生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 931-940.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.06.010
任宸剑1( ), 郝瑞霞1,3, 张杨2, 韩丽娟1,3,*(
), 郝瑞霞1,3, 张杨2, 韩丽娟1,3,*( ), 魏煜星1, 柴璐1
), 魏煜星1, 柴璐1
收稿日期:2024-10-20
出版日期:2025-06-18
发布日期:2025-06-11
通讯作者:
* 韩丽娟, E-mail: 作者简介:任宸剑(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事水力学及河流动力学研究。E-mail: 972909938@qq.com
基金资助:
REN Chenjian1( ), HAO Ruixia1,3, ZHANG Yang2, HAN Lijuan1,3,*(
), HAO Ruixia1,3, ZHANG Yang2, HAN Lijuan1,3,*( ), WEI Yuxing1, CHAI Lu1
), WEI Yuxing1, CHAI Lu1
Received:2024-10-20
Online:2025-06-18
Published:2025-06-11
摘要:
氨氮是引起河道富营养化的重要原因,了解水动力条件下河道底泥中氨氮的释放特性对了解河流水质的动态至关重要。为探究水动力作用对河道底泥起动与氨氮释放规律的影响,于汾河太原段下游取样开展室内实验,研究恒定和变化水动力条件下底泥再悬浮与氨氮浓度的时空变化以及释放速率等,构建不同强度水动力作用下近底切应力与底泥起动、上覆水浊度、氨氮浓度的相关关系。结果表明,水动力条件变化引起的近底切应力变化是影响上覆水浊度和氨氮浓度的关键因素。当近底切应力为1.07 N·m−2时,中值粒径d50=0.020 mm的底泥达到“普遍动”的起动状态,底泥向上覆水中大量悬浮;氨氮在扰动初期释放速率最快,前60 min氨氮释放量占总释放量的60.4%;当近底切应力小于0.260 N·m−2时,氨氮浓度在实验初期释放存在分层现象,底部氨氮浓度处于较高的水平,随着转速的增加和时间的推移(180 min后)垂向上氨氮浓度趋于一致;上覆水浊度和氨氮浓度随底泥面切应力的增加而增加,越强的水动力条件越有助于提高上覆水中氨氮浓度的阈值上限,该研究中氨氮质量浓度和释放速率最大值分别为0.569 mg·L−1、249 mg·m−2·d−1;近底切应力与底泥向上覆水释放的氨氮浓度呈线性增加关系,与水体浊度呈近似指数增加关系。
中图分类号:
任宸剑, 郝瑞霞, 张杨, 韩丽娟, 魏煜星, 柴璐. 水动力作用下河道底泥氨氮释放特性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 931-940.
REN Chenjian, HAO Ruixia, ZHANG Yang, HAN Lijuan, WEI Yuxing, CHAI Lu. The Release Characteristics of Ammonia Nitrogen from River Sediments Driven by Hydrodynamic Forces[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(6): 931-940.
| 底泥 深度/ cm | 总氮质量 分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 氨氮质量 分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 硝酸盐氮 质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 亚硝酸盐氮 质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-5 | 699±37.0 | 45.0±2.00 | 32.0±2.00 | 27.0±1.00 |
| 5-10 | 713±28.0 | 39.0±4.00 | 36.0±2.00 | 24.0±1.00 |
表1 底泥中不同形态氮的质量分数
Table 1 Mass fraction of different forms of nitrogen in the sediment
| 底泥 深度/ cm | 总氮质量 分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 氨氮质量 分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 硝酸盐氮 质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) | 亚硝酸盐氮 质量分数/ (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-5 | 699±37.0 | 45.0±2.00 | 32.0±2.00 | 27.0±1.00 |
| 5-10 | 713±28.0 | 39.0±4.00 | 36.0±2.00 | 24.0±1.00 |
| 工况 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转速Rs/(rad·min−1) | 0 | 150 | 250 | 350 | 450 |
表2 恒定水动力条件下氨氮释放工况(A1-A5)
Table 2 Experimental conditions for ammonia nitrogen release under steady hydrodynamic conditions (A1-A5)
| 工况 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转速Rs/(rad·min−1) | 0 | 150 | 250 | 350 | 450 |
| 阶段 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转速Rs/(rad·min−1) | 0 | 150 | 250 | 350 | 450 | 350 | 250 | 150 | 0 |
表3 变化水动力条件下氨氮释放工况(A6)
Table 3 Experimental conditions for ammonia nitrogen release under variable hydrodynamic conditions (A6)
| 阶段 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转速Rs/(rad·min−1) | 0 | 150 | 250 | 350 | 450 | 350 | 250 | 150 | 0 |
| 工况 | 释放速率/(mg·m−2·d−1) | 累计释放速率/ (mg·m−2·d−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-60 min | 60-540 min | ||
| A1 | 280 | 57.8 | 76.8 |
| A2 | 633 | 64.3 | 119 |
| A3 | 1.04×103 | 69.5 | 164 |
| A4 | 1.58×103 | 95.1 | 249 |
| A5 | 1.13×103 | 148 | 240 |
表4 上覆水中氨氮的释放速率
Table 4 Release rates of ammonia nitrogen in overlying water
| 工况 | 释放速率/(mg·m−2·d−1) | 累计释放速率/ (mg·m−2·d−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-60 min | 60-540 min | ||
| A1 | 280 | 57.8 | 76.8 |
| A2 | 633 | 64.3 | 119 |
| A3 | 1.04×103 | 69.5 | 164 |
| A4 | 1.58×103 | 95.1 | 249 |
| A5 | 1.13×103 | 148 | 240 |
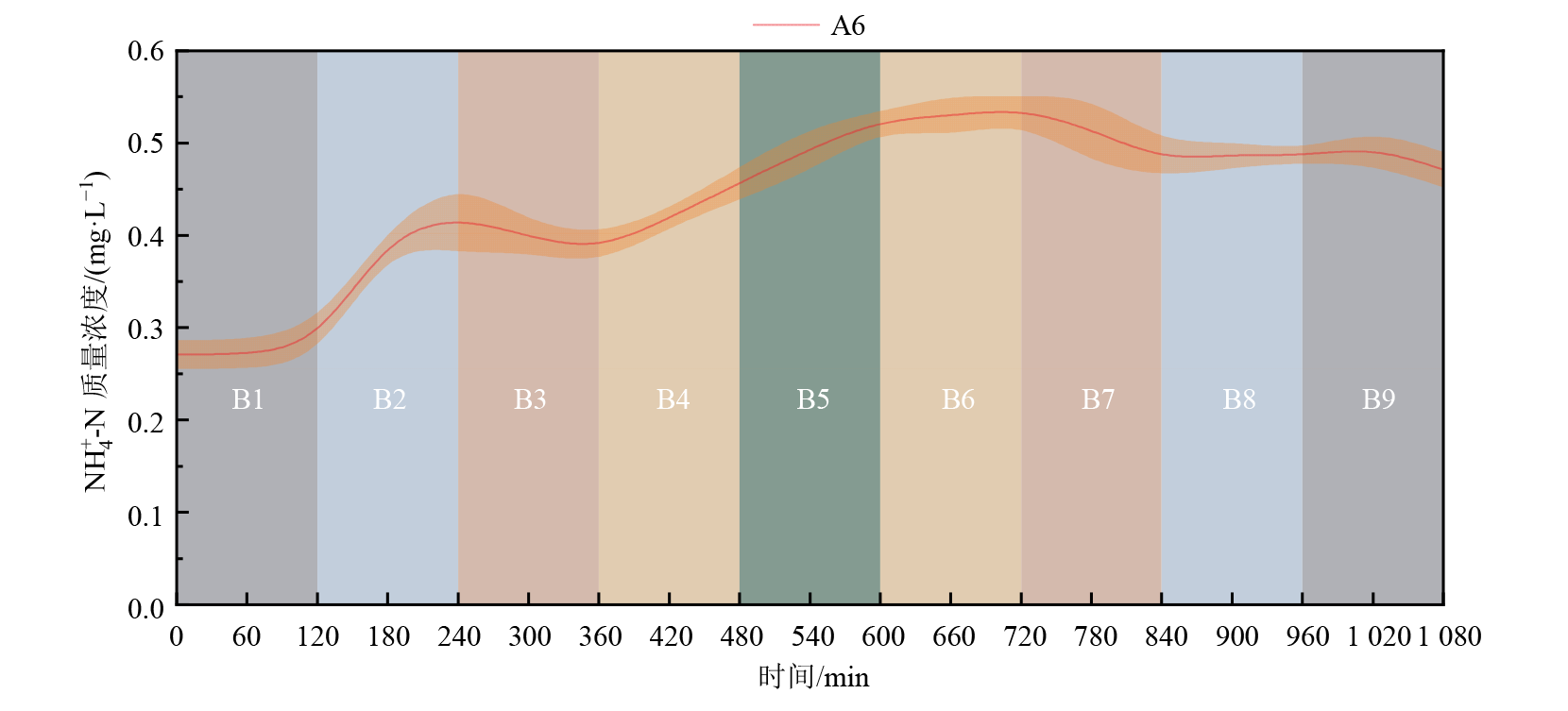
图8 变化水动力条件下(A6)上覆水中氨氮质量浓度随时间变化
Figure 8 Temporal variation in Ammonium nitrogen mass concentration in the overlaying water under variable hydrodynamic conditions (A6)
| 阶段 | 转速Rs/ (rad·min−1) | 氨氮平均质量浓度变化∆/(mg·L−1) | 释放速率/ (mg·m−2·d−1) | 累计释放速率/ (mg·m−2·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0 | 6.00×10−3 | 43.1 | 25.1 |
| 5.00×10−3 | 35.8 | 28.7 | ||
| B2 | 150 | 0.119 | 851 | 235 |
| 2.10×10−2 | 150 | 218 | ||
| B3 | 250 | −2.30×10−2 | −137 | 154 |
| −1.50×10−2 | −106 | 117 | ||
| B4 | 350 | 3.50×10−2 | 248 | 134 |
| 3.80×10−2 | 268 | 149 | ||
| B5 | 450 | 3.80×10−2 | 268 | 162 |
| 3.10×10−2 | 218 | 167 | ||
| B6 | 350 | 4.00×10−3 | 28.1 | 156 |
| 8.00×10−3 | 56.0 | 148 | ||
| B7 | 250 | −2.30×10−2 | −161 | 125 |
| −3.30×10−2 | −230 | 102 | ||
| B8 | 150 | 6.00×10−3 | 41.7 | 97.9 |
| −2.00×10−3 | −13.9 | 90.5 | ||
| B9 | 0 | 1.00×10−2 | 69.1 | 87.9 |
| −2.50×10−2 | −172 | 75.8 |
表5 变化水动力条件下(A6)氨氮质量浓度变化与释放速率计算结果
Table 5 Calculated results of ammonia nitrogen mass concentration changes and release rates (A6)
| 阶段 | 转速Rs/ (rad·min−1) | 氨氮平均质量浓度变化∆/(mg·L−1) | 释放速率/ (mg·m−2·d−1) | 累计释放速率/ (mg·m−2·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0 | 6.00×10−3 | 43.1 | 25.1 |
| 5.00×10−3 | 35.8 | 28.7 | ||
| B2 | 150 | 0.119 | 851 | 235 |
| 2.10×10−2 | 150 | 218 | ||
| B3 | 250 | −2.30×10−2 | −137 | 154 |
| −1.50×10−2 | −106 | 117 | ||
| B4 | 350 | 3.50×10−2 | 248 | 134 |
| 3.80×10−2 | 268 | 149 | ||
| B5 | 450 | 3.80×10−2 | 268 | 162 |
| 3.10×10−2 | 218 | 167 | ||
| B6 | 350 | 4.00×10−3 | 28.1 | 156 |
| 8.00×10−3 | 56.0 | 148 | ||
| B7 | 250 | −2.30×10−2 | −161 | 125 |
| −3.30×10−2 | −230 | 102 | ||
| B8 | 150 | 6.00×10−3 | 41.7 | 97.9 |
| −2.00×10−3 | −13.9 | 90.5 | ||
| B9 | 0 | 1.00×10−2 | 69.1 | 87.9 |
| −2.50×10−2 | −172 | 75.8 |
| 工况 | 转速Rs/ (rad·min−1) | 底泥起动状态 | 近底流速ub/ (m·s−1) | 近底处黏滞切应力τ1/ (N·m−2) | 近底处附加切应力τ2/ (N·m−2) | 近底处切应力τ/(N·m−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 | 李一平 | ||||||
| A1 | 0 | 未动 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - |
| A2 | 150 | 个别动 | 2.00×10−2 | 2.00×10−3 | 6.60×10−2 | 6.80×10−2 | - |
| A3 | 250 | 个别动 | 4.00×10−2 | 4.00×10−3 | 0.256 | 0.260 | 0.428 |
| A4 | 350 | 少量动 | 6.00×10−2 | 6.00×10−3 | 0.578 | 0.584 | 0.636 |
| A5 | 450 | 普遍动 | 8.10×10−2 | 9.00×10−3 | 1.06 | 1.07 | 1.04 |
表6 实验装置内的近底切应力
Table 6 Near-bottom shear stress in the experimental setup
| 工况 | 转速Rs/ (rad·min−1) | 底泥起动状态 | 近底流速ub/ (m·s−1) | 近底处黏滞切应力τ1/ (N·m−2) | 近底处附加切应力τ2/ (N·m−2) | 近底处切应力τ/(N·m−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 | 李一平 | ||||||
| A1 | 0 | 未动 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - |
| A2 | 150 | 个别动 | 2.00×10−2 | 2.00×10−3 | 6.60×10−2 | 6.80×10−2 | - |
| A3 | 250 | 个别动 | 4.00×10−2 | 4.00×10−3 | 0.256 | 0.260 | 0.428 |
| A4 | 350 | 少量动 | 6.00×10−2 | 6.00×10−3 | 0.578 | 0.584 | 0.636 |
| A5 | 450 | 普遍动 | 8.10×10−2 | 9.00×10−3 | 1.06 | 1.07 | 1.04 |
| 工况 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上覆水浊度/ FNU | 10.1±0.730 | 12.1±2.63 | 26.2±2.54 | 53.2±5.38 | 115±10.3 |
表7 A1-A5工况浊度
Table 7 Turbidity levels under steady hydrodynamic conditions (A1-A5)
| 工况 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上覆水浊度/ FNU | 10.1±0.730 | 12.1±2.63 | 26.2±2.54 | 53.2±5.38 | 115±10.3 |
| 时段 | 各阶段上覆水的浊度/FNU | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 | |
| 第1小时 | 3.17±0.210 | 4.17±0.530 | 10.1±2.75 | 30.8±2.46 | 110±9.56 | 87.4±7.94 | 74.3±8.77 | 52.8±3.93 | 33.6±1.74 |
| 第2小时 | 3.09±0.920 | 4.03±1.89 | 9.53±1.61 | 29.4±5.09 | 92.6±5.90 | 82.7±8.84 | 69.3±4.20 | 45.8±5.39 | 29.9±1.86 |
表8 变化水动力条件下(A6)浊度变化过程
Table 8 Turbidity variation process under variable hydrodynamic conditions (A6)
| 时段 | 各阶段上覆水的浊度/FNU | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 | |
| 第1小时 | 3.17±0.210 | 4.17±0.530 | 10.1±2.75 | 30.8±2.46 | 110±9.56 | 87.4±7.94 | 74.3±8.77 | 52.8±3.93 | 33.6±1.74 |
| 第2小时 | 3.09±0.920 | 4.03±1.89 | 9.53±1.61 | 29.4±5.09 | 92.6±5.90 | 82.7±8.84 | 69.3±4.20 | 45.8±5.39 | 29.9±1.86 |
| [1] | BAI Y, ZENG Y H, NIE B, et al., 2019. Hydrodynamic disturbance on phosphorus release across the sediment-water interface in Xuanwu Lake, China (Article)[J]. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 19(3): 735-742. |
| [2] | CHANDLER I D, 2012. Vertical variation in diffusion coefficient within sediments[D]. Coventry: University of Warwick:100-101. |
| [3] | DONG J W, XIA X H, WANG M H, et al., 2016. Effect of recurrent sediment resuspension-deposition events on bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aquatic environments[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 540: 934-946. |
| [4] |
HUANG J Z, GE X P, WANG D S, 2012. Distribution of heavy metals in the water column, suspended particulate matters and the sediment under hydrodynamic conditions using an annular flume[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(12): 2051-2059.
PMID |
| [5] | MALCOLM OG, GIOVANNI C, 2014. Review of wave-driven sediment resuspension and transport in estuaries[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 52(1): 77-117. |
| [6] | WU D, HUA Z L, 2014. The effect of vegetation on sediment resuspension and phosphorus release under hydrodynamic disturbance in shallow lakes[J]. Ecological Engineering, 69: 55-62. |
| [7] | XU S Y, LU J, CHEN L C, et al., 2023. Experiment on sediment ammonia nitrogen release of Chaohu Lake in varying hydrodynamic disturbance[J]. Sustainability, 15(2): 1581. |
| [8] | YUAN Y J, HE P C, LIU N N, et al., 2020. Effects of temperature and disturbance on nitrogen release from sediment of Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science), 43(5): 495-500. |
| [9] | ZHANG L, SHANG J G, HE W, et al., 2014. The role of tubificid worms (Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri) in sediment resuspension: A microcosm study[J]. International Review of the Red Cross, 50(3): 253-260. |
| [10] | 陈柏文, 拾兵, 王俊杰, 等, 2024. 紊动与盐度共同作用的黄河口黏性泥沙絮凝沉降试验研究[J]. 水利水运工程学报 (2): 91-99. |
| CHEN B W, SHI B, WANG J J, et al., 2024. Experimental study on flocculation and sedimentation of viscous sediment in the Yellow River estuary by the combined effect of turbulence and salinity[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering (2): 91-99. | |
| [11] | 段余杰, 刘小宁, 陈光耀, 等, 2017. 底泥再悬浮对上覆水水质的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(5): 837-842. |
| DUAN Y J, LIU X N, CHEN G Y, et al., 2017. Influence of sediment re-suspension on black-and-malodorous status and water quality of overlying water[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(5): 837-842. | |
| [12] | 范成新, 2019. 湖泊沉积物-水界面研究进展与展望[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(5): 1191-1218. |
| FAN C X, 2019. Advances and prospect in sediment-water interface of lakes: A review[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(5): 1194-1218. | |
| [13] | 李素珍, 夏星辉, 张菊, 2007. 不同河流水体颗粒物对硝化过程的影响[J]. 环境化学, 26(4): 419-424. |
| LI S Z, XIA X H, ZHANG J, 2007. Influence of particulate matter on nitrification processes in different river waters[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 26(4): 419-424. | |
| [14] | 李亚芳, 卢俊平, 张晓晶, 等, 2021. 不同温度、pH、水动力条件下寒旱区水库底泥中不同形态氮的释放特征模拟[J]. 环境污染与防治, 43(6): 669-673, 690. |
| LI Y F, LU J P, ZHANG X J, et al., 2021. Simulation of different nitrogen forms release characteristics from reservoir sediment in cold and arid region under different temperature, pH and hydrodynamic condition[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 43(6): 669-673, 690. | |
| [15] | 李一平, 逄勇, 吕俊, 等, 2004a. 水动力条件下底泥中氮磷释放通量[J]. 湖泊科学, 8(4): 318-324. |
| LI Y P, PANG Y, LÜ J, et al., 2004a. On the relation between the release rate of TN, TP from sediment and water velocity[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 8(4): 318-324. | |
| [16] | 李一平, 逄勇, 陈克森, 等, 2004b. 水动力作用下太湖底泥起动规律研究[J]. 水科学进展, 15(6): 770-774. |
| LI Y P, PENG Y, CHEN K S, et al., 2004b. Study on the starting principles of sediment by water force in Taihu Lake[J]. Advances in Water Science, 15(6): 770-774. | |
| [17] | 梁家雄, 张金凤, 周惟於, 等, 2021. 紊动和温度联合作用对黏性泥沙絮凝沉降影响试验研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 46(5): 9-14. |
| LIANG J X, ZHANG J F, ZHOU W Y, et al., 2021. Experimental study on the effect of combined action of turbulence and temperature on flocculation and sedimentation of cohesive sediment[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 46(5): 9-14. | |
| [18] | 裴海光, 贾自强, 杨静, 等, 2022. 汾河太原段沉积物氮、铜、铝含量及酶活性的分布及动态[J]. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 45(1): 237-246. |
| PEI H G, JIA Z Q, YANG J, et al., 2022. Distribution and dynamics of N, Cu, Al, and enzyme activity in the sediments of Taiyuan section of Fenhe River, Shanxi[J]. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 45(1): 237-246. | |
| [19] | 申豪勇, 李佳, 王志恒, 等, 2022. 黄河支流汾河流域水资源开发利用现状及生态环境问题[J]. 中国地质, 49(4): 1127-1138. |
| SHEN H Y, LI J, WANG Z H, et al., 2022. Water resources utilization and eco-environment problem of Fenhe River, branch of Yellow River[J]. Chinese Geology, 49(4): 1127-1138. | |
| [20] | 王春林, 吕亚云, 史亚婷, 等, 2010. 桨叶式搅拌槽内部流场数值模拟及PIV试验[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 28(4): 335-339. |
| WANG C L, LÜ Y Y, SHI Y T, et al., 2010. Numerical simulation and PIV test of internal flow field in paddle stirred tank[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 28(4): 335-339. | |
| [21] | 王亚博, 2022. 降雨影响岩口水库上游河流水质的关键过程解析及污染物溯源研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学:24. |
| WANG Y B, 2022. Exploring the key process of rainfall affecting the water quality of upstream rivers of Yankou Reservoir and the source of pollutants[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology:24. | |
| [22] | 夏波, 张庆河, 蒋昌波, 等, 2014. 水体紊动作用下湖泊泥沙解吸释放磷的实验研究[J]. 泥沙研究 (1): 74-80. |
| XIA B, ZHANG Q H, JIANG C B, et al., 2014. Experimental investigation of effect of flow turbulence on phosphorus release from lake sediment[J]. Journal of Sediment Research (1): 74-80. | |
| [23] | 辛冲, 2013. 汾河下游河道二维水流模拟[J]. 人民黄河, 35(12): 27-29. |
| XIN C, 2013. Two-dimensional flow simulation in the lower Fenhe River[J]. Yellow River, 35(12): 27-29. | |
| [24] | 郑淑君, 王铁运, 刘云根, 等, 2022. 水流扰动强度对高原山地农村沟渠底泥氮释放的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 38(8): 1076-1083. |
| ZHENG S J, WANG T Y, LIU Y G, et al., 2022. Effect of flow disturbance intensity on nitrogen release from bottom muddy of plateau rural ditches[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 38(8): 1076-1083. | |
| [25] | 钟小燕, 王船海, 庾从蓉, 等, 2017. 流速对太湖河道底泥泥沙、营养盐释放规律影响实验研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(8): 2862-2869. |
| ZHONG X Y, WANG C H, YU C R, et al., 2017. Characteristics of sediments and nutrient release under different flow velocity[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(8): 2862-2869. | |
| [26] | 朱广伟, 秦伯强, 高光, 2005. 风浪扰动引起大型浅水湖泊内源磷暴发性释放的直接证据[J]. 科学通报, 14(1): 66-71. |
| ZHU G W, QIN B G, GAO G, 2005. Direct evidence of explosive release of endogenous phosphorus in large shallow lakes caused by wind and wave disturbance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 14(1): 66-71. | |
| [27] | 朱红伟, 蒋基安, 程鹏达, 等, 2013. 泥沙污染物起动再悬浮释放机理[J]. 水科学进展, 24(4): 537-542. |
| ZHU H W, JIANG J A, CHENG P D, et al., 2013. Mechanism of pollutant release due to sediment re-suspension[J]. Advances in Water Science, 24(4): 537-542. |
| [1] | 潘璇, 罗竣潇, 唐炳然, 郭翔宇, 何强, 李宏. 载氧沸石与水丝蚓对沉积物-水剖面氮迁移转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(5): 763-772. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
