Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 1110-1117.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIA Enlong1( ), NONG Junqing1, WEI Songpo1,2, LIU Xizhen1, LIU Guanglu1,2,*(
), NONG Junqing1, WEI Songpo1,2, LIU Xizhen1, LIU Guanglu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-09-17
Online:2022-06-18
Published:2022-07-29
Contact:
LIU Guanglu
夏恩龙1( ), 农珺清1, 魏松坡1,2, 刘希珍1, 刘广路1,2,*(
), 农珺清1, 魏松坡1,2, 刘希珍1, 刘广路1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
刘广路
作者简介:夏恩龙(1981年生),男(满族),高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为竹林可持续经营和竹林认证研究。E-mail: xiaenlong@icbr.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
XIA Enlong, NONG Junqing, WEI Songpo, LIU Xizhen, LIU Guanglu. Changes in Soil Nutrient Characteristics in Moso Bamboo Forest Expanding into Broadleaved Forest[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117.
夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.005
| 样带编号 Transect No. | 海拔 Elevation/m | 坡向 Slope aspect | 坡度 Slope degree/(°) | 密度 Density/(ind∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/cm | 郁闭度 Canopy density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样带1 Transect No.1 | 374 | NE | 25 | 2142 | 9.18 | 0.67 |
| 样带2 Transect No.2 | 387 | NW | 15 | 2365 | 9.95 | 0.70 |
| 样带3 Transect No.3 | 402 | SE | 15 | 2597 | 10.71 | 0.72 |
Table 1 The basic condition of research belt transect
| 样带编号 Transect No. | 海拔 Elevation/m | 坡向 Slope aspect | 坡度 Slope degree/(°) | 密度 Density/(ind∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Mean DBH/cm | 郁闭度 Canopy density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样带1 Transect No.1 | 374 | NE | 25 | 2142 | 9.18 | 0.67 |
| 样带2 Transect No.2 | 387 | NW | 15 | 2365 | 9.95 | 0.70 |
| 样带3 Transect No.3 | 402 | SE | 15 | 2597 | 10.71 | 0.72 |
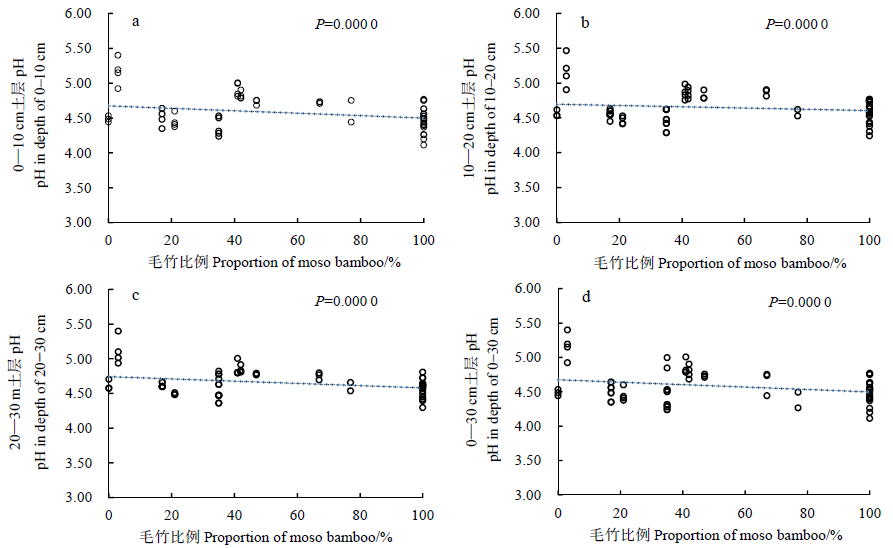
Figure 1 Variations of soil pH with moso bamboo expansion The number of samples in Figure 1a-c is 66 (n=66). The number of samples in Fig. 1d is 198 (n=198). The same below
| 指标 Index | pH | w(C) | w(N) | w(P) | w(K) | w(HN) | w(AP) | w(AK) | w(C):w(N) | w(C):w(P) | w(N):w(P) | w(HN):w(AP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| w(C) | -0.311** | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| w(N) | -0.249** | 0.957** | 1.000 | |||||||||
| w(P) | 0.197** | 0.482** | 0.468** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| w(K) | 0.363** | -0.206** | -0.160* | -0.094 | 1.000 | |||||||
| w(HN) | -0.317** | 0.931** | 0.916** | 0.468** | -0.286** | 1.000 | ||||||
| w(AP) | 0.154* | 0.165* | 0.183** | 0.548** | 0.010 | 0.162* | 1.000 | |||||
| w(AK) | -0.321** | 0.717** | 0.708** | 0.429** | -0.372** | 0.766** | 0.310** | 1.000 | ||||
| w(C):w(N) | -0.324** | 0.597** | 0.371** | 0.261** | -0.305** | 0.490** | 0.029 | 0.411** | 1.000 | |||
| w(C):w(P) | -0.404** | 0.940** | 0.902** | 0.186** | -0.215** | 0.874** | 0.020 | 0.648** | 0.590** | 1.000 | ||
| w(N):w(P) | -0.340** | 0.852** | 0.921** | 0.119 | -0.153* | 0.813** | 0.016 | 0.609** | 0.297** | 0.930** | 1.000 | |
| w(HN):w(AP) | -0.226** | -0.231** | -0.270** | -0.177* | -0.532** | -0.164* | -0.307** | -0.104 | 0.045 | -0.209** | -0.246** | 1.000 |
Table 2 Correlations between soil nutrients and ecological stoichiometric ratios
| 指标 Index | pH | w(C) | w(N) | w(P) | w(K) | w(HN) | w(AP) | w(AK) | w(C):w(N) | w(C):w(P) | w(N):w(P) | w(HN):w(AP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| w(C) | -0.311** | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| w(N) | -0.249** | 0.957** | 1.000 | |||||||||
| w(P) | 0.197** | 0.482** | 0.468** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| w(K) | 0.363** | -0.206** | -0.160* | -0.094 | 1.000 | |||||||
| w(HN) | -0.317** | 0.931** | 0.916** | 0.468** | -0.286** | 1.000 | ||||||
| w(AP) | 0.154* | 0.165* | 0.183** | 0.548** | 0.010 | 0.162* | 1.000 | |||||
| w(AK) | -0.321** | 0.717** | 0.708** | 0.429** | -0.372** | 0.766** | 0.310** | 1.000 | ||||
| w(C):w(N) | -0.324** | 0.597** | 0.371** | 0.261** | -0.305** | 0.490** | 0.029 | 0.411** | 1.000 | |||
| w(C):w(P) | -0.404** | 0.940** | 0.902** | 0.186** | -0.215** | 0.874** | 0.020 | 0.648** | 0.590** | 1.000 | ||
| w(N):w(P) | -0.340** | 0.852** | 0.921** | 0.119 | -0.153* | 0.813** | 0.016 | 0.609** | 0.297** | 0.930** | 1.000 | |
| w(HN):w(AP) | -0.226** | -0.231** | -0.270** | -0.177* | -0.532** | -0.164* | -0.307** | -0.104 | 0.045 | -0.209** | -0.246** | 1.000 |
| [1] | CHENG W, PARTON W J, GONZALEZ-MELER M A, et al., 2014. Synthesis and modeling perspectives of rhizosphere priming[J]. The New phytologist, 201(1): 31-44. |
| [2] |
HUANG P, ZHANG J B, XIN X L, et al., 2015. Proton accumulation accelerated by heavy chemical nitrogen fertilization and its long term impact on acidifying rate in a typical arable soil in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14(1): 148-157.
DOI |
| [3] | KUZYAKOV Y, 2002. Review: Factors affecting rhizosphere priming effects[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 22(4): 66-70. |
| [4] | LI L, XIA Z, YE R, et al., 2018. Soil microbial biomass size and soil carbon influence the priming effect from carbon inputs depending on nitrogen availability[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 119: 41-49. |
| [5] | MUELLER K E, EISSENSTAT D M, HOBBIE S E, et al., 2012. Tree species effects on coupled cycles of carbon, nitrogen, and acidity in mineral soils at a common garden experiment[J]. Biogeochemistry, 111(1-3): 601-614. |
| [6] | REINDS G J, POSCH M, LEEMANS R, 2009. Modelling recovery from soil acidification in European forests under climate change[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 407(21): 5663-5673. |
| [7] | SARDANS J, RIVAS-UBACH A, PEÑUELAS J, 2012. The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives[J]. Perspectives in Plant Ecology Evolution & Systematics, 14(1): 33-47. |
| [8] | SHI L, FAN S H, JIANG Z H, et al., 2015. Mixed leaf litter decomposition and N, P release with a focus on Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz. forest in subtropical southeastern China[J]. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae, 84(2): 207-214. |
| [9] | STEINBEISS S, BEßLER H, ENGELS C, et al., 2008. Plant diversity positively affects short-term soil carbon storage in experimental grasslands[J]. Global Change Biology, 14(12): 2937-2949. |
| [10] | TOSI M, CORREA O S, SORIA M A, et al., 2016. Land-use change affects the functionality of soil microbial communities: A chronosequence approach in the Argentinian Yungas[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 108: 118-127. |
| [11] | WANG Y X, BAI S B, BINKLEY D, et al., 2016. The independence of clonal shoot's growth from light availability supports moso bamboo invasion of closed-canopy forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 368: 105-110. |
| [12] |
ZHANG C F, JAMIESON R C, MENG F R, et al., 2016. Projecting in-stream dissolved organic carbon and total mercury concentrations in small watersheds following forest growth and clearcutting[J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution, DOI: 10.1007/s11270-016-3017-6.
DOI URL |
| [13] | ZHANG LX, BAI Y F, HAN X G, 2003. Application of N:P stoichiometry to ecology studies[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 45(9): 1009-1018. |
| [14] | ZHAO F Z, KANG D, HAN X H, et al., 2015. Soil stoichiometry and carbon storage in long-term afforestation soil affected by understory vegetation diversity[J]. Ecological Engineering, 74: 415-422. |
| [15] | 安树青, 洪必恭, 李朝阳, 等, 1997. 紫金山次生林林窗植被和环境的研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 8(3): 245-249. |
| AN S Q, HONG B G, LI Z Y, et al., 1997. Environmental and vegetation studies of the gaps of secondary forests on Zijin Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 8(3): 245-249. | |
| [16] |
白尚斌, 周国模, 王懿祥, 等, 2013. 天目山保护区森林群落植物多样性对毛竹入侵的响应及动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 21(3): 288-295.
DOI |
| BAI S B, ZHOU G M, WANG Y X, et al., 2013. Plant species diversity and dynamics in forests invaded by Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) in Tianmu Mountain Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiversity Science, 21(3): 288-295. | |
| [17] | 蔡泽江, 孙楠, 王伯仁, 等, 2011. 长期施肥对红壤pH、作物产量及氮、磷、钾养分吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 17(1): 71-78. |
| CAI Z J, SUN N, WANG B R, et al., 2011. Effects of long-term fertilization on pH of red soil, crop yield sand up takes of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 17(1): 71-78. | |
| [18] |
杜满义, 范少辉, 刘广路, 等, 2016. 中国毛竹林碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 40(8): 760-774.
DOI |
| DU M Y, FAN S H, LIU G L, et al., 2016. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in Phyllostachys edulis forests of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40(8): 760-774. | |
| [19] | 范少辉, 申景昕, 刘广路, 等, 2019. 毛竹向杉木林扩展对土壤养分含量及计量比的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 39(8): 1455-1462. |
| FAN S H, SHEN J X, LIU G L, et al., 2019. Soil Nutrients and Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics after Phyllostachys edulis Expansion to Cunninghamia lanceolata Forest[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 39(8): 1455-1462. | |
| [20] | 国家林业局, 1999. 森林土壤分析方法: LY/T 1210-1275-1999[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-108. |
| State Forestry Bureau, 1999. Forest Soil Analysis Method: LY/T 1210-1275-1999[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press: 1-108. | |
| [21] | 黄彪, 刘广路, 范少辉, 等, 2021. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程细根可塑性变化[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 41(10):11-19. |
| HUANG B, LIU G L, FAN S H, et al., 2021. The plasticity of fine root Phyllostachys edulis expanding into adjacent broadleaved forest[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 41(10): 11-19. | |
| [22] | 刘广路, 范少辉, 漆良华, 等, 2010. 闽西北不同类型毛竹林养分分布及生物循环特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(11): 2155-2161. |
| LIU G L, FAN S H, QI L H, et al., 2010. Nutrient distribution and biological cycle characteristics in different types of Phyllostachys pubescens forest in Northwest Fujian[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(11): 2155-2161. | |
| [23] | 刘希珍, 范少辉, 刘广路, 等, 2016. 毛竹林扩展过程中主要群落结构指标的变化特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(12): 3165-3171. |
| LIU X Z, FAN S H, LIU G L, et al., 2016. Changing characteristics of main structural indexes of community during the expansion of moso bamboo forests[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(12): 3165-3171. | |
| [24] | 刘希珍, 封焕英, 蔡春菊, 等, 2015. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中的叶功能性状研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 37(8): 8-17. |
| LIU X Z, FENG H Y, CAI C J, et al., 2015. Response of leaf functional traits of moso bamboo during the invading process into the broad- leaved forest[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 37(8): 8-17. | |
| [25] | 申景昕, 刘广路, 范少辉, 等, 2020. 毛竹向撂荒地扩展过程中的土壤养分特征[J]. 林业科学, 56(10): 26-33. |
| SHEN J X, LIU G L, FAN S H, et al., 2020. Characterization of soil nutrients of Phyllostachys edulis during the process of its expansion into abandoned land[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 56(10): 26-33. | |
| [26] | 王建林, 钟志明, 王忠红, 等, 2014. 青藏高原高寒草原生态系统土壤碳磷比的分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 23(2): 9-19. |
| WANG J L, ZHONG Z M, WANG Z H, et al., 2014. Soil C/P distribution characteristics of alpine steppe ecosystems in the Qinhai- Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 23(2): 9-19. | |
| [27] | 杨瑞吉, 杨祁峰, 牛俊义, 等, 2004. 表征土壤肥力主要指标的研究进展[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 39(1): 86-91. |
| YANG R J, YANG Q F, NIU J Y, et al., 2004. Research progress on soil fertility major indexes[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 39(1): 86-91. | |
| [28] | 杨歆歆, 赵庚星, 李涛, 等, 2016. 山东省土壤酸化特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 32(增刊): 155-160. |
| YANG X X, ZHAO G X, LI T, et al., 2016. Characteristics of soil acidification and its influencing factors in Shandong province[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 32(Supp. 2): 155-160. | |
| [29] | 于文睿南, 潘畅, 郭佳欢, 等, 2021. 杉木人工林表土有机质含量及其对土壤养分的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 29(11): 1931-1939. |
| YUWEN R N, PAN C, GUO J H, et al., 2021. Topsoil organic matter and its effect on the soil nutrients contents of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29(11): 1931-1939. | |
| [30] | 张静静, 刘尊驰, 鄢创, 等, 2021. 土壤pH值变化对3种草原类型土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 30(2): 69-81. |
| ZHANG J J, LIU Z C, YAN C, et al., 2021. Effects of soil pH on soil carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus ecological stoichiometry in three types of steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 30(2): 69-81. | |
| [31] | 朱齐超, 2017. 区域尺度中国土壤酸化定量研究及模型分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学. |
| ZHU Q C, 2017. Quantification and Modelling of Soil Acidification at Regional Scale of China[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University. |
| [1] | DONG Zhijin, ZHANG Chengchun, ZHAN Xiuli, ZHANG Weifu. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients of Biological Soil Crusts and Their Underlying Soil of Sandy Land in the East of Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | ZHANG Beier, WU Jianqiang, WANG Min, XIONG Lijun, TAN Juan, SHEN Cheng, HUANG Botao, HUANG Shenfa. Evaluation of Soil Health in Different Arable Land Ecological Conservation Projects [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [4] | LONG Jing, HUANG Yao, LIU Zhanfeng, JIAN Shuguang, WEI Liping, WANG Jun. Leaf Traits and Nutrient Resorption of Two Woody Species on A Tropical Coral Island [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [5] | YU Fei, YE Caihong, XU Tiaozi, ZHANG Zhongrui, ZHU Hangyong, ZHANG Geng, HUA Lei, DENG Jianfeng, DING Xiaogang. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Woodland Soil of Granite Area in Shaoguan City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [6] | SHENG Jifeng, LI Yao, YU MeiJia, HAN Yanying, YE Yanhui. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus An Addition on Soil Nutrients and Activity of Related Enzymes in Alpine Grassland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiaoli, WANG Guoli, CHANG Fangdi, ZHANG Hongyuan, PANG Huancheng, ZHANG Jianli, WANG Jing, JI Hongjie, LI Yuyi. Effects of Microbial Agents on Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Flora of Rhizosphere Saline-alkali Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [8] | SONG Xianchong, CAI Xuemei, CHEN Tao, PAN Wen, SHI Yuanyuan, TANG Jian, CAO Jizhao. Variation Characteristics of Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil Nutrient in Successive Eucalyptus Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| [9] | LIAO Yingchun, DUAN Honglang, SHI Xingxing, MENG Qingyin, LIU Wenfei, SHEN Fangfang, FAN Houbao, ZHU Tao. The Relationship between the Stand Growth and Root Biomass of Cunninghamia lanceolate Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1121-1128. |
| [10] | XU Wenyin, ZHANG Yupeng, DUAN Chengwei, CHAI Yu, SONG Xian, LI Xilai. Spatial Variability of Soil Nutrients in Degraded Alpine Meadows in Different Regions of the Yellow River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 1968-1975. |
| [11] | SUI Yanghui, GAO Jiping, WANG Yanbo, XIAO Wanxin, LIU Jing, SHI Lei, ZHAO Haiyan, ZHANG Yang. Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Effects on Soil Nutrient and Root Distribution in Dryland Maize [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2026-2032. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zixuan, NIU Beibei, LI Xinju. Effect of Different Improvement Modes on Physical and Chemical Characters of the Coastal Saline Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2020, 29(2): 275-284. |
| [13] | ZHANG Shasha, LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu. Ecological Stoichiometry of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantation Across An Elevation Gradient [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2020, 29(1): 97-104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
