生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1285-1292.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.001
• 研究论文 •
下一篇
姜超强1( ), 李晨2, 朱启法3, 徐海清3, 刘炎红2, 沈嘉1, 阎轶峰1, 余飞1, 祖朝龙1,*(
), 李晨2, 朱启法3, 徐海清3, 刘炎红2, 沈嘉1, 阎轶峰1, 余飞1, 祖朝龙1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-08
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
*祖朝龙(1964年生),男,研究员,主要从事作物栽培研究。E-mail: lcz2468@sina.com作者简介:姜超强(1980年生),男,副研究员,博士,主要从事作物营养与高效施肥研究。E-mail: chaoqjiang@163.com
基金资助:
JIANG Chaoqiang1( ), LI Chen2, ZHU Qifa3, XU Haiqing3, LIU Yanhong2, SHEN Jia1, YAN Yifeng1, YU Fei1, ZU Chaolong1,*(
), LI Chen2, ZHU Qifa3, XU Haiqing3, LIU Yanhong2, SHEN Jia1, YAN Yifeng1, YU Fei1, ZU Chaolong1,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-08
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
种植模式是影响农田生态系统碳汇效应和经济效益的关键因素。探明不同种植模式碳汇特征及经济效益,对于优化当地种植模式、发展低碳绿色农业和保障农业可持续发展具有重要意义。该研究在安徽皖南地区2020—2021年设置单季稻、烟稻轮作、稻麦轮作、再生稻种植等4种种植模式,采用生命周期评价法评价了各种植模式的净碳汇效应和经济效益,系统地分析了各模式及作物的碳足迹构成、大小及其影响因素。结果表明,(1)各处理经济净收益的大小表现为烟稻>再生稻>稻麦>单季稻。烟叶高产值保障烟稻轮作的高经济效益;再生稻种植的水稻(Oryza sativa L.)产量为各种植模式中最高,其头季和再生季产量合计为12921.5 kg∙hm-2。(2)各处理净碳汇大小表现为稻麦>再生稻>单季稻>烟稻。再生稻N2O排放量和碳排放总量比稻麦轮作分别显著降低37.2%和9.2%,再生稻生态系统的CH4和N2O分别占碳足迹构成的54.5%和18.0%。(3)通过控制农田水分、提高肥料利用率以及对再生稻适当高留桩等方式降低CH4排放是再生稻种植模式减少碳排放的关键。烤烟(Nicotiana tabacum L.)生态系统碳足迹构成中N2O、肥料和农膜所占总排放的比例均超过了20%,并且其劳动力(11.7%)和燃油(12.7%)所占比例远大于水稻和小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)。(4)各种植模式中,烟稻轮作具有较高的经济效益,是保障烟粮双丰收的高效种植模式,但是呈现负碳汇效应,因此,应重点加强该模式机械化生产和烟叶烘烤节能减耗方面的研究。而再生稻水稻产量高,且成本投入和碳排放较低,符合中国倡导的“双碳”理念,应在该区和类似区域大力推广。综上,该研究定量评价了皖南地区4种种植模式的经济效益和碳汇效应,为该区和类似区域农业节能减排和绿色高效生产提供了技术模式及理论依据。
中图分类号:
姜超强, 李晨, 朱启法, 徐海清, 刘炎红, 沈嘉, 阎轶峰, 余飞, 祖朝龙. 皖南不同种植模式碳汇效应及经济效益评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1285-1292.
JIANG Chaoqiang, LI Chen, ZHU Qifa, XU Haiqing, LIU Yanhong, SHEN Jia, YAN Yifeng, YU Fei, ZU Chaolong. Evaluation of Carbon Sink and Economic Benefit in Different Planting Patterns in Southern Anhui[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1285-1292.
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | 播种或移栽日期 Sowing or transplanting date | 收获日期 Harvest date | 肥料用量 Fertilizer application rate/(kg∙hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | ||||
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 2020-06-03 | 2020-10-07 | 180 | 90 | 90 |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 2020-03-21 | 2020-07-20 | 105 | 160 | 360 |
| 晚稻 | 2020-07-22 | 2020-10-26 | 75 | 40 | 40 | |
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 2020-06-03 | 2020-10-07 | 180 | 90 | 90 |
| 冬小麦 | 2020-10-30 | 2021-05-28 | 150 | 90 | 90 | |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 2020-04-20 | 2020-08-15 | 150 | 75 | 75 |
| 再生稻 | — | 2020-10-30 | 60 | 30 | 30 | |
表1 不同种植模式的农田管理情况
Table 1 Management practice of different planting patterns
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | 播种或移栽日期 Sowing or transplanting date | 收获日期 Harvest date | 肥料用量 Fertilizer application rate/(kg∙hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | ||||
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 2020-06-03 | 2020-10-07 | 180 | 90 | 90 |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 2020-03-21 | 2020-07-20 | 105 | 160 | 360 |
| 晚稻 | 2020-07-22 | 2020-10-26 | 75 | 40 | 40 | |
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 2020-06-03 | 2020-10-07 | 180 | 90 | 90 |
| 冬小麦 | 2020-10-30 | 2021-05-28 | 150 | 90 | 90 | |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 2020-04-20 | 2020-08-15 | 150 | 75 | 75 |
| 再生稻 | — | 2020-10-30 | 60 | 30 | 30 | |
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | 收获产量 Yield/(kg∙hm-2) | 收获产值 Output/(yuan∙hm-2) | 总产值 Total output/(yuan∙hm-2) | 总投入 Total input/(yuan∙hm-2) | 净收益 Net income/(yuan∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 9513.5 | 18265.9 | 18265.9d | 9150.0d | 9115.9c |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 1903.0 | 53284.0 | 68292.6a | 48576.0a | 19716.6a |
| 晚稻 | 7817.0 | 15008.6 | ||||
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 9293.5 | 18587.0 | 30216.8b | 17280.0b | 12936.8b |
| 冬小麦 | 6390.0 | 11629.8 | ||||
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 8557.0 | 17456.3 | 26359.9c | 12012.0c | 14347.9b |
| 再生稻 | 4364.5 | 8903.6 |
表2 不同种植模式作物产量及经济效益
Table 2 Yield and economic benefits of different planting patterns
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | 收获产量 Yield/(kg∙hm-2) | 收获产值 Output/(yuan∙hm-2) | 总产值 Total output/(yuan∙hm-2) | 总投入 Total input/(yuan∙hm-2) | 净收益 Net income/(yuan∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 9513.5 | 18265.9 | 18265.9d | 9150.0d | 9115.9c |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 1903.0 | 53284.0 | 68292.6a | 48576.0a | 19716.6a |
| 晚稻 | 7817.0 | 15008.6 | ||||
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 9293.5 | 18587.0 | 30216.8b | 17280.0b | 12936.8b |
| 冬小麦 | 6390.0 | 11629.8 | ||||
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 8557.0 | 17456.3 | 26359.9c | 12012.0c | 14347.9b |
| 再生稻 | 4364.5 | 8903.6 |
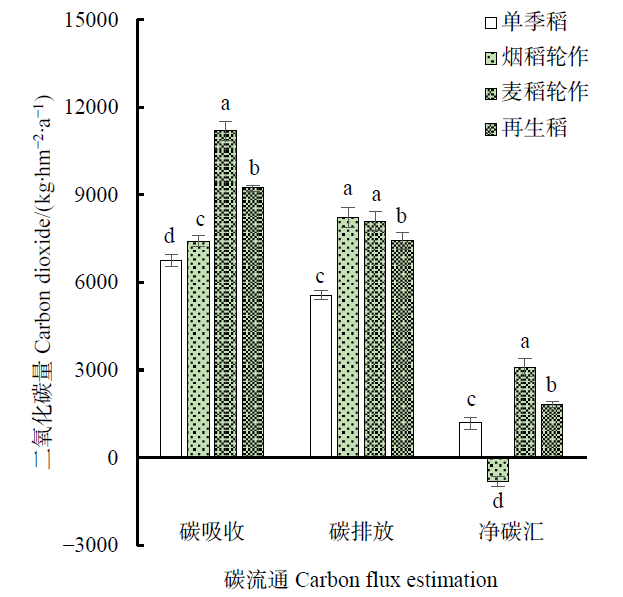
图1 不同种植模式农田生态系统生产中的碳流通 图中同一参数不同小写字母表示处理间差异达到显著差异(P<0.05,n=3)
Figure 1 Carbon flux estimation in paddy ecosystem production under different planting patterns Values followed by different lowercase letters in the same parameter are significantly different among the treatment (P<0.05, n=3)
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | 碳吸收 C adsorption/ (kg∙hm-2∙a-1) | 碳排放 C emission/ (kg∙hm-2∙a-1) | 净碳汇 Net C sink/ (kg∙hm-2∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 6761.0a | 5573.2a | 1187.9b |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 1836.6f | 3300.0c | -1463.4d |
| 晚稻 | 5581.3c | 4933.4b | 647.9c | |
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 6675.9a | 5573.2a | 1102.7b |
| 冬小麦 | 4523.2d | 2535.8d | 1987.4a | |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 6119.5b | 4801.5b | 1318.0b |
| 再生稻 | 3118.9e | 2624.4d | 494.5c |
表3 不同种植模式下农田生态系统不同作物的碳流通
Table 3 Carbon flux estimation of different crops in paddy ecosystem production under different planting patterns
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | 碳吸收 C adsorption/ (kg∙hm-2∙a-1) | 碳排放 C emission/ (kg∙hm-2∙a-1) | 净碳汇 Net C sink/ (kg∙hm-2∙a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 6761.0a | 5573.2a | 1187.9b |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 1836.6f | 3300.0c | -1463.4d |
| 晚稻 | 5581.3c | 4933.4b | 647.9c | |
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 6675.9a | 5573.2a | 1102.7b |
| 冬小麦 | 4523.2d | 2535.8d | 1987.4a | |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 6119.5b | 4801.5b | 1318.0b |
| 再生稻 | 3118.9e | 2624.4d | 494.5c |
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | CH4 | N2O | 肥料 Fertilizers | 劳力 Labor | 柴油 Diesel | 农药 Pesticides | 种子 Seeds | 农膜 Film | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 56.5 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 1.9 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 38.8 | 19.5 | 15.9 | 6.0 | 8.9 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 8.3 | 100 |
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 39.4 | 23.1 | 24.0 | 2.5 | 6.3 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 54.5 | 18.0 | 16.5 | 1.7 | 7.5 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 100 |
表4 不同种植模式的碳足迹构成
Table 4 Source of carbon footprint under different planting patterns %
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | CH4 | N2O | 肥料 Fertilizers | 劳力 Labor | 柴油 Diesel | 农药 Pesticides | 种子 Seeds | 农膜 Film | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 56.5 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 1.9 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 烟稻轮作 Tobacco-rice | 38.8 | 19.5 | 15.9 | 6.0 | 8.9 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 8.3 | 100 |
| 稻麦轮作 Rice-wheat | 39.4 | 23.1 | 24.0 | 2.5 | 6.3 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 54.5 | 18.0 | 16.5 | 1.7 | 7.5 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | CH4 | N2O | 肥料 Fertilizers | 劳力 Labor | 柴油 Diesel | 农药 Pesticides | 种子 Seeds | 农膜 Film | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 56.5 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 1.9 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 烟稻 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 1.4 | 24.4 | 26.2 | 11.7 | 12.7 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 20.7 | 100 |
| 晚稻 | 63.9 | 16.3 | 8.9 | 2.1 | 6.4 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 100 | |
| 稻麦 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 56.5 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 1.9 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 冬小麦 | 1.8 | 42.3 | 35.4 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 1.3 | 8.9 | 0.0 | 100 | |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 56.2 | 14.0 | 18.2 | 2.1 | 7.3 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 再生稻 | 51.4 | 25.5 | 13.3 | 1.0 | 8.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100 |
表5 不同作物的碳足迹构成
Table 5 Source of carbon footprint of different crops %
| 种植模式 Planting patterns | 作物种类 Crop types | CH4 | N2O | 肥料 Fertilizers | 劳力 Labor | 柴油 Diesel | 农药 Pesticides | 种子 Seeds | 农膜 Film | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单季稻 Single-cropping rice | 中稻 | 56.5 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 1.9 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 烟稻 Tobacco-rice | 烤烟 | 1.4 | 24.4 | 26.2 | 11.7 | 12.7 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 20.7 | 100 |
| 晚稻 | 63.9 | 16.3 | 8.9 | 2.1 | 6.4 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 100 | |
| 稻麦 Rice-wheat | 中稻 | 56.5 | 14.4 | 18.8 | 1.9 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 冬小麦 | 1.8 | 42.3 | 35.4 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 1.3 | 8.9 | 0.0 | 100 | |
| 再生稻 Ratoon rice | 头季稻 | 56.2 | 14.0 | 18.2 | 2.1 | 7.3 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 100 |
| 再生稻 | 51.4 | 25.5 | 13.3 | 1.0 | 8.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100 |
| [1] |
MA J, MA E D, XU H, et al., 2019. Wheat straw management affects CH4 and N2O emissions from rice fields[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41(5): 1022-1028.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
TANG H M, XIAO X P, LI C, et al., 2019. Effects of different soil tillage systems on soil carbon management index under double-cropping rice field in southern China[J]. Agronomy Journal, 111(1): 440-446.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
THANGARAJAN R, BOLAN N S, TIAN G L, et al., 2013. Role of organic amendment application on greenhouse gas emission from soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 465(1): 72-96.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZISKA L H, FLEISHER D H, LINSCOMBE S, 2018. Ratooning as an adaptive management tool for climatic change in rice systems along a northsouth transect in the southern Mississippi Valley[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 263: 409-416.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ZOU J W, LIU S W, QIN Y M, et al., 2009. Sewage irrigation increased methane and nitrous oxide emission from rice paddies in southeast China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 129(4): 516-522.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 卜容燕, 韩上, 程文龙, 等, 2022. 皖南单季稻区种植利用紫云英对水稻产量、氮肥利用率及稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, [2022-05-20] https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5498.S.20211203.1239.004.html. |
| BU R Y, HAN S, CHENG W L, et al., 2022. Effects of Chinese milk vetch on yield, nitrogen use efficiency and quality of rice in single cropping rice area of Southern Anhui Province[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, [2022-05-20] https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5498.S.20211203.1239.004.html. | |
| [7] | 陈中督, 徐春春, 纪龙, 等, 2019. 长江中游地区稻麦生产系统碳足迹及氮足迹综合评价[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25(7): 1125-1133. |
| CHEN Z D, XU C C, JI L, et al., 2019. Comprehensive evaluation for carbon and nitrogen footprints of rice-wheat rotation system in Middle Yangtze River Basin[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 25(7): 1125-1133. | |
| [8] | 邓桥江, 曹凑贵, 李成芳, 2019. 不同再生稻栽培模式对稻田温室气体排放和产量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(6): 11373-1380. |
| DENG Q J, CAO C G, LI C F, 2019. Effects of different ratooning cultivation modes on greenhouse gas emissions and grain yields in paddy fields[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(6): 1373-1380. | |
| [9] | 董建江, 邵伏文, 张林, 等, 2015. 不同耕作模式对稻田土壤理化性质及经济效益的影响[J]. 土壤, 47(3): 509-514. |
| DONG J J, SHAO F W, ZHANG L, et al., 2015. Effects of tillage patterns on physical and chemical properties of paddy soils and economic efficiency[J]. Soils, 47(3): 509-514. | |
| [10] | 高嵩涓, 周国朋, 曹卫东, 2020. 南方稻田紫云英作冬绿肥的增产节肥效应与机制[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(12): 2115-2126. |
| GAO S J, ZHOU G P, CAO W D, 2020. Effects of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) as winter green manure on rice yield and rate of fertilizer application in rice paddies in south China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(12): 2115-2126. | |
| [11] | 国家技术监督局, 1992. 烤烟: GB 2635-1992 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| The National Technical Supervision Bureau, 1992. Flue-cured tobacco: GB 2635-1992 [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press. | |
| [12] | 和智君, 罗会龙, 钟浩, 等, 2010. 烟叶烘烤密集型烤房节能技术途径分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 26(8): 337-340. |
| HE Z J, LUO H L, ZHONG H, et al., 2010. The energy saving technology analysis of bulk curing barn[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 26(8): 337-340. | |
| [13] | 胡乃娟, 史航, 朱利群, 2018. 不同麦秸还田方式对周年稻麦轮作农田碳足迹的影响[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 27(12): 2775-2783. |
| HU N J, SHI H, ZHU L Q, 2018. Effects of dfifferent straw returning modes on carbon footprint in a rice-wheat rotation system[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 27(12): 2775-2783. | |
| [14] | 胡志华, 李大明, 徐小林, 等, 2017. 不同有机培肥模式下双季稻田碳汇效应与收益评估[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 25(2): 157-165. |
| HU Z H, LI D M, XU X L, et al., 2017. Evaluation of net carbon sink effects and costs/benefits of double-cropped rice fields under different organic fertilizer applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 25(2): 157-165. | |
| [15] | 姜振辉, 杨旭, 刘益珍, 等, 2019. 春玉米-晚稻与早稻-晚稻种植模式碳足迹比较[J]. 生态学报, 39(21): 8091-8099. |
| JIANG Z H, YANG X, LIU Y Z, et al., 2019. Comparison of carbon footprint between spring maize-late rice and early rice-late rice cropping system[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(21): 8091-8099. | |
| [16] | 蒋静艳, 黄耀, 宗良纲, 2003. 水分管理与秸杆施用对稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 23(5): 552-556. |
| JIANG J Y, HUANG Y, ZONG L G, 2003. Influence of water controlling and straw application on CH4 and N2O from rice field[J]. China Environmental Science, 23(5): 552-556. | |
| [17] | 孔盼, 夏苏敬, 张海维, 等, 2021. 耕作方式对早稻-再生稻稻田氨挥发的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(8): 1627-1633. |
| KONG P, XIA S J, ZHANG H W, et al., 2021. Effects of tillage methods on ammonia volatilization of early season rice-ratooning rice fields[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(8): 1627-1633. | |
| [18] | 李得兰, 徐华, 蔡祖聪, 2008. 稻田CH4和N2O排放消长关系及其减排措施[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 27(6): 2123-2130. |
| LI D L, XU H, CAI Z C, 2008. Trade-off relationship and mitigation options of methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddy field[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 27(6): 2123-2130. | |
| [19] | 林文雄, 陈鸿飞, 张志兴, 等, 2015. 再生稻产量形成的生理生态特性与关键栽培技术的研究与展望[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 23(4): 392-401. |
| LIN W X, CHEN H F, ZHANG Z X, et al., 2015. Research and prospect on physio-ecological properties of ratoon rice yield formation and its key cultivation technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 23(4): 392-401. | |
| [20] |
刘青丽, 蒋雨洲, 邹焱, 等, 2020. 烟田生态系统碳收支研究[J]. 作物学报, 46(8): 1258-1265.
DOI |
|
LIU Q L, JIANG Y Z, ZOU Y, et al., 2020. The study of carbon budget on field-tobacco ecosystem[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 46(8): 1258-1265.
DOI URL |
|
| [21] | 刘青丽, 邹焱, 蒋雨洲, 等, 2021. 不同施肥措施下烟田生态系统碳收支研究[J]. 中国烟草科学, 42(3): 50-56. |
| LIU Q L, ZOU Y, JIANG Y Z, et al., 2021. Effects of fertilization measures on carbon budget of the tobacco-field ecosystem[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 42(3): 50-56. | |
| [22] | 刘巽浩, 徐文修, 李增嘉, 等, 2013. 农田生态系统碳足迹法:误区、改进与应用--兼析中国集约农作碳效率[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 34(6): 1-11. |
| LIU X H, XU W X, LI Z J, et al., 2013. The missteps, improvement and application of carbon footprint methodology in farmland ecosystems with the case study of analyzing the carbon efficiency of China’s intensive farming[J]. Journal of China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 34(6): 1-11. | |
| [23] | 吕泽芳, 高珍珍, 刘章勇, 等, 2020. 再生稻栽培模式下冬半年覆盖植被对土壤CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 59(15): 60-65. |
| LÜ Z F, GAO Z Z, LIU Z Y, et al., 2020. Effects of cover plant in winter on soil CH4 and N2O emission under the ratoon rice system[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science, 59(15): 60-65. | |
| [24] | 马怀英, 王上, 杨亚东, 等, 2021. 燕麦与豆科作物间作的产量、经济效益与碳足迹分析[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 26(8): 23-32. |
| MA H Y, WANG S, YANG Y D, et al., 2021. Intercropping of oat with mung bean, peanut, and soybean: Yield advantages, economic benefits and carbon footprints[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 26(8): 23-32. | |
| [25] | 孟宇辉, 金文俊, 董召荣, 等, 2019. 江淮地区不同水旱轮作模式的资源利用效率与经济效益比较[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(11): 3357-3365. |
| MENG Y H, JIN W J, DONG Z R, et al., 2019. Comparison of resource utilization efficiency and economic benefit of different paddy-upland rotation systems in Jianghuai region[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(11): 3357-3365. | |
| [26] | 佘玮, 黄璜, 官春云, 等, 2016. 我国典型农作区作物生产碳汇功能研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 18(1): 106-113. |
| SHE W, HUANG H, GUAN C Y, et al., 2016. Study on the carbon sink function of crop production in typical agricultural areas of China[J]. Engineering Science, 18(1): 106-113. | |
| [27] | 苏燕, 李婕, 曹雪颖, 等, 2020. 水旱轮作模式下马铃薯根际土壤细菌群落多样性分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 51(10): 2374-2382. |
| SU Y, LI J, CAO X Y, et al., 2020. Diversity analysis of bacterial community in potato rhizosphere soil under the mode of paddy-upland rotation[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 51(10): 2374-2382. | |
| [28] | 唐海明, 李超, 肖小平, 等, 2020. 不同耕作模式对双季稻田生态系统净碳汇效应及收益的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(2): 215-222. |
| TANG H M, LI C, XIAO X P, et al., 2020. Influences of different tillage on net carbon sink and economic benefit of paddy ecosystem under double-cropping rice field[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(2): 215-222. | |
| [29] | 田卡, 张丽, 钟旭华, 等, 2015. 稻草还田和冬种绿肥对华南双季稻产量及稻田CH4排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(3): 592-598. |
| TIAN K, ZHANG L, ZHONG X H, et al., 2015. Effects of rice straw and winter green manure incorporations on grain yields and methane emissions of double-season rice (Oryza sativa) field in south China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(3): 592-598. | |
| [30] | 王浩田, 姜超强, 蒋瑀霁, 等, 2020. 皖南沿江平原不同年限烟-稻轮作土壤团聚体组成与烤烟产质量的关系[J]. 土壤, 52(5): 1057-1067. |
| WANG H T, JIANG C Q, JIANG Y J, et al., 2020. Relationship between soil aggregate composition with yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco under different rice-tobacco rotation years in Yangtse plain South Anhui[J]. Soils, 52(5): 1057-1067. | |
| [31] | 王天宇, 樊迪, 宋开付, 等, 2021. 巢湖圩区再生稻田甲烷及氧化亚氮的排放规律研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(8): 1829-1838. |
| WANG T Y, FAN D, SONG K F, et al., 2021. Reduced methane and nitrous oxide emissions from ratoon rice paddy in Chaohu polder area, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(8): 1829-1838. | |
| [32] | 吴玉红, 王吕, 崔月贞, 等, 2021. 轮作模式及秸秆还田对水稻产量、稻米品质及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27(11): 1926-1937. |
| WU Y H, WANG L, CUI Y Z, et al., 2021. Rice yield, quality, and soil fertility in response to straw incorporation and rotation pattern[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 27(11): 1926-1937. | |
| [33] | 相智华, 方双红, 姚旺家, 等, 2020. 皖南烟区新型种植模式研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 48(3): 232-235. |
| XIANG Z H, FANG S H, YAO W J, et al., 2020. Research on new cropping system in Southern Anhui tobacco area[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 48(3): 232-235. | |
| [34] | 徐富贤, 熊洪, 张林, 等, 2015. 再生稻产量形成特点与关键调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 48(9): 1702-1717. |
| XU F X, XIONG H, ZHANG L, et al., 2015. Progress in research of yield formation of ratooning rice and its high-yielding key regulation technologies[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 48(9): 1702-1717. | |
| [35] | 曾昭海, 2018. 豆科作物与禾本科作物轮作研究进展及前景[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 26(1): 57-61. |
| ZENG Z H, 2018. Progress and perspective of legume-gramineae rotations[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 26(1): 57-61. | |
| [36] | 张浪, 徐华勤, 李林林, 等, 2019. 再生稻和双季稻田CH4排放对比研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 52(12): 2101-2113. |
| ZHANG L, XU H Q, LI L L, et al., 2019. Comparative study on CH4 emission from ratoon rice and double-cropping rice fields[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 52(12): 2101-2113. | |
| [37] | 张立成, 邵继海, 林毅青, 等, 2017. 稻-稻-油菜轮作对土壤微生物活性和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(2): 204-210. |
| ZHANG L C, SHAO J H, LIN Y Q, et al., 2017. Influence of microbial diversity and activity of soil on the rice-rice-rape rotation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(2): 204-210. | |
| [38] | 张鹏, 钟川, 周泉, 等, 2019. 不同冬种模式对稻田土壤碳库管理指数的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报 (中英文), 27(8): 1163-1171. |
| ZHANG P, ZHONG C, ZHOU Q, et al., 2019. Effects of different winter planting patterns on carbon management index of paddy field[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 27(8): 1163-1171. | |
| [39] | 张若焰, 陈儒, 王秀娟, 等, 2019. 现代烟草农业的碳效应核算与分析--以陕西省烟草合作社为例[J]. 中国生态农业学报 (中英文), 27(12): 1903-1915. |
| ZHANG R Y, CHEN R, WANG X J, et al., 2019. Carbon effect of modern tobacco agriculture: Based on tobacco cooperatives in Shaanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 27(12): 1903-1915. |
| [1] | 陈科屹, 林田苗, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 天保工程20年对黑龙江大兴安岭国有林区森林碳库的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [2] | 张露, 何雨霏, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 金军. 2011—2020年汾渭平原农田生态系统碳足迹的时空格局演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1149-1162. |
| [3] | 郝蕾, 翟涌光, 戚文超, 兰穹穹. 2001-2020年内蒙古植被碳源/碳汇时空动态及对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 825-834. |
| [4] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [5] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [6] | 吴昊平, 秦红杰, 贺斌, 尤毅, 陈金峰, 邹春萍, 杨思雨, 郝贝贝. 基于碳中和的农业面源污染治理模式发展态势刍议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1919-1926. |
| [7] | 李成伟, 刘章勇, 龚松玲, 杨伟, 李绍秋, 朱波. 稻作模式改变对稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 961-968. |
| [8] | 郝小雨, 王晓军, 高洪生, 毛明艳, 孙磊, 马星竹, 周宝库, 迟凤琴, 李伟群. 松嫩平原不同秸秆还田方式下农田温室气体排放及碳足迹估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 318-325. |
| [9] | 曹云, 孙应龙, 姜月清, 万君. 黄河流域净生态系统生产力的时空分异特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2101-2110. |
| [10] | 孔盼, 夏苏敬, 张海维, 朱建强. 耕作方式对早稻-再生稻稻田氨挥发的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1627-1633. |
| [11] | 韩芳, 包媛媛, 刘项宇, 张新永, 韦灯会, 张浩然, 田清龙. 不同轮作方式对马铃薯根际土壤真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1412-1419. |
| [12] | 夏梓泰, 程伟威, 赵吉霞, 李永梅, 范茂攀. 不同种植模式对玉米根系及土壤团聚体稳定性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2331-2338. |
| [13] | 赵其国, 沈仁芳, 滕应, 李秀华. 中国重金属污染区耕地轮作休耕制度试点进展、问题及对策建议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(12): 2003-2007. |
| [14] | 赵其国, 滕应, 黄国勤. 中国探索实行耕地轮作休耕制度试点问题的战略思考[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(1): 1-5. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
