生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1695-1705.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.016
潘国营1,2( ), 林凤莲1,2, 袁锋1,2, 罗倩1,2, 高倩倩1,2, 李键1,2, 吴承祯3, 陈灿1,2,*(
), 林凤莲1,2, 袁锋1,2, 罗倩1,2, 高倩倩1,2, 李键1,2, 吴承祯3, 陈灿1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-07
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
* E-mail: canchen@fafu.edu.cn作者简介:潘国营(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向城市林业。E-mail: panguoying1119@163.com
基金资助:
PAN Guoying1,2( ), LIN Fenglian1,2, YUAN Feng1,2, LUO Qian1,2, GAO Qianqian1,2, LI Jian1,2, WU Chengzhen3, CHEN Can1,2,*(
), LIN Fenglian1,2, YUAN Feng1,2, LUO Qian1,2, GAO Qianqian1,2, LI Jian1,2, WU Chengzhen3, CHEN Can1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-03-07
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
城镇化水污染对中国的水安全压力日益严重,而微生物在净化污水上潜力巨大。为筛选优良净化城市污水的优势真菌和细菌,揭示各菌株去除污水特性及规律,对来源于武夷山市污水处理厂处具有代表性的再力花(Thalia dealbata Link)、香根草(Vetiveria zizanioides L.)、花叶芦荻(Arundo donax var. versicolor)等植物根际土壤中的5株高效细菌(B)和5株高效真菌(F),分别投加到高、中、低质量浓度人工模拟污水和无菌超纯水对照组中,测定经12、24、36、48 h处理后污水中的总氮(TN)、氨氮(NH4+-N)、化学需氧量(COD)和总磷(TP)的质量浓度,并分析各菌株对污染物的去除规律和污水净化效果。结果表明,(1)各菌株对污水有较好的去除效果,且各菌株对污水去除率差异以及与对照之间差异均达到显著水平(P<0.05),去除效果总体表现为TN>NH4+-N>COD>TP,除TP外,均在中质量浓度污水中去除效果最好。各菌株对污染物去除率分别为53.75%—80.67%(TN)、27.5%—72.05%(NH4+-N)、36.55%—68.96%(COD)和22.15%—52.15%(TP)。(2)去除4种污染物优势菌株各不相同,可总结为3个类型组(F9、B3和B4;F7、F10和B4;F9和B1)以及一个独立真菌F7。去污能力方面,真菌去除污水能力(55.27%)优于细菌处理(52.14%)。(3)菌株在不同处理时间下去除效果差异明显,随时间推移TN、NH4+-N、COD和TP质量浓度均呈下降趋势,48 h去除效果最佳。(4)细菌菌株平均降解率符合多项式模型,真菌菌株平均降解率符合幂指数模型。该研究结果表明污水质量浓度大小、菌株自身特性和处理时间可能是影响污染物去除效果存在差异的主要原因。而微生物长时间持续性去污能力和规律还需进一步研究。
中图分类号:
潘国营, 林凤莲, 袁锋, 罗倩, 高倩倩, 李键, 吴承祯, 陈灿. 10株高效菌株对人工污水净化能力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1695-1705.
PAN Guoying, LIN Fenglian, YUAN Feng, LUO Qian, GAO Qianqian, LI Jian, WU Chengzhen, CHEN Can. Study on Purification Ability of 10 Highly Efficient Strains in Artificial Wastewater[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1695-1705.
| 湿地类型 Wetland type | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全氮 TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全磷 TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全钾 TK)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(水解氮 Hydrolyzed Nitrogen)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效磷 Available Phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效钾 Available potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 再力花 Thalia dealbata Link | 71.32 | 4.15 | 5.63 | 0.52 | 125.32 | 377.02 | 76.80 |
| 香根草 Vetiveria zizanioides L. | 74.87 | 2.93 | 6.02 | 0.75 | 260.55 | 412.79 | 91.48 |
| 花叶芦荻 A. donax var.versicolor | 67.77 | 4.06 | 5.10 | 0.39 | 115.05 | 395.00 | 62.24 |
表1 湿地系统的基础地力
Table 1 Soil fertility of wetland system
| 湿地类型 Wetland type | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全氮 TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全磷 TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全钾 TK)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(水解氮 Hydrolyzed Nitrogen)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效磷 Available Phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效钾 Available potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 再力花 Thalia dealbata Link | 71.32 | 4.15 | 5.63 | 0.52 | 125.32 | 377.02 | 76.80 |
| 香根草 Vetiveria zizanioides L. | 74.87 | 2.93 | 6.02 | 0.75 | 260.55 | 412.79 | 91.48 |
| 花叶芦荻 A. donax var.versicolor | 67.77 | 4.06 | 5.10 | 0.39 | 115.05 | 395.00 | 62.24 |
| 污水质量浓度 Mass concentration in sewage | 全氮 TN | 氨氮 NH4+-N | 全磷 TP | 化学需氧量COD | 镉 Cd2+ | 铅 Pb2+ | 锌 Zn2+ | 铜 Cu2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration (H) | 40 | 24 | 3 | 400 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration (M) | 30 | 18 | 2 | 300 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration (L) | 20 | 12 | 1 | 200 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
表2 不同质量浓度污水各项指标质量浓度
Table 2 The mass concentrations of indicators of different mass concentration wastewater mg∙L-1
| 污水质量浓度 Mass concentration in sewage | 全氮 TN | 氨氮 NH4+-N | 全磷 TP | 化学需氧量COD | 镉 Cd2+ | 铅 Pb2+ | 锌 Zn2+ | 铜 Cu2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration (H) | 40 | 24 | 3 | 400 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration (M) | 30 | 18 | 2 | 300 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration (L) | 20 | 12 | 1 | 200 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
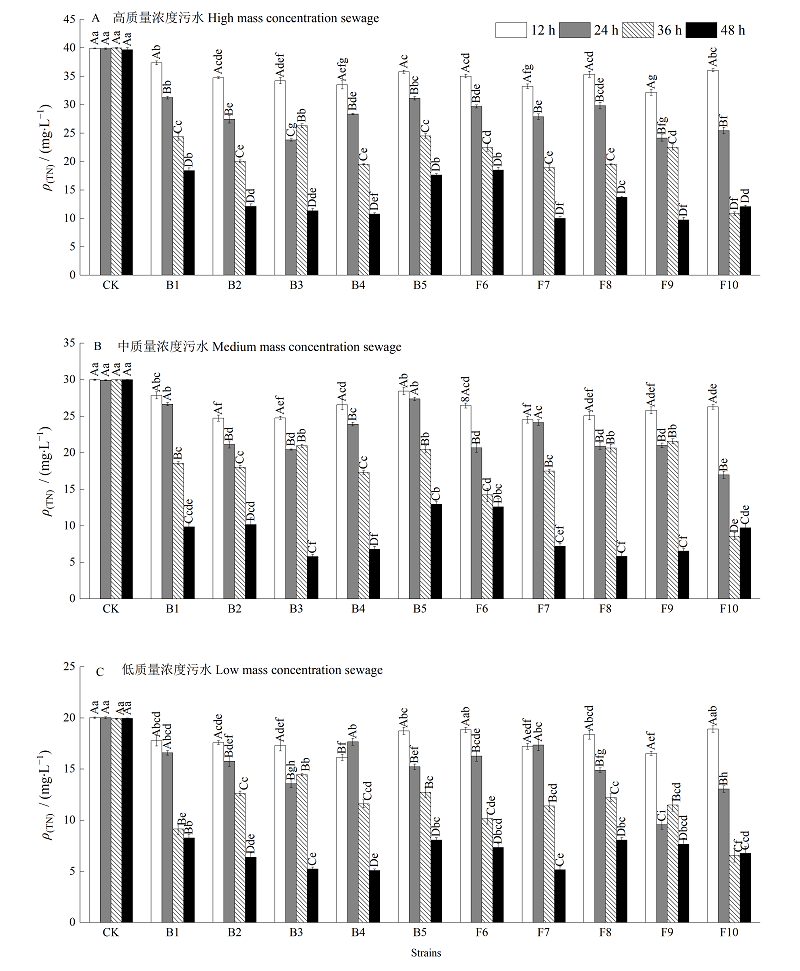
图1 各菌株处理下及未有菌株处理下污水中TN质量浓度大小变化 不同小写字母表示同一处理时间不同菌株间差异显著;不同大写字母表示同一菌株不同处理时间差异显著,n=3;下同
Fig. 1 Changes of TN mass concentration in swage with and without bacteria treatments Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different strains at the same treatment time; different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatment times of the same strain, n=3;the same below
| 变异来源 Source of variation | df | F | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮 TN | 氨氮 NH4+-N | 化学需氧量 COD | 全磷 TP | ||
| 校正模型 Calibration model | 131 | 433.485** | 176.183** | 393.199** | 1311.757** |
| 截距 Intercept | 1 | 271060.287** | 141796.804** | 294054.424** | 1942.975** |
| 质量浓度 Mass concentration | 2 | 8831.66** | 5094.498** | 14295.696** | 294.235** |
| 菌株 Strains | 10 | 893.397** | 202.431** | 748.072** | 101.183** |
| 时间 Time | 3 | 7469.366** | 2340.11** | 3756.656** | 35.719** |
| 质量浓度×菌株 Mass concentration×strains | 20 | 58.118** | 50.092** | 27.968** | 200.199** |
| 质量浓度×时间 Mass concentration×time | 6 | 281.593** | 95.853** | 200.51** | 60.442** |
| 菌株×时间 Strains×time | 30 | 137.928** | 29.986** | 67.645** | 300.128** |
| 质量浓度×菌株×时间 Mass concentration×strains×time | 60 | 13.189** | 22.831** | 6.254** | 600.037** |
表3 不同菌株处理下TN、NH4+-N、COD、TP质量浓度的动态变化的多因素分析
Table 3 Multi-factor Analysis of the dynamic changes of TN, NH4+-N, COD, TP mass concentration in different strains
| 变异来源 Source of variation | df | F | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮 TN | 氨氮 NH4+-N | 化学需氧量 COD | 全磷 TP | ||
| 校正模型 Calibration model | 131 | 433.485** | 176.183** | 393.199** | 1311.757** |
| 截距 Intercept | 1 | 271060.287** | 141796.804** | 294054.424** | 1942.975** |
| 质量浓度 Mass concentration | 2 | 8831.66** | 5094.498** | 14295.696** | 294.235** |
| 菌株 Strains | 10 | 893.397** | 202.431** | 748.072** | 101.183** |
| 时间 Time | 3 | 7469.366** | 2340.11** | 3756.656** | 35.719** |
| 质量浓度×菌株 Mass concentration×strains | 20 | 58.118** | 50.092** | 27.968** | 200.199** |
| 质量浓度×时间 Mass concentration×time | 6 | 281.593** | 95.853** | 200.51** | 60.442** |
| 菌株×时间 Strains×time | 30 | 137.928** | 29.986** | 67.645** | 300.128** |
| 质量浓度×菌株×时间 Mass concentration×strains×time | 60 | 13.189** | 22.831** | 6.254** | 600.037** |
| 测定指标 Measurement index | 细菌 Bacterial | 真菌 Fungi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合模型 Fit model | R2 | 拟合模型 Fit model | R2 | ||
| 全氮 TN | y=0.037x2-0.0049x+0.092 | 0.9881 | y=0.1334x1.185 | 0.9999 | |
| 氨氮 NH4+-N | y= -0.0059x2+0.1688x-0.0374 | 0.9976 | y=0.1151x1.0814 | 0.9883 | |
| 化学需氧量 COD | y= -0.0016x2+0.1379x-0.0184 | 0.9927 | y=0.1572x0.9493 | 0.9914 | |
| 全磷 TP | y= -0.029x2+0.2517x-0.173 | 0.9881 | y=0.1121x1.0105 | 0.9748 | |
| 平均去除率 Average adsorption rate | y=0.0002x2+0.1382x-0.034 | 1 | y=0.1292x1.0615 | 0.9885 | |
表4 细菌与真菌拟合模型表
Table 4 Fitting model table of bacteria and fungi
| 测定指标 Measurement index | 细菌 Bacterial | 真菌 Fungi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟合模型 Fit model | R2 | 拟合模型 Fit model | R2 | ||
| 全氮 TN | y=0.037x2-0.0049x+0.092 | 0.9881 | y=0.1334x1.185 | 0.9999 | |
| 氨氮 NH4+-N | y= -0.0059x2+0.1688x-0.0374 | 0.9976 | y=0.1151x1.0814 | 0.9883 | |
| 化学需氧量 COD | y= -0.0016x2+0.1379x-0.0184 | 0.9927 | y=0.1572x0.9493 | 0.9914 | |
| 全磷 TP | y= -0.029x2+0.2517x-0.173 | 0.9881 | y=0.1121x1.0105 | 0.9748 | |
| 平均去除率 Average adsorption rate | y=0.0002x2+0.1382x-0.034 | 1 | y=0.1292x1.0615 | 0.9885 | |
| [1] |
AHEMAD M, KIBRET M, 2014. Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Cu2+rrent perspective[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 26(1): 1-20.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BARLETTA M, LIMA A R A, COSTA M F, 2019. Distribution, sources and consequences of nutrients, persistent organic pollutants, metals and microplastics in South American estuaries[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 651(Pt 1): 1199-1218.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIU R T, CHI L N, WANG X Z, et al., 2018. Review of metal (hydr) oxide and other adsorptive materials for phosphate removal from water[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6(4): 5269-5280.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
MARTÍNM, GARGALLOS, HERNEZ-CRESPOC, et al., 2013. Phosphorus and nitrogen removal from tertiary treated urban wastewaters by avertical flow constructed wetland[J]. Ecological Engineering, 61(19): 34-42.
DOI URL |
| [5] | MEGHARAJ M, RAMAKRISHNAN B, VENKATESWARLU K, et al., 2011. Bioremediation approaches for organic pollutants: A critical perspective[J]. Environment International, 37(8): 1363-1370. |
| [6] |
VYMAZAL J, 2010. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment[J]. Water, 2(3): 530-549.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WIEBNER A, KAPPELMEYER U, KUSCHK P, et al., 2005. Influence of the redox condition dynamics on the removal efficiency of a laboratory-scale constructed wetland. Water Research, 39(1): 248-256.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
YONG G Z, YANG F, YAN L J, et al., 2015. Microbial community and removal of nitrogen via the addition of a carrier in a pilot-scale duckweed-based wastewater treatment system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 179: 549-558.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG H H, ZHAO Z F, LI S L, et al., 2019. Nitrogen removal by mix-cultured aerobic denitrifying bacteria isolated byultrasound: Performance, co-occurrence pattern and wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 372: 26-36.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 丁健生, 冯求宝, 李敬敏, 等, 2014. 城镇污水处理工艺研究进展[J]. 广东化工, 41(3): 155-156. |
| DING J S, FENG Q B, LI J M, et al., 2014. Research progress of urban sewage treatment technology[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 41(3): 155-156. | |
| [11] | 杜聪, 冯胜, 张毅敏, 等, 2018. 微生物菌剂对黑臭水体水质改善及生物多样性修复效果研究[J]. 环境工程, 36(8): 1-7. |
| DU C, FENG S, ZHANG Y M, et al., 2018. Study on the improvement of water quality and biological diversity of black and odorous water by mic roblal inoculants[J]. Environmental Engineering, 36(8): 1-7. | |
| [12] | 范彩彩, 2013. 鼠尾藻对水体重金属铅、铜、锌、镉的生物吸附效应研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋学院: 18-19. |
| FAN C C, 2013. Study on the bioadsorption effect of Sargassum on water heavy metal lead, copper, zinc and cadmium[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University: 18-19. | |
| [13] | 郭星, 赵光, 孙婷, 等, 2017. 厌氧氨氧化微生物学机制及其在污水脱氮工艺中的应用进展[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 39(1): 45-50. |
| GUO X, ZHAO G, SUN T, et al., 2017. Microbiological mechanism of anammox and its application progress in wastewater denitrification process[J]. World Science and Technology Research and Development, 39(1): 45-50. | |
| [14] | 侯庆杰, 裴海燕, 胡文容, 2011. XP1菌株强化湿地植物脱氮及其对根际微生物的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 24(8): 857-864. |
| HOU Q J, PEI H Y, HU W R, 2011. Enhanced Denitrification with Wetland Plants by Strain XP1 and Its Effect on Rhizosphere Microorganisms[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 24(8): 857-864. | |
| [15] | 胡智勇, 陆开宏, 梁晶晶, 2010. 根际微生物在污染水体植物修复中的作用[J]. 环境科学与技术, 33(5): 75-80. |
| HU Z Y, LU K H, LIANG J J, 2010. The role of rhizosphere microorganisms in phytoremediation of polluted waters[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 33(5): 75-80. | |
| [16] | 黄秋婷, 薛天福, 杨梅, 等, 2020. 几种低温微生物菌株及其组合对北方农村生活污水处理效果[J]. 北京化工大学学报 (自然科学版), 47(3): 50-57. |
| HUANG Q T, XUE T F, YANG M, et al., 2020. Effects of several psychrotroph strains and their combinations on the treatment of rural sewage in northern China[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition), 47(3): 50-57. | |
| [17] | 吉立, 刘晶, 李志威, 等, 2017. 2011-2015年我国水污染事件及原因分析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 33(9): 775-782. |
| JI L, LIU J, LI Z W, et al., 2017. Accidents of water pollution in China in 2011-2015 and their causes[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 33(9): 775-782. | |
| [18] | 金春英, 朱笔通, 赵春贵, 2019. 沼泽红假单胞菌CQV97对养殖水体无机三态氮的去除机制[J]. 华侨大学学报 (自然科学版), 40(6): 779-785. |
| JIN C Y, ZHU B T, ZHAO C G, 2019. Removal mechanism of inorganic tri-state nitrogen from aquaculture water by Rhodopseudomonas palustris CQV97[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University (Natural Science), 40(6): 779-785. | |
| [19] | 李国令, 徐洪斌, 马浩亮, 等, 2020. OAO和AO工艺处理城镇生活污水的微生物群落特征分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 14(3): 641-651. |
| LI G L, XU H B, MA H L, et al., 2020. Analysis of microbial community characteristics of OAO and AO processes for domestic wastewater treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 14(3): 641-651. | |
| [20] | 李静, 张璐, 王霖慧, 等, 2017. 一株石化废水中脱氮产微生物絮凝剂菌株的鉴定与性能[J]. 安全与环境学报, 17(3): 1117-1124. |
| LI J, ZHANG L, WANG L H, et al., 2017. Identification and performance of a strain of microbial flocculant produced by denitrification in petrochemical wastewater[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 17(3): 1117-1124. | |
| [21] | 刘飞, 张凤琴, 赵强忠, 2007. 添加枯草芽孢杆菌和营养物净化养痏污水的研究[J]. 农业环境科学报, 13(4): 55-57. |
| LIU F, ZHANG F Q, ZHAO Q Z., 2007. Study on adding Bacillus subtilis and nutrients to purify the sewage from calculi[J]. Journal of Agricultural Environment Science, 13(4): 55-57. | |
| [22] | 刘冠军, 2018. 城市污水处理的微生物技术应用策略[J]. 科技风 (24): 136, 149. |
| LIU G J, 2018. Application strategy of microbial technology in urban sewage treatment[J]. Technology Wind (24): 136, 149. | |
| [23] | 彭轶, 马斌, 委燕, 等, 2016. 基于生物强化技术实现城市污水处理系统稳定短程硝化[J]. 中南大学学报 (自然科学版), 47(11): 3965-3969. |
| PENG Y, MA B, WEI Y, et al., 2016. Achieving stable nitritation in domestic wastewater treatment system based on bioaugmentation technology[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 47(11): 3965-3969. | |
| [24] | 唐伟, 张远, 王书平, 等, 2019. 微生物菌剂在水体修复中的应用进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 9(2): 151-158. |
| TANG W, ZHANG Y, WANG S P, et al., 2019. Application progress of microbial agents in water remediation[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 9(2): 151-158. | |
| [25] | 王林, 李冰, 余家辉, 等, 2017. 不同湿地模型中根系微生物的多样性[J]. 环境科学, 38(8): 3312-33-18. |
| WANG L, LI B, YU J H, et al., 2017. Rhizosphere Microbial Diversity in Different Wetland Microcosms[J]. Environmental Science, 38(8): 3312-3318. | |
| [26] | 王书亚, 李志, 高仪璠, 等, 2019. 藻菌共培养体系优势菌株筛选及沼液处理[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 36(1): 121-126. |
| WANG S Y, LI Z, GAO Y F, et al., 2019. Screening of the dominant strains in the algae-bacteria symbiotic system and effects of biogas slurry treatment[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 36(1): 121-126. | |
| [27] | 温东辉, 张楠, 于聪, 等, 2014. 环境中生物膜的菌群结构与污染物降解特性[J]. 微生物学通报, 41(7): 1394-1401. |
| WEN D H, ZHANG N, YU C, et al., 2014. Community structure and contaminant degradation function of biofilm in environmental engineering systems[J]. Microbiology, 41(7): 1394-1401. | |
| [28] | 文武, 贾丽艳, 刘洪波, 等, 2007. 城市污水处理技术与工艺研究进展综述[J]. 环境保护科学, 33(6): 53-55, 77. |
| WEN W, JIA L Y, LIU H B, et al., 2007. Summary of research progress in urban sewage treatment technology and technology[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 33(6): 53-55, 77. | |
| [29] | 伍海全, 周丽蓉, 孙芬芬, 等, 2017. 应用生物强化技术处理高寒地区城市生活污水[J]. 环境工程学报, 6(11): 3511-3517. |
| WU H Q, ZHOU L R, SUN F F, et al., 2017. Application of biological enhancement technology on treating urban domestic sewage in alpine regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 6(11): 3511-3517. | |
| [30] | 谢武明, 毕小林, 黄子峻, 等, 2020. 纳米活性氧化铝负载磁性纳米零价铁对不同重金属的吸附机理[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(8): 2732-2740. |
| XIE W M, BI X L, HUANG Z J, et al., 2020. Adsorption mechanism of different heavy metals on the magnetic nano-zerovalent iron supported by nano-active alumina[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(8): 2732-2740. | |
| [31] | 叶春松, 郝洪铎, 王天平, 等, 2019. 微生物菌剂处理循环冷却水的作用原理及其工业应用试验[J]. 环境工程, 37(8): 42-46. |
| YE C S, HAO H D, WANG T P, et al., 2019. Principle of recirculating cooling water treated with microbial agents and its industrial test[J]. Environmental Engineering, 37(8): 42-46. | |
| [32] | 叶姜瑜, 彭德, 陆榆丰, 等, 2017. 聚甲醛废水的生物强化处理及微生物种群动态分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(5): 1681-1687. |
| YE J Y, PENG D, LU Y F, et al., 2017. Bioaugmentation treatment of polyoxymethylene (POM) wastewater and the dynamics of microbial community[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(5): 1681-687. | |
| [33] | 袁东海, 高士祥, 任全进, 等, 2004. 几种挺水植物净化生活污水总氮和总磷效果的研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 18(4): 77-80, 92. |
| YUAN D H, GAO S X, REN Q J, et al., 2004. Study on the effect of several emergent plants on the purification of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in domestic sewage[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 18(4): 77-80, 92. | |
| [34] | 张兰河, 田宇, 郭静波, 等, 2013. 微生物菌剂的构建及其在城市污水处理中的应用[J]. 化工进展, 32(8): 1943-1948. |
| ZHANG L H, TIAN Y, GUO J P, et al., 2013. Construction of microbial agent and its application in municipal wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 32(8): 1943-1948. | |
| [35] | 张庆云, 谢学辉, 俞承志, 等, 2017. 不同共代谢基质对活性黑5脱色菌群脱色性能及群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(9): 2572-2580. |
| ZHANG Q Y, XIE X H, YU C Z, et al., 2017. Effects of different co-metabolic substrates on the decolorization of reactive black 5 by bacterial and the community structure of bacterial flora[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(9): 2572-2580. | |
| [36] | 张琼, 包鹏, 彭永臻, 等, 2019. 低温条件对SBR工艺亚硝酸氧化菌种群结构的影响[J]. 环境工程, 37(3): 75-81. |
| ZHANG Q, BAO P, PENG Y Z, et al., 2019. The influence of low temperature conditions on the population structure of nitrite oxidizing bacteria in SBR process[J]. Environmental Engineering, 37(3): 75-81. | |
| [37] | 张泽钰, 李茹莹, 2020. 固定化微生物对河水的脱氮效果研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(1): 161-165. |
| ZHANG Z Y, LI R Y, 2020. Study on the nitrogen removal in river water by immobilized microorganisms[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(1): 161-165. | |
| [38] | 赵曦, 2006. 好氧微生物净化污水的机理与实践[D]. 天津: 天津大学: 27-29. |
| ZHAO X, 2006. The mechanism and practice of aerobic microorganism purification of sewage[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University: 27-29. | |
| [39] | 赵艳, 2012. 好氧/厌氧潜流人工湿地微生物多样性与水质净化的关系[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 20-23. |
| ZHAO Y, 2012. The relationship between microbial diversity and water purification in aerobic/anaerobic subsurface flow constructed wetlands[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China: 20-23. | |
| [40] | 支霞辉, 黄霞, 李朋, 等, 2009. 污水短程脱氮工艺中亚硝酸盐积累的影响因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 29(5): 486-492. |
| ZHI X H, HUANG X, LI P, et al., 2009. Influencing factors of nitrite accumulation in wastewater short-cut nitrogen removal process[J]. China Environmental Science, 29(5): 486-492. | |
| [41] | 朱胜杰, 李子武, 夏海锋, 2017. COD降解菌剂的构建及在污水处理中的评估[J]. 环境工程学报, 11(9): 5029-5034. |
| ZHU S J, LI Z W, XIA H F, 2017. Construction of microbial agent for COD degradation and its evaluate in wastewater treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 11(9): 5029-5034. |
| [1] | 刘宁, 刘洋, 续京平, 宋慧平, 冯政君, 程芳琴. 丛枝菌根真菌对人工湿地植物生长及水质净化的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1434-1441. |
| [2] | 孔盼, 夏苏敬, 张海维, 朱建强. 耕作方式对早稻-再生稻稻田氨挥发的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1627-1633. |
| [3] | 郝丽虹, 刘桂青, 张世晨, 苗宇萍. 城市加油站场地典型有机污染物空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2175-2184. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
