生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 1709-1718.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.09.018
• 研究论文 •
上一篇
高熙梣1( ), 孔涛1,*(
), 孔涛1,*( ), 李华孙2, 李多美1, 张加良1
), 李华孙2, 李多美1, 张加良1
收稿日期:2023-04-21
出版日期:2023-09-18
发布日期:2023-12-11
通讯作者:
*孔涛。E-mail: kongtao2005@126.com作者简介:高熙梣(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为生态修复理论研究。E-mail: gchengt@163.com
基金资助:
GAO Xichen1( ), KONG Tao1,*(
), KONG Tao1,*( ), LI Huasun2, LI Duomei1, ZHANG Jialiang1
), LI Huasun2, LI Duomei1, ZHANG Jialiang1
Received:2023-04-21
Online:2023-09-18
Published:2023-12-11
摘要:
煤矿开采区矸石山由于其有机质含量低、土壤物理结构不良,致使植物生长困难,复垦难度大。针对上述问题,将微生物菌剂与废弃资源配施,以期在矸石山建立适宜先锋植物定植的复垦环境并筛选最优施用方案。以黑麦草(Lolium perenne)为供试植物,选取废弃资源古龙酸母液(RAE)、长枝木霉菌(TL)与剩余活性污泥(AS)为改良剂在矸石山基质生境条件下进行盆栽试验,设置8种不同处理,分别为RAE、TL、AS、RAE+TL、RAE+AS、TL+AS、RAE+TL+AS及CK,评估不同处理对黑麦草生长生理、土壤酶活性及微生物量的影响。结果表明,1)各处理均能够提高黑麦草的生长指标,其中RAE+TL+AS三施对黑麦草总生物量的提高效果最好,比CK提高了2.52倍;同时各处理总体上能够降低叶片丙二醛含量,提高叶片过氧化氢酶活性、脯氨酸和可溶性糖含量,表明TL、RAE、AS是通过提高植物抗氧化功能而不是通过提高渗透压的方式来提高抗逆性。其中AS单施对提高黑麦草生长、生理性质的效果最好,其生长生理综合指数(PGPI)比CK提高了3.88倍。2)在土壤酶活性方面,单施处理中AS,配施处理中TL+AS,对蔗糖酶、脲酶、磷酸酶和过氧化氢酶活性提升效果最好。3)在土壤微生物量方面,RAE+TL+AS三施对微生物量碳的提高幅度最大,比CK提高了1.64倍。各处理中,AS单施处理的土壤微生物质量综合指数(SMQI)最高,但考虑到总生物量(复垦效果),建议矸石山复垦采用三施处理;从成本角度考虑,建议采用AS单施处理。该研究为矿区矸石山复垦提供有益的技术探索,也为古龙酸母液和剩余活性污泥的资源化利用提供了全新的见解和技术支持。
中图分类号:
高熙梣, 孔涛, 李华孙, 李多美, 张加良. 古龙酸母液、木霉菌与活性污泥配施对矸石山黑麦草生理特性及土壤微生物性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1709-1718.
GAO Xichen, KONG Tao, LI Huasun, LI Duomei, ZHANG Jialiang. Effect of Combined Application Residue after Evaporation, Trichoderma longibrachiatum and Activated Sludge on Physiological Characteristics of Perennial Ryegrass and Soil Microbial Properties in Gangue Hill[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1709-1718.
| 施用 材料 | 水分 含量/% | pH | w(OM)/ (g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/ (g∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/ (g∙kg−1) | w(速效钾)/ (g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAE | 67.35 | 0.27 | 743.81 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.37 |
| AS | 88.16 | 6.92 | 330.00 | 3.96 | 0.80 | 3.97 |
表1 施用材料理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of applied materials
| 施用 材料 | 水分 含量/% | pH | w(OM)/ (g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/ (g∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/ (g∙kg−1) | w(速效钾)/ (g∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAE | 67.35 | 0.27 | 743.81 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.37 |
| AS | 88.16 | 6.92 | 330.00 | 3.96 | 0.80 | 3.97 |
| 处理 | 施肥量 | 施用方式 |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 不施肥 | ‒ |
| RAE | 1.05%RAE | 浇灌 |
| TL | 0.25%TL | 拌土 |
| AS | 30%AS | 拌土 |
| RAE+TL | 1.05%RAE+0.25%TL | 先拌土, 后浇灌 |
| TL+AS | 0.25%TL+30%AS | 混合拌土 |
| RAE+AS | 1.05%RAE+30%AS | 先拌土, 后浇灌 |
| RAE+TL+AS | 1.05%RAE+0.25%TL+30%AS | 混合拌土, 再浇灌 |
表2 盆栽试验设计方案
Table 2 Pot experiment design scheme
| 处理 | 施肥量 | 施用方式 |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 不施肥 | ‒ |
| RAE | 1.05%RAE | 浇灌 |
| TL | 0.25%TL | 拌土 |
| AS | 30%AS | 拌土 |
| RAE+TL | 1.05%RAE+0.25%TL | 先拌土, 后浇灌 |
| TL+AS | 0.25%TL+30%AS | 混合拌土 |
| RAE+AS | 1.05%RAE+30%AS | 先拌土, 后浇灌 |
| RAE+TL+AS | 1.05%RAE+0.25%TL+30%AS | 混合拌土, 再浇灌 |

图1 配施处理在矸石山基质中对黑麦草株高、总生物量的影响 不同字母代表处理之间有显著性差异(P<0.05),n=3;CK:不施肥;TL:长枝木霉菌;RAE:古龙酸母液;AS:剩余活性污泥;RAE+TL:古龙酸母液+长枝木霉菌;TL+AS:长枝木霉菌+剩余活性污泥;RAE+AS:古龙酸母液+剩余活性污泥;RAE+TL+AS:古龙酸母液+长枝木霉菌+剩余活性污泥。下同
Figure 1 Effects of combined application treatment on plant height and plant total biomass of Lolium perenne L. in coal gangue
| 处理 | 地上生物量/ (g∙m−2) | 地下生物量/ (g∙m−2) | 地上/地下生物量比值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 45.80±3.90C | 161.17±11.41C | 0.28±0.08E |
| RAE | 65.37±6.88C | 167.27±24.19C | 0.39±0.12E |
| TL | 80.70±5.39C | 207.10±7.85C | 0.39±0.05E |
| AS | 489.30±43.28A | 173.07±34.93C | 2.83±0.14B |
| RAE+TL | 73.20±2.70C | 313.13±19.53B | 0.23±0.05E |
| TL+AS | 339.63±43.32B | 66.40±9.51D | 5.11±0.14A |
| RAE+AS | 338.27±27.44B | 386.93±74.55A | 0.87±0.14D |
| RAE+TL+AS | 448.33±10.35A | 279.38±15.14B | 1.60±0.04C |
表3 配施处理在矸石山基质中对黑麦草地上生物量、地下生物量的影响
Table 3 Effects of combined application treatment on plant aboveground biomass and belowground biomass of Lolium perenne L. in coal gangue
| 处理 | 地上生物量/ (g∙m−2) | 地下生物量/ (g∙m−2) | 地上/地下生物量比值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 45.80±3.90C | 161.17±11.41C | 0.28±0.08E |
| RAE | 65.37±6.88C | 167.27±24.19C | 0.39±0.12E |
| TL | 80.70±5.39C | 207.10±7.85C | 0.39±0.05E |
| AS | 489.30±43.28A | 173.07±34.93C | 2.83±0.14B |
| RAE+TL | 73.20±2.70C | 313.13±19.53B | 0.23±0.05E |
| TL+AS | 339.63±43.32B | 66.40±9.51D | 5.11±0.14A |
| RAE+AS | 338.27±27.44B | 386.93±74.55A | 0.87±0.14D |
| RAE+TL+AS | 448.33±10.35A | 279.38±15.14B | 1.60±0.04C |
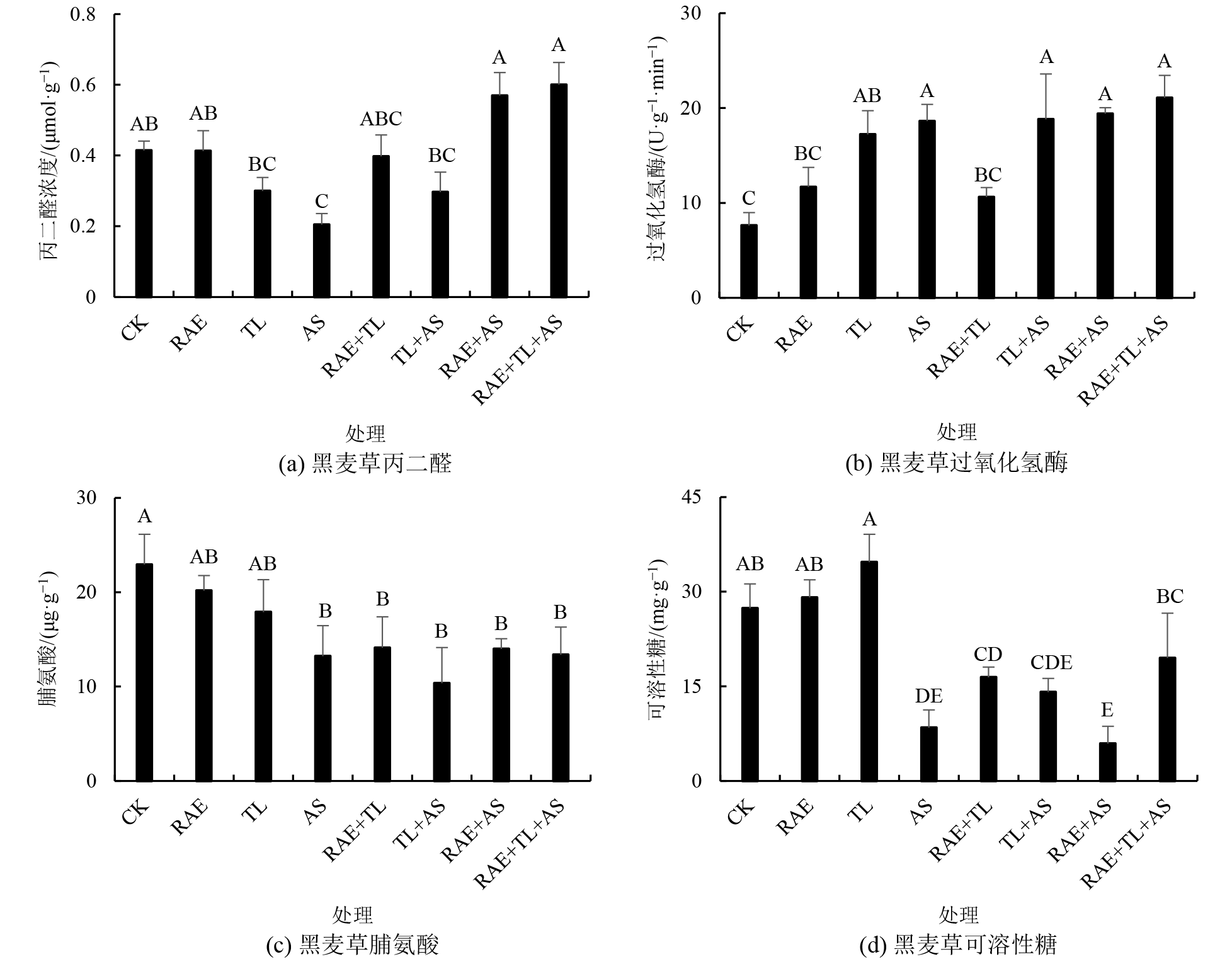
图2 配施处理在矸石山基质中对黑麦草丙二醛、过氧化氢酶、脯氨酸、可溶性糖的影响
Figure 2 Effects of combined application treatment on malonaldehyde, catalase, proline and soluble sugar of Lolium perenne L. in coal gangue
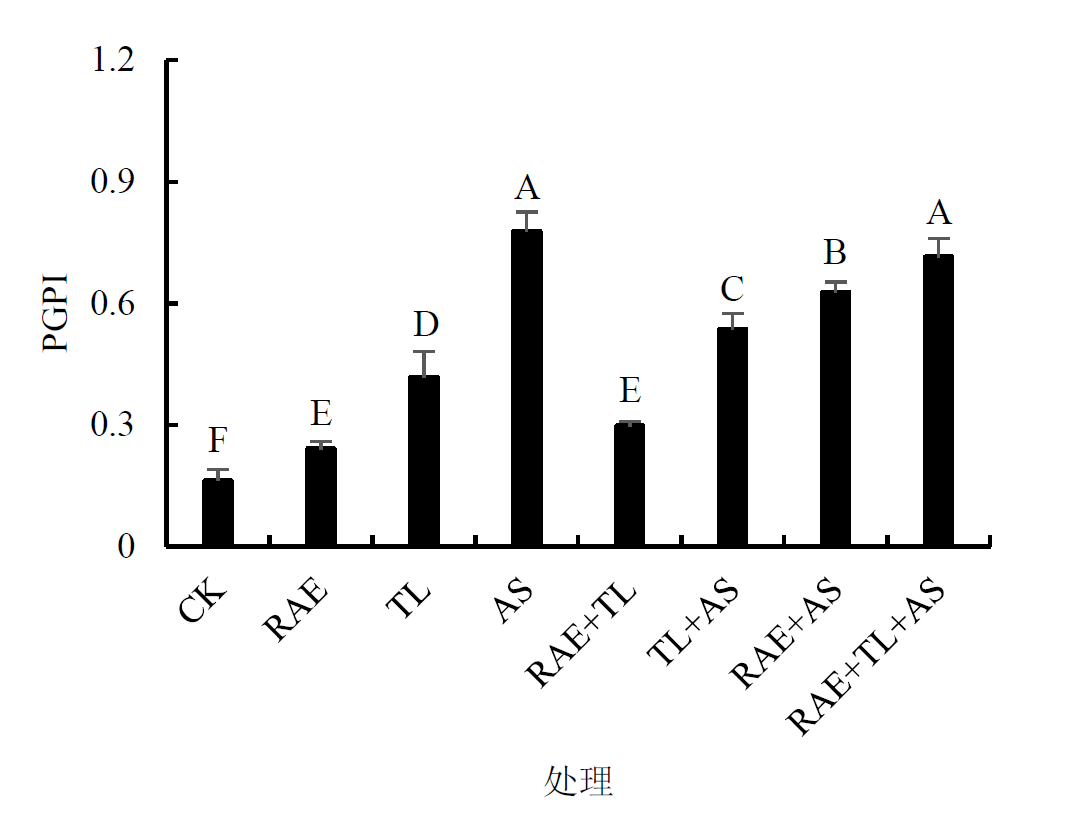
图3 配施处理对矸石山基质下对黑麦草生长生理综合指数的影响
Figure 3 Effects of combined application treatment on plant growth physiological index of Lolium perenne L. in coal gangue
| [1] |
AHIRWAL J, MAITI S K, 2016. Assessment of soil properties of different land uses generated due to surface coal mining activities in tropical Sal (Shorea robusta) forest, India[J]. Catena, 140: 155-163.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALEKSANDRA W, AGATA S, MAGDALENA D, 2022. Analysis of the bacterial biocenosis of activated sludge treated with leachate from municipal landfills[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3): 1801.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BAE S J, MOHANTA T K, CHUNG J Y, et al., 2016. Trichoderma metabolites as biological control agents against Phytophthora pathogens[J]. Biological Control, 92(4): 128-138.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BOAKYE T A, LI H, OSEI R, et al., 2022. Antagonistic effect of Trichoderma longibrachiatum (TL6 and TL13) on Fusarium solani and Fusarium avenaceum causing root rot on snow pea plants[J]. Journal of Fungi, 8(11): 1148.
DOI URL |
| [5] | GAO M F, SUN H, SHI M J, et al., 2021. 2-Keto-L-Gulonic acid improved the salt stress resistance of non-heading chinese cabbage by increasing l-ascorbic acid accumulation[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12: 2551. |
| [6] | HUANG L, ZHANG P, HU Y G, et al., 2015. Vegetation succession and soil infiltration characteristics under different aged refuse dumps at the Heidaigou opencast coal mine[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4(C): 255-263. |
| [7] | JIANG X, LU W X, ZHAO H Q, et al., 2014. Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy-metal pollution around coal gangue dump[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 14(6): 1599-1610. |
| [8] |
KCHAOU R, BAACCAR R, BOUZID J, et al., 2018. Agricultural use of sewage sludge under sub-humid Mediterranean conditions: effect on growth, yield, and metal content of a forage plant[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11(23): 746-752.
DOI |
| [9] | KLINK A A, 2017. A comparison of trace metal bioaccumulation and distribution in Typha latifolia and Phragmites australis: implication for phytoremediation[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 24(4): 3843-3852. |
| [10] | KONG T, XU H, WANG Z Y, et al., 2014. Effect of a residue after evaporation from industrial vitamin C fermentation on chemical and microbial properties of alkali-saline soil[J]. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 27(4): 1069-1074. |
| [11] |
LI J Y, WANG J M, 2019. Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: A review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 239: 117946.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI R D, TENG W C, LI Y L, et al., 2017. Potential recovery of phosphorus during the fluidized bed incineration of sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 140(2): 964-970.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI S Q, LIBER K, 2018. Influence of different revegetation choices on plant community and soil development nine years after initial planting on a reclaimed coal gob pile in the Shanxi mining area, China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 618: 1314-1323.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | LI W J, MENG R, LIU Y, et al., 2022. Heterografted chrysanthemums enhance salt stress tolerance by integrating reactive oxygen species, soluble sugar, and proline[J]. Horticulture Research, 9(1): 1685-1698. |
| [15] |
MACIAS-BENITEZ S, GARCIA-MARTINEZ A M, CABALLERO J P, et al., 2020. Rhizospheric organic acids as biostimulants: monitoring feedbacks on soil microorganisms and biochemical properties[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11: 633.
DOI URL |
| [16] | MUDRAK O, DOLEZAL J, FROUZ J, et al., 2016. Initial species composition predicts the progress in the spontaneous succession on post-mining sites[J]. Ecological engineering: The Journal of Ecotechnology, 95: 665-670. |
| [17] |
PANG G, CAI F, LI R X, et al., 2017. Trichoderma-enriched organic fertilizer can mitigate microbiome degeneration of monocropped soil to maintain better plant growth[J]. Plant and Soil, 416(1-2): 181-192.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SMITS M M, HERRMANN A M, DUANE M, et al., 2009. The fungal-mineral interface: Challenges and considerations of micro-analytical developments[J]. Fungal Biology Reviews, 23(4): 122-131.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SU Y W, HE X N, QU Z Q, 2019. Sustainable development of sludge disposal and resource utilization in Chinese farms[J]. IOP Conferenc Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 267(6): 062013.
DOI |
| [20] |
TAKIO N, MEERA Y, SINGH H Y, 2022. Plant catalase in silico characterization and phylogenetic analysis with structural modeling[J]. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 20(1): 1-18.
DOI |
| [21] |
TUO X Q, LI S, WU Q S, et al., 2015. Alleviation of waterlogged stress in peach seedlings inoculated with Funneliformis mosseae: Changes in chlorophyll and proline metabolism[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 197: 130-134.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
URRA J, ALKORTA I, MIJANGOS I, et al., 2019. Application of sewage sludge to agricultural soil increases the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes without altering the composition of prokaryotic communities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 647: 1410-1420.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WU J, JOERGENSEN R G, POMMEREING B, et al., 1990. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction-an automated procedure[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 22(8): 1167-1169.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANG W C, HAN L T, MANDLAA M, et al., 2017. A plate method for rapid screening of Ketogulonicigenium vulgare mutants for enhanced 2-keto-l-gulonic acid production[J] Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. 48(3): 397-402.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YANG X G, LI X L, SHI M M, et al., 2019. The effects of replaced topsoil of different depths on the vegetation and soil properties of reclaimed coal mine spoils in an alpine mining area[J]. Israel Journal of Ecology and Evolution, 65(3-4): 92-105.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHAO L, ZHANG Y Q, 2015. Effects of phosphate solubilization and phytohormone production of Trichoderma asperellum Q1 on promoting cucumber growth under salt stress[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14(8): 1588-1597.
DOI |
| [27] |
ZIMMERMAN A R, GAO B, AHN M Y, 2011. Positive and negative carbon mineralization priming effects among a variety of biochar-amended soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(6): 1169-1179.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 董晓芸, 柯凯恩, 胡自航, 等, 2021. 施用不同污泥堆肥对土壤理化性质及微生物活性的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 49(6): 70-75. |
| DONG X Y, KE K E, HU Z H, et al., 2021. Effect of different sludge composting on soil physical and chemical properties and microbial activity[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 49(6): 70-75. | |
| [29] | 冯国宝, 阮梦颖, 李海波, 等, 2021. 浅析常村煤矿矸石山植被生态重建技术及效益[J]. 中国煤炭, 47(2): 76-82. |
| FENG G B, RUAN M Y, LI H B, et al., 2021. Analysis on ecological reconstruction technology and benefit of vegetation in gangue dump of Changcun Coal Mine[J]. China Coal, 47(2): 76-82. | |
| [30] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzyme and its research method[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press. | |
| [31] | 蒋仙, 祝静, 于存, 2021. 2种木毒菌肥对马尾松幼苗生长及抗立枯病的影响[J]. 西部林业科学, 50(6): 103-109. |
| JIANG X, ZHU J, YU C, 2021. Effects of two kinds of Trichoderma fertilizers on the growth promotion and resistance to damping-of disease of Pinus massoniana seedlings[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 50(6): 103-109. | |
| [32] | 孔涛, 刘民, 马瑜, 等, 2015a. 黄瓜产量及土壤酶活性对基于古龙酸母液与废弃培养基有机肥的响应[J]. 环境化学, 34(12): 2275-2280. |
| KONG T, LIU M, MA Y, et al., 2015. Response of cucumber yield and soil enzyme activities to organic fertilizer of residue after evaporation from vitamin C fermentation and abandoned medium[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 34(12): 2275-2280. | |
| [33] | 孔涛, 孟凡浩, 关飞, 等, 2015b. 古龙酸母液对盐碱土壤微生物数量和酶活性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 34(11): 2053-2058. |
| KONG T, MENG F H, GUAN F, et al., 2015. Effect of residue gulomic acid residues after evaporation on microbes quantity and enzyme activities of alkali-saline soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 34(11): 2053-2058. | |
| [34] | 雷娇娇, 于存, 田力, 等, 2022. 长枝木霉菌肥优化及其对闽楠幼苗生长、生理及土壤养分的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(3): 473-478. |
| LEI J J, YU C, TIAN L, et al., 2022. Optimization of Trichoderma longibrachiatum biological fertilizer and its effects on growth, physiology and soil nutrients of Phoebe bournei seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(3): 473-478. | |
| [35] | 李松鹏, 崔琳琳, 程家森, 等, 2018. 两株哈茨木毒菌株防治水稻纹枯病及促进水稻生长的潜力研究[J]. 植物病理学报, 48(1): 98-107. |
| LI S P, CUI L L, CHENG J S, et al., 2018. Asessment of two Trichoderma harzianum sitrains for biocontrol acainst rice sheath blicht and growth promotion of ricer[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 48(1): 98-107. | |
| [36] | 尚明娟, 曹骏, 常智慧, 2017. 污泥对草坪草逆境生理的影响[J]. 草业科学, 34(8): 1591-1600. |
| SHANG M J, CAO J, CHANG Z H, 2017. Effect of biosolid on turf grass stress physiology[J]. Pratacultural Science, 34(8): 1591-1600. | |
| [37] |
孙文颖, 马维伟, 李广, 等, 2019. 尕海湿地植被退化过程中土壤蔗糖酶和淀粉酶活性的动态特征[J]. 草地学报, 27(1): 88-96.
DOI |
| SUN W Y, MA W W, LI G, et al., 2019. Dynamic characteristicsof soil sucrase and amylase activities during vegetation degradation in Gahai Wetland[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 27(1): 88-96. | |
| [38] | 闫晗, 葛蕊, 潘胜凯, 等, 2014. 恢复措施对排土场土壤酶活性和微生物量的影响[J]. 环境化学, 33(2): 327-333. |
| YAN H, GE R, PAN S K, et al., 2014. Effects of restoration measures on soil enzyme activities and micobial biomass in the coalmine dump[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 33(2): 327-333. | |
| [39] | 臧荫桐, 汪季, 丁国栋, 等, 2010. 采煤沉陷后风沙土理化性质变化及其评价研究[J]. 土壤学报, 47(2): 262-269. |
| ZANG Y T, WANG J, DING G D, et al., 2010. Variation of physico-chemical properties of aeolian sandy soil at coal mining subsidence and its evaluation[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 47(2): 262-269. | |
| [40] | 占婷婷, 李渊, 石辉, 等, 2019. 市政污泥直接施用对玉米生长和品质的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 39(5): 172-178. |
| ZHAN T T, LI Y, SHI H, et al., 2019. Effects of direct application of municipal sludge on growth and quality of Zea Mays[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 39(5): 172-178. | |
| [41] |
张秋芳, 吕春平, 贝昭贤, 等, 2016. 野外模拟增温对亚热带杉木叶片膜脂过氧化及保护酶活性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 40(12): 1230-1237.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Q F, LÜ C P, BEI Z X, et al., 2016. Effects of simulated warming outdoor on lipid peroxidation and protective enzyme activities in the subtropical species Cunninghamia lanceolate[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40(12): 1230-1237.
DOI URL |
|
| [42] |
祝静, 于存, 2022. 长枝木霉菌肥对玉米生长、土壤肥力和根际微生物的影响[J]. 生物技术通报, 38(4): 230-241.
DOI |
| ZHU J, YU C, 2022. Effects of Trichoderma longibrachiatum on maize growth, ysoil fertility and rhizosphere microorganism[J]. Biotechnolory Bulletin, 38(4): 230-241. | |
| [43] | 邹琦, 2000. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| ZOU Q, 2000. Experimental guidance of plant physiology[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. |
| [1] | 古琛, 贾志清, 杜波波, 何凌仙子, 李清雪. 中国退化草地生态修复措施综述与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1465-1475. |
| [2] | 刘祥宏, 尹勤瑞, 辛建宝, 刘伟, 许秀泉, 黄占斌, 安如意. 生态植被自然修复及其人工促进技术研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1476-1488. |
| [3] | 郭丽芳, 杨瑞, 孙蔚旻. 尾矿固氮菌的分离筛选及其植物促生效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2180-2188. |
| [4] | 辛未冬, 杜一丹, 刘华煜, 杨轶萌, 赵浩志, 杨丹. 地表节肢动物多样性对煤矸石山不同植被恢复方式的响应及生物指示作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2079-2088. |
| [5] | 李锋民, 陈琳, 姜晓华, 李晨光, 赵莎莎, 种云霄, 胡洪营, 高帅强. 水质净化与生态修复的水生植物优选指标体系构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2411-2422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
