Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 183-194.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.020
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Zheng1,2( ), CAO Yafei3, WANG Decai2, LIU Feng1,4, SONG Xiaodong1, ZHANG Ganlin1,4,5, WU Huayong1,4,*(
), CAO Yafei3, WANG Decai2, LIU Feng1,4, SONG Xiaodong1, ZHANG Ganlin1,4,5, WU Huayong1,4,*( )
)
Received:2022-10-07
Online:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-06
Contact:
WU Huayong
孙正1,2( ), 曹亚非3, 王德彩2, 刘峰1,4, 宋效东1, 张甘霖1,4,5, 吴华勇1,4,*(
), 曹亚非3, 王德彩2, 刘峰1,4, 宋效东1, 张甘霖1,4,5, 吴华勇1,4,*( )
)
通讯作者:
吴华勇
作者简介:孙正(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事资源环境遥感与空间分析研究。E-mail: zsun@issas.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
SUN Zheng, CAO Yafei, WANG Decai, LIU Feng, SONG Xiaodong, ZHANG Ganlin, WU Huayong. Spatial-temporal Evolution Characteristics and Trend Prediction of Electroplating Sites in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region over the Past 30 Years[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 183-194.
孙正, 曹亚非, 王德彩, 刘峰, 宋效东, 张甘霖, 吴华勇. 近30年京津冀电镀场地时空演变特征及趋势预测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 183-194.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.020
| 政策因素类型及层级 | 分值 |
|---|---|
| 国家级法律法规 | ±4 |
| 国家级规划纲要 | ±3 |
| 省级法律法规 | ±2 |
| 省级规划纲要及市级相关政策 | ±1 |
Table 1 Quantitative scoring rules for policy factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
| 政策因素类型及层级 | 分值 |
|---|---|
| 国家级法律法规 | ±4 |
| 国家级规划纲要 | ±3 |
| 省级法律法规 | ±2 |
| 省级规划纲要及市级相关政策 | ±1 |
| 城市 | 地区生产总值 | 第二产业总产值 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | d | q | p | d | q | ||
| 北京 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| 天津 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 石家庄 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 承德 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 张家口 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 秦皇岛 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 唐山 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 廊坊 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 保定 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 沧州 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 衡水 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 邢台 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 邯郸 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
Table 2 Summary of parameters in the ARIMA model
| 城市 | 地区生产总值 | 第二产业总产值 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | d | q | p | d | q | ||
| 北京 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| 天津 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 石家庄 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 承德 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 张家口 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 秦皇岛 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 唐山 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 廊坊 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 保定 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 沧州 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 衡水 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 邢台 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 邯郸 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 年份 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电镀场地数量 | 154 | 190 | 259 | 427 | 562 | 681 | 759 |
| 相对增长率/% | — | 23.38 | 36.32 | 64.86 | 31.62 | 21.17 | 11.45 |
Table 3 The number and relative growth rate of electroplating sites in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1990 to 2020
| 年份 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电镀场地数量 | 154 | 190 | 259 | 427 | 562 | 681 | 759 |
| 相对增长率/% | — | 23.38 | 36.32 | 64.86 | 31.62 | 21.17 | 11.45 |
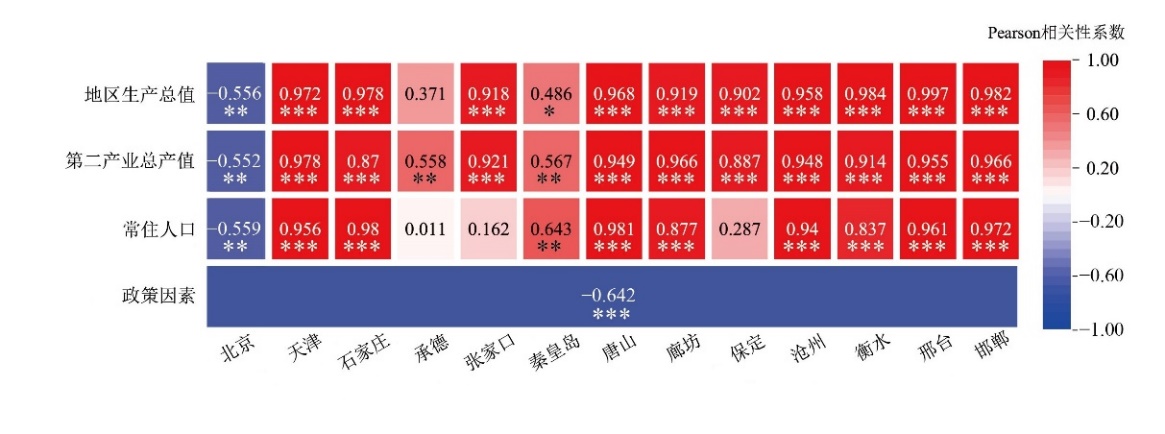
Figure 5 Correlation matrix between the number of electroplating sites and driving factors for each city in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1990 to 2020
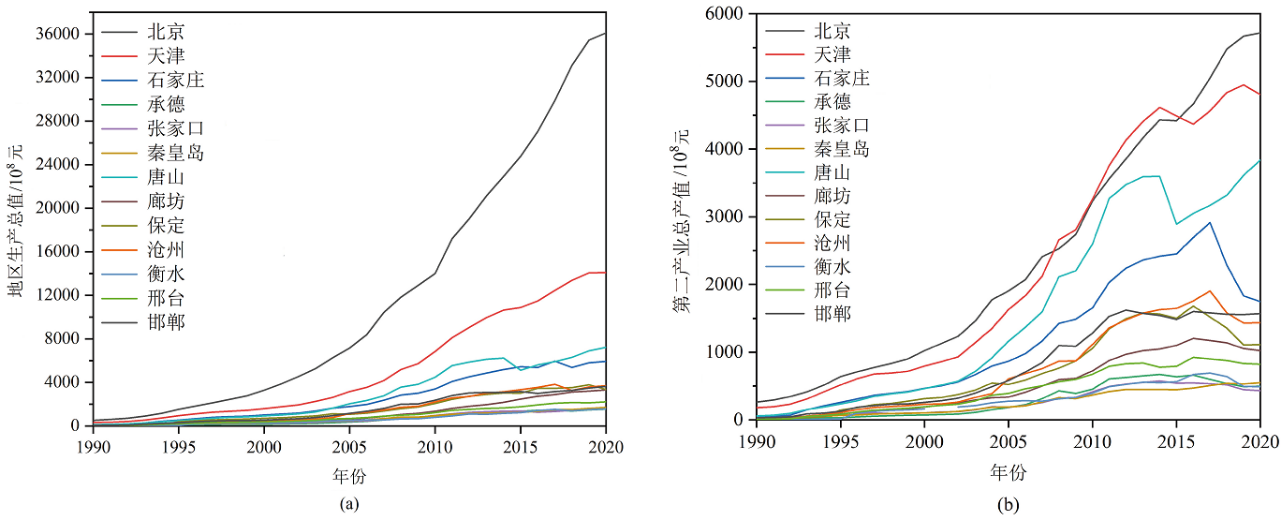
Figure 6 Gross regional product (a) and total output value of the secondary sector of the economy (b) of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1990 to 2020
| 地区 | 平均相对误差 | |
|---|---|---|
| 常住人口 | 政策因素 | |
| 北京 | 0.098 | 0.082 |
| 天津 | 0.091 | |
| 石家庄 | 0.052 | |
| 承德 | 0.078 | |
| 张家口 | 0.084 | |
| 秦皇岛 | 0.091 | |
| 唐山 | 0.095 | |
| 廊坊 | 0.099 | |
| 保定 | 0.097 | |
| 沧州 | 0.068 | |
| 衡水 | 0.071 | |
| 邢台 | 0.085 | |
| 邯郸 | 0.081 | |
Table 4 Mean relative error (MRE) for modelling resident population and policy factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
| 地区 | 平均相对误差 | |
|---|---|---|
| 常住人口 | 政策因素 | |
| 北京 | 0.098 | 0.082 |
| 天津 | 0.091 | |
| 石家庄 | 0.052 | |
| 承德 | 0.078 | |
| 张家口 | 0.084 | |
| 秦皇岛 | 0.091 | |
| 唐山 | 0.095 | |
| 廊坊 | 0.099 | |
| 保定 | 0.097 | |
| 沧州 | 0.068 | |
| 衡水 | 0.071 | |
| 邢台 | 0.085 | |
| 邯郸 | 0.081 | |
| [1] |
LIU J, ZHANG X H, TRAN H, et al., 2011. Heavy model contamination and risk assessment in water, paddy soil, and rice around an electroplating plant[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 18: 1623-1632.
DOI URL |
| [2] | HYNDMAN R, ATHANASOPOULOS G, BERGMEIR C, et al., 2022. forecast: Forecasting functions for time series and linear models[EB/OL]. (2022-11-21) [2022-12-09]. R package version 8.15. |
| [3] | R CORE TEAM, 2021. R: A language and environment for statistical computing[M]. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. |
| [4] |
REN Q, HE C Y, HUANG Q X, et al., 2022. Impacts of urban expansion on natural habitats in global drylands[J]. Nature Sustainability, 5: 869-878.
DOI |
| [5] | SILVERMAN B W, 1998. Density estimation for statistics and data analysis[M]. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC: 158-179. |
| [6] |
SONG W, DENG X Z, 2017. Land-use/land-cover change and ecosystem service provision in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 576: 705-719.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
STEHFEST E, VAN ZEIST W J, VALIN H, et al., 2019. Key determinants of global land-use projections[J]. Nature Communications, 10: 2166.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | ZHANG L, YANG L, ZOHNER C M, et al., 2022. Direct and indirect impacts of urbanization on vegetation growth across the world’s cities[J]. Science Advances, 27(8): eabo0095. |
| [9] |
ZHAO X F, ZHANG L, HUANG X J, et al., 2018. Evolution of the spatiotemporal pattern of urban industrial land use efficiency in China[J]. Sustainability, 10(7): 2174.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 蔡思彤, 尹倩婷, 2020. 广东省电镀行业“十三五”期间清洁生产水平评估与分析[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 39(13): 1671-1675. |
| CAI S T, YIN Q T, 2020. Assessment and analysis on clearer production level of electroplating industry in Guangdong province during the 13th Five-Year Plan period[J]. Electroplating & Finishing, 39(13): 1671-1675. | |
| [11] | 陈志良, 蒋晓璐, 周建民, 等, 2014. 重金属污染场地地下水污染特征与源解析研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 30(20): 202-207. |
| CHEN Z L, JIANG X L, ZHOU J M, et al., 2014. Study on pollution characteristics and source of groundwater pollution in heavy metal contaminated sites[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 30(20): 202-207. | |
| [12] | 董晓清, 李朝林, 邵培兵, 2011. 我国电镀行业节能减排的关键——促进中小电镀企业清洁生产实施的政策研究[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 30(9): 46-49. |
| DONG X Q, LI C L, SHAO P B, 2011. Keys to energy saving and emission reduction of electroplating industry in China: Study on policies for promoting the implementation of cleaner production in small and medium electroplating enterprises[J]. Electroplating & Finishing, 30(9): 46-19. | |
| [13] | 付强, 王志良, 梁川, 2002. 多变量自回归模型在三江平原井灌水稻需水量预测中的应用[J]. 水利学报, 33(8): 107-112. |
| FU Q, WANG Z L, LIANG C, 2002. Application of multi-variate auto-regression model to forecast water demand of well irrigated paddy[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 33(8): 107-112. | |
| [14] |
郭长庆, 迟文峰, 匡文慧, 等, 2022. 1990—2020年中国能源开采和加工场地多源数据综合制图与时空变化分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 24(1): 127-140.
DOI |
| GUO C Q, CHI W F, KUANG W H, et al., 2022. Mapping and spatio-temporal changes analysis of energy mining and producing sites in China using multi-source data from 1990 to 2020[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 24(1): 127-140. | |
| [15] | 郭瑞, 矫云阳, 杨强威, 等, 2020. 我国电镀行业危险废物环境管理对策[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 45(3): 112-115. |
| GUO R, JIAO Y Y, YANG Q W, et al., 2020. Environmental management of hazardous waste of electroplating industry in China[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 45(3): 112-115. | |
| [16] | 国务院第四次全国经济普查领导小组办公室, 2018. 中国经济普查年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| Office of the Leading Group for the Fourth National Economic Census of the State Council, 2018. China Economic Census Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press. | |
| [17] | 侯文隽, 龚星, 詹泽波, 等, 2019. 粤港澳大湾区丘陵地带某电镀场地重金属污染特征与迁移规律分析[J]. 环境科学, 40(12): 5604-5614. |
| HOU W J, GONG X, ZHAN Z B, et al., 2019. Heavy metal contamination and migration in correspondence of an electroplating site on the hilly lands of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, China[J]. Environmental Science, 40(12): 5604-5614. | |
| [18] |
匡文慧, 张树文, 杜国明, 等, 2022. 2015—2020年中国土地利用变化遥感制图及时空特征分析[J]. 地理学报, 77(5): 1056-1071.
DOI |
|
KUANG W H, ZHANG S W, DU G M, et al., 2022. Remotely sensed mapping and analysis of spatio-temporal patterns of land use change across China in 2015-2020[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 77(5): 1056-1071.
DOI |
|
| [19] | 赖东麟, 张奇, 陈亭亭, 等, 2020. 张家口市某机械厂原址电镀污染场地土壤修复工程实践[J]. 环境工程, 38(6): 75-80. |
| LAI D L, ZHANG Q, CHEN T T, et al., 2020. Remediation practice of hexavalent chromium and cyanide contaminated soil at the original site of a machinery plant in Zhangjiakou, China[J]. Environmental Engineering, 38(6): 75-80. | |
| [20] | 李桂芹, 黄立勇, 覃凤芝, 2019. 差分整合移动平均自回归模型在医院流感样病例监测中的应用[J]. 首都医科大学学报, 40(2): 286-291. |
| LI G Q, HUANG L Y, QIN F Z, 2019. Application of autoregressive integrated moving average model on monitoring influenza-like illness (ILI) case in hospital[J]. Journal of Capital Medical University, 40(2): 286-291. | |
| [21] | 刘纪远, 匡文慧, 张增祥, 等, 2014. 20世纪80年代以来中国土地利用变化的基本特征与空间格局[J]. 地理学报, 69(1): 3-14. |
|
LIU J Y, KUANG W H, ZHANG Z X, et al., 2014. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land use changes in China since the late 1980s[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 69(1): 3-14.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 刘乙敏, 李义纯, 肖荣波, 2013. 西方国家工业污染场地管理经验及其对中国的借鉴[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(8): 1438-1443. |
| LIU Y M, LI Y C, XIAO R B, 2013. Management experience of industrial contaminated sites in western countries and its implications for China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(8): 1438-1443. | |
| [23] | 马洪芳, 纪立杰, 孙华, 2003. 入世对我国电镀行业的影响[J]. 表面技术 (3): 48. |
| MA H F, JI L J, SUN H, 2003. The influence of entering WTO on electroplating industry in China[J]. Surface Technology (3): 48. | |
| [24] | 仇丽霞, 2018. 医学统计学[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社: 636. |
| QIU L X, 2018. Medical statistics[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press: 636. | |
| [25] | 孙强, 杨婧, 李俊昊, 2015. 电镀行业环境风险评价要点[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 34(21): 1247-1251. |
| SUN Q, YANG J, LI J H, 2015. Key points for environmental risk assessment of electroplating industry[J]. Electroplating & Finishing, 34(21): 1247-1251. | |
| [26] | 王士逯, 梁启民, 马学义, 1999. 改革开放20年天津电镀业大事记[J]. 电镀与精饰, 21(6): 18-22. |
| WANG S L, LIANG Q M, MA X Y, 1999. Major events of Tianjin electroplating industry in 20 years of reform and opening up[J]. Plating and Finishing, 21(6): 18-22. | |
| [27] | 许泽东, 柳福祥, 2016. 灰色GM(1, 1)模型优化研究进展综述[J]. 计算机科学, 43(S2): 6-10. |
| XU Z D, LIU F X, 2016. Survey on Gray GM (1, 1) Model[J]. Computer Science, 43(S2): 6-10. | |
| [28] | 杨智凯, 范彦勤, 印海廷, 等, 2021. 基于ARIMA模型对桂林市GDP的预测研究[J]. 桂林航空工业学院学报, 26(4): 477-483. |
| YANG Z K, FAN Y Q, YIN H T, et al., 2021. Research on GDP prediction of Guilin based on ARIMA model[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Aerospace Technology, 26(4): 477-483. | |
| [29] | 张万里, 郑永浩, 邢万丽, 等, 2022. 基于ARIMA模型的环渤海典型城市生活垃圾产量预测研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 12(3): 861-868. |
| ZHANG W L, ZHENG Y H, XING W L, et al., 2022. Study on prediction of municipal solid waste yield of typical cities around Bohai Region based on ARIMA model[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 12(3): 861-868. | |
| [30] | 中华人民共和国国家统计局, 2018. 国家数据[EB/OL]. (2018-05-14) [2022-12-09]. https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.html?cn=01. |
| National Bureau Statistics of the People’s Republic of China, 2018. National data[EB/OL]. (2018-05-14) [2022-12-09]. https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.html?cn=01. | |
| [31] | 周鼎, 周建民, 彭晓春, 等, 2014. 某电镀搬迁场地土壤重金属污染健康风险评估[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 40(3): 321-324. |
| ZHOU D, ZHOU J M, PENG X C, et al., 2014. Health risk assessments of soil polluted by heavy metals at a site of relocated electroplating[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 40(3): 321-324. |
| [1] | HAO Jinhu, WEI Wei, LI Shengnan, MA Muyuan, LI Xiaoxia, YANG Hongguo, JIANG Qiyu, CHAI Peidong. GEE Based Evaluation of the Spatial-temporal Pattern and Drivers of Long-term Water Body in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [2] | ZHENG Shiyu, ZHANG Lvshui, GUO Xiaomin, HUANG Zijun, XIAO Yihua. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Negative Oxygen Ions in the Air and Environmental Influencing Factors in Forest Environment with Different Canopy Densities: A Case Study of Maofeng Mountain in Guangzhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2204-2212. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
