生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 1686-1695.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.11.003
收稿日期:2024-08-17
出版日期:2024-11-18
发布日期:2024-12-06
通讯作者:
*乔云发。E-mail: qiaoyunfa@163.com作者简介:李天(1999年生),男,硕士研究生,从事土壤碳周转研究。E-mail: leetian1999@163.com
基金资助:
LI Tian( ), MIAO Shujie, YU Jie, ZHAO Yudie, QIAO Yunfa*(
), MIAO Shujie, YU Jie, ZHAO Yudie, QIAO Yunfa*( )
)
Received:2024-08-17
Online:2024-11-18
Published:2024-12-06
摘要:
凋落物输入会影响土壤有机碳(SOC)矿化过程,其影响程度主要受凋落物C/N、土壤肥力和温度条件的影响,然而,这三因素的综合影响仍不清楚。以低肥力土壤(LF)和高肥力土壤(HF)为研究对象,分别添加7种不同C/N的凋落物,并设置培养温度为23 ℃和33 ℃,进行恒温避光培养,期间动态监测CO2排放的变化,以揭示SOC矿化过程应对三因子的响应机制。结果显示,凋落物添加显著增加CO2峰值排放速率,且与C/N>30的凋落物相比,添加C/N<30的凋落物对CO2的峰值排放速率的促进作用更显著。CO2峰值排放速率同时受土壤肥力和培养温度影响,HF-33 ℃条件下的CO2峰值排放速率最高。添加C/N<30的凋落物显著增加了CO2累积排放量,在LF-23 ℃、LF-33 ℃、HF-23 ℃和HF-33 ℃条件下,最大增幅分别为407%、304%、345%和160%。相关分析显示,SOC矿化率与凋落物C/N间呈负相关关系,这说明低质量凋落物会抑制SOC矿化。在LF-23 ℃、LF-33 ℃、HF-23 ℃和HF-33 ℃处理下,与凋落物C/N最低的CN1相比,添加C/N最高的CN7后,SOC矿化率的降幅分别达3.53、3.04、1.71和2.06倍。土壤肥力影响SOC矿化,HF的SOC矿化率较LF高1.29-2.66倍。培养温度对SOC矿化的影响在HF中表现出显著差异,与CK相比,在HF中添加凋落物显著降低了SOC矿化温度敏感性(Q10)。综合PLS-PM模型可知,SOC矿化是凋落物C/N、土壤肥力和培养温度综合作用的结果。其中,凋落物的C/N比对SOC矿化产生显著的负效应,土壤肥力则对SOC矿化产生主要的正效应,而温度的正效应则相对较小。研究结果有助于进一步理解不同土壤肥力和温度背景下,C/N不同的外源有机物输入对SOC矿化的影响及其背后的综合效应。
中图分类号:
李天, 苗淑杰, 余洁, 赵玉蝶, 乔云发. 凋落物C/N对土壤有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1686-1695.
LI Tian, MIAO Shujie, YU Jie, ZHAO Yudie, QIAO Yunfa. The Influence of Litter C/N Ratios on Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(11): 1686-1695.
| 土壤 | pH | 土壤有机碳质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 土壤全磷质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低肥力土 (LF) | 5.35±0.01a | 23.39±0.27b | 2.53±0.04b | 0.82±0.03b | 9.25±0.05a |
| 高肥力土 (HF) | 5.28±0.01a | 41.46±0.85a | 4.42±0.05a | 1.01±0.00a | 9.38±0.15a |
表1 低肥力土和高肥力土基本理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of low- and high-fertility soils
| 土壤 | pH | 土壤有机碳质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 土壤全磷质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低肥力土 (LF) | 5.35±0.01a | 23.39±0.27b | 2.53±0.04b | 0.82±0.03b | 9.25±0.05a |
| 高肥力土 (HF) | 5.28±0.01a | 41.46±0.85a | 4.42±0.05a | 1.01±0.00a | 9.38±0.15a |
| 编号 | 凋落物种类 | 碳质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 氮质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 磷质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1 | 水稻地上部 Shoot of Oryza sativa L. | 293.70±2.54c | 25.19±0.19a | 2.97±0.19a | 11.66±0.17e |
| CN2 | 水稻根 Root of Oryza sativa L. | 261.07±5.79d | 16.24±0.12c | 2.56±0.06b | 16.08±0.34d |
| CN3 | 小麦地上部 Shoot of Triticum aestivum L. | 355.33±1.73b | 19.92±0.17b | 1.87±0.03c | 17.85±0.22d |
| CN4 | 小麦根 Root of Triticum aestivum L. | 332.74±4.90b | 13.36±0.46d | 0.71±0.01e | 24.99±1.25c |
| CN5 | 山油柑 Acronychia pedunculata (L.) Miq. | 337.81±7.10b | 12.16±0.07e | 2.35±0.11b | 27.77±0.53c |
| CN6 | 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis (Hance) Hemsl. | 418.44±3.20a | 11.69±0.21e | 1.27±0.01d | 35.81±0.87b |
| CN7 | 木荷 Schima superba Gardner & Champ. | 399.36±6.52a | 9.47±0.04f | 1.17±0.04d | 42.15±0.50a |
表2 凋落物的基本理化性质
Table 2 Physical and chemical properties of litters
| 编号 | 凋落物种类 | 碳质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 氮质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 磷质量分数/(g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1 | 水稻地上部 Shoot of Oryza sativa L. | 293.70±2.54c | 25.19±0.19a | 2.97±0.19a | 11.66±0.17e |
| CN2 | 水稻根 Root of Oryza sativa L. | 261.07±5.79d | 16.24±0.12c | 2.56±0.06b | 16.08±0.34d |
| CN3 | 小麦地上部 Shoot of Triticum aestivum L. | 355.33±1.73b | 19.92±0.17b | 1.87±0.03c | 17.85±0.22d |
| CN4 | 小麦根 Root of Triticum aestivum L. | 332.74±4.90b | 13.36±0.46d | 0.71±0.01e | 24.99±1.25c |
| CN5 | 山油柑 Acronychia pedunculata (L.) Miq. | 337.81±7.10b | 12.16±0.07e | 2.35±0.11b | 27.77±0.53c |
| CN6 | 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis (Hance) Hemsl. | 418.44±3.20a | 11.69±0.21e | 1.27±0.01d | 35.81±0.87b |
| CN7 | 木荷 Schima superba Gardner & Champ. | 399.36±6.52a | 9.47±0.04f | 1.17±0.04d | 42.15±0.50a |
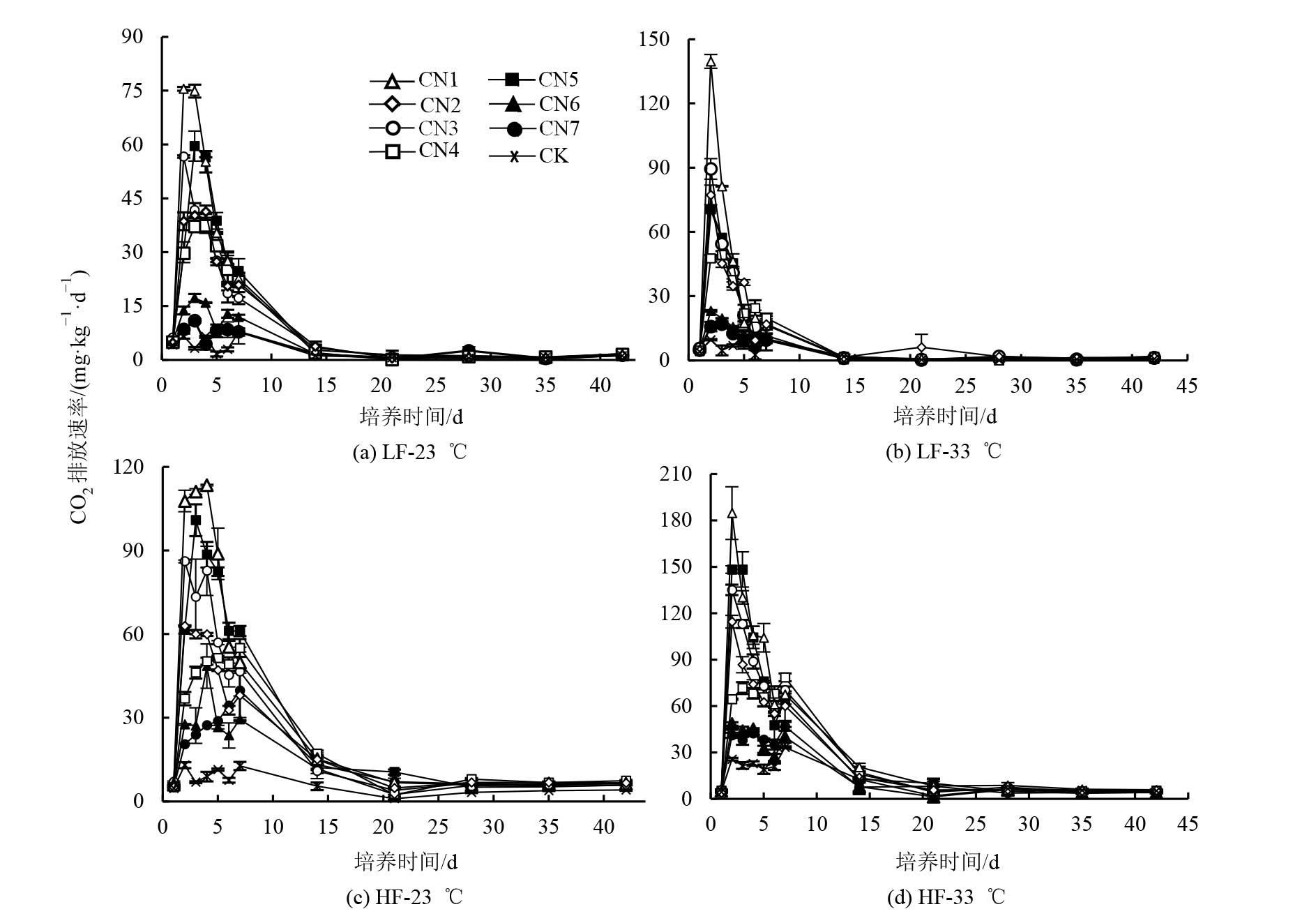
图1 不同C/N凋落物添加对土壤CO2排放速率随时间变化情况 CN1:水稻地上部;CN2:水稻根;CN3:小麦地上部;CN4:小麦根;CN5:山油柑;CN6:厚壳桂;CN7:木荷;CK:对照。LF:低肥力土;HF:高肥力土。下同
Figure 1 Soil CO2 emission rate with time after different C/N ratio litters addition
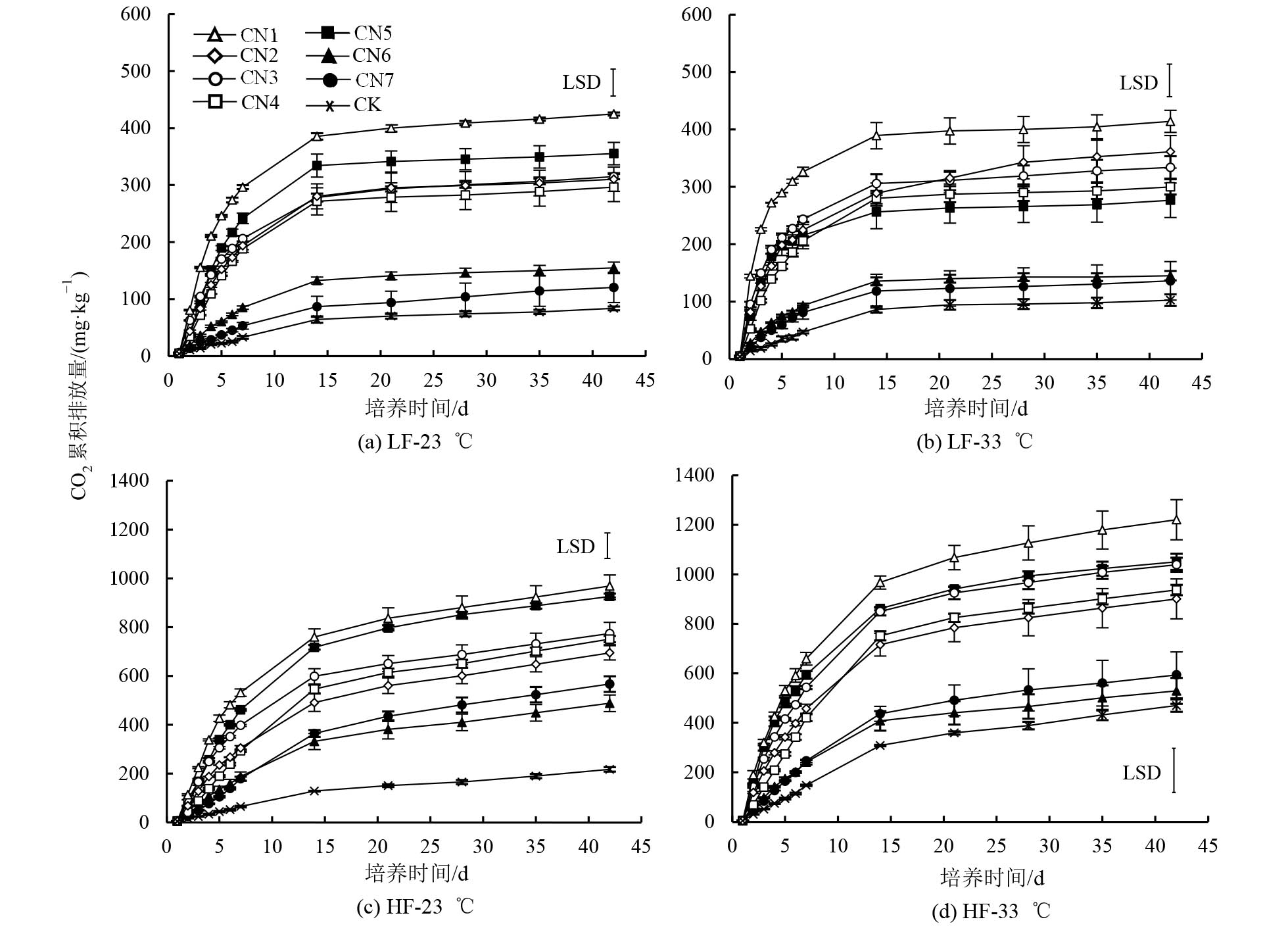
图2 不同C/N凋落物添加后CO2累积排放量随时间的变化 垂直线段表示实验结束时(42 d)不同处理间LSD值。下同
Figure 2 Effects of different C/N ratio litters additions on the dynamics values of cumulative mineralization of SOC
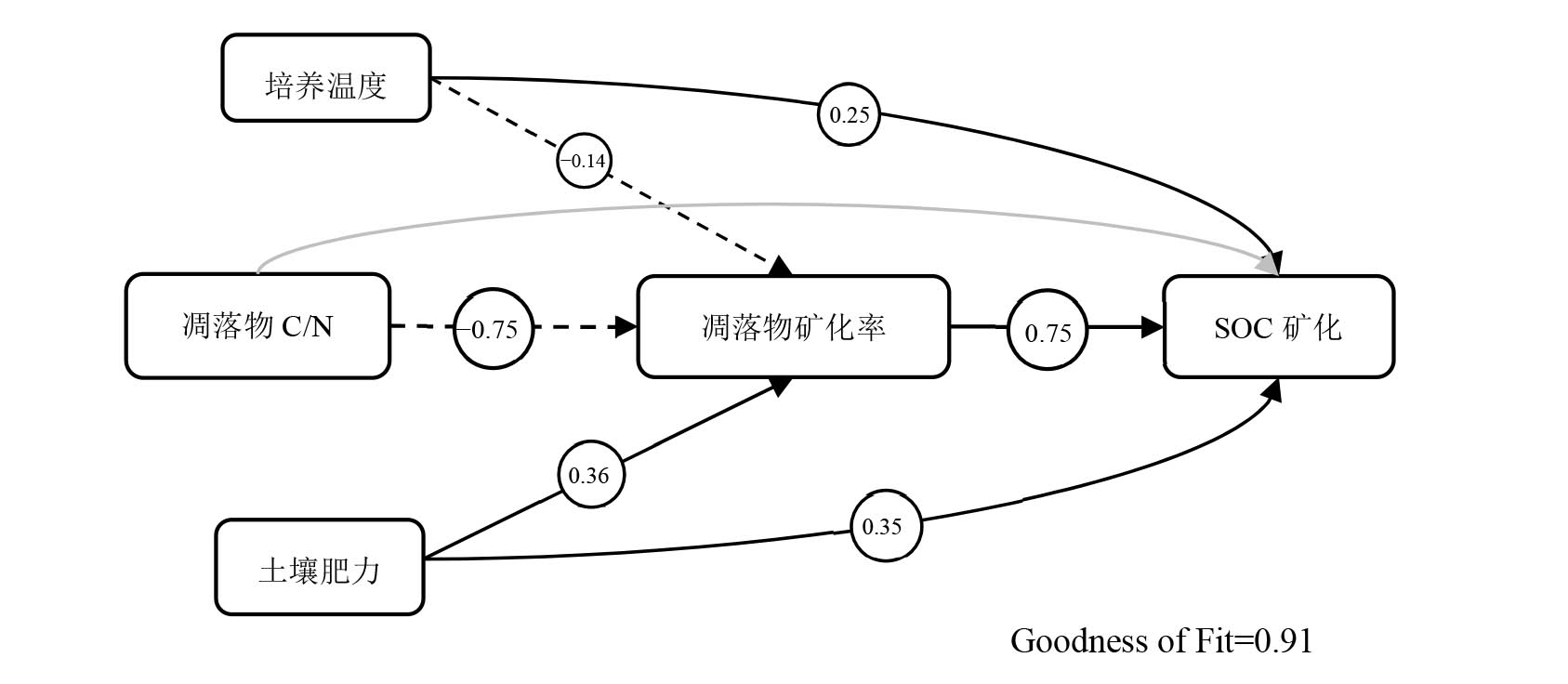
图6 SOC矿化率的偏最小二乘路径模型 箭头圆圈内的数值代表路径系数,圆圈大小或箭头粗细表示相关性的强弱。黑色实线箭头表示正相关,黑色虚线箭头表示负相关(p<0.05);灰色箭头表示关系不显著(p>0.05)。Goodness of Fit表示该模型的拟合程度,Goodness of Fit>0.8表示拟合程度好
Figure 6 PLS Path model of SOC mineralization rate
| [1] |
AVERILL C, HAWKES C V, 2016. Ectomycorrhizal fungi slow soil carbon cycling[J]. Ecology Letters, 19(8): 937-947.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | BASTIDA F, ELDRIDGE D J, GARCIA C, et al., 2021. Soil microbial diversity-biomass relationships are driven by soil carbon content across global biomes[J]. The ISME Journal, 15(7): 2081-2091. |
| [3] | BLAGODATSKAYA E, KUZYAKOV Y, 2013. Active microorganisms in soil: Critical review of estimation criteria and approaches[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 67: 192-211. |
| [4] | CHAO L, LIU Y, FRESCHET G T, et al., 2019. Litter carbon and nutrient chemistry control the magnitude of soil priming effect[J]. Functional Ecology, 33(5): 876-888. |
| [5] | FONTAINE S, HENAULT C, AAMOR A, et al., 2011. Fungi mediate long term sequestration of carbon and nitrogen in soil through their priming effect[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(1): 86-96. |
| [6] | GIARDINA C P, RYAN M G, HUBBARD R M, et al., 2001. Tree species and soil textural controls on carbon and nitrogen mineralization rates[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65(4): 1272-1279. |
| [7] | HART S C, NASON G E, MYROLD D D, et al., 1994. Dynamics of gross nitrogen transformations in an old-growth forest: The carbon connection[J]. Ecology, 75(4): 880-891. |
| [8] | KUZYAKOV Y, BOL R, 2006. Sources and mechanisms of priming effect induced in two grassland soils amended with slurry and sugar[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(4): 747-758. |
| [9] | LENKA S, TRIVEDI P, SINGH B, et al., 2019. Effect of crop residue addition on soil organic carbon priming as influenced by temperature and soil properties[J]. Geoderma, 347: 70-79. |
| [10] | LI C, XIAO C W, LI M X, et al., 2023. The quality and quantity of SOM determines the mineralization of recently added labile C and priming of native SOM in grazed grasslands[J]. Geoderma, 432: 116385. |
| [11] |
LIN J J, ZHU B, CHENG W X, 2015. Decadally cycling soil carbon is more sensitive to warming than faster-cycling soil carbon[J]. Global Change Biology, 21(12): 4602-4612.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | MORETTO A S, DISTEL R A, DIDONE N G, 2001. Decomposition and nutrient dynamic of leaf litter and roots from palatable and unpalatable grasses in a semi-arid grassland[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 18(1): 31-37. |
| [13] | RASUL M, CHO J W, SHIN H S, et al., 2022. Biochar-induced priming effects in soil via modifying the status of soil organic matter and microflora: A review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 805: 150304. |
| [14] | SCHLESINGER W H, 1977. Carbon balance in terrestrial detritus[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 8(1): 51-81. |
| [15] | SIX J, FREY S D, THIET R K, et al., 2006. Bacterial and fungal contributions to carbon sequestration in agroecosystems[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 70(2): 555-569. |
| [16] | SOONG J L, MARANON-JIMENEZ S, COTRUFO M F, et al., 2018. Soil microbial CNP and respiration responses to organic matter and nutrient additions: Evidence from a tropical soil incubation[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 122: 141-149. |
| [17] | TORRES I F, BASTIDA F, HERNANDEZ T, et al., 2014. The role of lignin and cellulose in the carbon-cycling of degraded soils under semiarid climate and their relation to microbial biomass[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 75: 152-160. |
| [18] | WANG Q K, HE T X, LIU J, 2016. Litter input decreased the response of soil organic matter decomposition to warming in two subtropical forest soils[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1): 33814. |
| [19] | XU X, ZHOU Y, RUAN H H, et al., 2010. Temperature sensitivity increases with soil organic carbon recalcitrance along an elevational gradient in the Wuyi Mountains, China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42(10): 1811-1815. |
| [20] |
陈甜, 元方慧, 张琳梅, 等, 2022. 不同化学性质叶凋落物添加对土壤有机碳矿化及激发效应的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(10): 2602-2610.
DOI |
|
CHEN T, YUAN F H, ZHANG L M, et al., 2022. Effects of addition of leaf litter with different chemical properties on soil organic carbon mineralization and priming effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 33(10): 2602-2610.
DOI |
|
| [21] | 黄锦学, 熊德成, 刘小飞, 等, 2017. 增温对土壤有机碳矿化的影响研究综述[J]. 生态学报, 37(1): 12-24. |
| HUANG J X, XIONG D C, LIU X F, et al., 2017. Effects of warming on soil organic carbon mineralization: A review[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(1): 12-24. | |
| [22] | 李梦娇, 陈甜, 洪小敏, 等, 2021. 不同化学结构外源碳添加对红壤和沙土有机碳矿化动态的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(6): 1609-1617. |
|
LI M J, CHEN T, HONG X M, et al., 2021. Effects of adding exogenous carbon with different chemical structure on the dynamics of organic carbon mineralization in red and sandy soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(6): 1609-1617.
DOI |
|
| [23] |
梁鑫, 韩亚峰, 郑柯, 等, 2023. 磁铁矿对稻田土壤碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(9): 1615-1622.
DOI |
| LIANG X, HAN Y F, ZHENG K, et al., 2023. Effects of Fe3O4 on soil carbon mineralization in paddy field[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32(9): 1615-1622. | |
| [24] | 刘金炜, 张文菊, 邬磊, 等, 2020. 长期施肥条件下红壤有机碳矿化对温度变化模式的响应[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (2): 10-16. |
| LIU J W, ZHANG W J, WU L, et al., 2020. Response of organic carbon mineralization to temperature changing pattern under long-term fertilization in red Soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (2): 10-16. | |
| [25] | 刘四义, 梁爱珍, 杨学明, 等, 2015. 不同部位玉米秸秆对两种质地黑土CO2排放和微生物量的影响[J]. 环境科学, 36(7): 2686-2694. |
| LIU S Y, LIANG A Z, YANG X M, et al., 2015. Effects of different residue part inputs of corn straws on CO2 efflux and microbial biomass in clay loam and sandy loam black soils[J]. Environmental Science, 36(7): 2686-2694. | |
| [26] |
裴蓓, 高国荣, 2018. 凋落物分解对森林土壤碳库影响的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 34(26): 58-64.
DOI |
|
PEI B, GAO G R, 2018. Impact of forest litter decomposition on soil carbon pool: A review[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 34(26): 58-64.
DOI |
|
| [27] | 彭少麟, 刘强, 2002. 森林凋落物动态及其对全球变暖的响应[J]. 生态学报, 22(9): 1534-1544. |
| PENG S L, LIU Q, 2002. The dynamics of forest litter and Its responses to global warming[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22(9): 1534-1544. | |
| [28] |
秦文宽, 张秋芳, 敖古凯麟, 等, 2024. 土壤有机碳动态对增温的响应及机制研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 48(4): 403-415.
DOI |
| QIN W K, ZHANG Q F, AO G K L, et al., 2024. Responses and mechanisms of soil organic carbon dynamics to warming: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 48(4): 403-415. | |
| [29] | 史方颖, 张风宝, 杨明义, 2022. 基于文献计量分析的土壤有机碳矿化研究进展与热点[J]. 土壤学报, 59(2): 381-392. |
| SHI F Y, ZHANG F B, YANG M Y, 2022. Research hotspots and progress of soil organic carbon mineralization based on bibliometrics method[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 59(2): 381-392. | |
| [30] | 史学军, 潘剑君, 陈锦盈, 等, 2009. 不同类型凋落物对土壤有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 环境科学, 30(6): 1832-1837. |
| SHI X J, PAN J J, CHEN J Y, et al., 2009. Effects of different types of litters on soil organic carbon mineralization[J]. Environmental Science, 30(6): 1832-1837. | |
| [31] |
宋珂辰, 王国会, 许冬梅, 等, 2021. 不同封育年限荒漠草原土壤有机碳矿化及温度敏感性[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 453-459.
DOI |
| SONG K C, WANG G H, XU D M, et al., 2021. Soil organic carbon mineralization and its temperature sensitivity in desert steppe with different enclosure ages[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 453-459. | |
| [32] |
田玉强, 陈颖, 欧阳胜男, 等, 2020. 外源性碳氮添加对北方半干旱草原土壤有机质矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(6): 1101-1108.
DOI |
| TIAN Y Q, CHEN Y, OUYANG S N, et al., 2020. The Effect of carbon and nitrogen addition on soil organic matter mineralization in the semi-arid grassland of north China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(6): 1101-1108. | |
| [33] | 王丹, 吕瑜良, 徐丽, 等, 2013. 水分和温度对若尔盖湿地和草甸土壤碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(20): 6436-6443. |
| WANG D, LÜ Y L, XU L, et al., 2013. The effect of moisture and temperature on soil C mineralization in wetland and steppe of the Zoige region, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(20): 6436-6443. | |
| [34] | 王永慧, 杨殿林, 红雨, 等, 2019. 不同地力玉米田土壤有机碳矿化特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(3): 590-599. |
| WANG Y H, YANG D L, HONG Y, et al., 2019. Characteristics of soil organic carbon mineralization in the soil of maize fields with different soil fertility[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(3): 590-599. | |
| [35] | 吴庆标, 王效科, 欧阳志云, 2006. 活性有机碳含量在凋落物分解过程中的作用[J]. 生态环境, 15(6): 1295-1299. |
| WU Q B, WANG X K, OUYANG Z Y, 2006. Effects of labile organic carbon on the litters decomposition process[J]. Ecology and Environment, 15(6): 1295-1299. | |
| [36] | 元方慧, 应宇馨, 陈子亮, 等, 2024. 不同培养温度下杉木叶凋落物添加对土壤CO2释放及激发效应的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 43(4): 993-999. |
| YUAN F H, YING Y X, CHEN Z L, et al., 2024. Effects of Chinese fir leaf litter addition on soil CO2 release and priming effect under different incubation temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 43(4): 993-999. | |
| [37] | 张薇, 王子芳, 王辉, 等, 2007. 土壤水分和植物残体对紫色水稻土有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 13(6): 1013-1019. |
| ZHANG W, WANG Z F, WANG H, et al., 2007. Organic carbon mineralization affected by water content and plant residues in purple paddy soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 13(6): 1013-1019. | |
| [38] | 张迎春, 王萍, 刘亚龙, 等, 2024. 长期种植作物对中国农田土壤有机碳影响的Meta分析[J]. 土壤学报, 61(6): 1628-1638. |
| ZHANG Y C, WANG P, LIU Y L, et al., 2024. Effects of long-term crop cultivation on soil organic carbon in China’s farmland: A meta-analysis[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 61(6): 1628-1638. | |
| [39] | 朱灵, 张梦瑶, 高永恒, 2020. 高寒草原土壤有机碳矿化对水氮添加的响应[J]. 水土保持通报, 40(1): 30-37. |
| ZHU L, ZHANG M Y, GAO Y H, 2020. Response of soil organic carbon mineralization to water and nitrogen addition in alpine steppe[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 40(1): 30-37. |
| [1] | 李彦林, 陈杨洋, 杨霜溶, 刘菊梅. 植物根系分泌的有机酸对土壤碳氮矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371. |
| [2] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [3] | 陈丽娟, 周文君, 易艳芸, 宋清海, 张一平, 梁乃申, 鲁志云, 温韩东, MOHD Zeeshan, 沙丽清. 云南哀牢山亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤CH4通量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 949-960. |
| [4] | 李梦丽, 徐墨馨, 陈永山, 叶丽丽, 蒋金平. 石灰性土壤添加不同量碳酸钙对秸秆有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2002-2009. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
