生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 1961-1967.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.003
所属专题: 生物多样性专题汇编
王琪1( ), 张峰1, 赵萌莉1, 张新宇2, 张军2,*(
), 张峰1, 赵萌莉1, 张新宇2, 张军2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-14
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
通讯作者:
* 张军(1980年生),男,副教授,硕士研究生导师,主要从事草地生态学。E-mail: zj325328333@163.com作者简介:王琪(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为草地生态学。E-mail: wangqi18247415901@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Qi1( ), ZHANG Feng1, ZHAO Mengli1, ZHANG Xinyu2, ZHANG Jun2,*(
), ZHANG Feng1, ZHAO Mengli1, ZHANG Xinyu2, ZHANG Jun2,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-14
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
探究不同放牧强度对短花针茅荒漠草原群落植物组成以及种间关系的影响,可为短花针茅荒漠草原制定合理科学的放牧制度提供理论依据。将短花针茅荒漠草原作为研究对象,以围封为对照(CK),设置轻度(LG)、中度(MG)及重度放牧(HG)处理进行植物群落调查,对总体关联指数(VR)和种间联结系数进行分析,结果表明:(1)CK、LG、MG和HG样地中物种数分别为39、34、32、25,表明植物物种数随放牧强度增加而减少;(2)CK和LG的VR指数小于1,MG和HG的VR指数大于1,围封和轻度放牧处理下植物群落整体呈负关联,表现为竞争关系,中度放牧和重度放牧处理下群落整体呈正关联,表现为亲和关系;(3)短花针茅 (Stipa breviflora)-无芒隐子草 (Cleistogenes songorica)、冷蒿 (Artemisia frigida)-银灰旋花(Convolvulus ammannii)在CK样地中呈正关联,在MG样地中呈负关联,在LG、HG样地中无关联;无芒隐子草-木地肤(Kochia prostrata)在CK样地中呈负关联,在MG、HG样地中呈正关联,在LG样地中无关联;短花针茅-木地肤、无芒隐子草-银灰旋花在MG样地中呈正关联,在CK、LG及HG样地中无关联,说明中度放牧可以使物种间的关系由负关联转变为正关联,也可使物种间的关系由正关联转变为负关联。该文可为短花针茅荒漠草原种间竞争、群落稳定性以及生态位的研究提供重要参考。
中图分类号:
王琪, 张峰, 赵萌莉, 张新宇, 张军. 放牧强度对短花针茅荒漠草原植物群落组成及种间关系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1961-1967.
WANG Qi, ZHANG Feng, ZHAO Mengli, ZHANG Xinyu, ZHANG Jun. Effects of Grazing Intensity Community Composition and Inter-species Relationships of Stipa breviflora Desert Steppe, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 1961-1967.
| 种B Population B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出现的样方数 Sample numbers of appearance | 不出现的样方数 Sample numbers of non-appearance | |||
| 种A Population A | 出现的样方数 Sample numbers of appearance | a | b | a+b |
| 不出现的样方数 Sample numbers of non-appearance | c | d | c+d | |
| a+c | b+d | a+b+c+d | ||
表1 两个物种存在与否的2×2列联表
Table 1 Contingency table of existence of two populations
| 种B Population B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出现的样方数 Sample numbers of appearance | 不出现的样方数 Sample numbers of non-appearance | |||
| 种A Population A | 出现的样方数 Sample numbers of appearance | a | b | a+b |
| 不出现的样方数 Sample numbers of non-appearance | c | d | c+d | |
| a+c | b+d | a+b+c+d | ||
| 植物种群 Plant popolation | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LG | MG | HG | |
| 短花针茅 Stipa breviflora | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 克氏针茅 Stipa krylovii | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 无芒隐子草 Cleistogenes songorica | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 冷蒿 Artemisia frigida | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 银灰旋花 Convolvulus ammannii | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 大籽蒿 Artemisia sieversiana | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 猪毛菜 Salsola collina | √ | √ | × | × |
| 糙隐子草 Cleistogenes squarrosa | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 冰草 Agropyron cristatum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 羊草 Leymus chinensis | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 狭叶锦鸡儿 Caragana stenophylla | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 小叶锦鸡儿 Caragana microphylla | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 木地肤 Kochia prostrata | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 驼绒藜 Ceratoides latens | √ | √ | × | × |
| 兔唇花 Lagochilus ilicifolius | √ | √ | × | √ |
| 蓖齿蒿/桎叶蒿 Neopallasia pectinata | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 寸草苔 Carex duriuscula | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 阿尔泰狗娃花 Heteropappus altaicus | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 大苞鸢尾 Iris bungei | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 草芸香 Ruta graveolens | × | √ | × | × |
| 扁蓿豆 Melissitus ruthenicus | √ | × | × | × |
| 兴安天门冬 Asparagus dauricus | √ | × | × | × |
| 二裂委陵菜 Potentilla bifurca | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 菊叶委陵菜 Potentilla tanacetifolia | × | √ | √ | √ |
| 乳白花黄芪 Astragalus galactites | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 糙叶黄芪 Astragalus scaberrimus | √ | × | √ | × |
| 多根葱 Allium polyrhizum | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 野韭 Allium ramosum | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 双齿葱 Allium bidentatum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 细叶葱 Allium tenuissimum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 细叶鸢尾 Iris tenuifolia | × | × | √ | × |
| 糙苏 Phlomis umbrosa | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 地锦 Parthenocissus tricuspidata | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 少花米口袋 Gueldenstaedtia verna | √ | × | √ | √ |
| 达乌里芯芭 Cymbaria dahurica | √ | √ | × | × |
| 砂珍棘豆 Oxytropis psamocharis | √ | × | × | √ |
| 鹤虱Carpesium abrotanoides | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 刺穗藜 Dysphania aristata | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 灰绿藜 Chenopodium glaucum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 唐松草 Thalictrum aquilegiifolium | √ | × | × | × |
| 黄蒿 Artemisia annua | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 山莓草 Sibbaldia procumbens | × | × | × | √ |
| 燥原荠 Ptilotricum canescens | √ | × | × | √ |
表2 不同放牧强度内植物种群存在状况
Table 2 Existence conditions of plant populations under grazing intensity
| 植物种群 Plant popolation | 处理 Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LG | MG | HG | |
| 短花针茅 Stipa breviflora | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 克氏针茅 Stipa krylovii | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 无芒隐子草 Cleistogenes songorica | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 冷蒿 Artemisia frigida | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 银灰旋花 Convolvulus ammannii | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 大籽蒿 Artemisia sieversiana | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 猪毛菜 Salsola collina | √ | √ | × | × |
| 糙隐子草 Cleistogenes squarrosa | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 冰草 Agropyron cristatum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 羊草 Leymus chinensis | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 狭叶锦鸡儿 Caragana stenophylla | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 小叶锦鸡儿 Caragana microphylla | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 木地肤 Kochia prostrata | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 驼绒藜 Ceratoides latens | √ | √ | × | × |
| 兔唇花 Lagochilus ilicifolius | √ | √ | × | √ |
| 蓖齿蒿/桎叶蒿 Neopallasia pectinata | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 寸草苔 Carex duriuscula | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 阿尔泰狗娃花 Heteropappus altaicus | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 大苞鸢尾 Iris bungei | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 草芸香 Ruta graveolens | × | √ | × | × |
| 扁蓿豆 Melissitus ruthenicus | √ | × | × | × |
| 兴安天门冬 Asparagus dauricus | √ | × | × | × |
| 二裂委陵菜 Potentilla bifurca | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 菊叶委陵菜 Potentilla tanacetifolia | × | √ | √ | √ |
| 乳白花黄芪 Astragalus galactites | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 糙叶黄芪 Astragalus scaberrimus | √ | × | √ | × |
| 多根葱 Allium polyrhizum | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 野韭 Allium ramosum | √ | √ | √ | × |
| 双齿葱 Allium bidentatum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 细叶葱 Allium tenuissimum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 细叶鸢尾 Iris tenuifolia | × | × | √ | × |
| 糙苏 Phlomis umbrosa | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 地锦 Parthenocissus tricuspidata | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 少花米口袋 Gueldenstaedtia verna | √ | × | √ | √ |
| 达乌里芯芭 Cymbaria dahurica | √ | √ | × | × |
| 砂珍棘豆 Oxytropis psamocharis | √ | × | × | √ |
| 鹤虱Carpesium abrotanoides | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 刺穗藜 Dysphania aristata | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 灰绿藜 Chenopodium glaucum | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 唐松草 Thalictrum aquilegiifolium | √ | × | × | × |
| 黄蒿 Artemisia annua | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 山莓草 Sibbaldia procumbens | × | × | × | √ |
| 燥原荠 Ptilotricum canescens | √ | × | × | √ |
| 处理 Treatment | 总体参数 The overall parameters | 总体关联性 Overall association VR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 物种数方差 Specie numbers variance | 频度方差 Frequency variance | ||
| CK | 2.95 | 3.07 | 0.96 |
| LG | 2.33 | 2.61 | 0.89 |
| MG | 2.03 | 1.70 | 1.19 |
| HG | 0.92 | 0.75 | 1.22 |
表3 植物种群总体关联性
Table 3 Overall association of plant populations
| 处理 Treatment | 总体参数 The overall parameters | 总体关联性 Overall association VR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 物种数方差 Specie numbers variance | 频度方差 Frequency variance | ||
| CK | 2.95 | 3.07 | 0.96 |
| LG | 2.33 | 2.61 | 0.89 |
| MG | 2.03 | 1.70 | 1.19 |
| HG | 0.92 | 0.75 | 1.22 |
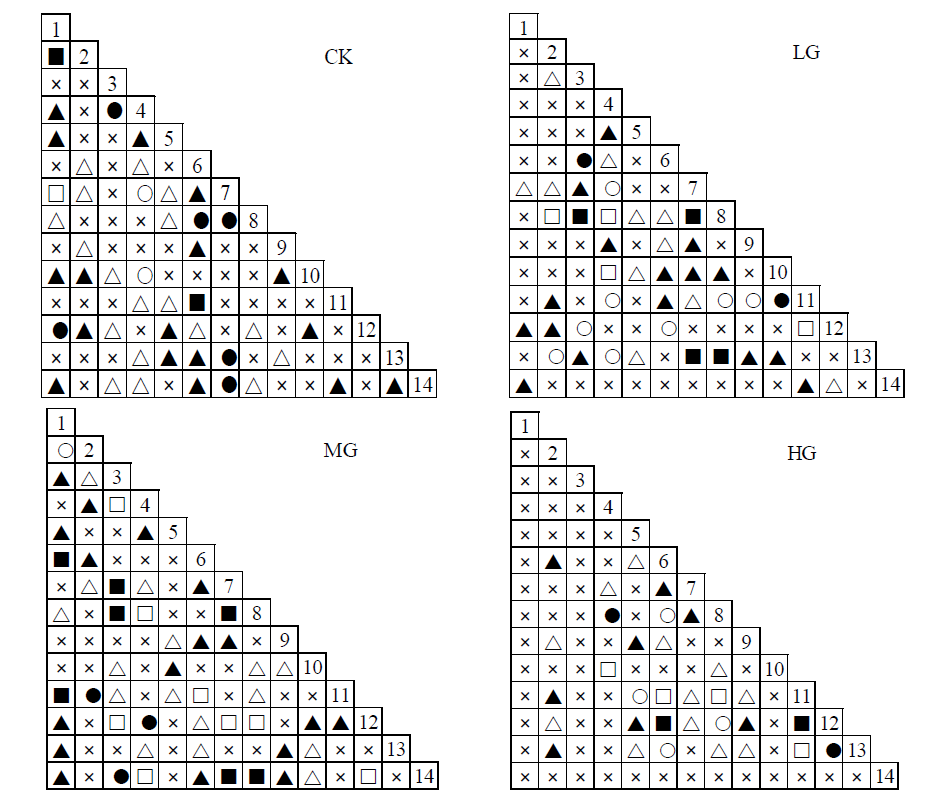
图2 种间关联半矩阵图 “■”表示极显著正关联,P≤0.01;“●”表示显著正关联,0.01<P≤0.05; “▲”表示存在正关联,0.05<P≤0.50;“□”表示极显著负关联,P≤0.01;“○”表示显著负关联,0.01<P≤0.05; “△”表示存在负关联,0.05<P≤0.50 1:短花针茅;2:无芒隐子草;3:冷蒿;4:银灰旋花;5:狭叶锦鸡儿;6:木地肤;7:寸草苔;8:二裂委陵;菜9:细叶葱;10:地锦;11:鹤虱;12:刺穗藜;13:灰绿藜;14:黄蒿
Fig. 2 Half matrix of inter-specific correlation “■” represents a extremely significant positive correlation, P≤0.01; “●”represents a significant positive correlation, 0.01<P≤0.05;“▲”represents positive correlation, 0.05<P≤0.50; “□” represents a extremely significant negative correlation, P≤0.01; “○” represents a significant negative correlation, 0.01<P≤0.05; “△” represents negative correlation, 0.05<P≤0.50. 1: Stipa breviflora; 2: Cleistogenes songorica; 3: Artemisia frigida; 4: Convolvulus ammannii; 5: Caragana stenophylla; 6: Kochia prostrata; 7: Carex duriuscula; 8: Potentilla bifurca; 9: Allium tenuissimum; 10: Parthenocissus tricuspidata; 11: Carpesium abrotanoides L; 12: Dysphania aristata; 13: Chenopodium glaucum; 14: Artemisia annua n=150
| [1] |
AIBA M, TAKAFUMI H, HIURA T, 2012. Interspecific differences in determinants of plant species distribution and the relationships with functional traits[J]. Journal of Ecology, 100(4):950-957.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DOLPH S, 1984. A Variance Test for Detecting Species Associations, with Some Example Applications[J]. Ecology, 65(3):998-1005.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LEVINE J M, HILLERISLAMBERS J, 2009. The importance of niches for the maintenance of species diversity[J]. Nature, 461(7261):254-257.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PERKINS T E, WILSON M V, 2005. The impacts of Phalaris arundinacea (reed canarygrass) invasion on wetland plant richness in the Oregon Coast Range, USA depend on beavers[J]. Biological Conservation, 124(2):291-295.
DOI URL |
| [5] | REN H Y, PHILIPP S, WAN H W, et al., 2012. Effects of Grazing Intensity and Environmental Factors on Species Composition and Diversity in Typical Steppe of Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Plos One, 7(12):1-10. |
| [6] | SUHANA S, 2011. Species composition and interspecific association of plants in primary succession of Mount Merapi, Indonesia[J]. Biodiversitas, 12(4):212-217. |
| [7] |
XUE W, BEZEMER T M, BERENDSE F, 2019. Soil heterogeneity and plant species diversity in experimental grassland communities: contrasting effects of soil nutrients and pH at different spatial scales[J]. Plant and Soil, 442(1-2):497-509.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 安渊, 李博, 杨持, 等, 2002. 不同放牧率对大针茅种群结构的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 26(2):163-169. |
| AN Y, LI B, YANG C, et al., 2002. Influence of grazing rates on the population structure of Stipa grandis[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 26(2):163-169. | |
| [9] | 包秀霞, 廉勇, 易津, 等, 2014. 放牧方式对中国和蒙古小针茅荒漠草原植物功能群特征的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(11):2966-2972. |
| BAO X X, LIAN Y, YI J, et al., 2014. Effects of grazing on plant functional group characteristics in Stipa klemenzii desert steppe in China and Mongolia[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(11):2966-2972. | |
| [10] | 崔树娟, 布仁巴音, 朱小雪, 等, 2014. 不同季节适度放牧对高寒草甸植物群落特征的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 34(2):349-357. |
| CUI S J, BU R B Y, ZHU X X, et al., 2014. Effects of Seasonal Moderate Grazing on Plant Community of Alpine Meadow[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 34(2):349-357. | |
| [11] | 董全民, 马玉寿, 李青云, 等, 2005. 牦牛放牧率对小嵩草高寒草甸暖季草场植物群落组成和植物多样性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 33(1):94-102. |
| DONG Q M, MA Y S, LI Q Y, et al., 2005. Effects of stocking rates for yak on community composition and plant diversity in Kobresia parva alpine meadow warm-season pasture[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 33(1):94-102. | |
| [12] | 方楷, 宋乃平, 魏乐, 等, 2012. 不同放牧制度对荒漠草原地上生物量及种间关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 21(5):12-22. |
| FANG K, SONG N P, WEI L, et al., 2012. The effect of different grazing systems on aboveground biomass and interspecific relationships in desert steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 21(5):12-22. | |
| [13] | 古琛, 2019. 载畜率对短花针茅荒漠草原植被生物量及其分配的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学: 23. |
| GU C, 2019. Effects of stocking rate on vegetation biomass and its distribution in Stipa breviflora Desert Steppe[D]. Hohot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: 23. | |
| [14] | 李潮, 谢应忠, 许冬梅, 等, 2013. 宁夏荒漠草原植物群落的种间关系[J]. 草业科学, 30(11):1801-1807. |
| LI C, XIE Y Z, XU D M, et al., 2013. Plant interspecific relationships in desert steppe of Ningxia[J]. Pratacultural Science, 30(11):1801-1807. | |
| [15] | 李永宏, 1988. 内蒙古锡林河流域羊草草原和大针茅草原在放牧影响下的分异和趋同[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 12(3):27-34. |
| LI Y H, 1998. The divergence and convergence of Aneurolepidium chinense steppe and Stipa grandis steppe under the grazing influence in Xilin river valley, Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 12(3):189-196. | |
| [16] | 梁茂伟, 梁存柱, 白雪, 等, 2016. 一年生植物功能群对放牧草原生物量和土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 草业科学, 33(12):2407-2417. |
| LIANG M W, LIANG C Z, BAI X, et al., 2016. Effects of annual plant functional group on biomass and soil respiration in agrazing community of a typical steppe grassland[J]. Pratacultural Science, 33(12):2407-2417. | |
| [17] | 刘冬伟, 张风承, 王明君, 等, 2012. 放牧强度对三江平原小叶章草甸群落特征及多样性的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 34(2):81-86. |
| LIU D W, ZHANG F C, WANG M J, et al., 2012. The influence of grazing intensity on community characteristics and diversity of Deyeuxia angustifolia meadow in Sanjiang plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 34(2):81-86. | |
| [18] | 刘菊红, 王忠武, 韩国栋, 2019b. 重度放牧对荒漠草原主要植物种间关系及群落稳定性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(9):2595-2602. |
| LIU J H, WANG Z W, HAN G D, 2019. Effects of heavy grazing on the interspecific relationship of main plant species and community stability in a desert steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(9):2595-2602. | |
| [19] | 刘菊红, 张军, 吕世杰, 等, 2019a. 荒漠草原主要植物种间关系对降水年型变化的响应[J]. 西北植物学报, 39(7):1289-1297. |
| LIU J H, ZHANG J, LV S J, et al., 2019. Response of interspecific relationships among main plant species to the change of precipitation years in desert steppe[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 39(7):1289-1297. | |
| [20] | 刘玉, 常小峰, 田福平, 等, 2016. 放牧对草地群落与土壤特征的影响[J]. 西部植物学报, 36(12):2524-2532. |
| LIU Y, CAHNG X F, TIAN F P, et al., 2016. Effects of grazing on community and soil characteristics in the semi-arid grassland[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 36(12):2524-2532. | |
| [21] | 吕世杰, 刘红梅, 吴艳玲, 等, 2014. 放牧对短花针茅荒漠草原建群种与优势种空间分布关系的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(12):3469-3474. |
| LV S J, LIU H M, WU Y L, et al., 2014. Effects of grazing on spatial distribution relationships between constructive and dominant species in Stipa breviflora desert steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(12):3469-3474. | |
| [22] | 吕世杰, 吴艳玲, 刘红梅, 等, 2016. 春季休牧后放牧强度变化对短花针茅草原植物种群种间关系的影响[J]. 草地学报, 24(2):302-308. |
| LV S J, WU Y L, LIU H M, et al., 2016. Effect of grazing intensity changes on population inter-specific relationship of Stipa breviflora steppe after banning in spring[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 24(2):302-308. | |
| [23] | 马少薇, 郭建英, 李锦荣, 等, 2016. 放牧强度对短花针茅群落特征及冠层截留的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 38(5):66-70. |
| MA S W, GUO J Y, LI J R, et al., 2016. Effect of grazing intensity on Stipa breviflora communities and canopy interception[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 38(5):66-70. | |
| [24] | 王博, 王亮, 王立龙, 等, 2017. 濒危植物裸果木 (Gymnocarpos przewalskii) 与其伴生种种间联结性及群落稳定性[J]. 中国沙漠, 37(1):86-92. |
| WANG B, WANG L, WANG L L, et al., 2017. Community stability and interspecific association between the endangered plant Gymnocarpos przewalskii and its associated species[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 37(1):86-92. | |
| [25] | 吴东丽, 上官铁梁, 薛红喜, 等, 2003. 滹沱河湿地植物群落的种间关系研究[J]. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 26(1):71-75. |
| WU D L, SHANG G T L, XUE H X, et al., 2003. Study on interspecific relationship of the plant communities of wetland in Hutuo river valley, Shanxi[J]. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 26(1):71-75. | |
| [26] | 吴艳玲, 吕世杰, 刘红梅, 等, 2016. 不同放牧强度对短花针茅草原植物种群种间关系的影响[J]. 生态科学, 35(6):34-40. |
| WU Y L, LV S J, LIU H M, et al., 2016. Effect of different grazing intensity on population inter-specific relationship of Stipa breviflora steppe[J]. Ecological Science, 35(6):34-40. | |
| [27] | 锡林塔娜, 蒙荣, 慕宗杰, 2008. 内蒙古四子王旗短花针茅荒漠草原群落种间关联分析[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 29(6):6-9. |
| XI L T N, MENG R, MU Z J, 2008. Correlation analysis of interspecific relationship of community in Stipa breviflora desert steppe in Siziwang banner in Inner Mongolia[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 29(6):6-9. | |
| [28] | 锡林塔娜, 2009. 不同载畜率下短花针茅荒漠草原群落种间关系研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学: 18. |
| XI L T N, 2009. Inter-specific relations of Stipa breviflora desert steppe community at different stocking rates[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: 18. | |
| [29] | 邢福, 宋日, 祁宝林, 2002. 糙隐子草草原狼毒种群与其他主要植物的种间联结分析[J]. 草业学报, 11(4):46-51. |
| XING F, SONG R, QI B L, 2002. Analysis to the interspecific association of Stellera chamaejasme population and other main plant species in Cleistogenes squarrosa steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 11(4):46-51. | |
| [30] | 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 等, 2016. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述[J]. 生态学报, 36(24):8224-8233. |
| XU M H, LIU M, ZHAI D T, et al., 2016. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(24):8224-8233. | |
| [31] | 殷建鹏, 高金龙, 冯琦胜, 等, 2018. 中国北方草地资源管理信息系统的设计与实现[J]. 草业科学, 35(5):1022-1029. |
| YIN J P, GAO J L, FEN Q S, et al., 2018. Design and implementation of a grassland resource management information system in northern China[J]. Pratacultural Science, 35(5):1022-1029. | |
| [32] | 袁月, 2014. 崇明东滩湿地芦苇与互花米草种群间关系格局与影响因素研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 15. |
| YUAN Y, 2014. Interspecific interactions of Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis and related factors in Chongming Dongtan[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 15. | |
| [33] | 张鹏, 王新杰, 凌威, 等, 2017. 北京鹫峰地区侧柏人工林草本层物种多样性及主要种种间关系研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 45(4):86-93. |
| ZHANG P, WANG X J, LING W, et al., 2017. Plant diversity and interspecific relationship of main herb species in Platycladus orientalis plantation in Jiufeng Mountain, Beijing[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 45(4):86-93. | |
| [34] | 张爽, 2020. 短花针茅荒漠草原主要植物种群间相互关系对放牧的响应[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学: 21. |
| ZHANG S, 2020. Response of main populations Interspecific Relationship to grazing in Stipa breviflora desert steppe[D]. Hohot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: 21. | |
| [35] | 周先叶, 王伯荪, 2000. 广东黑石顶自然保护区森林次生演替过程中群落的种间联结性分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 24(3):332-339. |
| ZHOU X Y, WANG B S, 2000. An analysis of interspecific associations in secondary succession forest communities in Heishiding Natural Reserve, Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24(3):332-339. |
| [1] | 侯晖, 颜培轩, 谢沁宓, 赵宏亮, 庞丹波, 陈林, 李学斌, 胡杨, 梁咏亮, 倪细炉. 贺兰山蒙古扁桃灌丛根际土壤AM真菌群落多样性特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [2] | 赵鸿彬, 白雪, 范宇凤, 张晓馥, 张涛, 李淑芬. 短花针茅StbCRY1和StbCRY2基因克隆与表达差异分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 866-877. |
| [3] | 周世强, Vanessa HULL, 张晋东, 刘巅, 谢浩, 黄金燕, 张和民. 野生大熊猫与放牧家畜利用生境的特征比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 309-319. |
| [4] | 姜倪皓, 张世浩, 张诗函. 哀牢山紫茎泽兰入侵群落主要物种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [5] | 朱奕豪, 李青梅, 刘晓丽, 李娜, 宋凤玲, 陈为峰. 不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 909-917. |
| [6] | 张苗苗, 陈书涛, 丁司丞, 王瑾, 章堃. 增温及秸秆施用对大豆-冬小麦轮作农田土壤真菌群落组成及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 759-770. |
| [7] | 杨世福, 马玲玲, 陈芸芝, 唐旭利. 鼎湖山季风常绿阔叶林演替系列土壤细菌群落的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2275-2282. |
| [8] | 郭佳琦, 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 黄佳乐, 赵丽娅, 李兆华. 喜旱莲子草入侵群落主要物种生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1607-1616. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
