生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1706-1715.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.017
收稿日期:2021-05-10
出版日期:2021-08-18
发布日期:2021-11-03
通讯作者:
* 王志康,男,教授,博士研究生。E-mail: wangzhikang@gzmu.edu.cn作者简介:张萍(1990年生),女,讲师,博士研究生,研究方向为污水处理技术与理论。E-mail: zhangping890511@163.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Ping( ), FANG Chun, ZHU Sihan, HAN Song, LI Kai, WANG Zhikang*(
), FANG Chun, ZHU Sihan, HAN Song, LI Kai, WANG Zhikang*( )
)
Received:2021-05-10
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
摘要:
微藻含有丰富的蛋白质、油脂、β-胡萝卜素和维生素等高价值营养成分,是重要的化工原料。利用含氮、磷和有机物的生活污水培养微藻可有效降低微藻高价值产品的生产成本,同时达到处理污水的目的。为此,以3种常见的产业微藻斜生栅藻(S. obliquus)、普通小球藻(C. vulgaris)和螺旋藻(Spirulina sp.)为研究对象,研究其在低、中、高浓度模拟生活污水中的生长情况及对污水的处理效果,并通过物料衡算探究其在氮、磷形态转化过程中的作用。结果表明:低浓度模拟生活污水中,斜生栅藻和普通小球藻均能维持较好的生长状态且普通小球藻生物量高于斜生栅藻;中、高浓度模拟生活污水中,斜生栅藻生长较好但普通小球藻生长状态较差,后期死亡;螺旋藻在低、中、高浓度的模拟生活污水中后期均出现死亡现象,表明其耐污能力较差。3种微藻对中、高浓度模拟生活污水的处理效果均不理想,但对低浓度污水处理效果较好。第6—7天,斜生栅藻、普通小球藻和螺旋藻对低浓度模拟生活污水中溶解性活性磷SRP的去除率分别为82.34%、85.67%和56.52%,对NH4+-N去除率分别为52.16%、61.86%和36.00%。表明斜生栅藻和普通小球藻能够有效地去除低浓度生活污水中的氮、磷物质。物料衡算结果显示,9天后,低质量浓度组胞内总磷TCP分别增加了0.66、0.91、0.59 mg∙L-1,表明微藻将污水中溶解态磷向颗粒态磷转化,这可能是去除污水中磷的主要途径;各浓度组NH4+-N均有减少,而胞内总氮TCN呈增加趋势,这是因为微藻将NH4+-N同化为有机氮。实验过程未发现NO2--N的存在,表明微藻脱氮是直接吸收NH4+-N,并非通过硝化和反硝化过程完成。研究结果表明,低、中浓度生活污水可用于斜生栅藻的产业化养殖,低浓度生活污水可用于普通小球藻的产业化养殖,且均对污水具有较高的脱氮除磷效果。
中图分类号:
张萍, 方淳, 朱思涵, 韩松, 李凯, 王志康. 生活污水处理中微藻的优选及氮、磷转化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1706-1715.
ZHANG Ping, FANG Chun, ZHU Sihan, HAN Song, LI Kai, WANG Zhikang. Optimization of Microalgae Species and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Conversion for Domestic Sewage Treatment[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1706-1715.
| 成分 Component | 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 高质量浓度 High mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K2HPO4∙3H2O | 18.4 | 55.25 | 110.5 |
| NH4Cl | 57.3 | 114.6 | 229.3 |
| C6H12O6 | 94.32 | 235.8 | 471.7 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| CaCl2∙2H2O | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| C6H8FeNO7 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| EDTA-Na2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H3BO3 | 2.86 | 2.86 | 2.86 |
| MnCl2∙4H2O | 1.86 | 1.86 | 1.86 |
| ZnSO4∙7H2O | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| CuSO4∙5H2O | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Na2MoO4∙2H2O | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| Co(NO3)2∙6H2O | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
表1 模拟生活污水的成分
Table 1 Simulated domestic sewage composition
| 成分 Component | 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 高质量浓度 High mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K2HPO4∙3H2O | 18.4 | 55.25 | 110.5 |
| NH4Cl | 57.3 | 114.6 | 229.3 |
| C6H12O6 | 94.32 | 235.8 | 471.7 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| CaCl2∙2H2O | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| C6H8FeNO7 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| EDTA-Na2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H3BO3 | 2.86 | 2.86 | 2.86 |
| MnCl2∙4H2O | 1.86 | 1.86 | 1.86 |
| ZnSO4∙7H2O | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| CuSO4∙5H2O | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Na2MoO4∙2H2O | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| Co(NO3)2∙6H2O | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
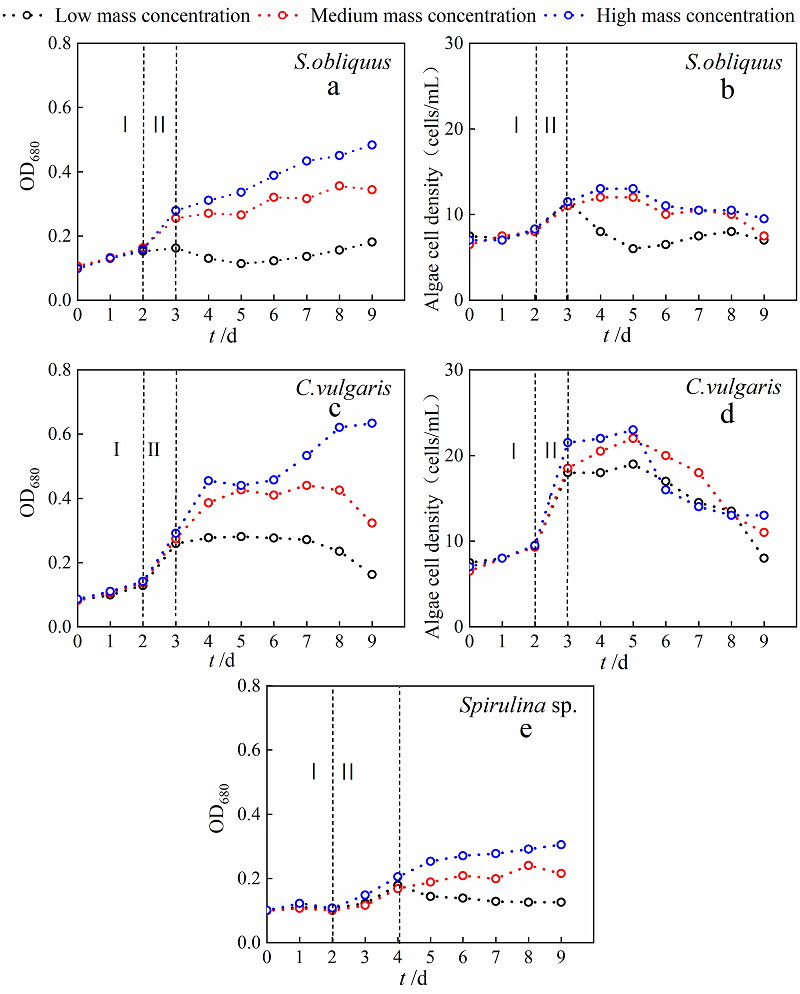
图1 不同质量浓度模拟生活污水中微藻生物量随时间变化 Ⅰ为适应期,Ⅱ为对数生长期;a,c和e为藻细胞OD680值,b和d为藻细胞密度
Fig. 1 Changes of microalgae biomass in simulated domestic sewage with different mass concentrations over time Ⅰ refer to adaptation phase, Ⅱ refer to logarithmic growth phase; a, c and e refer to algae cell OD680, b and d refer to algae cell density
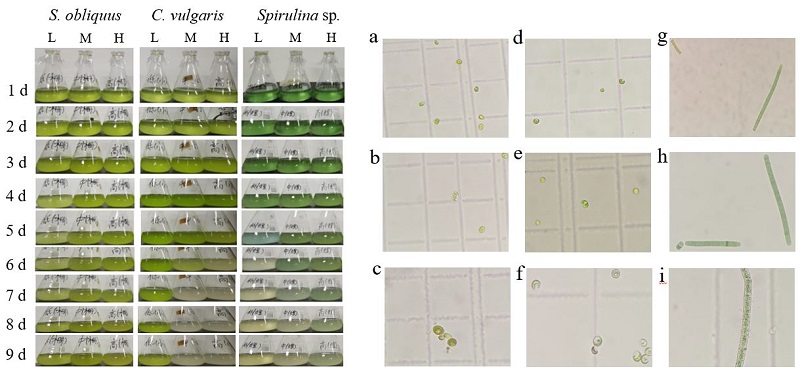
图2 低、中、高质量浓度模拟生活污水中各微藻生长情况 ×400倍显微镜视野:L,M,H分别表示低,中和高质量浓度;a—c斜生栅藻,d—f小球藻,g—i螺旋藻
Fig. 2 Growth of various microalgae in low, medium and high mass concentration simulated domestic sewage ×400 microscope field of view: L, M, H refer to low mass concentration, medium mass concentration, and high mass concentration; a-c refer to S. obliquus, d-f refer to C. vulgaris, g-i refer to Spirulina sp.
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | SRP 去除率 SRP removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 31.53 | 44.02 | 45.69 | 66.51 | 74.01 | 82.34 | 76.51 | 74.01 | 75.68 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 29.86 | 35.69 | 55.68 | 74.84 | 78.18 | 84.84 | 85.67 | 78.18 | 78.18 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 31.53 | 27.36 | 49.85 | 53.19 | 53.19 | 56.52 | 54.85 | 49.02 | 47.35 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 19.42 | 20.81 | 27.47 | 35.80 | 41.91 | 54.68 | 51.63 | 52.19 | 52.74 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 18.31 | 23.86 | 28.86 | 36.91 | 36.36 | 45.24 | 50.80 | 51.63 | 49.41 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 17.20 | 18.59 | 25.53 | 33.30 | 33.30 | 40.25 | 38.30 | 38.30 | 36.36 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 14.45 | 16.95 | 23.34 | 29.17 | 29.17 | 36.80 | 39.02 | 40.69 | 44.58 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 17.23 | 18.48 | 21.67 | 27.08 | 27.50 | 36.94 | 35.70 | 38.61 | 40.97 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 14.87 | 18.34 | 21.53 | 25.14 | 22.50 | 22.36 | 28.06 | 27.50 | 30.97 | ||
表2 3种微藻对不同质量浓度模拟生活污水中SRP的去除率
Table 2 Removal efficiency of SRP from simulated domestic sewage with different mass concentrations by three microalgae
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | SRP 去除率 SRP removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 31.53 | 44.02 | 45.69 | 66.51 | 74.01 | 82.34 | 76.51 | 74.01 | 75.68 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 29.86 | 35.69 | 55.68 | 74.84 | 78.18 | 84.84 | 85.67 | 78.18 | 78.18 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 31.53 | 27.36 | 49.85 | 53.19 | 53.19 | 56.52 | 54.85 | 49.02 | 47.35 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 19.42 | 20.81 | 27.47 | 35.80 | 41.91 | 54.68 | 51.63 | 52.19 | 52.74 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 18.31 | 23.86 | 28.86 | 36.91 | 36.36 | 45.24 | 50.80 | 51.63 | 49.41 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 17.20 | 18.59 | 25.53 | 33.30 | 33.30 | 40.25 | 38.30 | 38.30 | 36.36 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 14.45 | 16.95 | 23.34 | 29.17 | 29.17 | 36.80 | 39.02 | 40.69 | 44.58 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 17.23 | 18.48 | 21.67 | 27.08 | 27.50 | 36.94 | 35.70 | 38.61 | 40.97 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 14.87 | 18.34 | 21.53 | 25.14 | 22.50 | 22.36 | 28.06 | 27.50 | 30.97 | ||
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | NH4+-N去除率 NH4+-N removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 17.82 | 19.84 | 29.54 | 33.98 | 46.10 | 52.16 | 49.74 | 44.08 | 47.72 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 15.80 | 7.31 | 45.70 | 56.20 | 61.86 | 60.24 | 56.20 | 30.34 | 46.51 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 12.16 | -8.44 | 6.91 | 33.17 | 27.52 | 36.00 | 26.30 | 24.69 | 20.24 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -38.67 | -24.73 | -13.82 | -6.95 | 5.17 | 16.89 | 14.26 | 9.01 | 10.42 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.77 | -36.24 | -10.99 | -0.89 | -5.13 | 8.61 | 22.55 | 14.67 | 7.39 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -34.42 | -34.83 | -30.99 | -4.32 | -5.33 | 2.55 | 1.13 | 5.37 | -0.08 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -30.85 | -28.02 | -15.49 | -12.46 | -2.97 | 0.97 | -0.65 | 11.27 | 9.25 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.53 | -35.90 | -17.62 | -7.41 | -5.29 | -3.68 | 1.88 | 8.34 | 12.79 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -42.77 | -36.10 | -24.59 | -13.37 | -18.12 | -17.82 | -10.85 | -9.33 | -2.67 | ||
表3 3种微藻对不同质量浓度模拟生活污水中NH4+-N的去除率
Table 3 Removal efficiency of NH4+-N from simulated domestic sewage with different mass concentrations by three microalgae
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | NH4+-N去除率 NH4+-N removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 17.82 | 19.84 | 29.54 | 33.98 | 46.10 | 52.16 | 49.74 | 44.08 | 47.72 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 15.80 | 7.31 | 45.70 | 56.20 | 61.86 | 60.24 | 56.20 | 30.34 | 46.51 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 12.16 | -8.44 | 6.91 | 33.17 | 27.52 | 36.00 | 26.30 | 24.69 | 20.24 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -38.67 | -24.73 | -13.82 | -6.95 | 5.17 | 16.89 | 14.26 | 9.01 | 10.42 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.77 | -36.24 | -10.99 | -0.89 | -5.13 | 8.61 | 22.55 | 14.67 | 7.39 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -34.42 | -34.83 | -30.99 | -4.32 | -5.33 | 2.55 | 1.13 | 5.37 | -0.08 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -30.85 | -28.02 | -15.49 | -12.46 | -2.97 | 0.97 | -0.65 | 11.27 | 9.25 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.53 | -35.90 | -17.62 | -7.41 | -5.29 | -3.68 | 1.88 | 8.34 | 12.79 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -42.77 | -36.10 | -24.59 | -13.37 | -18.12 | -17.82 | -10.85 | -9.33 | -2.67 | ||
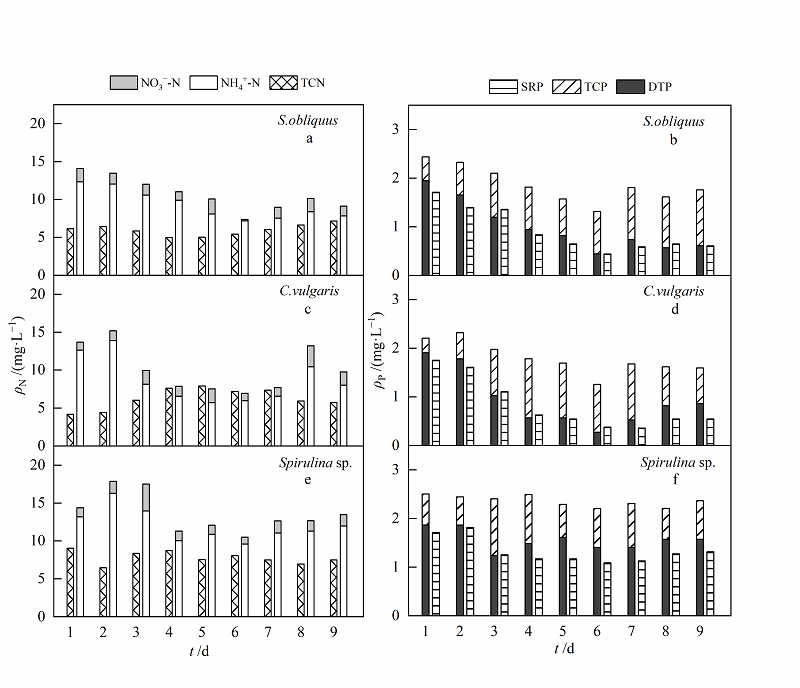
图4 低质量浓度模拟生活污水中氮、磷形态变化 a,c和e表示:斜生栅藻、普通小球藻和螺旋藻处理污水后,各形态氮质量浓度的变化情况;b,d和f表示:斜生栅藻、普通小球藻和螺旋藻处理污水后,各形态磷质量浓度的变化情况
Fig. 4 Transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus form in low mass concentration simulated domestic sewage a, c and e refer to different forms of nitrogen mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.;figure b, d and f refer to different forms of phosphorus mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.
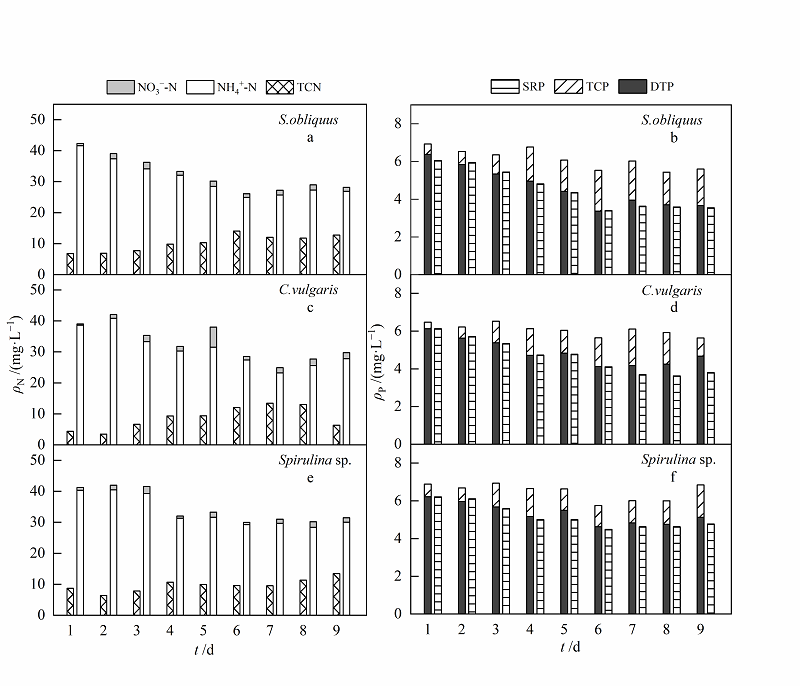
图5 中质量浓度模拟生活污水中氮、磷形态变化 a,c和e表示:斜生栅藻、普通小球藻和螺旋藻处理污水后,各形态氮质量浓度的变化情况;b,d和f表示:斜生栅藻、普通小球藻和螺旋藻处理污水后,各形态磷质量浓度的变化情况
Fig. 5 Transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus form in medium mass concentration simulated domestic sewage a, c and e refer to different forms of nitrogen mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.;figure b, d and f refer to different forms of phosphorus mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.
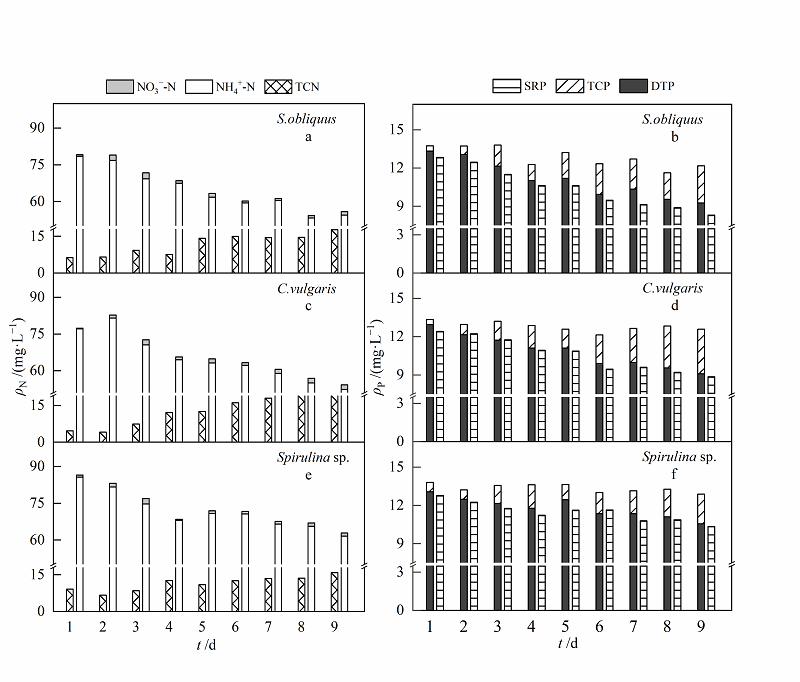
图6 高质量浓度模拟生活污水中氮、磷形态变化 a,c和e表示:斜生栅藻、普通小球藻和螺旋藻处理污水后,各形态氮质量浓度的变化情况;b,d和f表示:斜生栅藻、普通小球藻和螺旋藻处理污水后,各形态磷质量浓度的变化情况
Fig. 6 Transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus form in high mass concentration simulated domestic sewage a, c and e refer to different forms of nitrogen mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.;figure b, d and f refer to different forms of phosphorus mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.
| [1] | ALEJANDRO R M, MENDOZA-ESPINOSA L G, TOM S, 2010. Growth and nutrient removal in free and immobilized green algae in batch and semi-continuous cultures treating real wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 10(1): 58-64. |
| [2] |
ASLAN S, KAPDAN I K, 2006. Batch kinetics of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from synthetic wastewater by algae[J]. Ecological Engineering, 28(1): 64-70.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BEUCKELS A, SMOLDERS E, MUYLAERT K, 2015. Nitrogen availability influences phosphorus removal in microalgae-based wastewater treatment[J]. Water Research, 77: 98-106.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHAI W S, TAN W G, SITI H M H, et al., 2021. Multifaceted roles of microalgae in the application of wastewater biotreatment: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116236.
DOI |
| [5] |
CHEN H, WANG Q, 2020. Microalgae-based nitrogen bioremediation[J]. Algal Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.algal.2019.101775.
DOI |
| [6] |
CUELLAR-BERMUDEZ S P, ALEMAN-NAVA G S, CHANDRA R, et al., 2017. Nutrients utilization and contaminants removal. A review of two approaches of algae and cyanobacteria in wastewater[J]. Algal Research, 24: 438-449.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FEFFER A, NELSON Y, WOERTZ I, et al., 2009. Algae Grown on Dairy and Municipal Wastewater for Simultaneous Nutrient Removal and Lipid Production for Biofuel Feedstock[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 135(11): 1115-1122.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
FRANCHINO M, COMINO E, BONA F, et al., 2013. Growth of three microalgae strains and nutrient removal from an agro-zootechnical digestate[J]. Chemosphere, 92(6): 738-744.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI X, HU H Y, GAN K, et al., 2010. Growth and nutrient removal properties of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. LX1 under different kinds of nitrogen sources[J]. Ecological Engineering, 36(4): 379-381.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIANG Z J, LIU Y, GE F, et al., 2013. Efficiency assessment and pH effect in removing nitrogen and phosphorus by algae-bacteria combined system of Chlorella vulgaris and Bacillus licheniformis[J]. Chemosphere, 92(10): 1383-1389.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LU Q, ZHOU W G, MIN M, et al., 2015. Growing Chlorella sp. On meat processing wastewater for nutrient removal and biomass production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 198: 189-197.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MALIHE B, SADEGH H M, SAEED A, 2021. Direct brackish water desalination using Chlorella vulgaris microalgae[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 148: 237-248.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
OLGUÍN E J, 2003. Phycoremediation: key issues for cost-effective nutrient removal processes[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 22(1-2): 81-91.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ÓRPEZ R, MARTÍNEZ M E, HODAIFA G, et al., 2008. Growth of the microalga Botryococcus braunii in secondarily treated sewage[J]. Desalination, 246(1-3): 625-630.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PEREZ-GARCIA O, ESCALANTE F M E, DE-BASHAN L E, et al., 2011. Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: Metabolism and potential products[J]. Water Research, 45(1): 11-36.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PRANDINI J M, DA SILVA M L B, MEZZARI M P, et al., 2016. Enhancement of nutrient removal from swine wastewater digestate coupled to biogas purification by microalgae Scenedesmus spp.[J]. Bioresource Technology, 202: 67-75.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
REN H, TUO J, ADDY M M, et al., 2017. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris in a pilot-scale photobioreactor using real centrate wastewater with waste glycerol for improving microalgae biomass production and wastewater nutrients removal[J]. Bioresource Technology, 245: 1130-1138.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SANTOS-BALLARDO D U, ROSSI S, HERNÁNDEZ V, et al., 2015. A simple spectrophotometric method for biomass measurement of important microalgae species in aquaculture[J]. Aquaculture, 448: 87-92.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SU Y, MENNERICH A, URBAN B, 2011. Municipal wastewater treatment and biomass accumulation with a wastewater-born and settleable algal-bacterial culture[J]. Water Research, 45(11): 3351-3358.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG J, ZHOU W, YANG H, et al., 2015. Trophic mode conversion and nitrogen deprivation of microalgae for high ammonium removal from synthetic wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 196: 668-676.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 常婷, 许智慧, 程鹏飞, 等, 2019. 不同氨氮浓度对4株常见藻株生长及酶活性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(8): 3642-3649. |
| CHANG T, XU Z H, CHENG P F, et al., 2019. Effects of Different Concentrations of Ammonia Nitrogen on the Growth and Enzyme Activity of Four Common Algae Strains[J]. Environmental Science, 40(8): 3642-3649. | |
| [22] | 邓祥元, 丁婉婉, 樊玲波, 等, 2013. 2种微藻去除氮、磷能力的比较[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 35(6): 694-698, 726. |
| DENG X Y, DING W W, FAN L B, et al., 2013. Comparative Study on N and P Removal Ability of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 35(6): 694-698, 726. | |
| [23] | 苟尧, 2018. 菌藻生物反应器处理模拟生活污水的性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学: 23-25. |
| GOU Y, 2018. Performance of using algal-bacterial bioreactors for synthetic domestic wastewater treatment[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University: 23-25. | |
| [24] | 国家环境保护局水和污水监测分析方法编委会, 1997. 水和污水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Editorial board of water and waste water monitoring and analysis methods of State Environmental Protection Administration, 1997. Water and waste water monitoring and analysis methods[M]. Fourth Edition. Beijing: China Environmental Press. | |
| [25] | 韩佩, 2018. 螺旋藻协同沸石高效处理高氨氮废水的研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学: 27. |
| HAN P, 2018. Study on effective treatment of high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater by combination of spirulina and zeolite[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University: 27. | |
| [26] | 郝晓地, 靳景宜, 罗玉琪, 等, 2020. 可沉微藻转化油脂潜力及PHB合成试验研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 36(7): 1-6. |
| HAO X D, JIN J Y, LUO Y Q, et al., 2020. Lipids Conversion Potential and PHB Synthesis of Settleable Microalgae[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 36(7): 1-6. | |
| [27] | 胡洪营, 李鑫, 杨佳, 2009. 基于微藻细胞培养的水质深度净化与高价值生物质生产耦合技术[J]. 生态环境学报, 18(3): 1122-1127. |
| HU H Y, LI X, YANG J, 2009. Coupling of wastewater deep purification and high quality biomass production based on microalgae cultivation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(3): 1122-1127. | |
| [28] | 胡鸿钧, 魏印心, 2006. 中国淡水藻类-系统、分类及生态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 7. |
| HU H J, WEI Y X, 2006. The Freshwater Algae of China systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 7. | |
| [29] | 黄静依, 张皓驰, 李先宁, 2020. 水产养殖废水处理的菌藻共生系统中藻种优选及氮、磷转化特性[J]. 净水技术, 39(9): 57-66, 84. |
| HUANG J Y, ZHANG H C, LI X N, 2020. Optimization of Microalgae Species and Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Conversion in Algae-Bacteria Symbiotic System for Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment[J]. Water Purification Technology, 39(9): 57-66, 84. | |
| [30] | 黄添浩, 林磊, 王趁义, 等, 2019. 吸氮除磷材料的研究和应用现状[J]. 化工新型材料, 47(3): 39-42, 46. |
| HUANG T H, LIN L, WANG C Y, et al., 2019. Research and application of nitrogen and phosphorus removal material[J]. New Chemical Materials, 47(3): 39-42, 46. | |
| [31] | 贾纬, 聂毅磊, 陈宏, 等, 2021. 水产养殖废水脱氮除磷微藻的筛选[J]. 福建农业学报, 36(2): 1-6. |
| JIA W, NIE Y L, CHEN H, et al., 2021. Microalgae for Effective Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal from aquaculture Effluence[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 36(2): 1-6. | |
| [32] | 江红霞, 郑怡, 2003. 微藻的药用, 保健价值及研究开发现状 (综述)[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 32(1): 68-72. |
| JIANG H X, ZHENG Y. 2003. A review of pharmaceutical and health care value of microalgae and their current status of research and development[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 32(1): 68-72. | |
| [33] | 姜红鹰, 周玉玲, 张桂敏, 等, 2017. 普通小球藻对养殖污水脱氮除磷的效果研究[J]. 生物资源, 39(3): 204-210. |
| JIANG H Y, ZHOU Y L, ZHANG G M, et al., 2017. Effect of Chlorella vulgaris on nitrogen and phosphorus removal from breeding wastewater[J]. Biotic Resources, 39(3): 204-210. | |
| [34] | 李扬, 2020. 微藻处理污水研究进展[J]. 水资源开发与管理, 8(4): 13-18. |
| LI Y, 2020. Research progress on treatment of sewage by microalgae[J]. Water Resources Development and Management, 8(4): 13-18. | |
| [35] | 梁芳, 鸭乔, 杜伟春, 等, 2014. 微藻光密度与细胞密度及生物质的关系[J]. 生态学报, 34(21): 6156-6163. |
| LIANG F, YA Q, DU W C, et al., 2014. The relationships between optical density, cell number, and biomass of four microalgae[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(21): 6156-6163. | |
| [36] | 刘磊, 杨雪薇, 陈朋宇, 等, 2014. 3种微藻对人工污水中氮磷去除效果的研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 41(11): 172-176, 201. |
| LIU L, YANG X W, CHEN P Y, et al., 2014. Efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from artificial wastewater by three kinds of microalgae[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 41(11): 172-176, 201. | |
| [37] | 刘淑坡, 李飞, 2012. 固定化核蛋白小球藻对人工废水中不同形态氮和磷的去除[J]. 山东理工大学学报 (自然科学版), 26(4): 43-47. |
| LIU S P, LI F, 2012. Removal of different forms nitrogen and phosphorus in artificial wastewater by immobilized Chlorella pyrenoidosa[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 26(4): 43-47. | |
| [38] | 刘伟, 2006. 雨生红球藻规模化培养工艺的构建及相关生物学特性的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所: 1. |
| LIU W, 2006. Technological assembly and related biological study in a pilot scale culture of Haematococcus pluvialis[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1. | |
| [39] | 罗龙皂, 林小爱, 朱峰, 等, 2019. 曝二氧化碳气体对近具刺链带藻在高氨氮废水中生长的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 31(9): 1541-1548. |
| LUO L Z, LIN X A, ZHU F, et al., 2019. Effect of aeration with carbon dioxide on growth of Desmodesmus sp. CHX1 in wastewater with high concentration of ammonium nitrogen[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 31(9): 1541-1548. | |
| [40] | 皮永蕊, 吕永红, 柳莹, 等, 2019. 微藻-细菌共生体系在废水处理中的应用[J]. 微生物学报, 59(6): 1188-1196. |
| PI Y R, LV Y H, LIU Y, et al., 2019. Application of microalgae-bacteria symbiosis system in wastewater treatment[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 59(6): 1188-1196. | |
| [41] | 秦乐乐, 李菊芳, 徐微, 等, 2020. 好氧接触氧化-混凝沉淀-人工湿地处理洗涤废水[J]. 中国给水排水, 36(2): 89-92. |
| QIN L L, LI J F, XU W, et al., 2020. Treatment of washing wastewater by aerobic contact oxidation/coagulation precipitation/constructed wetland process[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 36(2): 89-92. | |
| [42] | 脱金华, 任洪艳, 刘方舟, 等, 2019. 利用实际市政污水培养小球藻及优化外加碳源[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(1): 184-190. |
| TUO J H, REN H Y, LIU F Z, et al., 2019. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using real municipal wastewater and optimization of external carbon source[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 25(1): 184-190. | |
| [43] | 王海英, 牟晓庆, 2011. 城市污水培养富油蛋白小球藻的研究[J]. 中南民族大学学报 (自然科学版), 30(3): 38-41. |
| WANG H Y, MU X Q, 2011. Cultivation of high oil content Chlorella pyrenoidosa on urban sewage[J]. Journal of South-Central University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 30(3): 38-41. | |
| [44] | 王璐瑶, 桑敏, 李爱芬, 等, 2012. 不同缺氮营养水平对金色奥杜藻生长及光合生理的影响[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 32(6): 48-56. |
| WANG L Y, SANG M, LI A F, et al., 2012. Effects of Different Nitrogen Nutrition Level on the Growth and Photosynthetic Physiology of Odontella aurita[J]. China Biotechnology, 32(6): 48-56. | |
| [45] | 徐凯, 2015. 微藻脂肪酸积累的调控优化研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛农业大学: 4-5. |
| XU K, 2015. Optimization of regulation on fatty acid accumulation in microalgae[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao Agricultural University: 4-5. | |
| [46] | 杨福利, 李秀辰, 白晓磊, 等, 2014. 小球藻脱氮除磷及其生物量增殖潜力的研究[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 29(2): 193-197. |
| YANG F L, LI X C, BAI X C, et al., 2014. The removal efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus wastes and multiplication in biomass in green alga Chlorella vulgaris[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 29(2): 193-197. | |
| [47] | 于殿江, 施定基, 何培民, 等, 2021. 微藻规模化培养研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 61(2): 333-345. |
| YU D J, SHI D J, HE P M, et al., 2021. Progress in large-scale culture of microalgae[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 61(2): 333-345. | |
| [48] | 于茜, 朱元荣, 王焕华, 等, 2016. 铜绿微囊藻培养过程中氨基酸的释放特征及其对水体有机质的贡献[J]. 环境科学研究, 29(3): 360-367. |
| YU X, ZHU Y R, WANG H H, et al., 2016. Release of Amino Acids from Microcystis aeruginosa and its contributions to organic matter[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 29(3): 360-367. | |
| [49] | 于媛, 刘艳, 韩芸芸, 等, 2006. 小球藻去除水产加工废水中氨态氮的初步研究[J]. 生物技术, 16(5): 73-74. |
| YU Y, LIU Y, HAN Y Y, et al., 2006. The Primary Studies on Ammonia-nitrogen Removal from Fisheries Process Wastewater by Chlorella vulgaris[J]. Biotechnology, 16(5): 73-74. | |
| [50] | 余江, 陶红群, 王亚婷, 等, 2019. 磷受控对酿酒废水-微藻培育耦合体系的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 54(3): 655-662. |
| YU J, TAO H Q, WANG Y T, et al., 2019. Influence of Phosphorus Control on Coupling System of Winery Wastewater and Microalgae Cultivation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 54(3): 655-662. | |
| [51] | 张军晓, 李绪录, 许春玲, 等, 2017. 深圳湾及邻近水域溶解有机磷的分布和来源及其生物利用率[J]. 环境科学研究, 30(2): 232-239. |
| ZHANG J X, LI X L, XU C L, et al., 2017. Distributions sources and bioavailability of dissolved organic phosphorus in Shenzhen Bay and adjacent coastal waters[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 30(2): 232-239. | |
| [52] | 章斐, 陈秀荣, 江子建, 等, 2015. 不同氮磷浓度下2种无毒微藻的生长特性和脱氮除磷效能[J]. 环境工程学报, 9(2): 559-566. |
| ZHANG F, CHEN X R, JIANG Z J, et al., 2015. Growth characteristics and removal efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus of two kinds of non-toxic microalgae under different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 9(2): 559-566. | |
| [53] | 赵秀侠, 杨坤, 方婷, 等, 2018. 3种微藻在龟鳖养殖废水中的生长与脱氮除磷特性[J]. 水资源保护, 34(1): 83-87, 94. |
| ZHAO X X, YANG K, FANG T, et al., 2018. Growth feature and nitrogen and phosphorus removal characteristics of three microalgae in turtle breeding wastewaterr[J]. Water Resources Protection, 34(1): 83-87, 94. | |
| [54] | 周海东, 轩玉梅, 胡涛, 等, 2020. 氮磷形态对铜绿微囊藻的生长影响[J]. 能源研究与信息, 36(1): 1-8. |
| ZHOU H D, XUAN Y M, HU T, et al., 2020. Influences of nitrogen and phosphorus species on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Energy Research and Information, 36(1): 1-8. |
| [1] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [2] | 刘美, 马志良. 增温和植物去除对青藏高原东部高寒灌丛土壤不同形态氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 470-477. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
