Ecology and Environment ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 247-255.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.02.007
• Research Article【Ecology】 • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Jiayi1( ), ZHANG Jun1, ZHANG Fan2, ZHANG Hui2, WANG Zihan2, LIU Juhong1, LÜ Shijie2,*(
), ZHANG Jun1, ZHANG Fan2, ZHANG Hui2, WANG Zihan2, LIU Juhong1, LÜ Shijie2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-18
Online:2025-02-18
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Lü Shijie
刘嘉怡1( ), 张军1, 张帆2, 张慧2, 王梓晗2, 刘菊红1, 吕世杰2,*(
), 张军1, 张帆2, 张慧2, 王梓晗2, 刘菊红1, 吕世杰2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
吕世杰
作者简介:刘嘉怡(2001年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为生物统计。E-mail: 8987081@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIU Jiayi, ZHANG Jun, ZHANG Fan, ZHANG Hui, WANG Zihan, LIU Juhong, LÜ Shijie. Effects of Enclosure on Interspecific Association of Dominant Species of Stipa breviflora in Desert Steppe[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2025, 34(2): 247-255.
刘嘉怡, 张军, 张帆, 张慧, 王梓晗, 刘菊红, 吕世杰. 围封对短花针茅荒漠草原优势种群种间联结性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 247-255.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.02.007
| 来源 | 因变量 | 自由度 df | 频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | |||
| 空间 | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 2 | 1.85 | 0.24 |
| 无芒隐子草 C. songorica | 2 | 2.22 | 0.19 | |
| 碱韭 A. polyrhizum | 2 | 0.38 | 0.70 | |
| 处理 | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 3 | 113.42 | <0.01 |
| 无芒隐子草 C. songorica | 3 | 95.49 | <0.01 | |
| 碱韭 A. polyrhizum | 3 | 462.77 | <0.01 | |
Table 1 Two-way analysis of variance for frequency of dominant population
| 来源 | 因变量 | 自由度 df | 频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | |||
| 空间 | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 2 | 1.85 | 0.24 |
| 无芒隐子草 C. songorica | 2 | 2.22 | 0.19 | |
| 碱韭 A. polyrhizum | 2 | 0.38 | 0.70 | |
| 处理 | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 3 | 113.42 | <0.01 |
| 无芒隐子草 C. songorica | 3 | 95.49 | <0.01 | |
| 碱韭 A. polyrhizum | 3 | 462.77 | <0.01 | |
| 空间尺度 | 围封 年限/a | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 无芒隐子草 C. songorica | 碱韭 A. polyrhizum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 m×30 m | 1 | 88.24% | 94.12% | 98.82% |
| 10 | 61.18% | 88.24% | 97.65% | |
| 19 | 69.41% | 94.12% | 98.82% | |
| 25 | 54.12% | 100.00% | 75.29% | |
| 35 m×35 m | 1 | 84.96% | 95.58% | 99.12% |
| 10 | 57.52% | 87.61% | 98.23% | |
| 19 | 69.03% | 95.58% | 99.12% | |
| 25 | 51.33% | 100.00% | 76.11% | |
| 40 m×40 m | 1 | 80.69% | 94.48% | 98.62% |
| 10 | 56.55% | 84.83% | 96.55% | |
| 19 | 72.41% | 93.79% | 99.31% | |
| 25 | 51.72% | 100.00% | 77.93% |
Table 2 The frequency of dominant populations in different spatial scales and enclosure years
| 空间尺度 | 围封 年限/a | 短花针茅 S. breviflora | 无芒隐子草 C. songorica | 碱韭 A. polyrhizum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 m×30 m | 1 | 88.24% | 94.12% | 98.82% |
| 10 | 61.18% | 88.24% | 97.65% | |
| 19 | 69.41% | 94.12% | 98.82% | |
| 25 | 54.12% | 100.00% | 75.29% | |
| 35 m×35 m | 1 | 84.96% | 95.58% | 99.12% |
| 10 | 57.52% | 87.61% | 98.23% | |
| 19 | 69.03% | 95.58% | 99.12% | |
| 25 | 51.33% | 100.00% | 76.11% | |
| 40 m×40 m | 1 | 80.69% | 94.48% | 98.62% |
| 10 | 56.55% | 84.83% | 96.55% | |
| 19 | 72.41% | 93.79% | 99.31% | |
| 25 | 51.72% | 100.00% | 77.93% |
| 空间尺度 | 围封年限/a | VR | W |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 m×30 m | 1 | 0.89 | 76.05 |
| 10 | 1.01 | 85.58 | |
| 19 | 0.84* | 71.44*1) | |
| 25 | 0.86 | 72.87 | |
| 35 m×35 m | 1 | 0.91 | 102.42 |
| 10 | 1.05 | 118.17 | |
| 19 | 0.87 | 98.64 | |
| 25 | 0.83 | 93.82 | |
| 40 m×40 m | 1 | 1.06 | 153.66 |
| 10 | 1.05 | 152.41 | |
| 19 | 0.85 | 123.70 | |
| 25 | 0.82 | 119.16 |
Table3 Variance ratio and W statistics at different spatial scales and enclosure years
| 空间尺度 | 围封年限/a | VR | W |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 m×30 m | 1 | 0.89 | 76.05 |
| 10 | 1.01 | 85.58 | |
| 19 | 0.84* | 71.44*1) | |
| 25 | 0.86 | 72.87 | |
| 35 m×35 m | 1 | 0.91 | 102.42 |
| 10 | 1.05 | 118.17 | |
| 19 | 0.87 | 98.64 | |
| 25 | 0.83 | 93.82 | |
| 40 m×40 m | 1 | 1.06 | 153.66 |
| 10 | 1.05 | 152.41 | |
| 19 | 0.85 | 123.70 | |
| 25 | 0.82 | 119.16 |
| 围封年限/a | 空间尺度 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 m×30 m | 35 m×35 m | 40 m×40 m | |||||||||
| 物种 | 1 | 2 | 物种 | 1 | 2 | 物种 | 1 | 2 | |||
| 1 | 2 | 0.02 | 2 | 0.10 | 2 | 1.71×10−3 | |||||
| 3 | 1.43 | 3.56 | 3 | 0.96 | 4.96*1) | 3 | 0.05 | 1.48 | |||
| 10 | 2 | 0.18 | 2 | 0.80 | 2 | 0.82 | |||||
| 3 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 3 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 3 | 2.36 | 0.88 | |||
| 19 | 2 | 1.06 | 2 | 1.08 | 2 | 2.33 | |||||
| 3 | 0.18 | 3.56 | 3 | 0.17 | 4.96* | 3 | 0.25 | 3.32 | |||
| 25 | 2 | 0.48 | 2 | 2.58 | 2 | 0.42 | |||||
| 3 | 1.16 | 8.70×10−5 | 3 | 2.58 | 1.08 | 3 | 3.93* | 0.01 | |||
Table4 χ 2 statistical matrix among populations at different spatial scales and enclosure years
| 围封年限/a | 空间尺度 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 m×30 m | 35 m×35 m | 40 m×40 m | |||||||||
| 物种 | 1 | 2 | 物种 | 1 | 2 | 物种 | 1 | 2 | |||
| 1 | 2 | 0.02 | 2 | 0.10 | 2 | 1.71×10−3 | |||||
| 3 | 1.43 | 3.56 | 3 | 0.96 | 4.96*1) | 3 | 0.05 | 1.48 | |||
| 10 | 2 | 0.18 | 2 | 0.80 | 2 | 0.82 | |||||
| 3 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 3 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 3 | 2.36 | 0.88 | |||
| 19 | 2 | 1.06 | 2 | 1.08 | 2 | 2.33 | |||||
| 3 | 0.18 | 3.56 | 3 | 0.17 | 4.96* | 3 | 0.25 | 3.32 | |||
| 25 | 2 | 0.48 | 2 | 2.58 | 2 | 0.42 | |||||
| 3 | 1.16 | 8.70×10−5 | 3 | 2.58 | 1.08 | 3 | 3.93* | 0.01 | |||
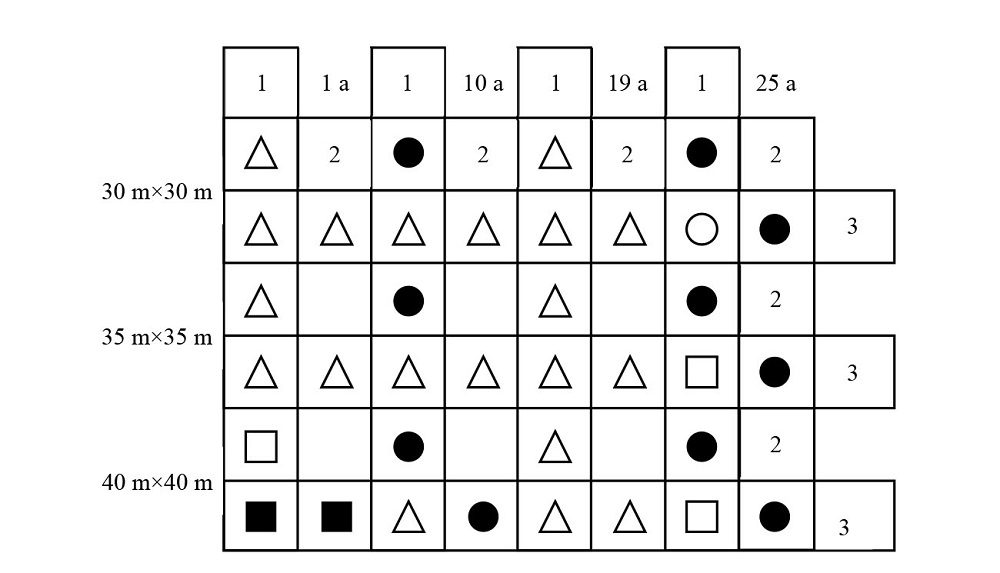
Figure 2 Association coefficient of 3 species at different spatial scales and enclosure years △?1≤AC≤?0.6, □?0.6≤AC<?0.3, ○?0.3≤AC<0, ●0<AC<0.3, ■0.3≤AC<0.6
| [1] | BROWN J H, DAVIS L, TURNER P, et al., 2019. The role of enclosure in intensifying interspecies competition in dryland ecosystems[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 162: 15-24. |
| [2] | CRDENAS R E, VALENCIA R, KRAFT N J B, et al., 2014. Plant traits predict inter-and intraspecifid variation in susceptibility to herbivory in a hyperdiverse Neotropical rain forest tree community[J]. Journal of Ecology, 102(4): 939-952. |
| [3] | DANG Z Q, GUO N, LI S S, et al., 2022. Effect of grazing exclusion on emission of greenhouse gases and soil organic carbon turnover in alpine shrub meadow[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 858(Part 1): 159758-159758. |
| [4] | FISHER R A, 1950. Statistical methods for research workers[M]. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd. |
| [5] | FORBES S A, 1907. On the local distribution of certain lllinois fishes: An essay in statistical ecology[J]. Bulletin of the Illinois State Nature History Survey, 7(8): 237-303. |
| [6] | GAO S, YANG Y, CHEN X, 2017. The effect of grazing exclusion on grassland communities in desert steppe: Species richness and interspecific interactions[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 125: 37-45. |
| [7] |
HOU D J, LIU J Y, LI N, et al., 2024. Grazing exclusion is more effective for vegetation restoration and nutrient transfer in the heavily degraded desert steppe[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 24(1): 408-408.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | HUBÁLEK Z, 1982. Coefficients of association and similarity, based on binary (presence-absence) data: An evaluation[J]. Biological Reviews, 57(4): 669-689. |
| [9] | JONES P L, ANDERSON M, CLARK R, et al., 2017. Long-term impacts of fencing on species competition and community dynamics in arid ecosystems[J]. Ecological Applications, 27(6): 1711-1720. |
| [10] | KLEIN J, MAUCHAMP A, LAVOREL S, 2020. Grazing management and biodiversity in semi-arid grasslands: responses of different taxonomic groups. Journal of Applied Ecology, 45(3): 1292-1301. |
| [11] | MARKOS M, ZELALEM M, 2023. Exclosure effects on soil physicochemical properties and woody species diversity in the south Rift valley basin of Ethiopia[J]. Environmental Research Communications, 5(11): 115001. |
| [12] | SCHLUTER D, 1984. A variance test for detecting species associations,with some example applications[J]. Ecology, 65(3): 998-1005. |
| [13] | SCHULZE, E D, LANGE, O L, MOONEY, H A, 1996. Dryland ecosystems:their structure, function,and management[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. |
| [14] | SMITH A B, JOHNSON T, WILLIAMS K, et al., 2018. Effects of spatial scale on species diversity and competition in grassland ecosystems[J]. Journal of Ecology, 106(3): 753-762. |
| [15] | 白如意, 伊布乐, 2022. 正镶白旗草原生态环境治理问题探讨[J]. 南方农业, 16(10): 197-200. |
| BAI R Y, YI B L, 2022. Discussion on ecological environment management of grassland in Zhengxiangbai Banner[J]. South China Agriculture, 16(10): 197-200. | |
| [16] | 何志斌, 赵文智, 常学向, 等, 2004. 荒漠植被植物种多样性对空间尺度的依赖[J]. 生态学报, 24(6): 1146-1149. |
| HE Z B, ZHAO W Z, CHANG X X, et al., 2004. Scale dependence in desert plant biodiversity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(6): 1146-1149. | |
| [17] | 贾丽欣, 2020. 放牧对短花针茅分蘖特征的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. |
| JIA L X, 2020. Effects of grazing on tiller characteristics of Stipa breviflora[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. | |
| [18] | 李景平, 刘桂香, 马治华, 等, 2006. 荒漠草原景观格局分析——以苏尼特右旗荒漠草原为例[J]. 中国草地学报, 28(5): 81-85. |
| LI J P, LIU G X, MA Z H, et al., 2006. Analysis on landscape pattern of desert-steppe: A case study on Suniteyou district[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 28(5): 81-85. | |
| [19] | 李丘霖, 宗秀虹, 邓洪平, 等, 2017. 赤水桫椤群落乔木层优势物种生态位与种间联结性研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 37(7): 1422-1428. |
| LI Q L, ZONG X H, DENG H P, et al., 2017. Niche and interspecific association of dominant species in tree layer of Chishui Alsophila spinulosa community[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 37(7): 1422-1428. | |
| [20] | 廖晗茹, INDREE T, 郭通, 等, 2020. 围封对蒙古荒漠草原和高山草原植物群落组成及稳定性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 56(3): 471-478. |
| LIAO H R, INDREE T, GUO T, et al., 2020. Effects of grazing exclusion on the vegetation community composition and the community stability of dry steppe and mountain steppe ecosystems in Mongolia[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 56(3): 471-478. | |
| [21] | 刘欢, 2023. 内蒙古草原围封效应研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. |
| LIU H, 2023. Research on the effect of grassland enclosure in Inner Mongolia[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. | |
| [22] | 南万璐, 谢应忠, 彭文栋, 等, 2024. 补播与围封对不同退化程度荒漠草地植被的恢复效果[J]. 草业科学, 41(5): 1068-1077. |
| NAN W L, XIE Y Z, PENG W D, et al., 2024. Restoration effects of reseeding and enclosure on the vegetation of different degraded desert steppes[J]. Pratacultural Science, 41(5): 1068-1077. | |
| [23] | 乔荣, 崔向新, 吕新丰, 等, 2014. 围封禁牧对退化草原土壤性状的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 34(5): 162-165. |
| QIAO R, CUI X X, LÜ X F, et al., 2014. Effect of enclosure and grazing prohibition on soil properties of degraded grassland[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(5): 162-165. | |
| [24] | 苏艳龙, 2023. 内蒙古荒漠草原不同围封年限围栏内外植被特征及土壤理化性质差异[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学. |
| SU Y L, 2023. Differences and effects of vegetation and soil physical chemical properties inside and outside for different years of enclosure in Inner Mongolia desert grassland[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University. | |
| [25] | 孙杰杰, 江波, 吴初平, 等, 2019. 浙江省檫木林生境与生态位研究[J]. 生态学报, 39(3): 884-894. |
| SUN J J, JIANG B, WU C P, et al., 2019. Study on the habitat and niche of Sassafras tzumu (Hemsl.) Hemsl. in Zhejiang Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(3): 884-894. | |
| [26] | 王伯荪, 彭少麟, 1985. 南亚热带常绿阔叶林种间联结测定技术研究——Ⅰ. 种间联结测式的探讨与修正[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学丛刊, 9(4): 274-285. |
| WANG B S, PENG S L, 1985. Studies on the measuring techniques of interspecific association of lower-subtropical evergreen-broadleaved forests: Ⅰ. The exploration and the revision on the measuring formulas of interspecific association[J]. Acta Phytoecologica et Geobotanica Sinica, 9(4): 274-285. | |
| [27] | 王淼, 代力民, 姬兰柱, 等, 2001. 长白山阔叶红松林主要树种对干旱胁迫的生态反应及生物量分配的初步研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 12(4): 496-500. |
| WANG M, DAI L M, JI L Z, et al., 2001. A preliminary study on the ecological response and biomass allocation of main tree species to drought stress in broad-leaved red pine forest in Changbai Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 12(4): 496-500. | |
| [28] |
王琪, 张峰, 赵萌莉, 等, 2021. 不同放牧强度对短花针茅荒漠草原植物群落组成及种间关系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(10): 1961-1967.
DOI |
| WANG Q, ZHANG F, ZHAO M L, et al., 2021. Effects of grazing intensity community composition and inter-species relationships of Stipa breviflora desert steppe, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(10): 1961-1967. | |
| [29] | 王琪, 郑佳华, 张峰, 等, 2022. 放牧强度对短花针茅荒漠草原植物种群生态位的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 44(10): 1-9. |
| WANG Q, ZHENG J H, ZHANG F, et al., 2022. Effects of grazing intensity on ecological niche of plant population in Stipa breviflora desert steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 44(10): 1-9. | |
| [30] | 王玉琴, 张千山, 王宏生, 等, 2024. 围封对黄帚橐吾型退化草地植被群落特征的影响[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 54(1): 1-7, 23. |
| WANG Y Q, ZHANG Q S, WANG H S, et al., 2024. Effects of enclosure on vegetation community characteristics of ligularia virgaurea-dominatedegraded grassland[J]. Chinese Qinghai Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 54(1): 1-7, 23. | |
| [31] | 王玉芝, 吕世杰, 杨溢文, 等, 2023. 围封对荒漠草原植物功能群的影响[J]. 内蒙古林业科技, 49(4): 1-5. |
| WANG Y Z, LÜ S J, YANG Y W, et al., 2023. Effects of enclosure on plant functional groups in desert steppe[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Forestry Science and Technology, 49(4): 1-5. | |
| [32] |
王梓晗, 吕世杰, 王忠武, 等, 2024. 放牧强度对优势种群重要值和物种多样性及其二者典型关系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(6): 869-876.
DOI |
| WANG Z H, LÜ S J, WANG Z W, et al., 2024. Effects of grazing intensity on dominant population and species diversity and their typical relationships[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(6): 869-876. | |
| [33] | 许宏斌, 苏艳龙, 张雷, 等, 2024. 围封10年对荒漠草原群落物种多样性与优势种空间分布格局的影响[J]. 生态学报, 44(10): 4334-4341. |
| XU H B, SU Y L, ZHANG L, et al., 2024. Effects of ten years of enclosure on species diversity and spatial distribution pattern of dominant species in desert steppe communities[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44(10): 4334-4341. | |
| [34] | 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 等, 2016. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述[J]. 生态学报, 36(24): 8224-8233. |
| XU M H, LIU M, ZHAI D T, et al., 2016. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(24): 8224-8233. | |
| [35] | 杨金涛, 张晓晗, 尹正辉, 等, 2024. 禁牧对西藏亏祖山温性草原主要植物生态位及种间联结的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 44(2): 330-337. |
| YANG J T, ZHANG X H, YIN Z H, et al., 2024. The influence of enclosure on the ecological niche and interspecific associations of dominant plant species in temperate grasslands of the Kuizu Mountains in Tibet[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 44(2): 330-337. | |
| [36] | 叶权平, 张文辉, 于世川, 等, 2018. 桥山林区麻栎群落主要乔木种群的种间联结性[J]. 生态学报, 38(9): 3165-3174. |
| YE Q P, ZHANG W H, YU S C, et al., 2018. Interspecific association of the main tree populations of the Quercus acutissima community in the Qiaoshan forest area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(9): 3165-3174. | |
| [37] | 余钱雯, 王玉琴, 王宏生, 等, 2023. 放牧和围封下黄帚橐吾型退化草地植物化学计量学及土壤养分特征的变化[J]. 中国草地学报, 45(6): 73-82. |
| YU Q W, WANG Y Q, WANG H S, et al., 2023. Variations in plant stoichiometry and soil nutrient characteristics in degraded grassland dominated by Ligularia virgaurea under grazing and enclosure[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland Science, 45(6): 73-82. | |
| [38] | 运向军, 2010. 短花针茅草原对禁牧休牧的响应及休牧期家畜舍饲研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. |
| YUN X J, 2010. Response of Stipa breviflora grassland to banning and defered grazing and livestock penfeeding system[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. | |
| [39] | 张盟, 郑俊鸣, 万佳艺, 等, 2022. 福建省东门屿优势木本植物的生态位与种间联结[J]. 森林与环境学报, 42(1): 11-19. |
| ZHANG M, ZHENG J M, WAN J Y, et al., 2022. Niche and interspecific associations of dominant woody plants in Dongmen Island, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 42(1): 11-19. | |
| [40] | 张金屯, 焦蓉, 2003. 关帝山神尾沟森林群落木本植物种间联结性与相关性研究[J]. 植物研究, 23(4): 458-463. |
| ZHANG J T, JIAO R, 2003. Interspecific association between woody plants in Shenweigou of Guandi Mountains, Shanxi Province[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 23(4): 458-463. | |
| [41] | 赵金花, 2010. 3种野生葱属植物的生态适应性及繁衍更新特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. |
| ZHAO J H, 2010. A study on ecological adaptability and reproduction feature of three wild allium plants[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. |
| [1] | DU Zhongyu, XING Wenli, DANG Ning, ZHAO Weibin, TAN Xumai, XIAO Jiang, GAI Xu, CHEN Guangcai. Niche and Interspecific Association Characteristics of Dominant Plants in Antimony Mining Damaged Ecological Site in Xihe, Gansu [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(7): 1036-1047. |
| [2] | WANG Zihan, LÜ Shijie, WANG Zhongwu, LIU Hongmei. Effects of Grazing Intensity on Dominant Population and Species Diversity and Their Typical Relationships [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(6): 869-876. |
| [3] | HU Fang, LIU Jutao, WEN Chunyun, HAN Liu, WEN Hui. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Evaluation of Aquatic Ecological Conditions in Fu River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [4] | ZHAO Yanchu, WANG Fei, WU Dan, HUANG Xin, CHEN Jialin, ZHOU Linpu, KONG Fanqing. Health Assessment of Haihe River Basin Based on Benthic Index of Biotic Integrity [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1785-1793. |
| [5] | WANG Ru, NONG Shouqian, PENG Wencheng, WU Biao, YANG Jia, LIAO Liguo. Tree Species Composition and Interspecific Associations of Rare and Endangered Plant Cephalotaxus hainanensis Community [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1741-1749. |
| [6] | JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Associations and Environmental Interpretation of the Dominant Species of the Communities Invaded by Ageratina adenophora in Ailao Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382. |
| [7] | LONG Jing, HUANG Yao, LIU Zhanfeng, JIAN Shuguang, WEI Liping, WANG Jun. Leaf Traits and Nutrient Resorption of Two Woody Species on A Tropical Coral Island [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [8] | XUE Wenkai, ZHU Pan, DE Ji, GUO Xiaofang. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Dominant Species of Cultivable Filamentous Fungi in Nam Co Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [9] | CHENG Junwei, CAI Shenwen, HUANG Mingqin. Bioconcentration of Heavy Metals in Dominant Plants of Xiangjiang Manganese Mining Area in Guizhou Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1742-1750. |
| [10] | GUO Jiaqi, CHEN Junchen, HUANG Xun, HUANG Jiale, ZHAO Liya, LI Zhaohua. Niche Characteristics and Interspecific Associations of the Dominant Species of the Communities Invaded by Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1607-1616. |
| [11] | YAN Dongfeng, ZHANG Yanyan, LV Kangting, ZHOU Mengli, WANG Ting, ZHAO Ning. Niche Characteristics of Dominant Tree Species in Natural Forests at Different Altitudes in the South of Taihang Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1571-1580. |
| [12] | NIU Xuekui, WU Xueyong, WANG Wei, AI Zhimin, WANG Shuting, HOU Juan, ZHOU Tao. Study on Enrichment Characteristics of Heavy Metals from Dominant Plants Around the Waste Slag Yard of Lead Smelting in A Typical Blast Furnace [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1293-1298. |
| [13] | JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Association and Environmental Interpretation of Dominant Herbaceous Species in Pinus yunnanensis Forest in the Western Suburbs of Chuxiong City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2109-2120. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
