Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1978-1987.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.11.008
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
PENG Shuang1,2( ), SONG Dan2, WANG Yiming2,*(
), SONG Dan2, WANG Yiming2,*( ), LIN Xiangui2
), LIN Xiangui2
Received:2023-02-23
Online:2023-11-18
Published:2024-01-17
Contact:
WANG Yiming
通讯作者:
王一明
作者简介:彭双(1986年生),女,副教授,主要研究方向为土壤微生物。E-mail: speng@issas.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
PENG Shuang, SONG Dan, WANG Yiming, LIN Xiangui. Transfer of Tetracycline Resistance Gene to Human Pathogenic Bacteria in Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1978-1987.
彭双, 宋丹, 王一明, 林先贵. 土壤环境中四环素抗性基因向病原菌的转移研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1978-1987.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.11.008
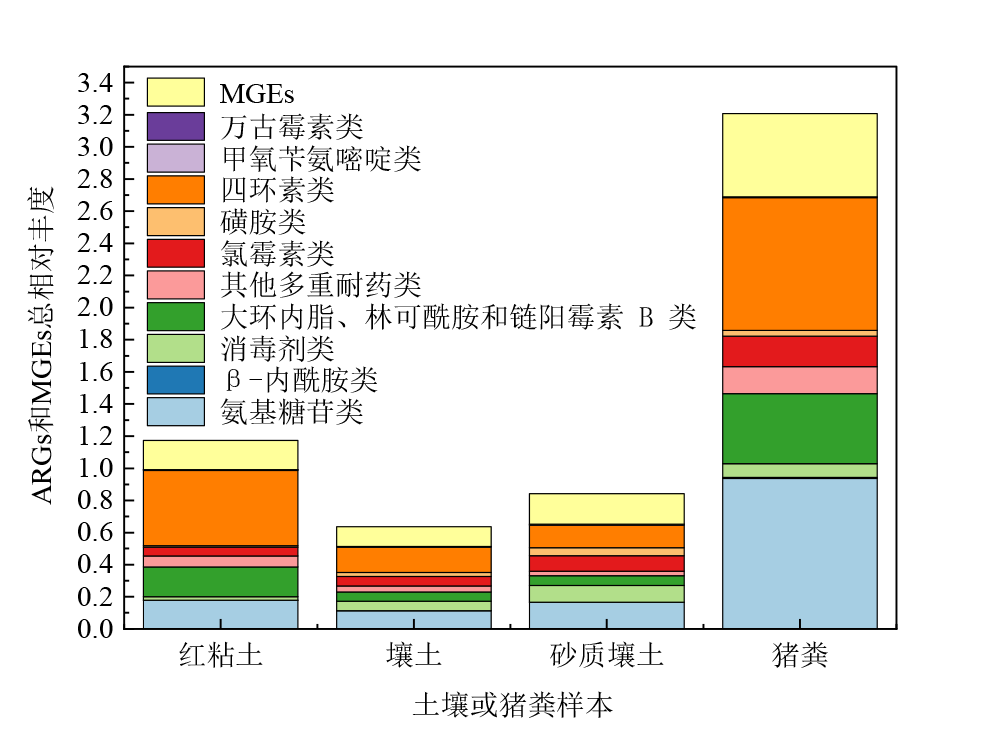
Figure 1 The relative abundance (ARG copies/16S rRNA gene copies) of ARGs and MGEs detected in pig manure and different types of soils under natural condition collected on the first day
| 生化管/培养基名称 | 沙门氏菌CICC 21484 | T1 | T2 | T3 | 大肠杆菌ATCC25922 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 色氨酸肉汤 | 黄色环 (−) | 黄色环 (−) | 黄色环 (−) | 黄色环 (−) | 玫红色环 (+) |
| 尿素酶 | 淡红色变黄色 (−) | 变黄 (−) | 变黄 (−) | 变黄 (−) | 变黄 (−) |
| 氰化钾对照 | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 生长 (+) |
| 氰化钾 | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) |
| 赖氨酸脱羧酶肉汤 | 维持紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) |
| 氨基酸脱羧酶对照 | 紫色变黄色 | 黄色 | 黄色 | 黄色 | 黄色 |
| 甘露醇 | 由蓝绿色变黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) |
| 山梨醇 | 由蓝绿色变黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 蓝绿色 (−) | 黄色 (+) |
| 水杨苷 | 维持蓝绿色,不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 黄色 (+) | 不变色 (−) |
| 丙二酸盐 | 维持淡绿色,不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) |
| 邻硝基酚−半乳糖苷 | 保持无色,不变色 (−) | 变黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) |
| 卫矛醇半固体 | 蓝绿色变为黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) |
| 西蒙氏枸橼酸盐 | 绿色变为蓝色 (+) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) |
| 吲哚试验 | 黄色环 (−) | 红色环 (+) | 红色环 (+) | 红色环 (+) | 红色环 (+) |
| HE琼脂 | 蓝绿色菌落,黑色中心 | + | + | + | 黄色菌落 |
| 沙门氏菌显色培养基 | 紫色菌落 | 乳白色 | 乳白色 | 浅绿色 | 蓝色 |
| SS琼脂 | 黑色菌落 | + | + | + | 桃红色 |
| 亚硫酸铋琼脂 (BS) | 黑色或灰绿色菌落, 有金属光泽 | + | + | + | 不生长 |
| 麦康凯琼脂 (MAC) | 无色至浅橙色, 透明或半透明, 菌落中心有时为暗色 | + | + | + | 桃红色菌落, 周围有胆盐沉淀环 |
| 三铁糖琼脂 | 黑色菌落 | + | + | + | 黄色 |
Table 1 Physiological and biochemical identification results of Salmonella, E. coli and three tetracycline resistant strains
| 生化管/培养基名称 | 沙门氏菌CICC 21484 | T1 | T2 | T3 | 大肠杆菌ATCC25922 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 色氨酸肉汤 | 黄色环 (−) | 黄色环 (−) | 黄色环 (−) | 黄色环 (−) | 玫红色环 (+) |
| 尿素酶 | 淡红色变黄色 (−) | 变黄 (−) | 变黄 (−) | 变黄 (−) | 变黄 (−) |
| 氰化钾对照 | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 生长 (+) |
| 氰化钾 | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) | 不生长 (−) |
| 赖氨酸脱羧酶肉汤 | 维持紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) | 紫色 (+) |
| 氨基酸脱羧酶对照 | 紫色变黄色 | 黄色 | 黄色 | 黄色 | 黄色 |
| 甘露醇 | 由蓝绿色变黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) |
| 山梨醇 | 由蓝绿色变黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) | 蓝绿色 (−) | 黄色 (+) |
| 水杨苷 | 维持蓝绿色,不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 黄色 (+) | 不变色 (−) |
| 丙二酸盐 | 维持淡绿色,不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) |
| 邻硝基酚−半乳糖苷 | 保持无色,不变色 (−) | 变黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 黄色 (+) |
| 卫矛醇半固体 | 蓝绿色变为黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 变黄色 (+) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) |
| 西蒙氏枸橼酸盐 | 绿色变为蓝色 (+) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) | 不变色 (−) |
| 吲哚试验 | 黄色环 (−) | 红色环 (+) | 红色环 (+) | 红色环 (+) | 红色环 (+) |
| HE琼脂 | 蓝绿色菌落,黑色中心 | + | + | + | 黄色菌落 |
| 沙门氏菌显色培养基 | 紫色菌落 | 乳白色 | 乳白色 | 浅绿色 | 蓝色 |
| SS琼脂 | 黑色菌落 | + | + | + | 桃红色 |
| 亚硫酸铋琼脂 (BS) | 黑色或灰绿色菌落, 有金属光泽 | + | + | + | 不生长 |
| 麦康凯琼脂 (MAC) | 无色至浅橙色, 透明或半透明, 菌落中心有时为暗色 | + | + | + | 桃红色菌落, 周围有胆盐沉淀环 |
| 三铁糖琼脂 | 黑色菌落 | + | + | + | 黄色 |
| 菌株名称 | 长度 | 相似度 | 相似序列 |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1701 | 1498/1503 (99%) | Escherichia coli strain SCDC-1 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence(HM576813.1) |
| T2 | 1696 | 1500/1504 (99%) | Escherichia coli strain C3, complete genome(CP010119.1) |
| T3 | 1694 | 1502/1504 (99%) | Escherichia coli strain ECCHD184 chromosome, complete genome(CP033250.1) |
| 沙门氏菌 CICC 21484 | 1702 | 1504/1505 (99%) | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium strain 22792, complete genome(CP017621.1) |
Table 2 Sequencing and NCBI comparison results of three tetracycline resistant strains
| 菌株名称 | 长度 | 相似度 | 相似序列 |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1701 | 1498/1503 (99%) | Escherichia coli strain SCDC-1 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence(HM576813.1) |
| T2 | 1696 | 1500/1504 (99%) | Escherichia coli strain C3, complete genome(CP010119.1) |
| T3 | 1694 | 1502/1504 (99%) | Escherichia coli strain ECCHD184 chromosome, complete genome(CP033250.1) |
| 沙门氏菌 CICC 21484 | 1702 | 1504/1505 (99%) | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium strain 22792, complete genome(CP017621.1) |
| 检测到的基因 | T1 | T2 | T3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 共有ARGs | aadA、aadA1、aadA2、acrA、acrB、acrF、acrR、ampC、aphA1、bacA、blaCMY2、blaCTX-M、blaKPC、blaOXY、blaSHV、cmlA1、cmlA5、dfrA12、floR、fox5、mepA、oprD、qacH、rarD、tetA、tetM、tetPB、tetR、tetZ、tolC、vanC、vanTC、mdtE/yhiU、mdtF、yceE/mdtG、yceL/mdtH、yidY/mdtL | ||
| 共有MGEs | intl1、IS1111、pBS228-IncP-1α、tnpA-03/ IS6、tnpA-05/IS26 | ||
| 特有ARGs | qacE∆1 | blaCMY、blaPAO、blaSFO cphA、tetW、vanHB、vanXA | aadA5、blaDHA、blaPAO blaSFO、cphA、tetO |
| 特有MGEs | tnpA-07/ISEcp1 intI3 | incW_trwAB、orf37-IS26、tnpA-01/Tn21、 tnpA-02/IS4tnpA-06/IS1216、pNI105map-F | incW_trwAB、orf37-IS26、tnpA-01/Tn21、 tnpA-02/IS4、tnpA-06/IS1216 |
Table 3 ARGs and MGEs carried by the three tetracycline resistant strains detected by HT-qPCR
| 检测到的基因 | T1 | T2 | T3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 共有ARGs | aadA、aadA1、aadA2、acrA、acrB、acrF、acrR、ampC、aphA1、bacA、blaCMY2、blaCTX-M、blaKPC、blaOXY、blaSHV、cmlA1、cmlA5、dfrA12、floR、fox5、mepA、oprD、qacH、rarD、tetA、tetM、tetPB、tetR、tetZ、tolC、vanC、vanTC、mdtE/yhiU、mdtF、yceE/mdtG、yceL/mdtH、yidY/mdtL | ||
| 共有MGEs | intl1、IS1111、pBS228-IncP-1α、tnpA-03/ IS6、tnpA-05/IS26 | ||
| 特有ARGs | qacE∆1 | blaCMY、blaPAO、blaSFO cphA、tetW、vanHB、vanXA | aadA5、blaDHA、blaPAO blaSFO、cphA、tetO |
| 特有MGEs | tnpA-07/ISEcp1 intI3 | incW_trwAB、orf37-IS26、tnpA-01/Tn21、 tnpA-02/IS4tnpA-06/IS1216、pNI105map-F | incW_trwAB、orf37-IS26、tnpA-01/Tn21、 tnpA-02/IS4、tnpA-06/IS1216 |
| 质粒名称 | 质粒长度/bp | 相似序列编号 | 覆盖率/% | 相似度/% | 相似序列描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 质粒1 (IncX1) | 40481 | NZ_CP018104.1 | 19.43 | 99.71 | Escherichia coli strain MRSN352231 plasmid pMR0716_tem1, complete sequence |
| NZ_CP026492.1 | 27.18 | 99.85 | Escherichia coli strain HS13-1 plasmid pHS13-1-IncHI2, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP010155.1 | 99.19 | 99.97 | Escherichia coli strain D9 plasmid C, complete genome | ||
| NZ_CP011062.1 | 21.71 | 99.68 | Escherichia coli str. Sanji plasmid pSJ_255, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP022451.1 | 22.22 | 99.66 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Indiana strain D90 plasmid pD90-1, complete sequence | ||
| 质粒2 (IncY) | 93314 | NZ_CP018104.1 | 16.32 | 99.93 | Escherichia coli strain MRSN352231 plasmid pMR0716_tem1, complete sequence |
| NZ_CP026492.1 | 33.89 | 99.86 | Escherichia coli strain HS13-1 plasmid pHS13-1-IncHI2, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP021937.1 | 19.26 | 99.66 | Escherichia coli strain AR_0055 plasmid unitig_3j3rc_linear, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP025740.1 | 27.04 | 97.44 | Escherichia coli strain Ec40 plasmid unnamed | ||
| NZ_CP017632.1 | 35.36 | 99.96 | Escherichia coli SLK172 plasmid pSLK172-1, complete sequence |
Table 4 Sequence comparison results of the two plasmids carried by strain T2
| 质粒名称 | 质粒长度/bp | 相似序列编号 | 覆盖率/% | 相似度/% | 相似序列描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 质粒1 (IncX1) | 40481 | NZ_CP018104.1 | 19.43 | 99.71 | Escherichia coli strain MRSN352231 plasmid pMR0716_tem1, complete sequence |
| NZ_CP026492.1 | 27.18 | 99.85 | Escherichia coli strain HS13-1 plasmid pHS13-1-IncHI2, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP010155.1 | 99.19 | 99.97 | Escherichia coli strain D9 plasmid C, complete genome | ||
| NZ_CP011062.1 | 21.71 | 99.68 | Escherichia coli str. Sanji plasmid pSJ_255, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP022451.1 | 22.22 | 99.66 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Indiana strain D90 plasmid pD90-1, complete sequence | ||
| 质粒2 (IncY) | 93314 | NZ_CP018104.1 | 16.32 | 99.93 | Escherichia coli strain MRSN352231 plasmid pMR0716_tem1, complete sequence |
| NZ_CP026492.1 | 33.89 | 99.86 | Escherichia coli strain HS13-1 plasmid pHS13-1-IncHI2, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP021937.1 | 19.26 | 99.66 | Escherichia coli strain AR_0055 plasmid unitig_3j3rc_linear, complete sequence | ||
| NZ_CP025740.1 | 27.04 | 97.44 | Escherichia coli strain Ec40 plasmid unnamed | ||
| NZ_CP017632.1 | 35.36 | 99.96 | Escherichia coli SLK172 plasmid pSLK172-1, complete sequence |
| 基因组序列 | ARDB (相似度大于98%) | CARD (相似度大于91%) |
|---|---|---|
| 染色体 | emrD、mdtF、mdtE、acrB、bacA、tolC、arnA、bcr、mdtK、mdfA、macB、mdtG、mdtH、acrA、acrB、ksga、mdtM、bl1_ec、mdtN、mdtO、mdtP、mdtL | tolC、bacA、patA、acrS、acrE、mdtL、adeG、cpxA、cpxR、mdtP、mdtO、mdtN、PmrB、PmrC、adiY、CRP、mdtM、leuO、adeG、kdpE、marA、marR、emrD、cysB、H-NS、mfd、mdtH、mdtG、msbA、mdfA、gadE、mdtE、mdtF、gadW、gadX、PmrE、mdtA、mdtC、mdtC、mdtD、baeS、baeR、YojI、GlpT、PmrF、arnA、evgS、adeG、emrR、emrA、emrB、alaS |
| 质粒1 (IncX1) | aph3ia、qnrS、cml_e3 | APH(3’)-Ia、QnrS2、floR |
| 质粒2 (IncY) | bl2b_tem1、tetA、tetM、dfra12、 ant2ia、cml_e1、ant3ia、ermE,sul3 | sul3、qacH、aadA、aadA17 dfrA12、tetO、TEM-1 |
Table 5 Antibiotic resistance gene annotated after comparing the whole genome sequence of strain T2 with ARDB and CARD
| 基因组序列 | ARDB (相似度大于98%) | CARD (相似度大于91%) |
|---|---|---|
| 染色体 | emrD、mdtF、mdtE、acrB、bacA、tolC、arnA、bcr、mdtK、mdfA、macB、mdtG、mdtH、acrA、acrB、ksga、mdtM、bl1_ec、mdtN、mdtO、mdtP、mdtL | tolC、bacA、patA、acrS、acrE、mdtL、adeG、cpxA、cpxR、mdtP、mdtO、mdtN、PmrB、PmrC、adiY、CRP、mdtM、leuO、adeG、kdpE、marA、marR、emrD、cysB、H-NS、mfd、mdtH、mdtG、msbA、mdfA、gadE、mdtE、mdtF、gadW、gadX、PmrE、mdtA、mdtC、mdtC、mdtD、baeS、baeR、YojI、GlpT、PmrF、arnA、evgS、adeG、emrR、emrA、emrB、alaS |
| 质粒1 (IncX1) | aph3ia、qnrS、cml_e3 | APH(3’)-Ia、QnrS2、floR |
| 质粒2 (IncY) | bl2b_tem1、tetA、tetM、dfra12、 ant2ia、cml_e1、ant3ia、ermE,sul3 | sul3、qacH、aadA、aadA17 dfrA12、tetO、TEM-1 |
| [1] |
ALEGBELEYE O O, SANT'ANA A S, 2020. Manure-borne pathogens as an important source of water contamination: An update on the dynamics of pathogen survival/transport as well as practical risk mitigation strategies[J]. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 227: 113524.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALVAREZ-MOLINA A, TRIGAL E, PRIETO M, et al., 2023. Assessment of a plasmid conjugation procedure to monitor horizontal transfer of an extended-spectrum beta-lactamase resistance gene under food chain scenarios[J]. Current Research in Food Science, 6: 100405.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BERENDONK T U, MANAIA C M, MERLIN C, et al., 2015. Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 13(5): 310-317.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
BLANCO G, DIAZ DE TUESTA J A, 2021. Seasonal and spatial occurrence of zoonotic Salmonella serotypes in griffon vultures at farmland environments: Implications in pathogen pollution and ecosystem services and disservices[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 758: 143681.
DOI URL |
| [5] | BOUANCHAUD D H, HELLIO R, BIETH G, et al., 1975. Physical studies of a plasmid mediating tetracycline resistance and hydrogen sulfide production in Escherichia coli[J]. Molecular & general genetics: MGG, 140(4): 355-359. |
| [6] |
BUSTAMANTE P, IREDELL J R, 2017. Carriage of type II toxin-antitoxin systems by the growing group of IncX plasmids[J]. Plasmid, 91: 19-27.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
CHEN X F, YIN H L, LI G Y, et al., 2019. Antibiotic-resistance gene transfer in antibiotic-resistance bacteria under different light irradiation: Implications from oxidative stress and gene expression[J]. Water Research, 149: 282-291.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
CHEN X M, DU Z, SONG X Y, et al., 2023. Evaluating the occurrence frequency of horizontal gene transfer induced by different degrees of heavy metal stress[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 382: 135371.
DOI URL |
| [9] | DROGE M, PUHLER A, SELBITSCHKA W, 2000. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of conjugative antibiotic resistance plasmids isolated from bacterial communities of activated sludge[J]. Molecular & General Genetics: MGG, 263(3): 471-482. |
| [10] |
DUNGAN R S, BJORNEBERG D L, 2020. Antibiotic resistance genes, class 1 integrons, and IncP-1/IncQ-1 plasmids in irrigation return flows[J]. Environmental Pollution, 257: 113568.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FAN X T, LI H, CHEN Q L, et al., 2019. Fate of Antibiotic Resistant Pseudomonas putida and Broad Host Range Plasmid in Natural Soil Microcosms[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10: 194.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
FANG J, JIN L, MENG Q K, et al., 2022. Biochar effectively inhibits the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes via transformation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 423(Part B): 127150.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
FORSBERG K J, PATEL S, GIBSON M K, et al., 2014. Bacterial phylogeny structures soil resistomes across habitats[J]. Nature, 509(7502): 612-616.
DOI |
| [14] |
GABALLAH M S, GUO J B, SUN H, et al., 2021. A review targeting veterinary antibiotics removal from livestock manure management systems and future outlook[J]. Bioresource Technology, 333: 125069.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HARNETT N, MANGAN L, BROWN S, et al., 1996. Thermosensitive transfer of antimicrobial resistances and citrate utilization and cotransfer of hydrogen sulfide production from an Escherichia coli isolate[J]. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease, 24(4): 173-178.
PMID |
| [16] | HAWKEY P, 2008. Molecular epidemiology of clinically significant antibiotic resistance genes[J]. British journal of pharmacology, 153: S406-S413. |
| [17] |
HERNANDO-AMADO S, COQUE T M, BAQUERO F, et al., 2019. Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from One Health and Global Health perspectives[J]. Nature Microbiology, 4(9): 1432-1442.
DOI |
| [18] |
HU X J, WAIGI M G, YANG B, et al., 2022. Impact of Plastic Particles on the Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes to Bacterium: Dependent on Particle Sizes and Antibiotic Resistance Gene Vector Replication Capacities[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(21): 14948-14959.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HUANG J L, MI J D, YAN Q F, et al., 2021. Animal manures application increases the abundances of antibiotic resistance genes in soil-lettuce system associated with shared bacterial distributions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 787: 147667.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
JIA Y Q, WANG Z Q, FANG D, et al., 2021. Acetaminophen promotes horizontal transfer of plasmid-borne multiple antibiotic resistance genes[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 782: 146916.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
JOHNSON T J, BIELAK E M, FORTINI D, et al., 2012. Expansion of the IncX plasmid family for improved identification and typing of novel plasmids in drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae[J]. Plasmid, 68(1): 43-50.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
KNAPP C W, DOLFING J, EHLERT P A I, et al., 2010. Evidence of increasing antibiotic resistance Gene abundances in archived soils since 1940[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(2): 580-587.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KRASOVSKY V N, STOTZKY G, 1987. Conjugation and genetic recombination in Escherichia coli in sterile and nonsterile soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 19: 631-638.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LI H, DECHESNE A, HE Z M, et al., 2023. Electrochemical disinfection may increase the spread of antibiotic resistance genes by promoting conjugal plasmid transfer[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 858(Part 1): 159846.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LI J Y, CHEN Q L, LI H L, et al., 2020. Impacts of different sources of animal manures on dissemination of human pathogenic bacteria in agricultural soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 266(Part 2): 115399.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LI Q, WAGAN S A, WANG Y B, 2021. An analysis on determinants of farmers’ willingness for resource utilization of livestock manure[J]. Waste Management., 120: 708-715.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LI W Y, ZHANG G S, 2022. Detection and various environmental factors of antibiotic resistance gene horizontal transfer[J]. Environment Research, 212(Part B): 113267.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LIN W F, LI S, ZHANG S T, et al., 2016. Reduction in horizontal transfer of conjugative plasmid by UV irradiation and low-level chlorination[J]. Water Research, 91: 331-338.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
LIU Y, GAO J F, ZHAO M Y, et al., 2023. Removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria, genes and inhibition of plasmid-mediated horizontal transfer by peroxymonosulfate: Efficiency and mechanisms[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 453(Part 1): 139728.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MACEDO G, OLESEN A K, MACCARIO L, et al., 2022. Horizontal Gene Transfer of an IncP1 Plasmid to Soil Bacterial Community Introduced by Escherichia coli through Manure Amendment in Soil Microcosms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(16): 11398-11408.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
NEILL A J, TETZLAFF D, STRACHAN N J C, et al., 2018. Using spatial-stream-network models and long-term data to understand and predict dynamics of faecal contamination in a mixed land-use catchment[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 612: 840-852.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
NICHOLSON F A, GROVES S J, CHAMBERS B J, 2005. Pathogen survival during livestock manure storage and following land application[J]. Bioresource Technology, 96(2): 135-143.
PMID |
| [33] | O’NEILL J, 2014. Antimicrobial resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations[R]. The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, 20: 1-16. |
| [34] |
PENG S, FENG Y Z, WANG Y M, et al., 2017. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in soils after continually applied with different manure for 30 years[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 340: 16-25.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
PENG S, SONG D, ZHOU B B, et al., 2022b. Persistence of Salmonella Typhimurium and antibiotic resistance genes in different types of soil influenced by flooding and soil properties[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 248: 114330.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
PENG S, ZHANG H Y, SONG D, et al., 2022a. Distribution of antibiotic, heavy metals and antibiotic resistance genes in livestock and poultry feces from different scale of farms in Ningxia, China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 440: 129719.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
PENG S, ZHOU B B, WANG Y M, et al., 2016. Bacteria play a more important role than nutrients in the accumulation of tetracycline resistance in manure-treated soil[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 52(5): 655-663.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
POPOWSKA M, RZECZYCKA M, MIERNIK A, et al., 2012. Influence of soil use on prevalence of tetracycline, streptomycin, and erythromycin resistance and associated resistance genes[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 56(3): 1434-1443.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | PORNSUKAROM S, THAKUR S, 2017. Horizontal dissemination of antimicrobial resistance determinants in multiple Salmonella serotypes following isolation from the commercial swine operation environment after manure application[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 83: e01503-1517. |
| [40] |
QIU X W, ZHOU G X, WANG H J, 2022. Nanoscale zero-valent iron inhibits the horizontal gene transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in chicken manure compost[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 422: 126883.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
QIU Z G, YU Y M, CHEN Z L, et al., 2012. Nanoalumina promotes the horizontal transfer of multiresistance genes mediated by plasmids across genera[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(13): 4944-4949.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
RAHMAN M M, SHAN J, YANG P P, et al., 2018. Effects of long-term pig manure application on antibiotics, abundance of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), anammox and denitrification rates in paddy soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 240: 368-377.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
SHI X D, XIA Y, WEI W, et al., 2022. Accelerated spread of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) induced by non-antibiotic conditions: Roles and mechanisms[J]. Water Research, 224: 119060.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
SOMMER M O A, 2014. Barriers to the spread of resistance[J]. Nature, 509(1): 567-568.
DOI |
| [45] |
SØRENSEN S J, BAILEY M, HANSEN L H, et al., 2005. Studying plasmid horizontal transfer in situ: A critical review[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 3(9): 700-710.
PMID |
| [46] |
SORINOLU A J, TYAGI N, KUMAR A, et al., 2021. Antibiotic resistance development and human health risks during wastewater reuse and biosolids application in agriculture[J]. Chemosphere, 265: 129032.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
TANG Z R, HUANG C H, LI W, et al., 2023. Horizontal transfer of intracellular and extracellular ARGs in sludge compost under sulfamethoxazole stress[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 454: 139968.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
THOMAS C M, NIELSEN K M, 2005. Mechanisms of, and Barriers to, Horizontal Gene Transfer between Bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 3(9): 711-721.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
WANG F H, SUN R B, HU H W, et al., 2022. The overlap of soil and vegetable microbes drives the transfer of antibiotic resistance genes from manure-amended soil to vegetables[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 828: 154463.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
WANG X X, LI H, CHEN Y, et al., 2022. A neglected risk of nanoplastics as revealed by the promoted transformation of plasmid-borne ampicillin resistance gene by Escherichia coli[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 24(10): 4946-4959.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
WANG Y, LU J, MAO L K, et al., 2019. Antiepileptic drug carbamazepine promotes horizontal transfer of plasmid-borne multi-antibiotic resistance genes within and across bacterial genera[J]. The ISME Journal, 13(2): 509-522.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
WU S, WU Y C, HUANG Q Y, et al., 2020. Insights into conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes affected by soil minerals[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 72(3): 1143-1153.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
XU H, CHEN Z Y, HUANG R Y, et al., 2021. Antibiotic resistance gene-carrying plasmid spreads into the plant endophytic bacteria using soil bacteria as carriers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(15): 10462-10470.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
YAN X J, LIU W W, WEN S F, et al., 2023. Effect of sulfamethazine on the horizontal transfer of plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance genes and its mechanism of action[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 127: 399-409.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
ZHAI H Y, GUO Y J, ZHANG L Y, et al., 2022. Presence of bromide and iodide promotes the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes during chlorination: A preliminary study[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 846: 157250.
DOI URL |
| [56] | ZHANG C P, FENG Y Q, LIU F, et al., 2017. A Phage-Like IncY Plasmid Carrying the mcr-1 Gene in Escherichia coli from a Pig Farm in China[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 61(3): e02035-16. |
| [57] |
ZHANG C, ZHAO X, WANG C, et al., 2022. Electrochemical flow-through disinfection reduces antibiotic resistance genes and horizontal transfer risk across bacterial species[J]. Water Research, 212: 118090.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
ZHANG H P, ZHANG Q K, SONG J J, et al., 2020. Tracking resistomes, virulence genes, and bacterial pathogens in longterm manure-amended greenhouse soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 396: 122618.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
ZHANG Y J, HU H W, CHEN Q L, et al., 2019. Transfer of antibiotic resistance from manure-amended soils to vegetable microbiomes[J]. Environment International, 130: 104912.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
ZHANG Y, CHENG D M, XIE J, et al., 2022. Impacts of farmland application of antibiotic-contaminated manures on the occurrence of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in soil: A meta-analysis study[J]. Chemosphere, 300: 134529.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
ZHAO W Y, DENG J B, CHI S L, et al., 2022. Sustainability assessment of topsoil ecology in Chongqing, China based on the application of livestock and poultry manure[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 358: 131969.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
ZHOU G X, QIU X W, WU X Y, et al., 2021. Horizontal gene transfer is a key determinant of antibiotic resistance genes profiles during chicken manure composting with the addition of biochar and zeolite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408: 124883.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
ZHOU R J, ZENG S Z, HOU D W, et al., 2019. Occurrence of human pathogenic bacteria carrying antibiotic resistance genes revealed by metagenomic approach: A case study from an aquatic environment[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 80: 248-256.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | ZHU Y G, JOHNSON T A, SU J Q, et al., 2013. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(9): 3435-3440. |
| [65] | 胡小婕, 秦超, 高彦征, 2022. 有机污染物对抗生素抗性基因水平转移的影响及机制[J]. 科学通报, 67(35): 4224-4235. |
| HU X J, QIN C, GAO Y Z, 2022. Organic contaminants influence the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67: 4224-4235 | |
| [66] | 吴府丽, 2017. 硫化氢阴性沙门菌遗传变异规律及硫化氢参与沙门菌耐药机制的研究[D]. 北京: 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院: 9-11. |
| WU F L, 2017. Study on the genetic variation patterns of hydrogen sulfide negative Salmonella and hydrogen sulfide participates in the mechanism of Salmonella resistance [D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Medical Sciences: 9-11. | |
| [67] | 张晓玲, 严谨, 张群, 2021. 产硫化氢大肠埃希菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 现代医药卫生, 37(16): 2779-2783. |
| ZHANG X L, YAN J, ZHANG Q, 2021. Isolation and identification of hydrogen sulfide producing Escherichia coli[J]. Journal of Modern Medicine and Health, 37(16): 2779-2783. |
| [1] | GAO Xiaoyu, WANG Lei. The Accumulation, Transfer and Elimination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Soil: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 2062-2071. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
