Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1757-1768.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.023
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LU Xuping( ), LI Fanglan, SHI Yafei, ZHANG Juanwei, YANG Wenwei, LUO Chengke*(
), LI Fanglan, SHI Yafei, ZHANG Juanwei, YANG Wenwei, LUO Chengke*( ), TIAN Lei, LI Peifu
), TIAN Lei, LI Peifu
Received:2021-05-25
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
Contact:
LUO Chengke
路旭平( ), 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科*(
), 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科*( ), 田蕾, 李培富
), 田蕾, 李培富
通讯作者:
罗成科
作者简介:路旭平(1995年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事水稻抗逆生理生态研究。E-mail: 577861974@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LU Xuping, LI Fanglan, SHI Yafei, ZHANG Juanwei, YANG Wenwei, LUO Chengke, TIAN Lei, LI Peifu. Physiological Differences of Seedlings of Different Rice Varieties in Response to Alkali Stress and Construction of Stress Levels[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1757-1768.
路旭平, 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科, 田蕾, 李培富. 不同水稻品种幼苗响应碱胁迫的生理差异及胁迫等级构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1757-1768.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.023
| 处理 Treatments | c(NaHCO3+Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | pH | n(NaHCO3)꞉ n(Na2CO3) | c(NaHCO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | c(Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 5.5±0.05 | ‒ | 0 | 0 |
| 10A | 10 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 9 | 1 |
| 10B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 5 | 5 | |
| 10C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 1 | 9 | |
| 20A | 20 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 18 | 2 |
| 20B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 10 | 10 | |
| 20C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 2 | 18 | |
| 30A | 30 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 27 | 3 |
| 30B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 15 | 15 | |
| 30C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 3 | 27 |
Table 1 Alkali composition and pH of each treatment
| 处理 Treatments | c(NaHCO3+Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | pH | n(NaHCO3)꞉ n(Na2CO3) | c(NaHCO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) | c(Na2CO3)/ (mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 5.5±0.05 | ‒ | 0 | 0 |
| 10A | 10 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 9 | 1 |
| 10B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 5 | 5 | |
| 10C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 1 | 9 | |
| 20A | 20 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 18 | 2 |
| 20B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 10 | 10 | |
| 20C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 2 | 18 | |
| 30A | 30 | 8.65±0.05 | 9꞉1 | 27 | 3 |
| 30B | 9.55±0.05 | 5꞉5 | 15 | 15 | |
| 30C | 10.50±0.05 | 1꞉9 | 3 | 27 |
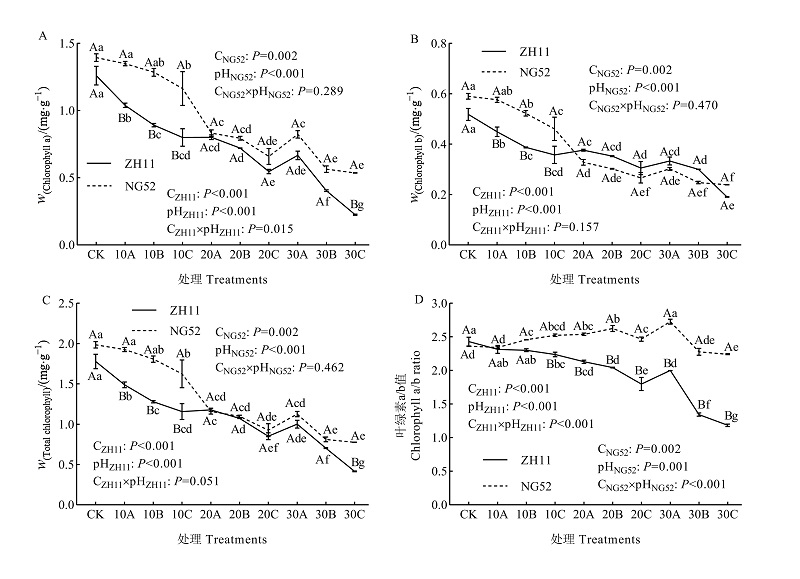
Fig. 1 Effects of alkali stress on chlorophyll contents of rice leaves n=3; 10, 20 and 30 respectively indicate alkali application levels of 10 mmol∙L-1, 20 mmol∙L-1 and 30 mmol∙L-1; A, B and C respectively indicate pH levels of 8.65, 9.55 and 10.50. Different small letters indicate significant difference of the same rice varieties in the different treatment at 0.05 level; Different capital letters indicate significant difference of different rice varieties in the same l treatment at 0.05 level. The same as below
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11特征向量 Eigenvector | NG52特征向量 Eigenvector | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分 PC1 | 第1主成分 PC1 | 第2主成分 PC2 | ||
| Chl a | -0.996 | -0.967 | -0.109 | |
| Chl b | -0.973 | -0.951 | -0.244 | |
| Chl | -0.994 | -0.965 | -0.150 | |
| Chl a/b | -0.937 | -0.099 | 0.968 | |
| RWC | -0.983 | -0.848 | 0.415 | |
| SOD | 0.834 | 0.966 | 0.120 | |
| POD | 0.878 | 0.912 | -0.092 | |
| CAT | 0.979 | 0.948 | 0.200 | |
| MDA | 0.957 | 0.980 | -0.030 | |
| LOX | 0.942 | 0.975 | 0.124 | |
| H2O2 | 0.983 | 0.991 | -0.091 | |
| O2·ˉ | 0.994 | 0.989 | -0.093 | |
| Pro | 0.984 | 0.995 | 0.065 | |
| SS | 0.981 | 0.995 | -0.037 | |
| SP | 0.980 | 0.989 | -0.097 | |
| ASA | 0.986 | 0.990 | -0.068 | |
| GSH | 0.985 | 0.965 | -0.031 | |
| 特征根 Eigenvalue | 15.787 | 14.901 | 1.321 | |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 7.768 | |
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 95.422 | |
Table 2 Principal component analysis of physiological parameter in rice leaves
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11特征向量 Eigenvector | NG52特征向量 Eigenvector | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分 PC1 | 第1主成分 PC1 | 第2主成分 PC2 | ||
| Chl a | -0.996 | -0.967 | -0.109 | |
| Chl b | -0.973 | -0.951 | -0.244 | |
| Chl | -0.994 | -0.965 | -0.150 | |
| Chl a/b | -0.937 | -0.099 | 0.968 | |
| RWC | -0.983 | -0.848 | 0.415 | |
| SOD | 0.834 | 0.966 | 0.120 | |
| POD | 0.878 | 0.912 | -0.092 | |
| CAT | 0.979 | 0.948 | 0.200 | |
| MDA | 0.957 | 0.980 | -0.030 | |
| LOX | 0.942 | 0.975 | 0.124 | |
| H2O2 | 0.983 | 0.991 | -0.091 | |
| O2·ˉ | 0.994 | 0.989 | -0.093 | |
| Pro | 0.984 | 0.995 | 0.065 | |
| SS | 0.981 | 0.995 | -0.037 | |
| SP | 0.980 | 0.989 | -0.097 | |
| ASA | 0.986 | 0.990 | -0.068 | |
| GSH | 0.985 | 0.965 | -0.031 | |
| 特征根 Eigenvalue | 15.787 | 14.901 | 1.321 | |
| 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 7.768 | |
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% | 92.867 | 87.653 | 95.422 | |
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11权重系数 ZH11 Weight coefficient/% | NG52权重系数 NG52 Weight coefficient/% |
|---|---|---|
| Chl a | 16.07 | 26.02 |
| SOD | 9.13 | 11.11 |
| MDA | 13.87 | 14.24 |
| H2O2 | 17.10 | 13.43 |
| SS | 23.26 | 15.43 |
| ASA | 20.58 | 19.77 |
Table 3 Weight coefficient of Chla, SOD, MDA, H2O2, SS and ASA
| 参数 Parameter | ZH11权重系数 ZH11 Weight coefficient/% | NG52权重系数 NG52 Weight coefficient/% |
|---|---|---|
| Chl a | 16.07 | 26.02 |
| SOD | 9.13 | 11.11 |
| MDA | 13.87 | 14.24 |
| H2O2 | 17.10 | 13.43 |
| SS | 23.26 | 15.43 |
| ASA | 20.58 | 19.77 |
| 处理 Treatments | ZH11 | NG52 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | |
| CK | 0 | 正常 Normal | 0 | 正常 Normal |
| 10A | 1.949 | 轻度 Mild | 1.402 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10B | 3.029 | 轻度 Mild | 2.429 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10C | 4.343 | 中度 Moderate | 3.465 | 轻度 Mild |
| 20A | 4.534 | 中度 Moderate | 4.315 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20B | 5.928 | 中度 Moderate | 5.317 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20C | 8.069 | 重度 Severe | 6.824 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30A | 6.733 | 中度 Moderate | 5.936 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30B | 9.411 | 重度 Severe | 8.125 | 重度 Severe |
| 30C | 11.276 | 特重度 Special severe | 9.547 | 重度 Severe |
Table 4 Changes of alkali stress index with different treatments
| 处理 Treatments | ZH11 | NG52 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | Z值 Z value | 等级 Degree | |
| CK | 0 | 正常 Normal | 0 | 正常 Normal |
| 10A | 1.949 | 轻度 Mild | 1.402 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10B | 3.029 | 轻度 Mild | 2.429 | 轻度 Mild |
| 10C | 4.343 | 中度 Moderate | 3.465 | 轻度 Mild |
| 20A | 4.534 | 中度 Moderate | 4.315 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20B | 5.928 | 中度 Moderate | 5.317 | 中度 Moderate |
| 20C | 8.069 | 重度 Severe | 6.824 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30A | 6.733 | 中度 Moderate | 5.936 | 中度 Moderate |
| 30B | 9.411 | 重度 Severe | 8.125 | 重度 Severe |
| 30C | 11.276 | 特重度 Special severe | 9.547 | 重度 Severe |
| [1] |
APEL K, HIRT H, 2004. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 55: 373-399.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAXTER A, MITTLER R, SUZUKI N, 2014. ROS as key players in plant stress signaling[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65(5): 1229-1240.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DEINLEIN U, STEPHAN A B, HORIE T, et al., 2014. Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 19(6): 371-379.
DOI URL |
| [4] | DODERER A, KOKKELINK I, VAN DER VEEN S, et al., 1992. Purification and characterization of two lipoxygenase isoenzymes from germinating barley[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1120(1): 97-104. |
| [5] |
FLOWERS T J, COLMER T D, 2008. Salinity tolerance in halophytes[J]. New Phytologist, 179(4): 945-963.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SZALAI G, KELLS T, GALIBA G, et al., 2009. Glutathione as an antioxidant and regulatory molecule in plants under abiotic stress conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 28(1): 66-80.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GUO H J, HUANG Z J, LI M Q, et al., 2020. Growth, ionic homeostasis, and physiological responses of cotton under different salt and alkali stresses[J]. Scientific Reports, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79045-z.
DOI |
| [8] |
GUO R, SHI L, YAN C, et al., 2017. Ionomic and metabolic responses to neutral salt or alkaline salt stresses in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings[J]. Bmc Plant Biology, DOI: 10.1186/s12870-017-0994-6.
DOI |
| [9] |
HASANUZZAMAN M, ALAM M M, RAHMAN A, et al., 2014. Exogenous proline and glycine betaine mediated upregulation of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems provides better protection against salt-induced oxidative stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties[J]. BioMed Research International, DOI: 10.1155/2014/757219.
DOI |
| [10] |
HUANG F, STUDART-WITKOWSKI C, SCHWAB W, 2010. Overexpression of hydroperoxide lyase gene in Nicotiana benthamiana using a viral vector system[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 8(7): 783-795.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUANG L, LI Z, PAN S, et al., 2019. Ameliorating effects of exogenous calcium on the photosynthetic physiology of honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) under salt stress[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 46(12): 1103-1113.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
IZADI-DARBANDI E, MEHDIKHANI H, 2018. Salinity effect on some of the morphophysiological traits of three plantago species (Plantago spp.)[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 236: 43-51.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KUMAR S, LI G J, YANG J J, et al., 2020. Investigation of an antioxidative system for salinity tolerance in Oenanthe javanica[J]. Antioxidants, DOI: 10.3390/antiox9100940.
DOI |
| [14] |
NIU K J, MA X, LIANG G L, et al., 2017. 5-Aminolevulinic acid modulates antioxidant defense systems and mitigates drought-induced damage in Kentucky bluegrass seedlings[J]. Protoplasma, 254(6): 2083-2094.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
QIN Y, BAI J H, WANG Y Q, et al., 2018. Comparative effects of salt and alkali stress on photosynthesis and root physiology of oat at anthesis[J]. Archives of Biological Sciences, 70(2): 329-338.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
RAVIKUMAR G, MANIMARAN P, VOLETI S R, et al., 2014. Stress-inducible expression of AtDREB1A transcription factor greatly improves drought stress tolerance in transgenic indica rice[J]. Transgenic Research, 23(3): 421-439.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
TUTEJA N, GILL S S, 2010. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12): 909-930.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG P, SUN X, LI C, et al., 2013. Long-term exogenous application of melatonin delays drought-induced leaf senescence in apple[J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 54(3): 292-302.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG S J, CHEN Q, LI Y, et al., 2017. Research on saline-alkali soil amelioration with FGD gypsum[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 121: 82-92.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
YE T T, WANG Y P, FENG Y Q, et al., 2021. Physiological and metabolomic responses of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) to alkali stress[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 171(1): 22-33.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG H H, LI X, CHE Y H, et al., 2020. A study on the effects of salinity and pH on PSII function in mulberry seedling leaves under saline-alkali mixed stress[J]. Trees-Structure and Function, 34(3): 693-706.
DOI URL |
| [22] | ZHANG H, LI X, NAN X, et al., 2017. Alkalinity and salinity tolerance during seed germination and early seedling stages of three alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars[J]. Legume Research, 40(5): 853-858. |
| [23] |
ZHANG H, LIU X, ZHANG R, et al., 2017. Root damage under alkaline stress is associated with reactive oxygen species accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01580.
DOI |
| [24] | 安玉艳, 梁宗锁, 2012. 植物应对干旱胁迫的阶段性策略[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(10): 2907-2915. |
| AN Y Y, LIANG Z S, 2012. Staged strategy of plants in response to drought stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(10): 2907-2915. | |
| [25] | 曹齐卫, 李利斌, 孔素萍, 等, 2015. 不同黄瓜品种幼苗对等渗Mg(NO3)2和NaCl胁迫的生理响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(4): 1171-1178. |
| CAO Q W, LI L B, KONG S P, et al., 2015. Physiological responses of different cucumber cultivars seedlings to iso-osmotic Mg(NO3)2 and NaCl stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(4): 1171-1178. | |
| [26] | 高立杨, 贾旭梅, 朱祖雷, 等, 2020. 盐碱复合胁迫下2种长富2号苹果砧穗组合的光合及生理特性[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 38(2): 177-184. |
| GAO L Y, JIA X M, ZHU Z L, et al., 2020. Photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of two rootstock combinations with Changfu 2 as scion under saline-alkali stress[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 38(2): 177-184. | |
| [27] | 黄洁, 白志刚, 钟楚, 等, 2020. 水稻耐盐生理及分子调节机制[J]. 核农学报, 34(6): 1359-1367. |
| HUANG J, BAI Z G, ZHONG C, et al., 2020. Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Salt Stress Tolerance in Rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 34(6): 1359-1367. | |
| [28] | 贾婷婷, 常伟, 范晓旭, 等, 2018. 盐胁迫下AM真菌对沙枣苗木光合与叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(4): 1337-1347. |
| JIA T T, CHANG W, FAN X X, et al., 2018. Effects of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(4): 1337-1347. | |
| [29] | 贾旭梅, 朱燕芳, 王海, 等, 2019. 垂丝海棠应对盐碱复合胁迫的生理响应[J]. 生态学报, 39(17): 6349-6361. |
| JIA X M, ZHU Y F, WANG H, et al., 2019. Study on Physiological Response of Malus halliana to Saline-alkali Stress[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(17): 6349-6361. | |
| [30] | 罗成科, 田蕾, 毕江涛, 等, 2019. 种稻年限对盐碱土微量元素及水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(8): 1577-1584. |
| LUO C K, TIAN L, BI J T, et al., 2019. Effects of rice planting years on saline-alkali soil trace elements, rice yield and quality[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(8): 1577-1584. | |
| [31] | 冷春旭, 郑福余, 赵北平, 等, 2020. 水稻耐碱性研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 36(11): 103-111. |
| LENG C X, ZHENG F Y, ZHAO B P, et al., 2020. Advances on Alkaline Tolerance of Rice[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 36(11): 103-111. | |
| [32] | 梁银培, 孙健, 索艺宁, 等, 2017. 水稻耐盐性和耐碱性相关性状的QTL定位及环境互作分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 50(10): 1747-1762. |
| LIANG Y P, SUN J, SUO Y N, et al., 2017. QTL mapping and QTL×environment interaction analysis of salt and alkali tolerance- related traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 50(10): 1747-1762. | |
| [33] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 等, 2020. 外源H2S对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗叶片渗透胁迫的调节作用[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(12): 3989-3997. |
| LIU J X, LIU R R, JIA H Y, et al., 2020. Regulation of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on osmotic stress in leaves of naked oat seedlings under saline-alkali mixed stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(12): 3989-3997. | |
| [34] | 罗姗姗, 曹昀, 纪欣圣, 等, 2019. 水深对黑藻叶绿素含量和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(1): 221-228. |
| LUO S S, CAO Y, JI X S, et al., 2020. Effects of water depth on chlorophyll content and antioxidant enzyme activity of Hydrilla verticillata[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(1): 221-228. | |
| [35] | 穆阳杰, 詹玉洁, 许卫锋, 等, 2020. 高pH胁迫下拟南芥根转录组学与网络应答[J]. 土壤学报, 57(3): 691-701. |
| MU Y J, ZHAN Y J, XU W F, et al., 2020. Transcriptome and network response of arabidopsis root under high pH stress[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(3): 691-701. | |
| [36] | 王慧, 刘宁, 姚延梼, 等, 2017. 晋北干旱区盐碱地柽柳叶总有机碳与营养元素含量的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(12): 2036-2044. |
| WANG H, LIU N, YAO Y T, et al., 2017. The Relationship between Foliar TOC of Tamarix chinensis Lour. and Nutrient Elements’ Content in Saline-alkali Soil of North Shanxi[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(12): 2036-2044. | |
| [37] | 徐超, 王明田, 杨再强, 等, 2021. 高温对温室草莓光合生理特性的影响及胁迫等级构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(1): 231-240. |
| XU C, WANG M T, YANG Z Q, et al., 2021. Effects of high temperature on photosynthetic physiological characteristics of strawberry seedlings in greenhouse and construction of stress level[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(1): 231-240. | |
| [38] | 徐宁, 陈冰嬬, 王明海, 等, 2017. 绿豆品种资源萌发期耐碱性鉴定[J]. 作物学报, 43(1): 112-121. |
|
XU N, CHENG B R, WANG M H, et al., 2017. Identification of Alkali Tolerance of Mungbean Germplasm Resources during Germination[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 43(1): 112-121.
DOI URL |
|
| [39] | 姚栋萍, 吴俊, 胡忠孝, 等, 2019. 水稻耐盐碱的生理机制及育种策略[J]. 杂交水稻, 34(4): 1-7. |
| YAO D P, WU J, HU Z X, et al., 2019. Physiological Mechanism and Breeding Strategy of Rice Saline-Alkaline Tolerance[J]. Hybrid Rice, 34(4): 1-7. | |
| [40] | 杨佳佳, 姜琦刚, 赵静, 等, 2011. 基于环境减灾卫星高光谱数据的盐碱地等级划分[J]. 农业工程学报, 27(10): 118-124. |
| YANG J J, JIANG Q G, ZHAO J, et al., 2011. Quantitative retrieval and classification of saline soil using HJ-1A hyperspectral data[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2011, 27(10): 118-124. | |
| [41] | 赵怀玉, 林鸿宣, 2020. 植物响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 土壤与作物, 9(2): 103-113. |
| ZHAO H Y, LIN H X, 2020. Molecular mechanism of plants in responses to salt and alkali stress[J]. Soils and Crops, 9(2): 103-113. | |
| [42] | 钟嘉文, 单晓冉, 章家恩, 等, 2021. 酸雨对生菜的光合、抗氧化系统和产量的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 532-540. |
| ZHONG J W, SHAN X R, ZHANG J E, et al., 2021. Study on the effects of acid rain on the photosynthetic and antioxidant systems and yield of lettuce[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 532-540. | |
| [43] | 邹琦, 2000. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| ZOU Q, 2000. Plant physiology experiment guidance[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. |
| [1] | HU Qirui, JI Chunrong, LI Yingchun, WANG Xuejiao, YANG Mingfeng, GUO Yanyun. Effects of Drought Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Yield of Cotton at Bud Stage under Mulched Drip Irrigation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1045-1052. |
| [2] | LI Haipeng, HUANG Yuehua, SUN Xiaodong, CAO Qimin, FU Fangxing, SUN Chuhan. Correlation Analysis of the Occurrence of the Tomato Bacterial Wilt and Different Types of Texture of Latosols and Its Bacterial Community in Cropland in Hainan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1062-1069. |
| [3] | ZHENG Qingzhou, HE Jun, LI Shenzhi, DENG Chengzhi, WU Zhipeng, HUANG Xiaolin, WU Xia. Analysis on the Differences and Influencing Factors of Human Comfort between Urban and Rural Areas in Chongqing [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1089-1097. |
| [4] | WANG Jing, MENG Ke, CHEN Xuan, ZHANG Jiaen, XIANG Huimin, ZHONG Jiawen, SHI Zhaoji. Effects of Acid Rain on Yield, Quality and Physiological Characteristics of Lettuce and Brassica chinensis L. [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1098-1107. |
| [5] | WANG Jiayi, SUN Tingting, SHA Runyu, CHEN Tinghong, XING Ran, QIN Boqiang, SHI Wenqing. Study on the Synergic Effect of Algae Salvage on Pollution Control and Carbon Emission Reduction in Eutrophic Lakes [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [6] | HUANG Yingmei, ZHONG Songxiong, ZHU Yiwen, WANG Xiangqin, LI Fangbai. Effects and Mechanism of Element Sulfur Inhibiting Methylmercury Accumulation in Rice Plants [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [7] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [8] | WANG Chao, YANG Qiannan, ZHANG Chi, LIU Tongxu, ZHANG Xialong, CHEN Jing, LIU Kexue. The Characteristics of Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Their Availability under Different Land Use Types in Danxia Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [9] | YANG Kai, YANG Jingrui, CAO Peipei, LÜ Chunhua, SUN Wenjuan, YU Lingfei, DENG Xi. Dynamic Response of Rice Plant Height, Tillering and SPAD under Elevated CO2 Concentration and Their Simulation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [10] | PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [11] | WANG Tiezheng, QU Xinyue, LIU Chunxiang, LI Youzhi. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Water Quality in the Dongjiang Lake and Their Relationships with Land Use in the Watershed [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [12] | WANG Xinyu, GAO Dengzhou, LIU Bolin, WANG Bin, ZHENG Yanling, LI Xiaofei, HOU Lijun. The Tidal-cycle Variation and Influencing Factors of Dark Carbon Fixation Process in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 733-743. |
| [13] | HU Fang, LIU Jutao, WEN Chunyun, HAN Liu, WEN Hui. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Evaluation of Aquatic Ecological Conditions in Fu River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [14] | YU Fei, ZENG Hailong, FANG Huaiyang, FU Lingfang, LIN Shu, DONG Jiahao. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Water Quality Evaluation in the Typical Tidal River Network [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [15] | ZHAO Liangxia, GAO Kun, HUANG Tingting, GAO Ye, JU Tangdan, JIANG Qiuyang, JIN Heng, XIONG Lei, TANG Zailin, GAO Canhong. The Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Maize Inbred Lines with High/Low Grain Cadmium Accumulation at Different Growth Stages [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
