Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 36-46.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-10-17
Online:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-06
Contact:
LIU Xilin
通讯作者:
刘希林
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIU Xilin, ZHUO Ruina. Influential Factors and Their Critical Thresholds of Initial Runoff Production Time on the Benggang Colluvial Slopes[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 36-46.
刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.005
| 崩积体 编号 | 初始产流时间/ min | 降雨量/ mm | 降雨历时/ min | 降雨强度/ (mm·min-1) | 崩积体坡度/ (°) | 不同深度土体初始含水率/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 cm | 20 cm | 30 cm | 40 cm | 60 cm | 100 cm | ||||||
| 1—1 | 1.6 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 25 | 0.2 | 8.4 | 22.7 | 28.2 | 32.5 | 26.5 |
| 1—1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 25 | 3.1 | 10.8 | 24.9 | 29.4 | 36.6 | 27.6 |
| 1—2 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 38 | 9.8 | 26.1 | 31.0 | 36.2 | 36.7 | 36.9 |
| 1—3 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 27 | 5.8 | 14.2 | 19.0 | 22.9 | 24.4 | 31.9 |
| 2—1 | 2.6 | 3.2 | 2.7 | 1.2 | 32 | 11.8 | 21.0 | 25.4 | 22.9 | 25.1 | 34.9 |
| 2—1 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 32 | 20.5 | 30.6 | 32.3 | 29.2 | 28.9 | 37.6 |
| 2—2 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 21 | 6.3 | 11.6 | 16.5 | 23.7 | 29.6 | 21.0 |
| 3—1 | 5.7 | 17.4 | 5.6 | 3.1 | 9 | 19.3 | 21.9 | 23.0 | 31.7 | 35.1 | 24.6 |
| 3—1 | 8.3 | 6.6 | 8.3 | 0.8 | 9 | 18.7 | 23.4 | 24.6 | 29.7 | 35.5 | 31.6 |
| 4—1 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 30 | 7.8 | 20.0 | 23.7 | 25.7 | 34.5 | 31.8 |
| 4—1 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 3.8 | 30 | 10.8 | 27.2 | 30.2 | 32.2 | 37.3 | 30.8 |
| 4—2 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 24 | 1.5 | 6.1 | 21.8 | 40.5 | 35.5 | 32.6 |
Table 1 Initial runoff production time and their actual measurement data on colluvial slopes
| 崩积体 编号 | 初始产流时间/ min | 降雨量/ mm | 降雨历时/ min | 降雨强度/ (mm·min-1) | 崩积体坡度/ (°) | 不同深度土体初始含水率/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 cm | 20 cm | 30 cm | 40 cm | 60 cm | 100 cm | ||||||
| 1—1 | 1.6 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 25 | 0.2 | 8.4 | 22.7 | 28.2 | 32.5 | 26.5 |
| 1—1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 25 | 3.1 | 10.8 | 24.9 | 29.4 | 36.6 | 27.6 |
| 1—2 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 38 | 9.8 | 26.1 | 31.0 | 36.2 | 36.7 | 36.9 |
| 1—3 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 27 | 5.8 | 14.2 | 19.0 | 22.9 | 24.4 | 31.9 |
| 2—1 | 2.6 | 3.2 | 2.7 | 1.2 | 32 | 11.8 | 21.0 | 25.4 | 22.9 | 25.1 | 34.9 |
| 2—1 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 32 | 20.5 | 30.6 | 32.3 | 29.2 | 28.9 | 37.6 |
| 2—2 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 21 | 6.3 | 11.6 | 16.5 | 23.7 | 29.6 | 21.0 |
| 3—1 | 5.7 | 17.4 | 5.6 | 3.1 | 9 | 19.3 | 21.9 | 23.0 | 31.7 | 35.1 | 24.6 |
| 3—1 | 8.3 | 6.6 | 8.3 | 0.8 | 9 | 18.7 | 23.4 | 24.6 | 29.7 | 35.5 | 31.6 |
| 4—1 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 30 | 7.8 | 20.0 | 23.7 | 25.7 | 34.5 | 31.8 |
| 4—1 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 3.8 | 30 | 10.8 | 27.2 | 30.2 | 32.2 | 37.3 | 30.8 |
| 4—2 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 24 | 1.5 | 6.1 | 21.8 | 40.5 | 35.5 | 32.6 |
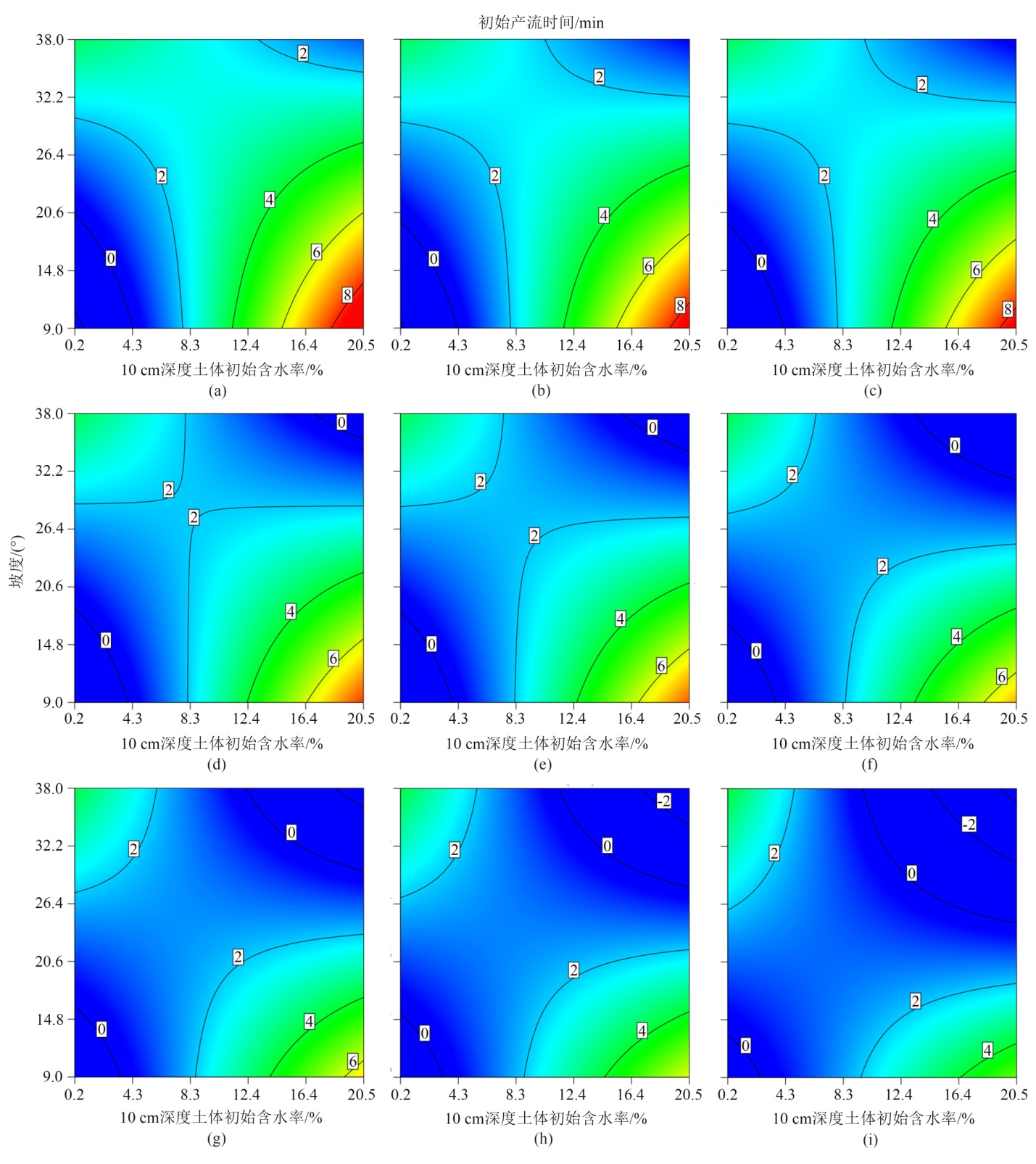
Figure 6 Influences of the different slopes and 10 cm depth initial soil moistures on the initial runoff production time under different rainfall intensities
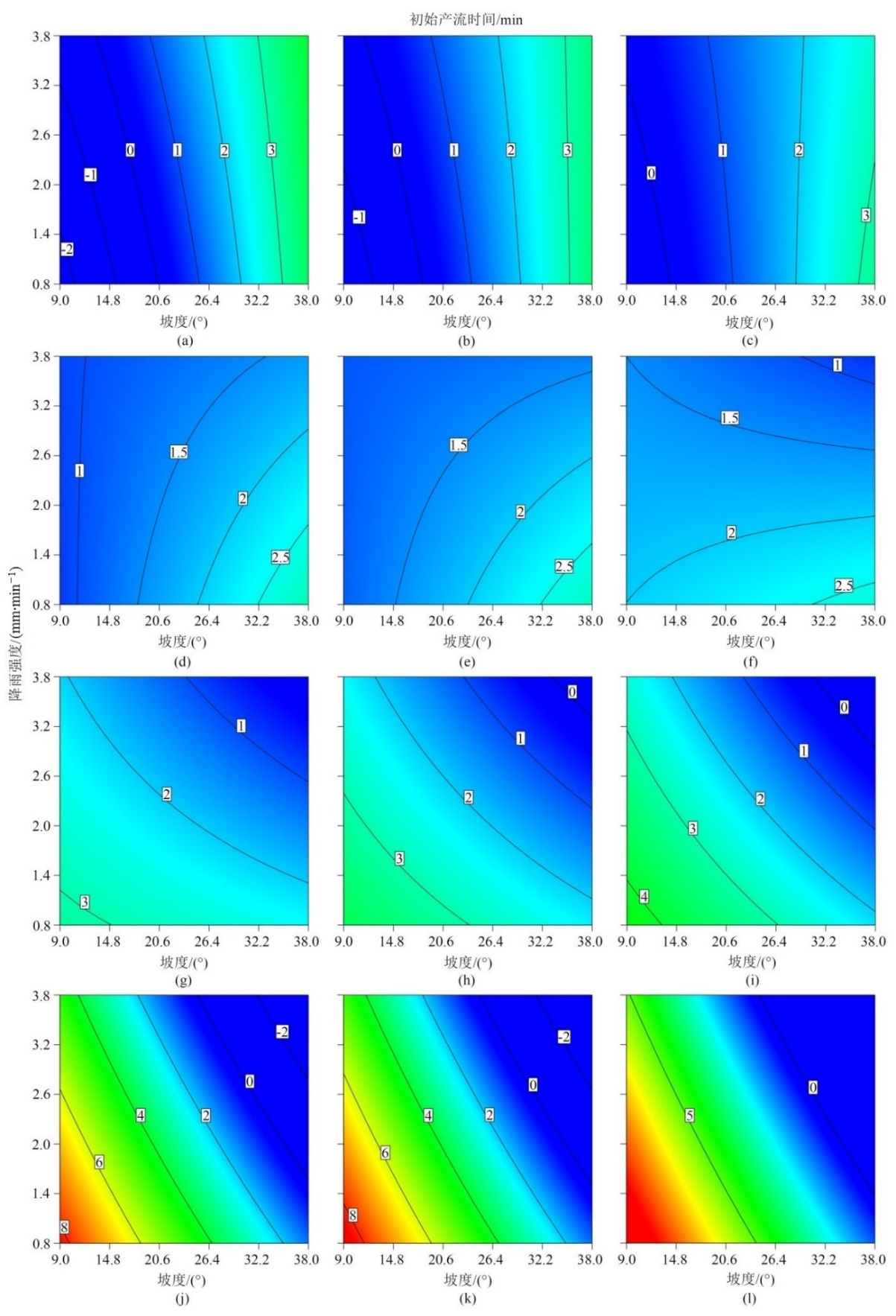
Figure 7 Influences of the different rainfall intensities and slopes on the initial runoff production time under different 10 cm depth initial soil moistures
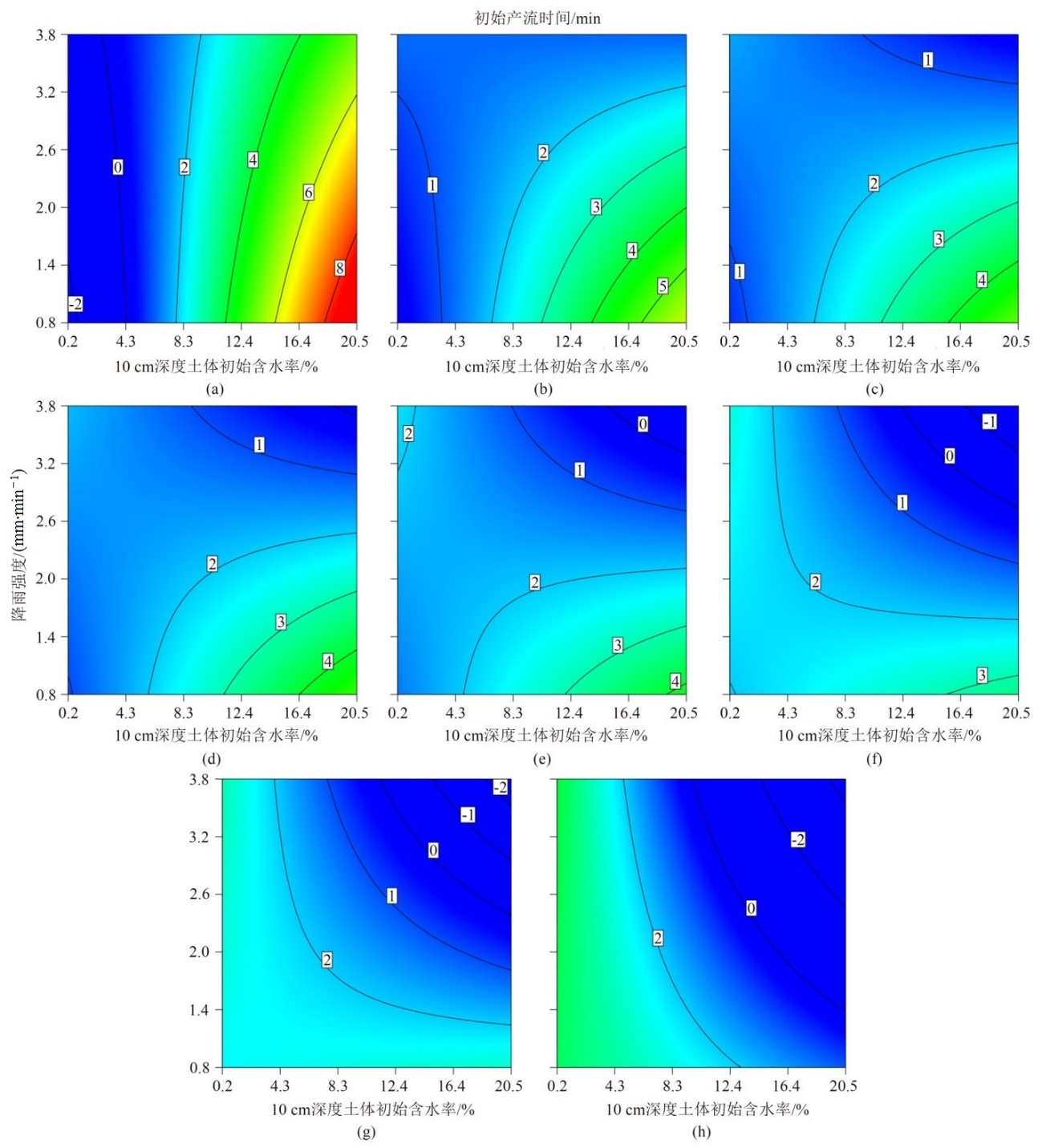
Figure 8 Influences of the different rainfall intensities and 10 cm depth initial soil moistures on the initial runoff production time under different slopes
| [1] |
BLIJENBERG H M, GRAAF P J D, HENDRIKS M R, et al., 1996. Investigation of infiltration characteristics and debris flow initiation conditions in debris flow source areas using a rainfall simulator[J]. Hydrological Processes, 10(11): 1527-1543.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HUANG J, WU P T, ZHAO X N, 2013. Effects of rainfall intensity, underlying surface and slope gradient on soil infiltration under simulated rainfall experiments[J]. Catena, 104: 93-102.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIU X L, QIU J A, ZHANG D L, 2018. Characteristics of slope runoff and soil water content in Benggang colluvium under simulated rainfall[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18(1): 39-48.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WILDHABER Y S, BANNINGER D, BURRI K, et al., 2012. Evaluation and application of portable rainfall simulator on subalpine grassland[J]. Catena, 91: 56-62.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 常松涛, 黄少燕, 查轩, 等, 2019. 雨强和植被覆盖度对红壤坡面产流产沙的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(3): 58-63. |
| CHANG S T, HUANG S Y, ZHA X, et al., 2019. Effects of rainfall intensity and vegetation coverage on runoff and sediment yield on red soil slope[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(3): 58-63. | |
| [6] | 陈俊杰, 孙莉英, 刘俊体, 等, 2013. 不同坡长与雨强条件下坡度对细沟侵蚀的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 33(2): 1-5. |
| CHEN J J, SUN L Y, LIU J T, et al., 2013. Effect of slope gradient on rill erosion under different rainfall intensities and slope lengths[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(2): 1-5. | |
| [7] | 耿晓东, 郑粉莉, 张会茹, 2009. 红壤坡面降雨入渗及产流产沙特征试验研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 23(4): 39-43. |
| GENG X D, ZHENG F L, ZHANG H R, 2009. Effect of rainfall intensities and slope gradients on characteristics of rainfall infiltration runoff and sediment on red soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(4): 39-43. | |
| [8] | 霍云梅, 毕华兴, 朱永杰, 等, 2015. 模拟降雨条件下南方典型粘土坡面土壤侵蚀过程及其影响因素[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(4): 23-26. |
| HUO Y M, BI H X, ZHU Y J, et al., 2015. Erosion process and its affecting factors of southern typical clay slope under simulated rainfall condition[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(4): 23-26. | |
| [9] | 吉恒莹, 邵明安, 贾小旭, 2018. 土壤剖面结构特征对坡面产流产沙过程的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 49(2): 441-446. |
| JI H Y, SHAO M A, JIA X X, 2018. Impact of layered soil structure on infiltration and erosion processes[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 49(2): 441-446. | |
| [10] | 蒋秋玲, 信忠保, 余新晓, 等, 2019. 北京山区侧柏林地坡面初始产流时间影响因素[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 17(4): 1-8. |
| JIANG Q L, XIN Z B, YU X X, et al., 2019. Factors affecting the initial runoff time of Platycladus orientilis plantation hillslope in Beijing mountainous area[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 17(4): 1-8. | |
| [11] |
柯奇画, 张科利, 2022. 基于文献计量的中国水土流失尺度效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(7): 1489-1498.
DOI URL |
| KE Q H, ZHANG K L, 2022. Scale effect on water and soil loss in China: A bibliometric analysis[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(7): 1489-1498. | |
| [12] | 廖义善, 唐常源, 袁再健, 等, 2018. 南方红壤区崩岗侵蚀及其防治研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 55(6): 1297-1312. |
| LIAO Y S, TANG C Y, YUAN Z J, et al., 2018. Research progress on Benggang erosion and its prevention measure in red soil region of southern China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 55(6): 1297-1312. | |
| [13] |
刘希林, 2018. 全球视野下崩岗侵蚀地貌及其研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 37(3): 342-351.
DOI |
|
LIU X L, 2018. Benggang erosion landform and research progress in a global perspective[J]. Progress in Geography, 37(3): 342-351.
DOI |
|
| [14] |
刘希林, 张大林, 贾瑶瑶, 2013. 崩岗地貌发育的土体物理性质及其土壤侵蚀意义——以广东五华县莲塘岗崩岗为例[J]. 地球科学进展, 28(7): 802-811.
DOI |
| LIU X L, ZHANG D L, JIA Y Y, 2013. Soil physical properties of collapsing hill and gully and their indications for soil erosion: An example of Liantanggang collapsing hill and gully in Wuhua County of Guangdong[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 28(7): 802-811. | |
| [15] | 刘希林, 唐川, 张大林, 2015. 野外模拟崩岗崩积体坡面产流过程及水分分布[J]. 农业工程学报, 31(11): 179-185. |
| LIU X L, TANG C, ZHANG D L, 2015. Simulated runoff processes on colluvial deposits of Liantanggang Benggang and their water distributions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(11): 179-185. | |
| [16] | 邱锦安, 2019. 崩岗崩积体坡面侵蚀产流产沙试验研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学: 1-94. |
| QIU J A, 2019. Experimental study on runoff and sediment yield in the slope of Benggang colluvium[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-Sen University: 1-94. | |
| [17] | 卫喜国, 严昌荣, 魏永霞, 等, 2009. 坡度和降雨强度对坡耕地入渗的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 28(4): 114-116. |
| WEI X G, YAN C R, WEI Y X, et al., 2009. Influence of slope gradient and rainfall intensity on infiltration in sloping farm land[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 28(4): 114-116. | |
| [18] | 武敏, 范昊明, 杨晓珍, 等, 2015. 模拟沟灌条件下辽西褐土产流起始时间的影响因素[J]. 水土保持通报, 35(3): 34-38. |
| WU M, FAN H M, YANG X Z, et al., 2015. Factors affecting initial time of runoff under simulated furrow irrigation in western Liaoning cinnamon soil[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 35(3): 34-38. | |
| [19] | 吴发启, 赵西宁, 佘雕, 2003. 坡耕地土壤水分入渗影响因素分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 23(1): 16-19. |
| WU F Q, ZHAO X N, SHE D, 2003. Analysis on affecting factors of soil infiltration in slope farmland[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(1): 16-19. | |
| [20] | 辛伟, 朱波, 唐家良, 等, 2008. 紫色土丘陵区典型坡地产流及产沙模拟试验研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 28(2): 31-35. |
| XIN W, ZHU B, TANG J L, et al., 2008. Simulation study of characteristics of runoff and sediment yield in the hill area with purple soils[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(2): 31-35. | |
| [21] | 杨景春, 李有利, 2017. 地貌学原理[M]. 第4版. 北京: 北京大学出版社: 1-243. |
| YANG J C, LI Y L, 2017. Principles of geomorphology[M]. 4th Edition. Beijing: Peking University Press: 1-243. | |
| [22] | 余长洪, 李就好, 陈凯, 等, 2015. 强降雨条件下砖红壤坡面产流产沙过程研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(2): 7-10. |
| YU C H, LI J H, CHEN K, et al., 2015. Study on process of runoff and sediment on laterite slope in condition of strong rainstorm[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(2): 7-10. | |
| [23] | 岳梦, 刘希林, 2022. 崩岗泥砂流流体和流动特性及其输沙研究——以广东德庆县径深崩岗为例[J]. 山地学报, 40(6): 859-874. |
| YUE M, LIU X L, 2022. Hydrodynamic properties of Benggang- related mud-sand flow and sediment yield: A case study of Jingshen mud-sand flow at Deqing county of Guangdong, China[J]. Mountain Research, 40(6): 859-874. | |
| [24] |
张赫斯, 张丽萍, 朱晓梅, 等, 2010. 红壤坡地降雨产流产沙动态过程模拟试验研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(5): 1210-1214.
DOI URL |
| ZHANG H S, ZHANG L P, ZHU X M, et al., 2010. Research on the processes of rainfall, surface runoff and sediment on sloping field with red loam by simulated rainfall experiment[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(5): 1210-1214. | |
| [25] | 朱高立, 黄炎和, 林金石, 等, 2015. 模拟降雨条件下秸秆覆盖对崩积体侵蚀产流产沙的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(3): 27-31. |
| ZHU G L, HUANG Y H, LIN J S, et al., 2015. Effect of straw mulch on colluvial soil erosion and yield of runoff and sediment under simulated rainfall[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(3): 27-31. | |
| [26] | 朱高立, 肖泽干, 刘晓静, 等, 2016. 模拟降雨条件下崩积体坡面产流产沙特征及其响应关系[J]. 水土保持通报, 36(6): 1-7. |
| ZHU G L, XIAO Z G, LIU X J, et al., 2016. Processes and responses of runoff and sediment yield on colluvial deposits under simulated rainfall[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 36(6): 1-7. | |
| [27] | 朱高立, 王雪琪, 李发志, 等, 2017. 秸秆覆盖对崩积体坡面产流产沙影响的模拟试验[J]. 土壤, 49(3): 601-607. |
| ZHU G L, WANG X Q, LI F Z, et al., 2017. Simulation of straw mulch on colluvial soil erosion and yield of runoff and sediment[J]. Soils, 49(3): 601-607. | |
| [28] | 卓瑞娜, 刘希林, 岳梦, 2022. 崩岗土体物理化学性质及其内部分异——以广东省德庆县3个典型崩岗为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 42(2): 38-45. |
| ZHUO R N, LIU X L, YUE M, 2022. Physical and chemical properties of Benggang soils and their interior differentiation: Three cases of typical Benggangs at Deqing County, Guangdong Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 42(2): 38-45. |
| [1] | WANG Yun, ZHENG Xilai, CAO Min, LI Lei, SONG Xiaoran, LIN Xiaolei, GUO Kai. Study on Denitrification Performance and Control Factors in Brackish-Freshwater Transition Zone of Coastal Aquifer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [2] | ZHANG Lin, ZHOU Piao, QI Shi, ZHANG Dai, WU Bingchen, CUI Ranran. Difference Influence of Spatial Structure of Platycladus orientalis Plantations on Diversity of Understory Herbaceous and Its Correlation Degree [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1794-1801. |
| [3] | LIU Shasha, CHEN Nuo, YANG Xiaoyin. Research Progress on Adsorption-Desorption Characteristics of Organic Pollutants by Microplastics and Their Combined Toxic Effects [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 610-620. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn

