生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 301-309.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.02.014
李荣杰1( ), 李惠梅1,*(
), 李惠梅1,*( ), 武非非1(
), 武非非1( ), 赵明德2,*(
), 赵明德2,*( ), 王诗涵1, 孙雪颖1
), 王诗涵1, 孙雪颖1
收稿日期:2023-10-23
出版日期:2024-02-18
发布日期:2024-04-03
通讯作者:
赵明德。E-mail: zmd1226@163.com作者简介:李荣杰(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事土地资源管理研究。E-mail: 1362711877@qq.com;#李荣杰与武非非为共同第一作者
基金资助:
LI Rongjie1( ), LI Huimei1,*(
), LI Huimei1,*( ), WU Feifei1(
), WU Feifei1( ), ZHAO mingde2,*(
), ZHAO mingde2,*( ), WANG Shihan1, SUN xueying1
), WANG Shihan1, SUN xueying1
Received:2023-10-23
Online:2024-02-18
Published:2024-04-03
摘要:
在青海湖流域拟建国家公园的背景下,生态系统服务空间分异及其驱动因素的探析,可以极大的促进生态环境保护与修复政策制定及区域可持续发展。以青海湖流域为研究对象,基于2010-2020年的土地利用变化,分析生态系统服务的动态变化,探讨了生态系统服务的空间异质性,并引入地理探测器模型探究了生态系统服务空间分异的自然和社会经济驱动因素。结果表明,1)2010-2020年草地作为主要地类变化幅度小;水域面积增幅最大,其主要源于未利用地和草地的转入。2010-2020年ESV表现为弱递增趋势,总生态系统服务价值(ESV)由1.35×103亿元增加到1.37×103亿元,增加了1.48%;其中,水域贡献率最大(1.04×103亿元以上),其次是草地(274亿元以上)。生态服务功能以调节服务为主,贡献量达到1.12×103亿元以上。2)青海湖流域ESV呈现出从湖体向周围递减的空间格局,并表现出显著的高程依赖性;流域ESV存在显著的空间正相关(Moran's I均为正数)和聚集分布;高高值和低低值聚集区为空间上的主要聚集区,高高值聚集区主要聚集在低海拔区,低低值聚集区则主要分布在高海拔区,高高值和低低值聚集区在2010-2020年均呈递增趋势,但低低值聚集区增幅极小。3)ESV空间异质性是自然地理和社会经济因素协同作用的结果,自然因素影响力表现出更高的敏感性,海拔和气候所体现出的空间异质性是ESV的主要驱动因素。低海拔地区ESV空间聚集性等结果表明,今后仍需关注人类活动和气候变化对ESV的影响和权衡,以缓解人地矛盾进而推进青海湖国家公园建设。该研究可为区域生态系统保护和管理奠定科学基础,也可为决策者评估生态屏障区的生态安全提供理论基础和参考。
中图分类号:
李荣杰, 李惠梅, 武非非, 赵明德, 王诗涵, 孙雪颖. 青海湖流域生态系统服务空间分异规律及驱动力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 301-309.
LI Rongjie, LI Huimei, WU Feifei, ZHAO mingde, WANG Shihan, SUN xueying. Study on the Spatial Differentiation Pattern and Driving Force of Ecosystem Services in Qinghai Lake Basin[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 301-309.
| 生态服务功能 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2020年 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESV/ 109元 | 比例/ % | ESV/ 109元 | 比例/ % | ESV/ 109元 | 比例/ % | |||
| 供给服务 | 9.74 | 7.27 | 9.78 | 7.2 | 9.88 | 7.22 | ||
| 调节服务 | 112 | 82.9 | 113 | 83.1 | 114 | 83.2 | ||
| 支持服务 | 10.4 | 7.70 | 10.5 | 7.72 | 10.5 | 7.66 | ||
| 文化服务 | 3.06 | 2.27 | 3.08 | 2.26 | 3.09 | 2.26 | ||
| 总计 | 135 | 100 | 136 | 100 | 137 | 100 | ||
表1 青海湖流域2010-2020年生态系统服务功能
Table 1 Ecosystem Service Functions of Qinghai Lake Basin from 2010 to 2020
| 生态服务功能 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2020年 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESV/ 109元 | 比例/ % | ESV/ 109元 | 比例/ % | ESV/ 109元 | 比例/ % | |||
| 供给服务 | 9.74 | 7.27 | 9.78 | 7.2 | 9.88 | 7.22 | ||
| 调节服务 | 112 | 82.9 | 113 | 83.1 | 114 | 83.2 | ||
| 支持服务 | 10.4 | 7.70 | 10.5 | 7.72 | 10.5 | 7.66 | ||
| 文化服务 | 3.06 | 2.27 | 3.08 | 2.26 | 3.09 | 2.26 | ||
| 总计 | 135 | 100 | 136 | 100 | 137 | 100 | ||
| 年份 | ESV及比例 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 水域 | 建设用地 | 未利用地 | 总计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010年 | ESV/109元 | 0.290 | 2.69 | 27.5 | 104 | 0 | 0.515 | 135 |
| 比例/% | 0.215 | 1.99 | 20.4 | 77.0 | 0.00 | 0.381 | 100 | |
| 2015年 | ESV/109元 | 0.289 | 2.76 | 27.6 | 105 | 0 | 0.499 | 136 |
| 比例/% | 0.212 | 2.03 | 20.3 | 77.1 | 0.00 | 0.367 | 100 | |
| 2020年 | ESV/109元 | 0.289 | 2.69 | 27.4 | 106 | 0 | 0.502 | 137 |
| 比例/% | 0.211 | 1.97 | 20.0 | 77.4 | 0.00 | 0.370 | 100 |
表2 青海湖流域2010-2020年不同土地利用类型ESV
Table 2 ESV of different land use types in Qinghai Lake Basin from 2010 to 2020
| 年份 | ESV及比例 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 水域 | 建设用地 | 未利用地 | 总计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010年 | ESV/109元 | 0.290 | 2.69 | 27.5 | 104 | 0 | 0.515 | 135 |
| 比例/% | 0.215 | 1.99 | 20.4 | 77.0 | 0.00 | 0.381 | 100 | |
| 2015年 | ESV/109元 | 0.289 | 2.76 | 27.6 | 105 | 0 | 0.499 | 136 |
| 比例/% | 0.212 | 2.03 | 20.3 | 77.1 | 0.00 | 0.367 | 100 | |
| 2020年 | ESV/109元 | 0.289 | 2.69 | 27.4 | 106 | 0 | 0.502 | 137 |
| 比例/% | 0.211 | 1.97 | 20.0 | 77.4 | 0.00 | 0.370 | 100 |
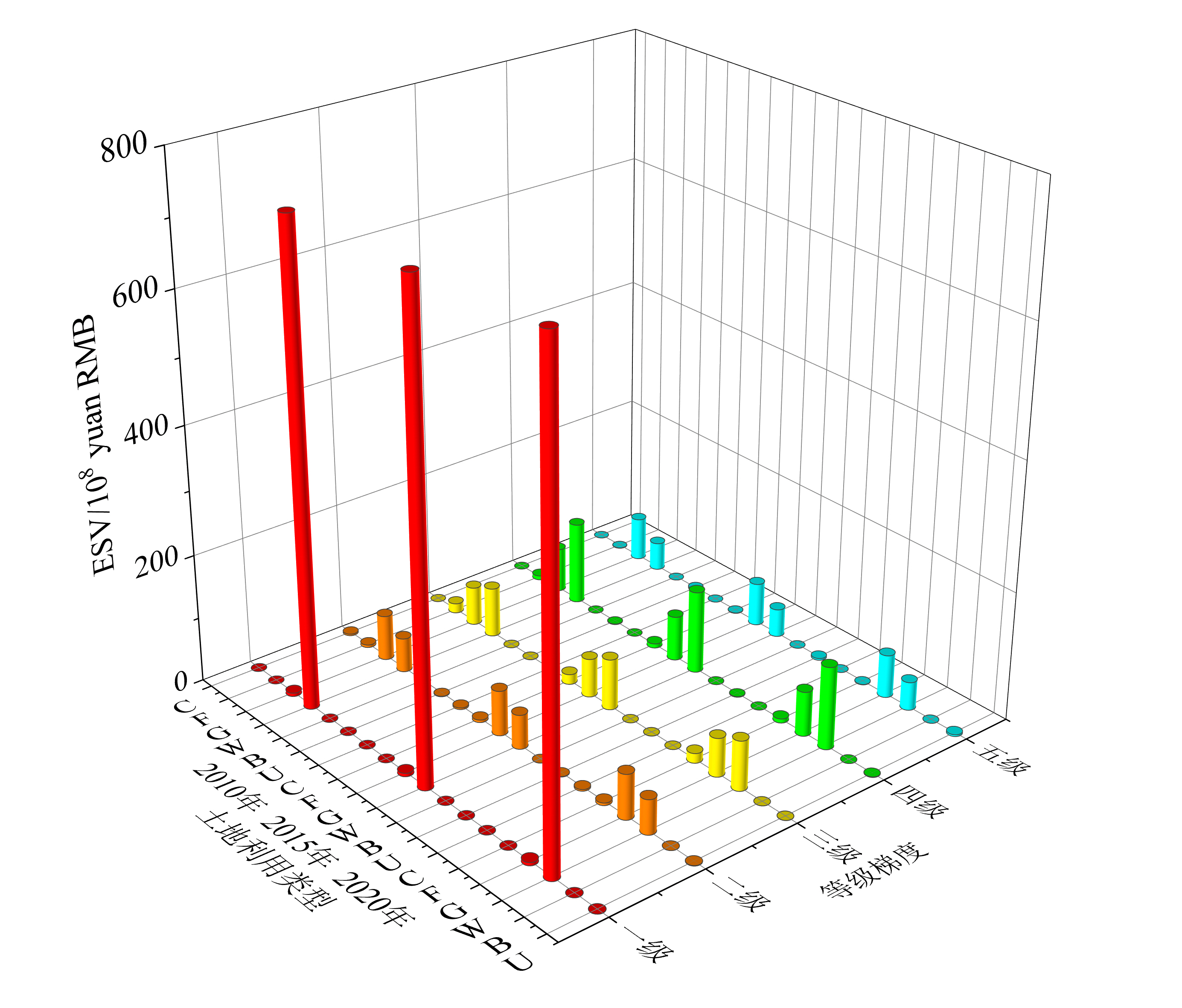
图4 青海湖流域2010-2020年不同海拔梯度ESV C、F、G、W、B、U分别表示耕地、林地、草地、水域、建设用地、未利用地
Figure 4 ESV of different elevation gradients in Qinghai Lake Basin from 2010 to 2020
| 指数 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2020年 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moran's I | 0.885 | 0.884 | 0.892 |
| z scores | 153 | 152 | 161 |
| P value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
表3 全局空间自相关显著性检验
Table 3 Significance test for global Moran's I
| 指数 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2020年 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moran's I | 0.885 | 0.884 | 0.892 |
| z scores | 153 | 152 | 161 |
| P value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 年份 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | ||||||
| 2010 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.117 | 0.000 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.214 | 0.000 | 0.350 | 0.000 | 0.031 | 0.000 | |||||
| 2015 | 0.031 | 0.000 | 0.134 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.124 | 0.226 | 0.000 | 0.356 | 0.000 | 0.061 | 0.000 | |||||
| 2020 | 0.031 | 0.000 | 0.142 | 0.000 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 0.240 | 0.000 | 0.377 | 0.000 | 0.111 | 0.000 | |||||
表4 单因子探测结果
Table 4 Single-factor probe results
| 年份 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | ||||||
| 2010 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.117 | 0.000 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.214 | 0.000 | 0.350 | 0.000 | 0.031 | 0.000 | |||||
| 2015 | 0.031 | 0.000 | 0.134 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.124 | 0.226 | 0.000 | 0.356 | 0.000 | 0.061 | 0.000 | |||||
| 2020 | 0.031 | 0.000 | 0.142 | 0.000 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 0.240 | 0.000 | 0.377 | 0.000 | 0.111 | 0.000 | |||||
| [1] |
COSTANZA R, ARGE R, DE GROOT R, et al., 1997. The value of the world's ecosystem services and natural capital[J]. Nature, 387(6630): 253-260.
DOI |
| [2] | DAILY G C, 1997. Nature's services: societal dependence on natural ecosystems[M]. Washington, DC: Island Press. |
| [3] |
JIA Z X, WANG X F, FENG X M, et al., 2023. Exploring the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services and influencing factors on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau[J]. Ecological Indicators, 154(6479): 110521.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
SHIFAW E, SHA J, LI X, et al., 2019. An insight into land-cover changes and their impacts on ecosystem services before and after the implementation of a comprehensive experimental zone plan in Pingtan Island, China[J]. Land Use Policy 82( 3): 631-642.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ZHAO L, DU M X, ZHANG W, et al., 2022. Functional zoning in national parks under multifactor trade-off guidance: A case study of Qinghai Lake National Park in China[J]. Journal Of Geographical Sciences, 32(10): 1969-1997.
DOI |
| [6] | 程俭, 刘昌华, 刘凯, 2021. 2004年以来青海湖快速扩张对人居设施与草地的潜在影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 33(3): 922-934. |
|
LIU C H, LIU K, 2021. Potential impact of the dramatical expansion of Lake Qinghai on the habitat facilities and grassland since 2004[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 33(3): 922-934.
DOI URL |
|
| [7] |
曹生奎, 曹广超, 陈克龙, 等, 2014. 青海湖高寒湿地生态系统服务价值动态[J]. 中国沙漠, 34(5): 1402-1409
DOI |
| CAO G C, CHEN K L, et al., 2014. Dynamics of ecosystem service value of Qinghai Lake alpine wetland[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 34(5): 1402-1409. | |
| [8] |
戴尔阜, 王亚慧, 2020. 横断山区产水服务空间异质性及归因分析[J]. 地理学报, 75(3): 607-619.
DOI |
|
WANG Y H, 2020. Spatial heterogeneity and driving mechanisms of water yield service in the Hengduan Mountain region[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(3): 607-619.
DOI |
|
| [9] | 范耘恺, 马书明, 2023. 多情景模拟土地利用变化下的生态系统服务评估及其权衡/协同研究——以辽宁省沈抚地区为例[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(10):419-434. |
| MA S M, 2023. Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service assessment and its trade-off/synergy under land use change: A case study of Shenfu area, Liaoning Province[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiac, 43(10): 419-434. | |
| [10] | 国土资源部, 2017. 土地利用现状分类: GB/T 21010—2017[S]. 北京. 中国国家标准化委员会: 5-9. |
| Ministry of Land and Resources, 2017. Classification of land use status: GB/T 21010—2017[S]. Beijing: China National Committee for Standardization: 5-9. | |
| [11] | 国家发展和改革委员会价格司, 2021. 2020年全国农产品成本收益资料汇编[M]. 北京: 中国市场出版社: 3-29. |
| Price Department of the National Development and Reform Commission, 2021. Compilation of national agricultural product cost benefit data in 2020[M]. Beijing: China Market Publishing House: 3-29. | |
| [12] | 韩艳莉, 于德永, 陈克龙, 等, 2022. 2000-2018年青海湖流域气温和降水量变化趋势空间分布特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 45(4): 999-1009. |
| YU D Y, CHEN K L, 2022. Spatial distribution characteristics of temperature and precipitation trend in Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2018[J]. Arid Land Geography, 45(4): 999-1009. | |
| [13] |
何再军, 程江浩, 刘悦俊, 等, 2023. 1990-2020年土地利用和气候变化对青藏高原生态系统调节服务的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 45(5): 1616-1628.
DOI |
| HE Z J, CHENG J H, LIU Y J, et al., 2023. Impacts of land use and climate change on ecosystem regulation services in the Tibetan Plateau from 1990 to 2020[J]. Glacier permafrost, 45(5): 1616-1628. | |
| [14] | 姜晗, 吴群, 2021. 基于LUCC的江苏省生态系统服务价值评估及时空演变特征研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 30(11): 2712-2725. |
| JIANG H, WU Q, 2021. Ecological service value evaluation and temporal-spatial evolution characteristics in Jiangsu province based on LUCC[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 30(11): 2712-2725. | |
| [15] | 李昊冉, 刘喆, 李晓溪, 等, 2023. 基于社交媒体文本的城市滨河绿地生态系统文化服务评价[J]. 风景园林, 30(8): 80-88. |
| LIU Z, LI X X, et al., 2023. Evaluation of cultural ecosystem services in urban riverside green space based on online social media commentary[J]. Landscape Architecture, 30(8): 80-88. | |
| [16] | 李惠梅, 张安录, 高泽兵, 等, 2012. 青海湖地区生态系统服务价值变化分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 31(12): 1747-1754. |
| ZHANG A L, GAO Z B, et al., 2012. Analysis on the change of ecosystem service value in Qinghai Lake area[J]. Advances in Geographical Science, 31(12): 1747-1754. | |
| [17] | 李振南, 雷伟伟, 王一帆, 等, 2023. 基于多源卫星测高数据的青海湖水位变化研究[J]. 测绘科学, 48(5): 140-151. |
| LEI W W, WANG Y F, et al., 2023. Water level variation of Qinghai Hu based on multi-source satellite altimetry data[J]. Science ofSurveying and Mapping, 48(5): 140-151. | |
| [18] | 李江宁, 2021. 青海湖水位上涨当地牧民获补偿3990万元[N]. 中国新闻网,2021-12-09(16). |
| LI J N, 2021. The water level of Qinghai Lake rises, and local herders receive 39.9 million yuan in compensation[N]. China News Network, 2021-12-09( 16). | |
| [19] | 连喜红, 祁元, 王宏伟, 等, 2023. 人类活动影响下的青海湖流域生态系统服务空间格局[J]. 冰川冻土, 41(5): 1254-1263. |
| QI Y, WANG H W, et al., 2023. Spatial pattern of ecosystem services under the influence of human activities in Qinghai Lake watershed[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 41(5): 1254-1263. | |
| [20] | 刘纪远, 匡文慧, 张增祥, 等, 2014. 20世纪80年代末以来中国土地利用变化的基本特征与空间格局[J]. 地理学报, 69(1): 3-14. |
|
KUANG W H, ZHANG Z X, et al., 2014. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land use changes in China since the late 1980s[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 69(1): 3-14.
DOI |
|
| [21] | 马小霞, 2021. 新时代中国高原湖泊流域保护治理的几点思考[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 34(7): 14-19. |
| 2021. Thoughts on the protection and management of plateau lake basin in new era in China[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 34(7): 14-19. | |
| [22] |
乔斌, 祝存兄, 曹晓云, 等, 2020. 格网尺度下青海玛多县土地利用及生态系统服务价值空间自相关分析[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(5): 1660-1672.
DOI |
|
ZHU C X, CAO X Y, et al., 2020. Spatial autocorrelation analysis of land use and ecosystem service value in Maduo County, Qinghai Province, China at the grid scale[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(5): 1660-1672.
DOI |
|
| [23] | 乔伟峰, 盛业华, 方斌, 等, 2013. 基于转移矩阵的高度城市化区域土地利用演变信息挖掘——以江苏省苏州市为例[J]. 地理研究, 32(8): 1497-1507. |
| SHENG Y H, FANG B, et al., 2013. Land use change information mining in highly urbanized area based on transfer matrix: A case study of Suzhou, Jiangsu province geographical research[J]. Geographical Research, 32(8): 1497-1507. | |
| [24] |
谭昭昭, 陈毓遒, 丁憬枫, 等, 2023. 浙江东部沿海城市土地利用模拟及生态系统服务价值评估[J]. 应用生态学报, 34(10): 2777-2787.
DOI |
| CHEN Y Q, DING J F, et al., 2023. Land use simulation and ecosystem service value assessment of coastal cities in eastern Zhejiang[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 34(10): 2777-2787. | |
| [25] | 王丹, 荆延德, 韩善梅, 等, 2022. 基于格网的南四湖流域土地利用碳排放与其生态系统服务价值时空关系分析[J]. 生态学报, 42(23): 9604-9614. |
| JING Y D, HAN S M, et al., 2022. Spatio-temporal relationship of land-use carbon emission and ecosystem service value in Nansi Lake Basin based upon a grid square[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(23): 9604-9614. | |
| [26] |
王劲峰, 徐成东, 2017. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
|
XU C D, 2017. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(1): 116-134.
DOI |
|
| [27] | 吴恒飞, 陈克龙, 张乐乐, 2022. 气候变化下青海湖流域生态健康评价研究[J]. 生态科学, 41(4): 41-48. |
| CHEN K L, ZHANG L L, 2022. Study on ecological health evaluation of Qinghai Lake Basin under climate change[J]. Ecological Science, 41(4): 41-48. | |
| [28] | 肖建设, 乔斌, 陈国茜, 等, 2020. 黄河源区玛多县土地利用和生态系统服务价值的演变[J]. 生态学报, 40(2): 510-521. |
| QIAO B, CHEN G Q, et al., 2020. Land use change and evolution of ecosystem service value in Maduo County of source region of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(2): 510-521. | |
| [29] | 谢高地, 张彩霞, 张雷明, 等, 2015. 基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进[J]. 自然资源学报, 30(8): 1243-1254. |
|
ZHANG C X, ZHANG L M, et al., 2015. Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 30(8): 1243-1254.
DOI |
|
| [30] | 熊侣英, 师学义, 2018. 黄土山丘区土地利用变化对生态系统服务价值的影响——以长河流域为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(2): 335-340. |
| SHI X Y, 2018. Efferts of land use change on ecosystem service value in the loess hilly area: A case study of the Changhe River Basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(2): 335-340. | |
| [31] | 严长安, 杨汝兰, 付潇华, 等, 2023. 土地利用变化对滇池流域生态系统服务价值的影响[J]. 生态学报, 43(15): 6194-6202. |
| YAN C A, YANG R L, FU X H, et al., 2023. Impact of land-use change on ecosystem services value in Dianchi Lake Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(15): 6194-6202. | |
| [32] |
张卫红, 谢家丽, 刘志鹏, 等, 2023. 2000-2020年宁夏生态系统服务价值变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 43(4):157-167.
DOI |
| XIE J L, LIU Z P, et al., 2023. Changes in ecosystem service value in Ningxia from 2000 to 2020[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 43(4):157-167. |
| [1] | 田成诗, 孙瑞欣. 长江经济带市域生态环境质量空间分异与影响因素分析——基于三生空间的土地利用转型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1173-1184. |
| [2] | 李惠梅, 李荣杰, 晏旭昇, 武非非, 高泽兵, 谭永忠. 青海湖流域生态风险评价及生态功能分区研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1185-1195. |
| [3] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [4] | 付蓉, 武新梅, 陈斌. 城市地表温度空间分异及驱动因子差异性分析——以合肥市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 110-122. |
| [5] | 刘香华, 王秀明, 刘谞承, 张音波, 刘飘. 基于外溢生态系统服务价值的广东省生态补偿机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1024-1031. |
| [6] | 聂桐, 董国涛, 蒋晓辉, 郭欣伟, 党素珍, 郑嘉昊, 李立缠, 王江. 榆林地区植被时空分异特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 26-36. |
| [7] | 齐静, 邓伟, 周渝, 刘婷, 罗旭. 重庆市生态保护红线成效评估方法与应用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1532-1540. |
| [8] | 雷金睿, 陈宗铸, 陈毅青, 陈小花, 李苑菱, 吴庭天. 1990—2018年海南岛湿地景观生态安全格局演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(2): 293-302. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
