Ecology and Environmental Sciences ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 134-146.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2026.01.012
• Research Article [Environmental Science] • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Xuan1,2( ), YU Jiali3,4, CHEN Bi3,4, LOU Yunkai1,2, HE Min3,4, MIAO Peng1,2, YANG Fan3,4,*(
), YU Jiali3,4, CHEN Bi3,4, LOU Yunkai1,2, HE Min3,4, MIAO Peng1,2, YANG Fan3,4,*( ), TANG Tao1,*(
), TANG Tao1,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-20
Revised:2025-09-05
Accepted:2025-11-19
Online:2026-01-18
Published:2026-01-05
吴璇1,2( ), 余佳丽3,4, 陈笔3,4, 娄云剀1,2, 何敏3,4, 苗芃1,2, 杨帆3,4,*(
), 余佳丽3,4, 陈笔3,4, 娄云剀1,2, 何敏3,4, 苗芃1,2, 杨帆3,4,*( ), 唐涛1,*(
), 唐涛1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 作者简介:吴璇(1997年生),女,博士研究生,主要从事河流生态学研究。E-mail: wuxuan@ihb.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
WU Xuan, YU Jiali, CHEN Bi, LOU Yunkai, HE Min, MIAO Peng, YANG Fan, TANG Tao. The Ecological Carrying Capacity of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Chishui River Basin Based on Stress-response Relationship[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2026, 35(1): 134-146.
吴璇, 余佳丽, 陈笔, 娄云剀, 何敏, 苗芃, 杨帆, 唐涛. 基于胁迫-响应关系的赤水河氮磷生态承载力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2026, 35(1): 134-146.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2026.01.012
| 数据名称 | 分辨率 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 数字高程模型(DEM) | 30 m | 地理空间数据云ASTER GDEM |
| 土地利用数据 | 30 m | 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所 2020年中国土地利用遥感监测数据 |
| 土壤数据 | 1 km | 世界土壤数据库(HWSD) |
| 气象数据 | - | 气象站实测数据 |
| 中国大气同化数据驱动集(CMADS v1.0) | ||
| 水文数据 | - | 中华人民共和国水文年鉴 |
Table 1 Input data and their sources for the SWAT model
| 数据名称 | 分辨率 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|
| 数字高程模型(DEM) | 30 m | 地理空间数据云ASTER GDEM |
| 土地利用数据 | 30 m | 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所 2020年中国土地利用遥感监测数据 |
| 土壤数据 | 1 km | 世界土壤数据库(HWSD) |
| 气象数据 | - | 气象站实测数据 |
| 中国大气同化数据驱动集(CMADS v1.0) | ||
| 水文数据 | - | 中华人民共和国水文年鉴 |
| 指标 | 平均值(范围) |
|---|---|
| 总氮质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | 3.04(0.35-9.14) |
| 总磷质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | 0.09(0.01-2.64) |
| 样点藻类物种数/种 | 51(26-92) |
| 样点藻类生物量/(mg·cm−2) | 0.67(0.029-2.37) |
Table 2 TN, TP and algae statistic data of Chishui River
| 指标 | 平均值(范围) |
|---|---|
| 总氮质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | 3.04(0.35-9.14) |
| 总磷质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | 0.09(0.01-2.64) |
| 样点藻类物种数/种 | 51(26-92) |
| 样点藻类生物量/(mg·cm−2) | 0.67(0.029-2.37) |
| 藻类参数 | Metrics | 阈值分析方法 | ρ(TN)/ (mg·L−1) | ρ(TP)/ (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群落生物量 | Chla | 分段回归 | 1.119 | 0.013 |
| 非参数突变点分析nCPA | 3.131 | 0.054 | ||
| 物种丰富度 | Richness | 分段回归 | 1.251 | 0.017 |
| 非参数突变点分析nCPA | 2.867 | 0.024 | ||
| 负响应物种 | Z− taxa | 临界指示物种分析TITAN | 1.445 | 0.022 |
| 正响应物种 | Z+ taxa | 4.810 | 0.039 | |
| 群落组成 | - | 梯度森林GF | 2.560 | 0.018 |
Table 3 TN and TP thresholds for the species richness, community structure, and biomass of benthic algae
| 藻类参数 | Metrics | 阈值分析方法 | ρ(TN)/ (mg·L−1) | ρ(TP)/ (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群落生物量 | Chla | 分段回归 | 1.119 | 0.013 |
| 非参数突变点分析nCPA | 3.131 | 0.054 | ||
| 物种丰富度 | Richness | 分段回归 | 1.251 | 0.017 |
| 非参数突变点分析nCPA | 2.867 | 0.024 | ||
| 负响应物种 | Z− taxa | 临界指示物种分析TITAN | 1.445 | 0.022 |
| 正响应物种 | Z+ taxa | 4.810 | 0.039 | |
| 群落组成 | - | 梯度森林GF | 2.560 | 0.018 |
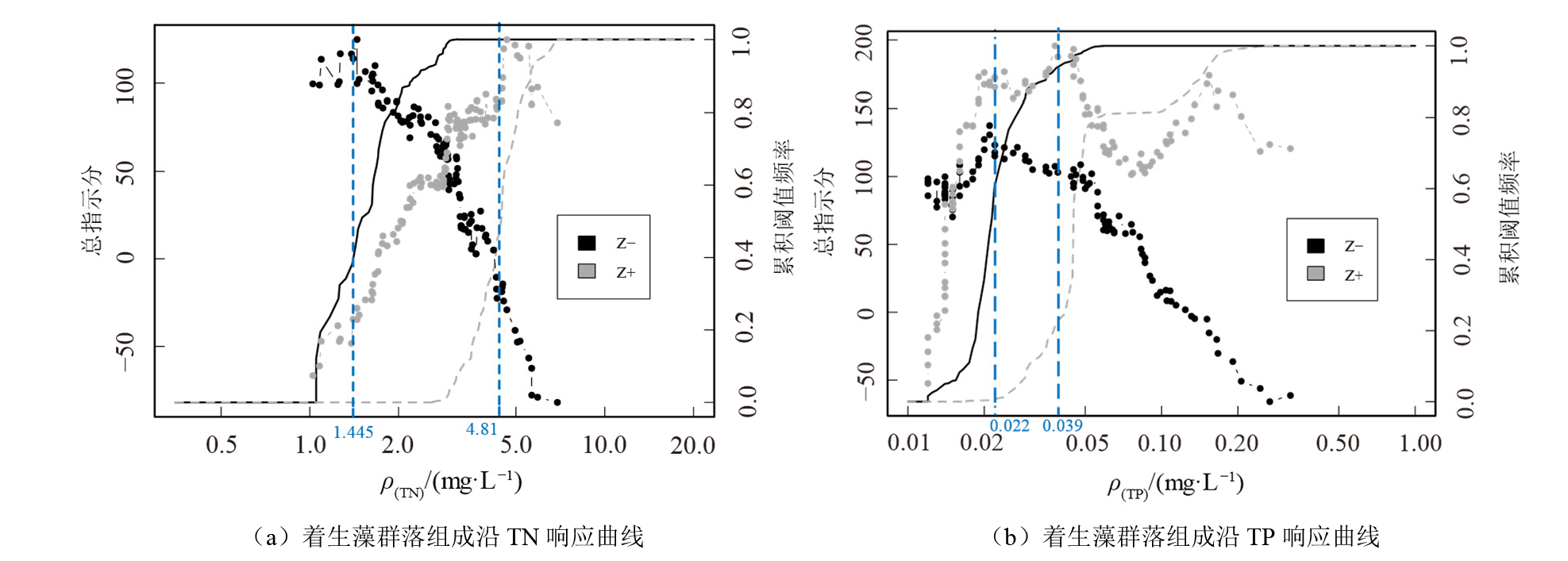
Figure 5 The response curves of the negative response (z?) and positive response (z+) groups of the benthic algae community fitted by TITAN along the TN and TP gradients
| [1] |
ALVES R A, RUDKE A P, DE MELO SOUZA S T, et al., 2024. Flood vulnerability mapping in an urban area with high levels of impermeable coverage in southern Brazil[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 24(3): 96.
DOI |
| [2] | BAJYA S, JAKHAR R S, BHATESHWAR V, et al., 2023. Role of soil organic matter in soil health and crop productivity improvement[C]// Advancement and innovations in agriculture. Karnataka: Iterative International: 135-147. |
| [3] | BAKER M E, KING R S, 2010. A new method for detecting and interpreting biodiversity and ecological community thresholds[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolutionx, 1(1): 25-37. |
| [4] |
BATEY T, 2009. Soil compaction and soil management: A review[J]. Soil Use and Management, 25(4): 335-345.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BIGGS B J F, 2000. Eutrophication of streams and rivers: dissolved nutrient-chlorophyll relationships for benthic algae[J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 19(1): 17-31.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
BLACK R W, MORAN P W, FRANKFORTER J D, 2011. Response of algal metrics to nutrients and physical factors and identification of nutrient thresholds in agricultural streams[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175(1-4): 397-417.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
BOMBINO G, DENISI P, GÓMEZ J A, et al., 2019. Water infiltration and surface runoff in steep clayey soils of olive groves under different management practices[J]. Water, 11(2): 240.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
BROM J, DUFFKOVÁ R, HABERLE J, et al., 2021. Identification of infiltration features and hydraulic properties of soils based on crop water stress derived from remotely sensed data[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(20): 4127.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
BU J H, LI C H, WANG X, et al., 2020. Assessment and prediction of the water ecological carrying capacity in Changzhou city, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 277: 123988.
DOI URL |
| [10] | BURFORD M A, LU J, 2024. The Nitrogen Cycle[C]// Wetzel’s Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems. Fourth edition. London: Academic Press: 325-357. |
| [11] |
CHAMBERS P A, CULP J M, ROBERTS E S, et al., 2012. Development of environmental thresholds for streams in agricultural watersheds[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 41(1): 1-6.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
CHARLES D F, KELLY M G, STEVENSON R J, et al., 2021. Benthic algae assessments in the EU and the US: Striving for consistency in the face of great ecological diversity[J]. Ecological Indicators, 121: 107082.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
CHEN Y Z, LU H W, LI J, et al., 2021. Multi-criteria decision making and fairness evaluation of water ecological carrying capacity for inter-regional green development[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28: 6470-6490.
DOI |
| [14] |
CUTLER D R, EDWARDS JR T C, BEARD K H, et al., 2007. Random forests for classification in ecology[J]. Ecology, 88(11): 2783-2792.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
D’AMARIO S C, REARICK D C, FASCHING C, et al., 2019. The prevalence of nonlinearity and detection of ecological breakpoints across a land use gradient in streams[J]. Scientific Reports, 9(1): 3878.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | DILLON P J, MOLOT L A, 2024. The phosphorus cycle[C]// Wetzel’s Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems. Fourth edition. London: Academic Press: 359-425. |
| [17] |
DODDS W K, CLEMENTS W H, GIDO K, et al., 2010. Thresholds, breakpoints, and nonlinearity in freshwaters as related to management[J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 29(3): 988-997.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DODDS W K, OAKES R M, 2004. A technique for establishing reference nutrient concentrations across watersheds affected by humans[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2(10): 333-341.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DONEVA K, KERCHEVA M, DIMITROV E, et al., 2022. Thermal properties of Cambisols in mountain regions under different vegetation covers[J]. Soil and Water Research, 17(2): 113-122.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
EDWARDS T M, PUGLIS H J, KENT D B, et al., 2024. Ammonia and aquatic ecosystems: A review of global sources, biogeochemical cycling, and effects on fish[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 907: 167911.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ELLIS N, SMITH S J, PITCHER C R, 2012. Gradient forests: calculating importance gradients on physical predictors[J]. Ecology, 93(1): 156-168.
PMID |
| [22] |
EVANS-WHITE M A, HAGGARD B E, SCOTT J T, 2013. A review of stream nutrient criteria development in the United States[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42(4): 1002-1014.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
FANG X, HE W J, WEN F G, et al., 2025. SWAT model application for calculating ecological flow in sub-basins of the Huangshui River Basin[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 380: 124837.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
GROFFMAN P M, BARON J S, BLETT T, et al., 2006. Ecological thresholds: The key to successful environmental management or an important concept with no practical application?[J]. Ecosystems, 9: 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HU G Z, ZENG W H, YAO R H, et al., 2021. An integrated assessment system for the carrying capacity of the water environment based on system dynamics[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 295: 113045.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
JARGAL N, AN K G, 2023. Seasonal and interannual responses of blue-green algal taxa and chlorophyll to a monsoon climate, flow regimes, and N: P ratios in a temperate drinking-water reservoir[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 896: 165306.
DOI URL |
| [27] | JESSUP B, 2015. New Mexico nutrient thresholds for perennial wadeable streams[R]. New Mexico: Tetra Tech: 1-110. |
| [28] |
KELLER A A, CAVALLARO L, 2008. Assessing the US Clean Water Act 303(d) listing process for determining impairment of a waterbody[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 86(4): 699-711.
PMID |
| [29] |
KELLY M G, PHILLIPS G, TEIXEIRA H, et al., 2022. Establishing ecologically-relevant nutrient thresholds: A tool-kit with guidance on its use[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 807(Part 3): 150977.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
KUKHARETS S, ZABRODSKYI A, SHELUDCHENKO B, et al., 2025. Assessment of changes in soil contact stress depending on tractor tire parameters[J]. Scientific Reports, 15(1): 172.
DOI |
| [31] |
MASIOL M, SQUIZZATO S, CHALUPA D C, et al., 2018. Long-term trends in submicron particle concentrations in a metropolitan area of the northeastern United States[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 633: 59-70.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
MAZOR R D, SUTULA M, THEROUX S, et al., 2022. Eutrophication thresholds associated with protection of biological integrity in California wadeable streams[J]. Ecological Indicators, 142: 109180.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
PAMUKCU P, SERENGIL Y, YURTSEVEN I, 2014. Role of forest cover, land use change and climate change on water resources in Marmara basin of Turkey[J]. iForest, 8(4): 480-486.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
PIMENTEL H F, OYAGUE E, SÁNCHEZ E, 2022. Environmental quality assessment in central Andean Rivers: Using the ecological thresholds concept, environmental quality standards, and biotic indexes[J]. River Research and Applications, 38(7): 1305-1320.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
QIAN S S, KING R S, RICHARDSON C J, 2003. Two statistical methods for the detection of environmental thresholds[J]. Ecological Modelling, 166(1-2): 87-97.
DOI URL |
| [36] | SHAABAN M, 2024. Acidic Soils[C]// Planet Earth: Scientific Proposals to Solve Urgent Issues. Cham: Springer International Publishing: 293-306. |
| [37] |
SONSRI K, WATANABE A, 2023. Insights into the formation and stability of soil aggregates in relation to the structural properties of dissolved organic matter from various organic amendments[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 232: 105774.
DOI URL |
| [38] | STĂTESCU F, ZAUCĂ D C, PAVEL L V, 2013. Soil structure and water-stable aggregates[J]. Environmental Engineering and Management, 12(4): 741-746. |
| [39] |
STEVENSON R J, BENNETT B J, JORDAN D N, et al., 2012. Phosphorus regulates stream injury by filamentous green algae, DO, and pH with thresholds in responses[J]. Hydrobiologia, 695: 25-42.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
STEVENSON R J, HILL B H, HERLIHY A T, et al., 2008. Algae-P relationships, thresholds, and frequency distributions guide nutrient criterion development[J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 27(3): 783-799.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SU J, JI D F, LIN M, et al., 2017. Developing surface water quality standards in China[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 117(Part B): 294-303.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
SULTANA J, TIBBY J, RECKNAGEL F, et al., 2020. Comparison of two commonly used methods for identifying water quality thresholds in freshwater ecosystems using field and synthetic data[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 724: 137999.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
SUN F H, MU Y S, LEUNG K M Y, et al., 2021. China is establishing its water quality standards for enhancing protection of aquatic life in freshwater ecosystems[J]. Environmental Science and Policy, 124: 413-422.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
SUNDERMANN A, LEPS M, LEISNER S, et al., 2015. Taxon-specific physico-chemical change points for stream benthic invertebrates[J]. Ecological Indicators, 57: 314-323.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
TANG T, JIA X H, JIANG W X, et al., 2016. Multi-scale temporal dynamics of epilithic algal assemblages: evidence from a Chinese subtropical mountain river network[J]. Hydrobiologia, 770: 289-299.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
TANG T, STEVENSON R J, 2023. Striving for consistent bioassessment across diverse landscapes: Using land use matters for classifying reference and disturbed sites for index development[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 900: 165849.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
TANG T, STEVENSON R J, GRACE J B, 2020. The importance of natural versus human factors for ecological conditions of streams and rivers[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 704: 135268.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
TANG T, TANG T, TAN L, et al., 2017. Identifying community thresholds for lotic benthic diatoms in response to human disturbance[J]. Scientific Reports, 7(1): 4134.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
TONG Y B, LEI K, WANG L, et al., 2024. Spatial-temporal characteristics and the importance of environmental factors in relation to algal blooms in coastal seas[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 957: 177686.
DOI URL |
| [50] | TÓTH G, MONTANARELLA L, STOLBOVOY V, et al., 2008. Soils of the European union[R]. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: 1-85. |
| [51] |
WAITE I R, PAN Y, EDWARDS P M, 2020. Assessment of multi-stressors on compositional turnover of diatom, invertebrate and fish assemblages along an urban gradient in Pacific Northwest streams (USA)[J]. Ecological Indicators, 112: 106047.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
WANG T X, XU S G, 2015. Dynamic successive assessment method of water environment carrying capacity and its application[J]. Ecological Indicators, 52: 134-146.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
WANG Z Y, FU X T, 2023. Scheme simulation and predictive analysis of water environment carrying capacity in Shanxi Province based on system dynamics and DPSIR model[J]. Ecological Indicators, 154: 110862.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZHOU F, ZHANG W S, JIANG A N, et al., 2023. Spatial-temporal variation characteristics and coupling coordination of the “water resources-water environment-water ecology” carrying capacity in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Ecological Indicators, 154: 110874.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHU K H, CHEN L, CHEN S B, et al., 2022. New framework for managing the water environmental capacity integrating the watershed model and stochastic algorithm[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 816: 151659.
DOI URL |
| [56] | 毕节市人民政府, 2024. 毕节市环境质量年报 (2023年)[R]. [2025-2-12]. https://www.bijie.gov.cn/bm/bjssthjj/hjzl/hjzlyb/202401/t20240124_83611755.html. |
| Bijie Municipal People’s Government, 2024. Bijie Municipal Environmental Quality Annual Report (2023)[R]. [2025-2-12]. https://www.bijie.gov.cn/bm/bjssthjj/hjzl/hjzlyb/202401/t20240124_83611755.html. | |
| [57] | 陈妍, 翟俊, 杨旻, 等, 2023. 赤水河流域生态状况与变化特征综合评估[J]. 环境工程, 41(4): 185-194. |
| CHEN Y, ZHAI J, YANG M, et al., 2023. Analysis of ecological protection situation and its variation characteristics of the Chishui River Basin[J]. Environmental Engineering, 41(4): 185-194. | |
| [58] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002a. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002a. Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method[M]. The fourth edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [59] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002b. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002b. Environmental quality standards for surface water: GB 3838—2002 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [60] | 李家英, 齐雨藻, 2018. 中国淡水藻志 (第19卷): 硅藻门, 舟形藻科(III)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| LI J Y, QI Y Z, 2018. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Timus XXIII): Bacillariophyta, Naviculaceae (III)[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [61] | 刘家威, 蔡宏, 郑婷婷, 等, 2022. 基于SWAT模型的赤水河流域径流年内分配特征及其对降水的响应研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 42(3): 180-187. |
| LIU J W, CAI H, ZHENG T T, et al., 2022. Annual distribution characteristics of Chishui River watershed runoff and its response to precipitation based on SWAT model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 42(3): 180-187. | |
| [62] | 泸州市生态环境局, 2024. 2024泸州市2024年1-10月水环境质量状况通报[R]. [2025-2-12]. https://sthjj.luzhou.gov.cn/hbyw/shjgl/content_1049088. |
| Luzhou Ecological Environment Bureau, 2024. Luzhou Water Environment Quality Status Report from January to October, 2024[R]. [2025-2-12]. https://sthjj.luzhou.gov.cn/hbyw/shjgl/content_1049088. | |
| [63] | 马欢, 冯朝阳, 宋婷, 等, 2021. 1990-2018年赤水河流域土地利用变化分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 11(3): 428-436. |
| MA H, FENG C Y, SONG T, et al., 2021. Study on the characteristics of land use change in Chishui River Basin from 1990 to 2018[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 11(3): 428-436. | |
| [64] | 苗蔚, 欧延静, 吴秋双, 等, 2025. 基于多种方法的赤水河营养物基准制定研究[J/OL]. 环境科学研究, 1-16[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2025.03.23. |
| MIAO W, OU Y T, WU Q S, et al., 2025. A Study on Nutrient Criteria Development in the Chishui River based on Multiple Approaches[J/OL]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 1-16[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2025.03.23. | |
| [65] | 齐雨藻. 1995. 中国淡水藻志 (第4卷): 硅藻门, 中心纲[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| QI Y Z, 1995. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Timus IV): Bacillariophyta, Centricae[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [66] | 齐雨藻, 李家英, 2004. 中国淡水藻志 (第10卷): 硅藻门, 羽纹纲[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| QI Y Z, LI J Y, 2004. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Timus X): Bacillariophyta, Pennatae[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [67] | 施之新, 2004. 中国淡水藻志 (第12卷): 硅藻门, 异极藻科[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| SHI Z X, 2004. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Timus XII): Bacillariophyta, Gomphonemataceae Kützing[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [68] | 施之新, 2013. 中国淡水藻志 (第16卷): 硅藻门, 桥弯藻科[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| SHI Z X, 2013. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Timus XVI): Bacillariophyta, Cymbellaceae Agardh[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [69] | 王全喜, 2018. 中国淡水藻志 (第22卷): 硅藻门, 管壳缝目[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WANG Q X, 2018. Flora Algarum Sinicarum Aquae Dulcis (Timus XXII): Bacillariophyta, Aulonoraphidinales[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [70] | 王啸天, 逄勇, 吴昌淦, 等, 2024. 基于MIKE11的毛河流域水环境容量计算研究[J]. 四川环境, 43(1): 42-51. |
| WANG X T, PANG Y, WU C G, et al., 2024. Study on calculation of environment capacity of water of Maohe River Basin based on MIKE11[J]. Sichuan Environment, 43(1): 42-51. | |
| [71] | 薛亚婷, 孙文锦, 邹长武, 等, 2020. 基于SWAT模型的赤水河流域面源污染研究[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 15(3): 17-23. |
| XUE Y T, SUN W J, ZOU C W, et al., 2020. Study on non-point source pollution in Chishui River Watershed based on SWAT model[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 15(3): 17-23. | |
| [72] | 昭通市人民政府, 2024. 昭通市地表水环境状况公报(2024年上半年)[R]. [2025-2-12]. http://www.zt.gov.cn/contents/4506/231703.html. |
| Zhaotong Municipal People’s Government, 2024. Zhaotong surface water environment status bulletin (the first half of 2024)[R]. [2025-2-12]. http://www.zt.gov.cn/contents/4506/231703.html. | |
| [73] | 周玮, 高渐飞, 王苑, 2022. 赤水河流域水质演变特征及污染源识别[J]. 环境保护科学, 48(4): 74-78. |
| ZHOU W, GAO J F, WANG Y, 2022. Water quality evolution characteristics and pollution source identification in Chishui River Basin[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 48(4): 74-78. | |
| [74] | 遵义市生态环境局, 2024. 2023年遵义市生态环境状况公报[R]. [2025-2-12]. https://zyepb.zunyi.gov.cn/xwzx/tzgg/202406/t20240604_84724479.html. |
| Zunyi Ecological Environment Bureau, 2024. Zunyi ecological environment status bulletin, 2023[R]. [2025-2-12]. https://zyepb.zunyi.gov.cn/xwzx/tzgg/202406/t20240604_84724479.html. |
| [1] | ZHAO Wenqi, ZHANG Jiahua, ZHANG Peng, BAI Linyan, YAO Fengmei. Progress of Vegetation Phenology Monitoring Technology and Remote Sensing Inversion Method [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(9): 1473-1482. |
| [2] | MENG Jie, ZHU Xingyu, XU Mingyue, RONG Lingyun, WU Chuanfu, WANG Qunhui. Experimental Study and Modeling Analysis on the Removal of Simulated Ammonia Containing Odor by Decomposed Cow Manure Residue [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(6): 922-930. |
| [3] | WANG Wei, XIA Yuxuan. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 in Urban Block Based on Remote Sensing Technology and Machine Learning: Taking Binhu New District of Hefei City as an Example [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(9): 1426-1437. |
| [4] | YANG Keming, PENG Lishun, ZHANG Yanhai, GU Xinru, CHEN Xinyang, JIANG Kegui. Research on Biomass Inversion of Multiple Vegetation Types on the Surface of Mining Areas [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(7): 1027-1035. |
| [5] | WEN Ni, WANG Chongyang, CHEN Xingda, CHEN Shuisen, ZHOU Xia, YU Guorong. High-Resolution Remote Sensing Estimation of Ammonia Nitrogen Concentrations in Coastal Urban River Networks Based on Machine Learning Models [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(11): 1737-1747. |
| [6] | WANG Xuemei, YANG Xuefeng, ZHAO Feng, AN Baisong, HUANG Xiaoyu. Estimation of Aboveground Biomass in the Arid Oasis Based on the Machine Learning Algorithm [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [7] | JIANG Peng, QIN Mei’ou, LI Rongping, MENG Ying, YANG Feiyun, WEN Rihong, SUN Pei, FANG Yuan. Seasonal Variability of GPP and Its Influencing Factors in the Typical Ecosystems in China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(4): 643-651. |
| [8] | SU Hailei, LI Xinru, TAO Yanru, SHI Di, WEI Yuan, SHEN Yaqin, CHEN Yanqing, SUN Fuhong. Study on Water Quality Standard Formulation of USA and Its Revelation to China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(11): 2267-2274. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
