生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1581-1588.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.004
李巧玉( ), 张小晶, 陈娟, 刘媛, 刘锦春, 陶建平*(
), 张小晶, 陈娟, 刘媛, 刘锦春, 陶建平*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-08
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
* 陶建平,教授,E-mail: taojp@swu.edu.cn作者简介:李巧玉(1993年生),女,博士研究生,研究方向为森林生态学。E-mail: lethe@email.swu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Qiaoyu( ), ZHANG Xiaojing, CHEN Juan, LIU Yuan, LIU Jinchun, TAO Jianping*(
), ZHANG Xiaojing, CHEN Juan, LIU Yuan, LIU Jinchun, TAO Jianping*( )
)
Received:2021-03-08
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
彩叶林是川西亚高山森林景观的重要组成部分,是川西地区重要的美学资源,提供了多种重要的生态系统服务,对区域生态旅游和经济发展起着重要作用。探讨彩叶林景观分布格局及其与地形因子的关系,有助于为亚高山彩叶林旅游资源的有效保护和规划利用提供依据。以四川省理县317国道沿线彩叶林为研究对象,基于外业调查的森林资源数据绘制景观类型分布图,通过景观类型分布图与数字高程模型(Digital Elevation Model,DEM)数据叠加分析地形因子对彩叶林景观分布格局的影响,并分析植被演替对亚高山彩叶林景观格局动态的影响。结果表明,(1)研究区域彩叶林面积占森林景观面积的49.60%,彩叶林类型共18种。(2)典范对应分析(Canonical Correspondence Analysis,CCA)结果表明,海拔高度是影响整体彩叶林分布的主要因子,其次是坡向。(3)研究区彩叶林多数处于混交林阶段,其次为阔叶林和灌丛林阶段,随着恢复演替正向进行,彩叶林将面临退化消失的风险。因此,在彩叶林管理中需要加强对混交林类型彩叶林的动态监测,同时可考虑适当人工干预将彩叶林维持在最有利于观赏游憩的演替阶段。
中图分类号:
李巧玉, 张小晶, 陈娟, 刘媛, 刘锦春, 陶建平. 川西亚高山彩叶林景观分布格局及其地形影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1581-1588.
LI Qiaoyu, ZHANG Xiaojing, CHEN Juan, LIU Yuan, LIU Jinchun, TAO Jianping. Landscape Distribution Pattern of Subalpine Color-leaved Forests and the Influence of Topographic Factors in Western Sichuan[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1581-1588.
| 代码 Code | 景观类型 Landscape type |
|---|---|
| T1 | 白桦林 Betula platyphylla forest |
| T2 | 糙皮桦林 Betula utilis forest |
| T3 | 川梣林 Fraxinus sargentiana forest |
| T4 | 川滇柳林 Salix rehderiana forest |
| T5 | 川滇长尾槭林 Acer caudatum forest |
| T6 | 川陕鹅耳枥林 Carpinus fargesiana forest |
| T7 | 红麸杨林 Rhus punjabensis forest |
| T8 | 槲栎林 Quercus aliena forest |
| T9 | 陕甘花楸林 Sorbus koehneana forest |
| T10 | 黄栌林 Cotinus coggygria forest |
| T11 | 亮叶桦林 B. luminifera forest |
| T12 | 日本落叶松林 Larix kaempferi forest |
| T13 | 青麸杨林 Rhus potaninii forest |
| T14 | 青榨槭林 Acer davidii forest |
| T15 | 山杨林 Populus davidiana forest |
| T16 | 四川红杉林 Larix mastersiana forest |
| T17 | 五裂槭林 Acer oliverianum forest |
| T18 | 响叶杨林 Populus adenopoda forest |
| T19 | 非彩叶林 Non color-leaved forest |
| T20 | 非林地 Non forest |
表1 研究区景观类型划分
Table 1 Classification of landscape types in the study area
| 代码 Code | 景观类型 Landscape type |
|---|---|
| T1 | 白桦林 Betula platyphylla forest |
| T2 | 糙皮桦林 Betula utilis forest |
| T3 | 川梣林 Fraxinus sargentiana forest |
| T4 | 川滇柳林 Salix rehderiana forest |
| T5 | 川滇长尾槭林 Acer caudatum forest |
| T6 | 川陕鹅耳枥林 Carpinus fargesiana forest |
| T7 | 红麸杨林 Rhus punjabensis forest |
| T8 | 槲栎林 Quercus aliena forest |
| T9 | 陕甘花楸林 Sorbus koehneana forest |
| T10 | 黄栌林 Cotinus coggygria forest |
| T11 | 亮叶桦林 B. luminifera forest |
| T12 | 日本落叶松林 Larix kaempferi forest |
| T13 | 青麸杨林 Rhus potaninii forest |
| T14 | 青榨槭林 Acer davidii forest |
| T15 | 山杨林 Populus davidiana forest |
| T16 | 四川红杉林 Larix mastersiana forest |
| T17 | 五裂槭林 Acer oliverianum forest |
| T18 | 响叶杨林 Populus adenopoda forest |
| T19 | 非彩叶林 Non color-leaved forest |
| T20 | 非林地 Non forest |
| 森林类型 Forest type | 灌丛林 Shrub forest | 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 针叶林 Coniferous forest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积百分比 Percentage area/% | 10.69 | 10.96 | 75.87 | 2.48 |
表2 不同演替阶段彩叶林面积百分比
Table 2 Percentage of the color-leaved forest area in different succession stages
| 森林类型 Forest type | 灌丛林 Shrub forest | 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 针阔混交林 Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest | 针叶林 Coniferous forest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积百分比 Percentage area/% | 10.69 | 10.96 | 75.87 | 2.48 |
| Level | LT | NP | PD | TPA | MPA | MSI | MFRPAC | MENN | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class level | T1 | 72 | 0.24 | 3251.79 | 45.16 | 1.58 | 1.07 | 0.39 | 94.13 |
| T2 | 27 | 0.09 | 3958.92 | 146.63 | 1.75 | 1.08 | 0.72 | 96.06 | |
| T3 | 2 | 0.01 | 5.58 | 2.79 | 1.33 | 1.06 | 3.42 | 88.89 | |
| T4 | 13 | 0.04 | 27.99 | 2.15 | 1.54 | 1.08 | 0.62 | 70.14 | |
| T5 | 21 | 0.07 | 131.49 | 6.26 | 1.34 | 1.06 | 0.42 | 88.26 | |
| T6 | 4 | 0.01 | 29.34 | 7.34 | 1.21 | 1.04 | 0.39 | 91.54 | |
| T7 | 5 | 0.02 | 5.76 | 1.15 | 1.18 | 1.05 | 0.23 | 75 | |
| T8 | 3 | 0.01 | 47.79 | 15.93 | 1.24 | 1.04 | 0.27 | 95.07 | |
| T9 | 18 | 0.06 | 100.89 | 5.61 | 1.41 | 1.07 | 2.11 | 84.92 | |
| T10 | 76 | 0.26 | 1287.99 | 16.95 | 1.44 | 1.06 | 0.31 | 91.1 | |
| T11 | 2 | 0.01 | 62.91 | 31.46 | 1.36 | 1.06 | 0.06 | 96.95 | |
| T12 | 64 | 0.22 | 235.71 | 3.68 | 1.28 | 1.05 | 0.43 | 82.9 | |
| T13 | 2 | 0.01 | 7.56 | 3.78 | 1.18 | 1.04 | 1.06 | 92.62 | |
| T14 | 79 | 0.27 | 2505.42 | 31.71 | 1.52 | 1.07 | 0.24 | 93.43 | |
| T15 | 3 | 0.01 | 55.89 | 18.63 | 1.39 | 1.06 | 6.56 | 94.71 | |
| T16 | 16 | 0.05 | 65.61 | 4.1 | 1.38 | 1.07 | 1.53 | 83.05 | |
| T17 | 42 | 0.14 | 524.88 | 12.5 | 1.43 | 1.07 | 0.69 | 90.3 | |
| T18 | 2 | 0.01 | 23.13 | 11.57 | 1.24 | 1.04 | 0.42 | 95.43 | |
| T19 | 115 | 0.39 | 12530.07 | 108.96 | 1.8 | 1.08 | 0.17 | 95.27 | |
| T20 | 75 | 0.25 | 4618.17 | 61.58 | 2.12 | 1.09 | 0.19 | 89.97 | |
| Landscape level | TC | 451 | 3.66 | 12317.67 | 27.31 | 1.46 | 1.07 | 0.58 | 93.65 |
| TT | 641 | 2.17 | 29476.89 | 45.99 | 1.6 | 1.07 | 0.46 | 93.77 |
表3 研究区景观格局基本特征
Table 3 Basic features of the landscape pattern in the study area
| Level | LT | NP | PD | TPA | MPA | MSI | MFRPAC | MENN | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class level | T1 | 72 | 0.24 | 3251.79 | 45.16 | 1.58 | 1.07 | 0.39 | 94.13 |
| T2 | 27 | 0.09 | 3958.92 | 146.63 | 1.75 | 1.08 | 0.72 | 96.06 | |
| T3 | 2 | 0.01 | 5.58 | 2.79 | 1.33 | 1.06 | 3.42 | 88.89 | |
| T4 | 13 | 0.04 | 27.99 | 2.15 | 1.54 | 1.08 | 0.62 | 70.14 | |
| T5 | 21 | 0.07 | 131.49 | 6.26 | 1.34 | 1.06 | 0.42 | 88.26 | |
| T6 | 4 | 0.01 | 29.34 | 7.34 | 1.21 | 1.04 | 0.39 | 91.54 | |
| T7 | 5 | 0.02 | 5.76 | 1.15 | 1.18 | 1.05 | 0.23 | 75 | |
| T8 | 3 | 0.01 | 47.79 | 15.93 | 1.24 | 1.04 | 0.27 | 95.07 | |
| T9 | 18 | 0.06 | 100.89 | 5.61 | 1.41 | 1.07 | 2.11 | 84.92 | |
| T10 | 76 | 0.26 | 1287.99 | 16.95 | 1.44 | 1.06 | 0.31 | 91.1 | |
| T11 | 2 | 0.01 | 62.91 | 31.46 | 1.36 | 1.06 | 0.06 | 96.95 | |
| T12 | 64 | 0.22 | 235.71 | 3.68 | 1.28 | 1.05 | 0.43 | 82.9 | |
| T13 | 2 | 0.01 | 7.56 | 3.78 | 1.18 | 1.04 | 1.06 | 92.62 | |
| T14 | 79 | 0.27 | 2505.42 | 31.71 | 1.52 | 1.07 | 0.24 | 93.43 | |
| T15 | 3 | 0.01 | 55.89 | 18.63 | 1.39 | 1.06 | 6.56 | 94.71 | |
| T16 | 16 | 0.05 | 65.61 | 4.1 | 1.38 | 1.07 | 1.53 | 83.05 | |
| T17 | 42 | 0.14 | 524.88 | 12.5 | 1.43 | 1.07 | 0.69 | 90.3 | |
| T18 | 2 | 0.01 | 23.13 | 11.57 | 1.24 | 1.04 | 0.42 | 95.43 | |
| T19 | 115 | 0.39 | 12530.07 | 108.96 | 1.8 | 1.08 | 0.17 | 95.27 | |
| T20 | 75 | 0.25 | 4618.17 | 61.58 | 2.12 | 1.09 | 0.19 | 89.97 | |
| Landscape level | TC | 451 | 3.66 | 12317.67 | 27.31 | 1.46 | 1.07 | 0.58 | 93.65 |
| TT | 641 | 2.17 | 29476.89 | 45.99 | 1.6 | 1.07 | 0.46 | 93.77 |
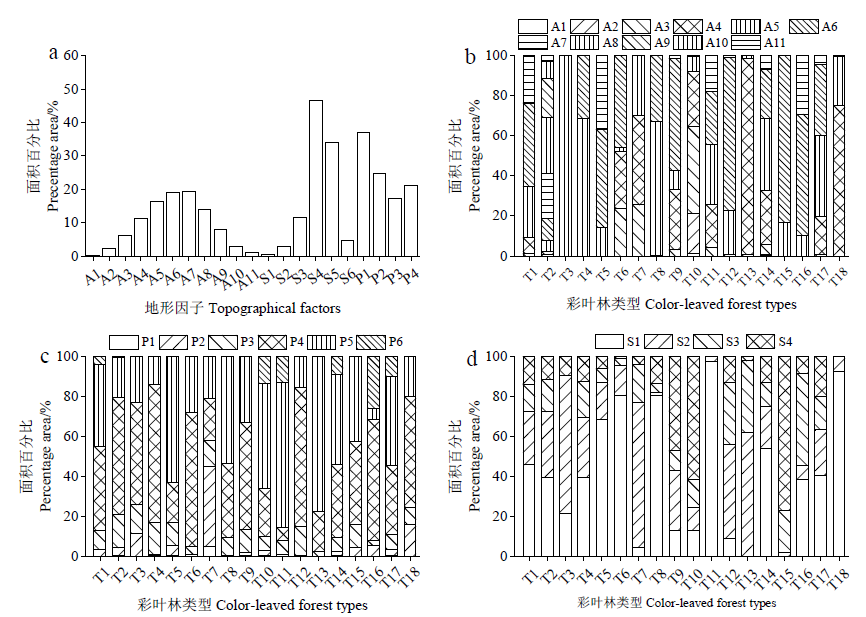
图4 不同地形因子中彩叶林面积百分比 (a)总体彩叶林面积百分比Percentage area of all color-leaved forests;(b)不同海拔梯度中彩叶林面积百分比Percentage area of each color-leaved forest in different altitude classes;(c)不同坡度中彩叶林面积百分比Percentage area of each color-leaved forest in different slope classes;(d)不同坡向中彩叶林面积百分比Percentage area of each color-leaved forest in different aspect classes
Fig. 4 Percentage area of eighteen color-leaved forests in different topographical factors
| 地形因子 Topographical factors | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 | 解释度 Explain/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.917 | 0.051 | -0.034 | 0.000 | 20.4 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.114 | -0.123 | -0.297 | 0.000 | 4.5 |
| 坡向 Aspect | -0.057 | 0.718 | -0.028 | 0.000 | 1.0 |
| CCA排序概要 Summary of CCA ordination | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 | |
| 物种-环境相关 Species-environment correlations | 0.925 | 0.723 | 0.304 | 0.000 | |
| 物种环境关系的方差累积比例 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relation/% | 80.4 | 97.8 | 100.0 | 0.0 | |
| 所有典范轴的显著性检验 Test of significance of all canonical axes | P=0.002 |
表4 地形因子与CCA排序轴相关系数和排序概要
Table 4 Correlation coefficients between topographical factors and CCA ordination axes and ordination summary
| 地形因子 Topographical factors | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 | 解释度 Explain/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.917 | 0.051 | -0.034 | 0.000 | 20.4 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.114 | -0.123 | -0.297 | 0.000 | 4.5 |
| 坡向 Aspect | -0.057 | 0.718 | -0.028 | 0.000 | 1.0 |
| CCA排序概要 Summary of CCA ordination | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 | |
| 物种-环境相关 Species-environment correlations | 0.925 | 0.723 | 0.304 | 0.000 | |
| 物种环境关系的方差累积比例 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relation/% | 80.4 | 97.8 | 100.0 | 0.0 | |
| 所有典范轴的显著性检验 Test of significance of all canonical axes | P=0.002 |
| [1] |
BADANO E, CAVIERES L, MONTENEGRO M, et al., 2005. Slope aspect influences plant association patterns in the Mediterranean matorral of central Chile[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 62(1): 93-108.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BOSSARD C C, CAO Y, WANG J, et al., 2015. New patterns of establishment and growth of Picea Abies and Betula tree species in subalpine forest gaps of Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, southwestern China in a changing environment[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 356(356): 84-92.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HE Y N, CHEN G, COBB R C, et al., 2021. Forest landscape patterns shaped by interactions between wildfire and sudden oak death disease[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2021.118987.
DOI |
| [4] |
HULSHOFF R, 1995. Landscape indices describing a Dutch landscape[J]. Landscape Ecology, 10(2): 101-111.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MÅREN I, KARKI S, PRAJAPATI C, et al., 2015. Facing north or south: does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley?[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 121(1): 112-123.
DOI URL |
| [6] | MOESLUND J, ARGE L, BØCHER P, et al., 2013. Topographically controlled soil moisture is the primary driver of local vegetation patterns across a lowland region[J]. Ecosphere, 4(7): 26-91. |
| [7] |
SCHIRPKE U, TASSER E, TAPPEINER U, 2013. Predicting scenic beauty of mountain regions[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 111(1): 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
TAKAHASHI K, MURAYAMA Y, 2014. Effects of topographic and edaphic conditions on alpine plant species distribution along a slope gradient on Mount Norikura, central Japan[J]. Ecological Research, 29(5): 823-833.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
WANG Y C, KRONENFELD B, LARSEN C, 2009. Spatial distribution of forest landscape change in western New York from presettlement to the present[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 39(1): 76-88.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WU J Z, ZHONG Y D, DENG J Y, 2019. Assessing and mapping forest landscape quality in China[J]. Forests, 10(8): 684.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHU M, FENG Q, QIN Y Y, et al., 2017. Soil organic carbon as functions of slope aspects and soil depths in a semiarid alpine region of northwest China[J]. Catena, 152(1): 94-102.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 陈文波, 肖笃宁, 李秀珍, 2002. 景观空间分析的特征和主要内容[J]. 生态学报, 22(7): 1135-1142. |
| CHEN W B, XIAO D N, LI X Z, 2002. The characteristics and contents of landscape spatial analysis[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22(7): 1135-1142. | |
| [13] | 葛雨萱, 赵阳, 甘长青, 等, 2011. 不同光环境对黄栌光合特性及生长势和叶色的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 27(19): 19-22. |
| GE Y X, ZHAO Y, GAN C Q, et al., 2011. The effects of different light environments on photosynthetic characteristics, growth potential and leaves color of Cotinus coggygria Scop[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(19): 19-22. | |
| [14] | 郭剑英, 2015. 四川红叶彩林资源特征分析[J]. 四川林勘设计 (3): 50-53. |
| GUO J Y, 2015. Analysis on the characteristics of Sichuan red-leaf color forest resources[J]. Sichuan Forestry Exploration and Design (3): 50-53. | |
| [15] | 郭泺, 余世孝, 夏北成, 等, 2006. 地形对山地森林景观格局多尺度效应[J]. 山地学报, 24(2): 150-155. |
| GUO L, YU S X, XIA B C, et al., 2006. Analysis of the muti-scale effect of topography on forest landscape pattern of mountains[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 24(2): 150-155. | |
| [16] | 郭珊, 2010. 基于IRS-6的理县森林资源调查研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学. |
| GUO S, 2010. The investigation of forest resource base on IRS-6 in Lixian[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. | |
| [17] | 何方永, 2016. 地质背景条件对光雾山彩叶景观制约研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学: 136. |
| HE F Y, 2016. Study on restriction of geological backgrounds and conditions to colorful-leaf forest landscape in Guangwu Mountain[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology: 136. | |
| [18] | 胡淑萍, 刘鹏举, 高开通, 等, 2013. 北京九龙山自然保护区植物群落物种多样性分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 20(4): 125-130. |
| HU S P, LIU P J, GAO K T, et al., 2013. Analysis of species diversity of plant communities in Jiulongshan Nature Reserve, Beijing[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(4): 125-130. | |
| [19] | 蒋有绪, 1982. 川西亚高山森林植被的区系、种间关联和群落排序的生态分析[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学丛刊, 6(4): 281-301. |
| JIANG Y Y, 1982. Ecological analysis of flora, species correlation and ordination of subapline forest vegetation in western Sichuan[J]. Acta Phytoecological et Geobotanica Sinica, 6(4): 281-301. | |
| [20] | 孔繁花, 李秀珍, 尹海伟, 等, 2004. 地形对大兴安岭北坡林火迹地森林景观格局影响的梯度分析[J]. 生态学报, 24(9): 1863-1870. |
| KONG F H, LI X Z, YIN H W, et al., 2004. Gradient analysis on the influence of terrain on the forest landscape pattern in the burned blanks of the north slope of Mt. Daxing’anling[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(9): 1863-1870. | |
| [21] | 赖长鸿, 胡庭兴, 赵安玖, 2006. 川西亚高山道孚林区森林景观格局地形分异研究[J]. 四川林业科技, 27(2): 63-67. |
| LAI C H, HU T X, ZHAO A J, 2006. Topographic variation of forest landscape patterns in subalpine Daofu forest region in western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 27(2): 63-67. | |
| [22] | 雷金睿, 陈宗铸, 陈毅青, 等, 2020. 1990-2018年海南岛湿地景观格局演变及其驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(1): 59-70. |
| LEI J R, CHEN Z Z, CHEN Y Q, et al., 2020. Landscape pattern changes and driving factors analysis of wetland in Hainan Island during 1990-2018 [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(1): 59-70. | |
| [23] | 李海龙, 李端亮, 2009. 黄栌属植物研究进展[J]. 陕西林业科技, 1(6): 22-27. |
| LI H L, LI D L, 2009. Advances in studies on Genus Cotinus (Tourn.) Mill[J]. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, 1(6): 22-27. | |
| [24] | 梁艳艳, 周年兴, 谢慧玮, 等, 2013. 庐山森林景观格局变化的长期动态模拟[J]. 生态学报, 33(24): 7807-7818. |
| LIANG Y Y, ZHOU N X, XIE H W, et al., 2013. Long-term dynamic simulation on forest landscape pattern changes in Mount Lushan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(24): 7807-7818. | |
| [25] | 刘彬, 杨万勤, 吴福忠, 2010. 亚高山森林生态系统过程研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 30(16): 4476-4483. |
| LIU B, YANG W Q, WU F Z, 2010. Advances in the subalpine forest ecosystem processes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(16): 4476-4483. | |
| [26] | 刘庆, 吴彦, 何海, 2001. 中国西南亚高山针叶林的生态学问题[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 1(2): 63-69. |
| LIU Q, WU Y, HE H, 2001. Ecological Problems of Subalpine Coniferous Forest in the Southwest of China[J]. World Science and Technology Research and Development, 1(2): 63-69. | |
| [27] | 欧阳勋志, 廖为明, 俞社保, 等, 2005. 婺源县森林景观空间格局及其与景观美学质量关系探析[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 27(6): 880-884. |
| OUYANG X Z, LIAO W M, YU S B, et al., 2005. Approach to the spatial pattern and its relationship to aesthetic quality of forest landscape in Wuyuan County[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis, 27(6): 880-884. | |
| [28] | 任学敏, 杨改河, 王得祥, 等, 2012. 环境因子对巴山冷杉-糙皮桦混交林物种分布及多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(2): 605-613. |
|
REN X M, YANG G H, WANG D X, et al., 2012. Effects of environmental factors on species distribution and diversity in an Abies fargesii-Betula utilis mixed forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(2): 605-613.
DOI URL |
|
| [29] | 史立新, 王金夕, 宿以明, 等, 1988. 川西米亚罗地区暗针叶林采伐迹地早期植被演替过程的研究[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 12(4): 64-71. |
| SHI L X, WANG J X, SU Y M, et al., 1988. Earlier-stage succession of vegetation on the clear-cuts in Miyaluo forest district in western Sichuan[J]. Acta Phytoecologica et Geobotanica Sinica, 12(4): 64-71. | |
| [30] | 王臣立, 徐丹, 林文鹏, 2021. 红河哈尼梯田世界文化景观遗产的遥感监测与土地覆盖变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(2): 233-241. |
| WANG C L, XU D, LIN W P, 2021. Remote sensing monitoring and land cover change of the world cultural landscape heritage in Honghe Hani Terrace, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(2): 233-241. | |
| [31] | 韦新良, 周国模, 余树全, 1997. 森林景观分类系统初探[J]. 中南林业调查规划, 1(3): 41-44. |
| WEI X L, ZHOU G M, YU S Q, 1997. Preliminary study on forest landscape classification system[J]. Central South Forestry Survey Planning, 1(3): 41-44. | |
| [32] | 易成波, 2010. 九寨沟自然保护区景观动态分析与可持续性旅游发展[D]. 成都: 四川大学: 127. |
| YI C B, 2010. Tourism-induced landscape changes and sustainable tourism in Jiuzhaigou National Park, China[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University: 127. | |
| [33] | 曾豪, 何方永, 彭培好, 2016. 四川光雾山彩叶景观格局研究[J]. 四川林业科技, 37(4): 34-38. |
| ZENG H, HE F Y, PENG P H, 2016. Research on colorful leaf forest landscape in Mt. Guangwu of Sichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 37(4): 34-38. | |
| [34] | 钟章成, 1982. 四川主要森林植被地理学[J]. 西南师范学院学报, 1(2): 5-12. |
| ZHONG Z C, 1982. Geography of major forest vegetation in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University, 1(2): 5-12. |
| [1] | 杨世福, 马玲玲, 陈芸芝, 唐旭利. 鼎湖山季风常绿阔叶林演替系列土壤细菌群落的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2275-2282. |
| [2] | 杨丹荔, 罗辑, 贾龙玉, 陈云飞. 海螺沟冰川退缩区原生演替生态系统中铅累积的历史记录[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2393-2402. |
| [3] | 王浩, 陈永金, 刘加珍, 万波, 张丽. 黄河三角洲新生湿地3种柽柳灌丛对土壤有机碳空间分布的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 9-16. |
| [4] | 汪益敏, 陶玥琛, 程致远, 李博文. 高速公路路堑边坡客土喷播的长期防护效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1724-1731. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
