生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1662-1671.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.013
赵晓亮1,*( ), 郭猛1, 吕美婷1, 赵雪莹1, 姜瑰国1, 黄媛媛1, 王凡2, 姬亚芹3
), 郭猛1, 吕美婷1, 赵雪莹1, 姜瑰国1, 黄媛媛1, 王凡2, 姬亚芹3
收稿日期:2021-04-19
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
*作者简介:赵晓亮(1981年生),男,副教授,博士,主要从事粉尘污染控制研究。E-mail: zhaoxiaoliang2008@126.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Xiaoliang1,*( ), GUO Meng1, LV Meiting1, ZHAO Xueying1, JIANG Guiguo1, HUANG Yuanyuan1, WANG Fan2, JI Yaqin3
), GUO Meng1, LV Meiting1, ZHAO Xueying1, JIANG Guiguo1, HUANG Yuanyuan1, WANG Fan2, JI Yaqin3
Received:2021-04-19
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
以阜新市4个功能区6种绿化树种云杉(Picea asperata)、油松(Pinus tabuliformis)、金叶榆(Ulmus pumila)、紫丁香(Syringa oblata)、紫叶李(Prunus cerasifera)和银杏(Ginkgo biloba)为试材,采用洗脱法测定叶片单位面积滞尘量,使用电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS)测定重金属Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni及Pb的质量浓度,探究了不同绿化树种叶片对大气颗粒物及重金属的滞留能力,并分析了叶面尘中重金属相关性及可能来源。结果表明,(1)6种绿化树种叶片滞尘能力因季节变化或功能区不同而产生明显差异。采样期间,阜新市绿化树种滞尘能力排序为:云杉>金叶榆>油松>紫丁香>紫叶李>银杏,其中,常青针叶类的云杉和油松在春、冬季的滞尘量高于夏、秋季,且云杉年平均单位叶片滞尘量是油松的1.77倍;落叶阔叶类的金叶榆在夏、秋两季的滞尘量分别是银杏的3.37、3.66倍。(2)绿化树种叶片滞留重金属的能力与季节、功能区密切相关。春、冬季,云杉对5种重金属的滞留能力均较强;夏、秋季,则金叶榆和紫叶李的滞留效果较好;环保局、辽工大主校区、辽工大北校区树种叶片滞尘中含量最多的重金属分别为Pb、Cr、Cu,露天矿最多的则为Cd和Ni。(3)绿化树种叶面滞尘中重金属相关性分析表明Ni-Pb、Cd-Ni、Cd-Pb之间均呈现显著正相关性,表明Cd、Ni、Pb同源性很强;主成分分析得出阜新市绿化树种叶面滞尘中重金属主要来源于电厂与采暖热电厂煤炭燃烧、城市机动车尾气排放及鞣革等重点工业排烟。该研究结论可为阜新市绿化树种优化筛选和大气颗粒物污染防控提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
赵晓亮, 郭猛, 吕美婷, 赵雪莹, 姜瑰国, 黄媛媛, 王凡, 姬亚芹. 阜新市绿化树种对大气颗粒物及重金属滞留能力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1662-1671.
ZHAO Xiaoliang, GUO Meng, LV Meiting, ZHAO Xueying, JIANG Guiguo, HUANG Yuanyuan, WANG Fan, JI Yaqin. Study on Retention Capacity of Green Tree Species to Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Heavy Metals in Fuxin[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1662-1671.
| 物种 Species | 冬季Winter | 春季Spring | 夏季Summer | 秋季Autumn | 季平均Seasonal average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云杉 Picea asperata | 0.808 | 0.711 | 0.510 | 0.510 | 0.635 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 0.456 | 0.409 | 0.325 | 0.243 | 0.358 |
| 金叶榆 Ulmus pumila | - | - | 0.749 | 0.811 | 0.780 |
| 紫丁香 Syringa oblata | - | - | 0.531 | 0.555 | 0.543 |
| 紫叶李 Prunus cerasifera | - | - | 0.487 | 0.494 | 0.491 |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | - | - | 0.222 | 0.250 | 0.236 |
表1 阜新市区树种叶片单位面积滞尘量时间变化
Table 1 Time variation of dust retention per unit area in leaves of tree species in Fuxin urban area g∙m-2
| 物种 Species | 冬季Winter | 春季Spring | 夏季Summer | 秋季Autumn | 季平均Seasonal average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云杉 Picea asperata | 0.808 | 0.711 | 0.510 | 0.510 | 0.635 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 0.456 | 0.409 | 0.325 | 0.243 | 0.358 |
| 金叶榆 Ulmus pumila | - | - | 0.749 | 0.811 | 0.780 |
| 紫丁香 Syringa oblata | - | - | 0.531 | 0.555 | 0.543 |
| 紫叶李 Prunus cerasifera | - | - | 0.487 | 0.494 | 0.491 |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | - | - | 0.222 | 0.250 | 0.236 |
| 物种 Species | 主校区 Main campus | 北校区 North campus | 环保局 Environmental protection agency | 露天矿 Open-pit mine | 阜新市区 Fuxin city |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云杉 Picea asperata | 0.654 | 0.675 | 0.614 | 0.626 | 0.642 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 0.314 | 0.332 | 0.309 | 0.324 | 0.320 |
| 金叶榆 Ulmus pumila | 0.805 | 0.750 | 0.775 | 0.789 | 0.780 |
| 紫丁香 Syringa oblata | 0.576 | 0.482 | 0.556 | 0.559 | 0.543 |
| 紫叶李 Prunus cerasifera | 0.588 | 0.416 | 0.431 | 0.347 | 0.446 |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | 0.194 | 0.226 | 0.245 | 0.199 | 0.216 |
表2 阜新市不同采样区树种叶片单位面积滞尘量
Table 2 Dust retention per unit area of leaves of tree species in different sampling areas in Fuxin city g∙m-2
| 物种 Species | 主校区 Main campus | 北校区 North campus | 环保局 Environmental protection agency | 露天矿 Open-pit mine | 阜新市区 Fuxin city |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云杉 Picea asperata | 0.654 | 0.675 | 0.614 | 0.626 | 0.642 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 0.314 | 0.332 | 0.309 | 0.324 | 0.320 |
| 金叶榆 Ulmus pumila | 0.805 | 0.750 | 0.775 | 0.789 | 0.780 |
| 紫丁香 Syringa oblata | 0.576 | 0.482 | 0.556 | 0.559 | 0.543 |
| 紫叶李 Prunus cerasifera | 0.588 | 0.416 | 0.431 | 0.347 | 0.446 |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | 0.194 | 0.226 | 0.245 | 0.199 | 0.216 |
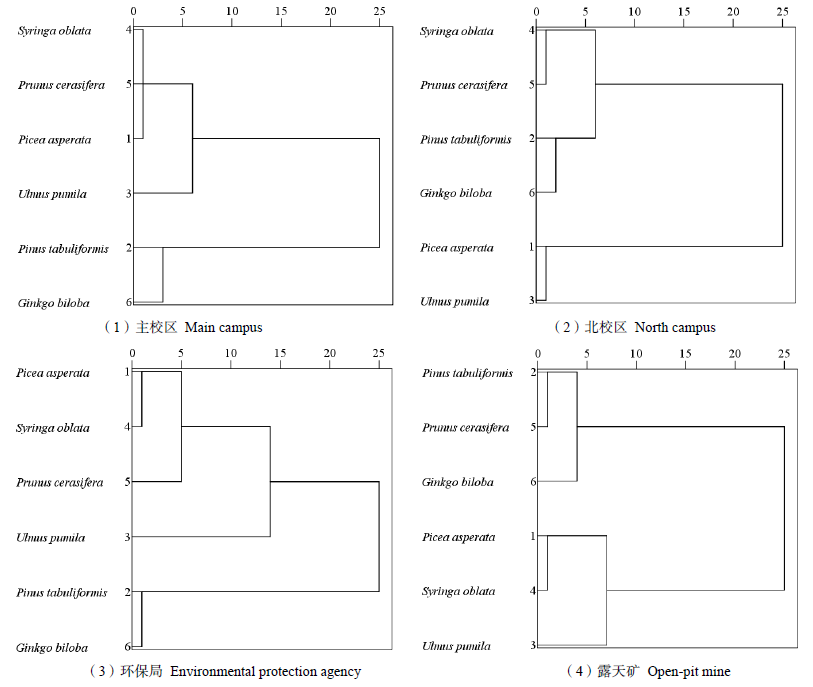
图2 阜新市不同采样区树种单位叶面积滞尘量聚类分析结果
Fig. 2 Cluster analysis results of dust retention per unit leaf area of tree species in different sampling areas in Fuxin City
| 元素 Element | Cd | Cu | Cr | Ni | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | ||||
| Cu | -0.594 | 1 | |||
| Cr | -0.268 | 0.244 | 1 | ||
| Ni | 0.821** | -0.250 | -0.095 | 1 | |
| Pb | 0.811** | -0.352 | -0.042 | 0.966** | 1 |
表3 叶面尘各重金属的斯皮尔曼相关系数
Table 3 Spearman correlation coefficient of heavy metals in foliar dust
| 元素 Element | Cd | Cu | Cr | Ni | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | ||||
| Cu | -0.594 | 1 | |||
| Cr | -0.268 | 0.244 | 1 | ||
| Ni | 0.821** | -0.250 | -0.095 | 1 | |
| Pb | 0.811** | -0.352 | -0.042 | 0.966** | 1 |
| 元素 Element | 主成分1 PC 1 | 主成分2 PC 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.946 | -0.169 |
| Cu | -0.405 | 0.877 |
| Cr | -0.459 | 0.308 |
| Ni | 0.922 | -0.347 |
| Pb | 0.927 | -0.363 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 2.980 | 1.146 |
| 方差 Variance/% | 59.591 | 22.912 |
| 累计方差 Accumulative variance/% | 59.591 | 82.503 |
表4 叶面滞尘中重金属在主成分的载荷
Table 4 Leaf dust heavy metal loads in principal components
| 元素 Element | 主成分1 PC 1 | 主成分2 PC 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.946 | -0.169 |
| Cu | -0.405 | 0.877 |
| Cr | -0.459 | 0.308 |
| Ni | 0.922 | -0.347 |
| Pb | 0.927 | -0.363 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 2.980 | 1.146 |
| 方差 Variance/% | 59.591 | 22.912 |
| 累计方差 Accumulative variance/% | 59.591 | 82.503 |
| [1] |
BARIMA Y S S, ANGAMAN D M, N’GOURAN K P, et al., 2016. Involvement of leaf characteristics and wettability in retaining air particulate matter from tropical plant species[J]. Environmental Engineering Research, 21(2): 121-131.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DZIZANOWSKI K, POPEK R, GAWRORISKA H, et al., 2011. Deposition of particulate matter of different size fractions on leaf surfaces and in waxes of urban forest species[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 13(10): 1037-1046.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HSU C Y, CHIANG H C, CHEN M J, et al., 2017. Ambient PM2.5 in the residential area near industrial complexes: Spatiotemporal variation, source apportionment, and health impact[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 590-591: 204-214.
DOI URL |
| [4] | HUANG X J, LIU Z R, LIU J Y, et al. 2017. Chemical characterization and source identification of PM2.5 at multiple sites in the Beijing-Tianjin- Hebei region, China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17(21): 12941-12962. |
| [5] | SAFIFIUR R M, KHAN M D H, JOLLY Y N, et al., 2019. Assessing risk to human health for heavy metal contamination through street dust in the Southeast Asian Megacity: Dhaka, Bangladesh[J]. Science of Total Environment, 600: 1610-1622. |
| [6] |
SHAHID M, DUMAT C, KHALID S, et al., 2017. Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: A comparison of foliar and root metal uptake[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 325: 36-58.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SUN X D, LI H M, GUO X, et al., 2018. Capacity of six shrub species to retain atmospheric particulates with different diameters[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(3): 2643-2650.
DOI URL |
| [8] | TREBY D L, CASTLEY J G, 2015. Distribution and abundance of Hollow-Bearing Trees in urban forest fragments[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 14(3): 655-663. |
| [9] |
WANG G X, ZENG C, ZHANG F, et al., 2017. Traffic-related trace elements in soils along six highway segments on the Tibetan Plateau: Influence factors and spatial variation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 581-582: 811-821.
DOI URL |
| [10] | WANG H X, SHI H, LI Y Y, 2011. Leaf mass per area and photosynthetic pigments of greening plant species under different urban atmospheric environment[J]. China Environmental Science, 31(7): 1134-1142. |
| [11] |
XU Y S, XU W, MO L, et al., 2018. Quantifying particulate matter accumulated on leaves by 17 species of urban trees in Beijing, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(13): 12545-12556.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG L L, JIN X W, JOHNSON A C, et al., 2016. Hazard posed by metals and as in PM2.5 in air of five megacities in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China during APEC[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(17): 17603-17612.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHOU L, LIU G J, SHEN M C, et al., 2019. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in indoor dust from different functional areas in HeFei, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 251: 839-849.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 陈波, 李少宁, 鲁绍伟, 等, 2018. 北京西山冬季针叶树种叶片滞纳PM2.5功能研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 41(6): 28-33. |
| CHEN B, LI S N, LU S W, et al., 2018. Function study of coniferous species leaf retention of PM2.5in winter in Xishan Mountain of Beijing[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(6): 28-33. | |
| [15] | 董世豪, 谢扬, 皇甫延琦, 等, 2019. 扬州市PM2.5中重金属来源及潜在健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 40(2): 30-37. |
| DONG S H, XIE Y, HUANGFU Y Q, et al., 2019. Source apportionment and health risk quantification of heavy metals in PM2.5 in Yangzhou, China[J]. Environmental Science, 40(2): 540-547. | |
| [16] | 段海静, 邢戎光, 王亚琪, 等, 2019. 开封市不同功能区叶面尘重金属含量及潜在生态风险[J]. 环境科学学报, 39(12): 4226-4234. |
| DUAN H J, XING R G, WANG Y Q, et al., 2019. Content and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in foliar dust of different functional of Kaifeng City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(12): 4226-4234. | |
| [17] | 段嵩岚, 闫淑君, 吴艳芳, 等, 2018. 福州市15种常用灌木滞留颗粒物效应的时空特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 33(2): 244-251. |
| DUAN S L, YAN S J, WU Y F, et al., 2018. Temporal-spatial variation characteristics of the particulate matter retention effects of fifteen widely roadside greening shrubs in Fuzhou[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 33(2): 244-251. | |
| [18] | 符小晴, 彭晓武, 王钰钰, 等, 2018. 广州市大气PM2.5中元素特征及重金属健康风险评价[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 35(2): 154-158. |
| FU X Q, PENG X W, WANG Y Y, et al., 2018. Characteristic of elements in PM2.5 and health risk assessment of heavy metals in Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 35(2): 154-158. | |
| [19] | 高海波, 2019. 9个园林树种叶片表面吸附颗粒物特点及其滞留重金属能力[J]. 南方农业学报, 50(5): 1035-1041. |
| GAO H B, 2019. The ability of absorbing particulate matters and retaining heavy metal on the leaf surface of nine garden tree species[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 50(5): 1035-1041. | |
| [20] | 顾家伟, 2019. 我国城市大气颗粒物重金属污染研究进展与趋势[J]. 地球与环境, 47(3): 385-396. |
| GU J W, 2019. A review on heavy metals in atmospheric suspended particles of China cities and its implication for future references[J]. Earth and Environment, 47(3): 385-396. | |
| [21] | 侯聪, 邵龙义, 王静, 等, 2016. 燃煤排放可吸入颗粒物中微量元素的分布特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 41(3): 760-768. |
| HOU C, SHAO L Y, WANG J, et al., 2016. Distribution of trace elements in inhalable particulate matter emitted from coal burning[J]. Journal of China Coal Society 41(3): 760-768. | |
| [22] | 雷文凯, 李杏茹, 张兰, 等. 2021. 保定地区PM2.5中重金属元素的污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 42(1): 38-44. |
| LEI W K, LI X R, ZHANG L, et al., 2021. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5collected in Baoding[J]. Environmental Science, 42(1): 38-44. | |
| [23] | 李晶, 徐玉玲, 黎桂英, 等, 2019. 兰州市交通道路主要乔灌木植物叶片重金属积累及生理特性的分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5): 999-1006. |
| LI J, XU Yuling, LI Guiying, et al., 2019. Analyses of heavy metal accumulation and physiological characteristics in leaves of main arbor and shrub plants in traffic roads of Lanzhou City[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(5): 999-1006. | |
| [24] | 李少宁, 田少强, 赵云阁, 等, 2017. 北京七种常见经济林吸滞重金属的特征[J]. 北方园艺 (1): 75-82. |
| LI S N, TIAN S Q, ZHAO Y G, et al., 2017. Characteristics of heavy metals in seven common economic forest of Beijing[J]. Northern Horticulture (1): 75-82. | |
| [25] | 李诗瑶, 牛玉斌, 樊瑾, 等, 2021. 基于叶面微结构的火电厂周边绿化树种的滞尘能力分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(2): 604-614. |
| LI S Y, NIU Y B, FAN J, et al., 2021. Analysis on dust retention capability of greening tree species surrounding coal-fired power plant based on leaf surface micro-structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(2): 604-614. | |
| [26] | 李新宇, 赵松婷, 郭佳, 等, 2016. 基于扫描电镜定量评价植物滞留大气颗粒物能力[J]. 西北林学院学报, 31(1): 286-291. |
| LI X Y, ZHAO S T, GUO J, et al., 2016. Evaluation of the retention capability of air particulates by common trees based on SEM[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 31(1): 286-291. | |
| [27] | 刘新蕾, 欧阳婉约, 张彤, 2021. 大气颗粒物重金属组分的化学形态及健康效应[J]. 环境化学, 40(4): 974-989. |
| LIU X L, OUYANG W Y, ZHANG T, 2021. Chemical speciation and health effect of heavy metals in atmospheric particulate matter[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 40(4): 974-989. | |
| [28] | 吕晓倩, 张银龙, 2020. 城市攀缘植物对大气颗粒物的吸附效果及重金属累积研究[J]. 中国园林, 36(12): 101-105. |
| LV X Q, ZHANG Y L, 2020. Deposition of particular matter and accumulation of heavy metal on six climbing plants[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 36(12): 101-105. | |
| [29] | 马远, 贾雨龙, 王成, 等, 2018. 北京市3种道路防护林春季滞尘规律研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 31(2): 147-155. |
| MA Y JIA, Y L, WANG C, et al., 2018. Dust-retention effect of 3 road protection forests in spring in Beijing[J]. Forest Research, 31(2): 147-155. | |
| [30] | 么旭阳, 胡耀升, 刘艳红, 2014. 北京市8种常见绿化树种滞尘效应[J]. 西北林学院学报, 29(3): 92-95, 104. |
| YAO X Y, HU Y S, LIU Y H, 2014. Dust-retention effect of 8 common greening tree species in Beijing[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29(3): 92-95, 104. | |
| [31] | 乔冠皓, 陈警伟, 刘肖瑜, 等, 2017. 两种常见绿化树种对大气颗粒物的滞留与再悬浮[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(1): 266-272. |
| QIAO G H, CHEN J W, LIU X Y, et al., 2017. Retention and resuspension of atmospheric particles with two common urban greening trees[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(1): 266-272. | |
| [32] | 孙晓丹, 李海梅, 郭霄, 等, 2017. 10种灌木树种滞留大气颗粒物的能力[J]. 环境工程学报, 11(2): 1047-1054. |
| SUN X D, LI H M, GUO X, et al., 2017. Atmospheric particulates-retaining capacity of ten shrubs species[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 11(2): 1047-1054. | |
| [33] | 王洪涛, 张俊华, 张天宁, 等, 2016. 开封惠济河水系底泥重金属污染与潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 35(8): 1567-1577. |
| WANG H T, ZHANG J H, ZHANG T L, et al., 2016. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of surface sediments of Huiji River System in Kaifeng, China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 35(8): 1567-1577. | |
| [34] | 王会霞, 石辉, 李秧秧, 等, 2012. 城市植物叶面尘粒径和几种重金属 (Cu、Zn、Cr、Cd、Pb、Ni)的分布特征[J]. 安全与环境学报, 12(1): 172-176. |
| WANG H X, SHI H, LI Y Y, et al., 2012. Distribution features of particle size and heavy metal elements in foliage-captured dust[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 12(1): 170-174. | |
| [35] | 王磊, 黄利斌, 万欣, 等, 2016. 城市森林对大气颗粒物 (尤其PM2.5) 调控作用研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 40(5): 148-154. |
| WANG L, HUANG L B, WAN X, et al., 2016. Progress on the regulating effects of urban forest vegetation on atmospheric particulate matter (especially PM2.5)[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 40(5): 148-154. | |
| [36] | 王琴, 冯晶红, 黄奕, 等, 2020. 武汉市15种阔叶乔木滞尘能力与叶表微形态特征[J]. 生态学报, 40(1): 213-222. |
| WANG Q, FENG J H, HUANG Y, et al., 2020. Dust-retention capability and leaf surface micromorphology of 15 broad-leaved tree species in Wuhan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(1): 213-222. | |
| [37] | 王书恒, 朱晓宇, 田如男, 等, 2021. 南京市6种常见园林植物滞尘效益的综合分析[J]. 中国园林, 37(6): 111-116. |
| WANG S H, ZHU X Y, TIAN R N, et al., 2021. Comprehensive analysis of dust retention efficiency of six common garden plants in Nanjing[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 37(6): 111-116. | |
| [38] | 魏海英, 饶雷振, 章博函, 等, 2021. 太原市叶面尘中重金属分布特征及其健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(3): 1050-1057. |
| WEI H Y, RAO L Z, ZHANG B H, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in foliage dust in Taiyuan City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(3): 1050-1057. | |
| [39] | 阴丽淑, 李金娟, 郭兴强, 等, 2017. 贵州“两控区”城市PM2.5及其阴阳离子污染特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(2): 416-423. |
| YIN L S, LI J J, GUO X Q, et al., 2017. Pollution characteristics of concentrations and it’s ions in PM2.5 of sulfur and acid-rain Control Zone Cities, Guizhou[J]. China Environmental Science, 37(2): 416-423. | |
| [40] | 殷卓君, 沈小雪, 李瑞利, 等, 2020. 深圳市常见园林植物滞尘效应研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 56(6): 1081-1090. |
| YIN Z J, SHEN X X, LI R L, et al., 2020. Study on the dust retention effect of common garden plants in Shenzhen[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 56(6): 1081-1090. | |
| [41] | 余海龙, 黄菊莹, 2012. 城市绿地滞尘机理及其效应研究进展[J]. 西北林学院学报, 27(6): 238-241, 247. |
| YU H l, HUANG J Y, 2012. Research advances in mechanism and effect of dust retention of urban green areas[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 27(6): 238-241, 247. | |
| [42] | 张伯镇, 雷沛, 潘延安, 等, 2015. 重庆主城区次级河流表层沉积物重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(7): 2185-2192. |
| ZHANG B Z, LEI P, PAN Y A, et al., 2015. Pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments from the tributaries in the main urban districts, Chongqing City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(7): 2185-2192. | |
| [43] | 张丹龙, 方凤满, 姚有如, 等, 2016. 淮南市不同功能区叶面尘和地表灰尘中重金属分布特征、来源及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(9): 3322-3332. |
| ZHANG D L, FANG F M, YAO Y R, et al., 2016. Distribution, sources and health risk assessment of heavy metals in foliar and surface dust of different functional areas of Huainan City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(9): 3322-3332. | |
| [44] | 中国环境监测总站, 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 330-381. |
| China Environmental Monitoring Center, 1990. Background value of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 330-381. | |
| [45] | 赵晓亮, 孙杰, 李俊华, 等, 2017. 阜新城区降尘重金属污染及其健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 30(9): 1346-1354. |
| ZHAO X L, SUN J, LI J H, et al., 2017. Pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in Fuxin City[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 30(9): 1346-1354. | |
| [46] | 赵晓亮, 岳阳霞, 许端平, 等, 2020. 阜新市秋冬季节PM2.5中无机元素污染特征及来源[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(10): 4247-4258. |
| ZHAO X L, YUE Y X, XU D P, et al., 2020. The pollution characteristics and source analysis of inorganic elements in PM2.5 during autumn and winter in Fuxin[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(10): 4247-4258. | |
| [47] | 周安琪, 刘建伟, 周旭, 等, 2021. 北京大气PM2.5载带金属浓度、来源及健康风险的城郊差异[J]. 环境科学, 42(6): 2595-2603. |
| ZHOU A Q, LIU J W, ZHOU X, et al., 2021. Concentration, source, and health risk of PM2.5 carrier metal in Beijing urban area and suburb[J]. Environmental Science, 42(6): 2595-203. | |
| [48] | 周蕴薇, 田忠平, 苏欣, 2017. 哈尔滨市常见绿化树种叶表面形态与滞尘能力的关系[J]. 西北林学院学报, 32(1): 287-292. |
| ZHOU Y W, TIAN Z P, SU X, 2017. Relationships between leaf epidermal morphology and dust capacity of common street trees in Harbin municipality[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 32(1): 287-292. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 刘紫薇, 葛继稳, 王月环, 杨诗雨, 姚东, 谢金林. 大九湖泥炭湿地甲烷通量变异特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 706-714. |
| [3] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [4] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [5] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [6] | 李海燕, 杨小琴, 简美鹏, 张晓然. 城市水体中微塑料的来源、赋存及其生态风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 407-420. |
| [7] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [8] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [9] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [10] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [11] | 李莹, 张洲, 杨高明, 祖艳群, 李博, 陈建军. 湿地植物根系泌氧能力和根表铁膜与根系吸收重金属的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [12] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [13] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [14] | 孙建波, 畅文军, 李文彬, 张世清, 李春强, 彭明. 香蕉不同生育期根际微生物生物量及土壤酶活的变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1169-1174. |
| [15] | 彭红丽, 谭海霞, 王颖, 魏建梅, 冯阳. 不同种植模式下土壤重金属形态分布差异与生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
