | 0.679** | 0.001 | -0.375** | 0.197 | 0.344** | 1 | |
| 有效锰AM | -0.654** | 0.260* | 0.594** | -0.058 | -0.424** | 0.312** | 0.578** | 0.422** | 1 |
| 用地类型 Land use types | pH | 有机质OM | 碱解氮AN | 有效磷AP | 速效钾AK | 有效铜AC | 有效锌AZ | 有效铁AF | 有效锰AM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红层蚀地 Red bed erosion hillock | 0.175 | 0.065 | 0.063 | 0.080 | 0.501 | 0.119 | 0.046 | 0.010 | 0.023 |
| 裸岩地 Red bed bare rock hillock | 0.120 | 0.112 | 0.132 | 0.051 | 0.740 | 0.182 | 0.092 | 0.018 | 0.077 |
| 草丛地 Grassland | 0.350 | 0.356 | 0.328 | 0.147 | 0.586 | 0.251 | 0.302 | 0.187 | 0.225 |
| 灌木地 Shrubland | 0.329 | 0.252 | 0.291 | 0.128 | 0.500 | 0.305 | 0.354 | 0.085 | 0.223 |
| 乔木地 Arbor woodland | 0.567 | 0.367 | 0.549 | 0.079 | 0.786 | 0.273 | 0.473 | 0.352 | 0.329 |
| 农用地 Farmland | 0.221 | 0.185 | 0.256 | 0.445 | 0.317 | 0.371 | 0.338 | 0.140 | 0.137 |
表4 土壤质量指标隶属度
Table 4 Membership degree of soil properties
| 用地类型 Land use types | pH | 有机质OM | 碱解氮AN | 有效磷AP | 速效钾AK | 有效铜AC | 有效锌AZ | 有效铁AF | 有效锰AM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红层蚀地 Red bed erosion hillock | 0.175 | 0.065 | 0.063 | 0.080 | 0.501 | 0.119 | 0.046 | 0.010 | 0.023 |
| 裸岩地 Red bed bare rock hillock | 0.120 | 0.112 | 0.132 | 0.051 | 0.740 | 0.182 | 0.092 | 0.018 | 0.077 |
| 草丛地 Grassland | 0.350 | 0.356 | 0.328 | 0.147 | 0.586 | 0.251 | 0.302 | 0.187 | 0.225 |
| 灌木地 Shrubland | 0.329 | 0.252 | 0.291 | 0.128 | 0.500 | 0.305 | 0.354 | 0.085 | 0.223 |
| 乔木地 Arbor woodland | 0.567 | 0.367 | 0.549 | 0.079 | 0.786 | 0.273 | 0.473 | 0.352 | 0.329 |
| 农用地 Farmland | 0.221 | 0.185 | 0.256 | 0.445 | 0.317 | 0.371 | 0.338 | 0.140 | 0.137 |
| 土壤质量指标 Soil quality indexes | 第一主成分 First principal Component | 第二主成分 Second principal Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 负荷量 Capacity | 权重 Weight | 负荷量 Capacity | 权重 Weight | ||
| pH | 0.943 | 0.384 | -0.221 | -0.142 | |
| 有机质OM | 0.942 | 0.384 | -0.083 | -0.054 | |
| 碱解氮AN | 0.993 | 0.405 | -0.080 | -0.052 | |
| 有效磷AP | 0.095 | 0.039 | 0.965 | 0.622 | |
| 速效钾AK | 0.281 | 0.114 | -0.895 | -0.577 | |
| 有效铜AC | 0.624 | 0.254 | 0.730 | 0.471 | |
| 有效锌AZ | 0.958 | 0.390 | 0.251 | 0.162 | |
| 有效铁AF | 0.948 | 0.386 | -0.080 | -0.052 | |
| 有效锰AM | 0.984 | 0.401 | -0.095 | -0.061 | |
| 特征值 Eigen value | 6.024 | 2.406 | |||
| 方差贡献率 Variance contribution/% | 66.933 | 26.737 | |||
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution/% | 66.933 | 93.671 | |||
表5 土壤质量指标主成分结果与指标的权重
Table 5 Results of soil properties from principal component analysis and weight values of soil properties
| 土壤质量指标 Soil quality indexes | 第一主成分 First principal Component | 第二主成分 Second principal Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 负荷量 Capacity | 权重 Weight | 负荷量 Capacity | 权重 Weight | ||
| pH | 0.943 | 0.384 | -0.221 | -0.142 | |
| 有机质OM | 0.942 | 0.384 | -0.083 | -0.054 | |
| 碱解氮AN | 0.993 | 0.405 | -0.080 | -0.052 | |
| 有效磷AP | 0.095 | 0.039 | 0.965 | 0.622 | |
| 速效钾AK | 0.281 | 0.114 | -0.895 | -0.577 | |
| 有效铜AC | 0.624 | 0.254 | 0.730 | 0.471 | |
| 有效锌AZ | 0.958 | 0.390 | 0.251 | 0.162 | |
| 有效铁AF | 0.948 | 0.386 | -0.080 | -0.052 | |
| 有效锰AM | 0.984 | 0.401 | -0.095 | -0.061 | |
| 特征值 Eigen value | 6.024 | 2.406 | |||
| 方差贡献率 Variance contribution/% | 66.933 | 26.737 | |||
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution/% | 66.933 | 93.671 | |||
| [1] |
ADEJUWON J O, EKANADE O, 1988. A comparison of soil properties under different landuse types in a part of the Nigerian cocoa belt[J]. Catena, 15(3-4): 319-331.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ANDREWS S S, KARLEN D L, MITCHELL, J P, 2002. A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment. 90(1): 25-45.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN L Q, GUO F S, LIU F J, et al., 2019. Origin of Tafoni in the Late Cretaceous Aeolian Sandstones, Danxiashan UNESCO Global Geopark, South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 93(2): 451-463.
DOI URL |
| [4] | LUO G S, PENG H, ZHANG S Y, et al., 2021. Exploring the variations of Redbed badlands and their driving forces in the Nanxiong Basin, Southern China: A Geographically Weighted Regression with Gridded Data[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2021(8): 1-13. |
| [5] |
MIKI T, 1992. Sedimentologic and palaeoclimatic classification of Cretaceous red beds in East Asia: A general view[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 7(2-3): 179-184.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
MOHAMED E O, LAHCEN K, BADRE E, et al., 2021. Stratigraphic and geodynamic characterization of Jurassic-Cretaceous “red beds” on the Msemrir-Errachidia E-W transect (central High Atlas, Morocco)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, DOI: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2021.104330.
DOI |
| [7] |
PARCERISA D, GÓMEZ-GRAS D, TRAVÉ A, et al., 2005. Fe and Mn in calcites cementing red beds: A record of oxidation-reduction conditions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 89(1-3): 318-321.
DOI URL |
| [8] | XIONG Z Y, ZHENG J B, WANG D, et al., 2021. Characteristics of dissolved organic carbon loss in purple soil sloping fields with different fertilization treatments[J]. Environmental Science, 42(2): 967-976. |
| [9] |
YAMASHITA I, SURINKUM A, WADA Y, et al., 2010. Paleomagnetism of the Middle-Late Jurassic to Cretaceous red beds from the Peninsular Thailand: Implications for collision tectonics[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(3): 784-796.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
YAN L B, HE R X, KAŠANIN-GRUBIN M, et al., 2017. The dynamic change of vegetation cover and associated driving forces in Nanxiong Basin, China[J]. Sustainability, 9(3): 443-457.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
YAN L B, PENG H, ZHANG S Y, et al., 2019a. The spatial patterns of red beds and Danxia Landforms: Implication for the formation factors-China[J]. Scientific Reports, 9(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
YAN L B, KAŠANIN-GRUBIN M, 2019b. Land and degradation and management of red beds in China: Two case studies[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 16(11): 2591-2604.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
YAN L B, LIU P, PENG H, et al., 2019c. Laboratory study of the effect of temperature difference on the disintegration of redbed softroc k[J]. Physical Geography, 40(2): 149-163.
DOI URL |
| [14] | YAN P, PENG H, YAN L B, et al., 2019. Spatial variability in soil pH and land use as the main influential factor in the red beds of the Nanxiong Basin, China[J]. Peer J, 28(4): 2961-2972. |
| [15] |
YAN P, LIN K R, WANG Y R, et al., 2021a. Assessment of Influencing Factors on the Spatial Variability of SOM in the Red Beds of the Nanxiong Basin of China, Using GIS and Geo-Statistical Methods[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(6): 366-379.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YAN P, LIN K R, WANG Y R, et al., 2021b. Spatial interpolation of red bed soil moisture in Nanxiong basin, South China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, DOI: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2021.103860.
DOI |
| [17] |
ZHANG X L, LIU J B, WANG Y, et al., 2018. Onset of the middle Telychian (Silurian) clastic marine red beds on the western Yangtze Platform, South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 497: 52-65.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHAO J, WAN S Z, LI Z A, et al., 2012. Dicranopteris-dominated understory as major driver of intensive forest ecosystem in humid subtropical and tropical region[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 49: 78-87.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHAO M T, MA M M, HE M, et al., 2021. Evaluation of the four potential Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) boundaries in the Nanxiong Basin based on evidences from volcanic activity and paleoclimatic evolution[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(4): 631-641.
DOI URL |
| [20] | ZHU Z D, CUI S H, 1995. Desertification in China: Status, Trends, and Strategies[J]. Journal of Chinese Geography, 5(3): 32-43. |
| [21] | 程分生, 尤龙辉, 叶功富, 等, 2021. 亚热带红壤侵蚀区马尾松不同套种模式生态系统碳平衡[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(4): 1163-1174. |
| CHENG F S, YOU L H, YE G F, et al., 2021. Carbon balance in an interplanting Pinus massoniana stand in subtropical eroded red soil region, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(4): 1163-1174. | |
| [22] | 邓岚, 1991. 南雄县紫色砂页岩地区水土流失及其防治对策[J]. 水土保持通报, 11(6): 30-34. |
| DENG L, 1991. Water and soil losses and its controlling counter measures in the purple sand shade areas in Nanxiong country of Guangdong[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 11(6): 30-34. | |
| [23] | 丁文斌, 蒋光毅, 史东梅, 等, 2017. 紫色土坡耕地土壤属性差异对耕层土壤质量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(19): 6480-6493. |
| DING W B, JIANG G Y, SHI D M, et al., 2017. Effect of different soil properties on plow-layer soil quality of sloping farmland in purple hilly areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(19): 6480-6493. | |
| [24] | 广东省水利水电科学研究所广东省水利厅水保农水处, 1997. 北江上游水土流失与治理[J]. 水土保持研究, 4(3): 1-77. |
| Soil and Water Conservation Office of Water Conservancy Department in Guangdong Province, 1997. Soil and Water Loss and Its Control in the Upper Reaches of Beijiang River[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 4(3): 1-77. | |
| [25] | 蒋涛, 2019. 紫色土退化区不同治理措施下土壤和芒萁的生态化学计量特征及生态效应[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学. |
| JIANG T, 2019. Study on the ecochemometrical characteristics and ecological effects of soil and Dicranopteris dichotoma under different control measures in the region of degraded purple soil[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University. | |
| [26] |
金远亮, 彭华, 闫罗彬, 等, 2015. 中国南方湿润区“荒漠化”问题讨论[J]. 地理科学进展, 34(6): 772-780.
DOI |
| JIN Y L, PENG H, YAN L B, et al., 2015. Discussion on desertification of humid region in southern China[J]. Progress in Geography, 34(6): 772-780. | |
| [27] | 刘世梁, 傅伯杰, 陈利顶, 等, 2003. 两种土壤质量变化的定量评价方法比较[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 12(5): 422-426. |
| LIU S L, FU B J, CHEN L D, et al., 2003. Comparison of two quantitative methods in assessing soil quality in different land uses[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 12(5): 422-426. | |
| [28] | 刘占锋, 傅伯杰, 刘国华, 等, 2006. 土壤质量与土壤质量指标及其评价[J]. 生态学报, 26(3): 901-913. |
| LIU Z F, FU B J, LIU G H, et al., 2006. Soil quality: concept, indicators and its assessment[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(3): 901-913. | |
| [29] | 鲁如坤, 1999. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 1999. Soil Chemical Analysis Methods[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [30] |
罗谷松, 彭华, 闫罗彬, 等, 2016. 南方“红层荒漠”旅游开发价值分析[J]. 地理科学, 36(4): 555-563.
DOI |
| LUO G S, PENG H, YAN L B, et al., 2016. Tourism development value of “Red Beds Desert” in South China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 36(4): 555-563. | |
| [31] | 孟涛, 2007. 紫色土钾素淋失与利用研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学. |
| MENG T, 2007. Study on Leakage loss and utilization of Potassium in Purple soil[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University. | |
| [32] | 莫江明, 彭少麟, BROWN S, 等, 2004. 鼎湖山马尾松林群落生物量生产对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生态学报, 24(2): 193-200. |
| MO J M, PENG S L, BROWN S, et al., 2004. Response of biomass production to human impacts in a pine forest in subtropical China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(2): 193-200. | |
| [33] | 穆桂珍, 罗杰, 蔡立梅, 等, 2019. 广东揭西县土壤微量元素与有机质和pH的关系分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 40(10): 208-215. |
| MU G Z, LUO J, CAI L M, et al., 2019. Relationship between soil trace elements with organic matter and pH in jiexi county, Guangdong province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 40(10): 208-215. | |
| [34] |
潘志新, 任舫, 彭华, 2018. 美国西部红层地貌发育及与中国东南部丹霞地貌的对比[J]. 地理研究, 37(12): 2399-2410.
DOI |
| PAN Z X, REN F, PENG H, 2018. Development of red bed landform in the western United States and a comparison with Danxia landform in southeast China[J]. Geographical Research, 37(12): 2399-2410. | |
| [35] | 彭华, 吴志才, 2003. 关于红层特点及分布规律的初步探讨[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5): 109-113. |
| PENG H, WU Z C, 2003. A preliminary study on the characteristics and the distribution of red beds[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 42(5): 109-113. | |
| [36] | 彭华, 2011. 中国南方湿润区红层地貌及相关问题探讨[J]. 地理研究, 30(10): 1739-1752. |
| PENG H, 2011. Perspectives on the red beds landforms in humid area of southern China and some related problems[J]. Geographical Research, 30(10): 1739-1752. | |
| [37] |
彭华, 潘志新, 闫罗彬, 等, 2013. 国内外红层与丹霞地貌研究述评[J]. 地理学报, 68(9): 1170-1181.
DOI |
|
PENG H, PAN Z X, YAN L B, et al., 2013. A review of the research on red beds and Danxia landform[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68(9): 1170-1181.
DOI |
|
| [38] |
彭华, 闫罗彬, 陈智, 等, 2015. 中国南方湿润区红层荒漠化问题[J]. 地理学报, 70(11): 1699-1707.
DOI |
|
PENG H, YAN L B, CHEN Z, et al., 2015. A preliminary study of desertification in red beds in the humid region of Southern China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 70(11): 1699-1707.
DOI |
|
| [39] | 青长乐, 牟树森, 朱波, 等, 2009. 紫色土母质的分布及其地质环境——紫色土再研究[J]. 山地学报, 27(6): 740-746. |
| QING C L, MU S S, ZHU B, et al., 2009. Worldwide distributions and geological environments of parent rocks of purple soil-more insight into purple soil[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 27(6): 740-746. | |
| [40] | 舒韦维, 卢立华, 李华, 等, 2021. 林分密度对杉木人工林林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 41(11): 4521-4530. |
| SHU W W, LU L H, LI H, et al., 2021. Effects of stand density on understory vegetation and soil properties of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(11): 4521-4530. | |
| [41] | 宋艳红, 史正涛, 王连晓, 等, 2018. 热带地区橡胶林土壤退化特征及演变[J]. 林业资源管理 (2): 91-97. |
| SONG Y H, SHI Z T, WANG L X, et al., 2018. Soil degradation characteristics and evolution of rubber plantation in the tropical area[J]. Forest Resources Management (2): 91-97. | |
| [42] | 王改玲, 王青杵, 2014. 晋北黄土丘陵区不同人工植被对土壤质量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(6): 1487-1491. |
| WANG G L, WANG Q C, 2014. Effects of artificial vegetation types on soil quality in loess hilly area in Northern Shanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(6): 1487-1491. | |
| [43] | 王雨豪, 2017. 粤北南雄盆地构造演化及其对红层地貌发育的影响[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学. |
| WANG Y H, 2017. Structural evolution of Nanxiong Basin, North Guangdong and the impact to development of red bed landform[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei GEO University. | |
| [44] | 文志, 赵赫, 刘磊, 等, 2019. 基于土地利用变化的热带植物群落功能性状与土壤质量的关系[J]. 生态学报, 39(1): 371-380. |
| WEN Z, ZHAO H, LIU L, et al., 2019. Relationships between plant community functional traits and soil quality based on land use changes in tropical region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(1): 371-380. | |
| [45] | 吴志才, 彭华, 2006. 广东红层形成及其发育规律研究[J]. 热带地理, 26(3): 207-210. |
| WU Z C, PENG H, 2006. A study on the formation and development rules of the red beds in Guangdong province[J]. Tropical Geography, 26(3): 207-210. | |
| [46] | 徐海军, 姚琴, 王晓飞, 等, 2020. 大庆不同土地利用下土壤理化性质及肥力变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 36(35): 55-63. |
| XU H J, YAO Q, WANG X F, et al., 2020. Soil physical and chemical properties and fertility under different land use patterns in Daqing[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 36(35): 55-63. | |
| [47] | 徐永辉, 杨达源, 陈可锋, 等, 2006. 长江三峡库区紫色土的元素迁移特征[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 42(3): 316-323. |
| XU Y H, YANG D Y, CHEN K F, et al., 2006. Chemical transferring features of the purple soil in the Three Gorges Area, Central China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 42(3): 316-323. | |
| [48] | 杨平平, 徐仁扣, 黎星辉, 2012. 淋溶条件下马尾松针对土壤的酸化作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(11): 1817-1821. |
| YANG P P, XU R K, LI X H, 2012. Soil acidification induced by Pinus massoniana needles under leaching conditions[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(11): 1817-1821. | |
| [49] | 杨小林, 花可可, 李义玲, 等, 2019. 紫色土区土壤质量敏感因子空间分异特征及其对土地利用方式变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(1): 29-38. |
| YANG X L, HUA K K, LI Y L, et al., 2019. Spatial variation of soil quality sensitive factor and its response to the land uses in the purple soil area of China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(1): 29-38. | |
| [50] | 于寒青, 2009. 长期施肥下红壤地区三种母质土壤熟化过程中肥力的变化特征[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. |
| YU H Q, 2009. The characteristics of fertility in anthropogenic mellowing of three parent material raw soils in red soil area under long-term fertilization[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [51] | 曾昭璇, 黄少敏, 1978. 中国东南部红层地貌[J]. 华南师院学报(自然科学版) (1): 56-73. |
| ZENG Z X, HUANG S M, 1978. Red bed landform in Southeast China[J]. Journal of South China Normal College: Natural Science (1): 56-73. | |
| [52] | 张文猛, 王兴祥, 2012. 亚热带典型人工林土壤酸化特征及其生物学机理初步分析[J]. 土壤, 44(6): 1021-1028. |
| ZHANG W M, WANG X X, 2012. Characteristics of soil acidification and primary study of biological mechanism of typical forest plantation in subtropical China[J]. Soils, 44(6): 1021-1028. | |
| [53] | 张显球, 张喜满, 侯明才, 等, 2013. 南雄盆地红层岩石地层划分[J]. 地层学杂志, 37(4): 441-451. |
| ZHANG X Q, ZHANG X M, HOU M C, et al., 2013. Lithostratigraphic subdivision of red beds in Nanxiong Basin, Guangdong, China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 37(4): 441-451. | |
| [54] | 张显球, 李罡, 2015. 南雄盆地上湖组坪岭段的时代探讨[J]. 地层学杂志, 39(1): 74-80. |
| ZHANG X Q, LI G, 2015. Discussion on geological age of the Pingling member of Shanghu formation in the Nanxiong Basin, Guangdong province[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 39(1): 74-80. | |
| [55] | 赵凯丽, 王伯仁, 徐明岗, 等, 2019. 我国南方不同母质土壤pH剖面特征及酸化因素分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25(8): 1308-1315. |
| ZHAO K L, WANG B R, XU M G, et al., 2019. Changes in pH with depths of soils derived from different parent materials and analysis of acidification in Southern China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 25(8): 1308-1315. | |
| [56] | 赵资奎, 叶捷, 王强, 2017. 南雄盆地白垩纪-古近纪交界恐龙灭绝和哺乳动物复苏[J]. 科学通报, 62(17): 1869-1881. |
| ZHAO Z K, YE J, WANG Q, 2017. Dinosaur extinction and subsequent mammalian recovery during the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K/Pg) transition in the Nanxiong Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 62(17): 1869-1881. | |
| [57] | 郑粉莉, 张锋, 王彬, 2010. 近100年植被破坏侵蚀环境下土壤质量退化过程的定量评价[J]. 生态学报, 30(22): 6044-6051. |
| ZHENG F L, ZHANG F, WANG B, 2010. Quantifying soil quality degradation over 100 years after deforestation under erosional environments[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(22): 6044-6051. | |
| [58] | 朱波, 彭奎, 高美荣, 等, 2001. 川中丘陵区土地利用变化的生态环境效应——以中国科学院盐亭紫色土农业生态试验站集水区为例[J]. 山地学报, 19(增刊): 14-19. |
| ZHU B, PENG K, GAO M R, et al., 2001. Land use change and effects on Eco-environment in hilly area of central Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 19(S1): 14-19. | |
| [59] | 朱震达, 1991. 中国的脆弱生态带与土地荒漠化[J]. 中国沙漠, 11(4): 15-26. |
| ZHU Z D, 1991. Fragile ecological zones and land desertification in China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 11(4): 15-26. |
| [1] | 王铁铮, 瞿心悦, 刘春香, 李有志. 东江湖水质时空变化规律及其与流域土地利用的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [2] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [3] | 杨贤房, 陈朝, 郑林, 万智巍, 陈永林, 王远东. 稀土矿区不同土地利用类型土壤细菌群落特征及网络分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 793-801. |
| [4] | 陈双双, 朱宁华, 周光益, 袁星明, 尚海, 王迤翾. 不同等级石漠化环境下人工乔木林的植被与土壤物理特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 52-61. |
| [5] | 孙文泰, 马明, 董铁, 牛军强, 尹晓宁, 刘兴禄. 西北旱地苹果细根分布及水力特征对长期覆膜的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1375-1385. |
| [6] | 王宇姝, 盛海彦, 罗莎莎, 胡月明, 余玲玲. 环青海湖4种生境土壤中原核微生物群落结构及分子网络特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1393-1403. |
| [7] | 张鹏, 刘玮, 王铁杆, 钟晨辉, 陶月良. 无机砷短期胁迫对铜藻幼苗氧化损伤、抗氧化酶及抗氧化物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1034-1041. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
