Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 514-524.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.009
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Yarui1( ), WANG Meijing1, WANG Tao1,2, YANG Meihuan1
), WANG Meijing1, WANG Tao1,2, YANG Meihuan1
Received:2022-11-22
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
作者简介:吴雅睿(1984年生),女,副教授,博士,主要从事环境监测与治理研究。E-mail: wuyarui@xust.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
WU Yarui, WANG Meijing, WANG Tao, YANG Meihuan. Effect of COVID-19 on Temporal and Spatial Distribution of NO2 Concentration and Socio-Economic Life: A Case Study of Shaanxi Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 514-524.
吴雅睿, 王美景, 王涛, 杨梅焕. 新冠疫情下NO2时空变化特征——以陕西省为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 514-524.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.009

Figure 4 Histogram of the decrease rate of epidemic phase I compared with the year-on-year period, the sequential period and the epidemic phase II in Shaanxi Province
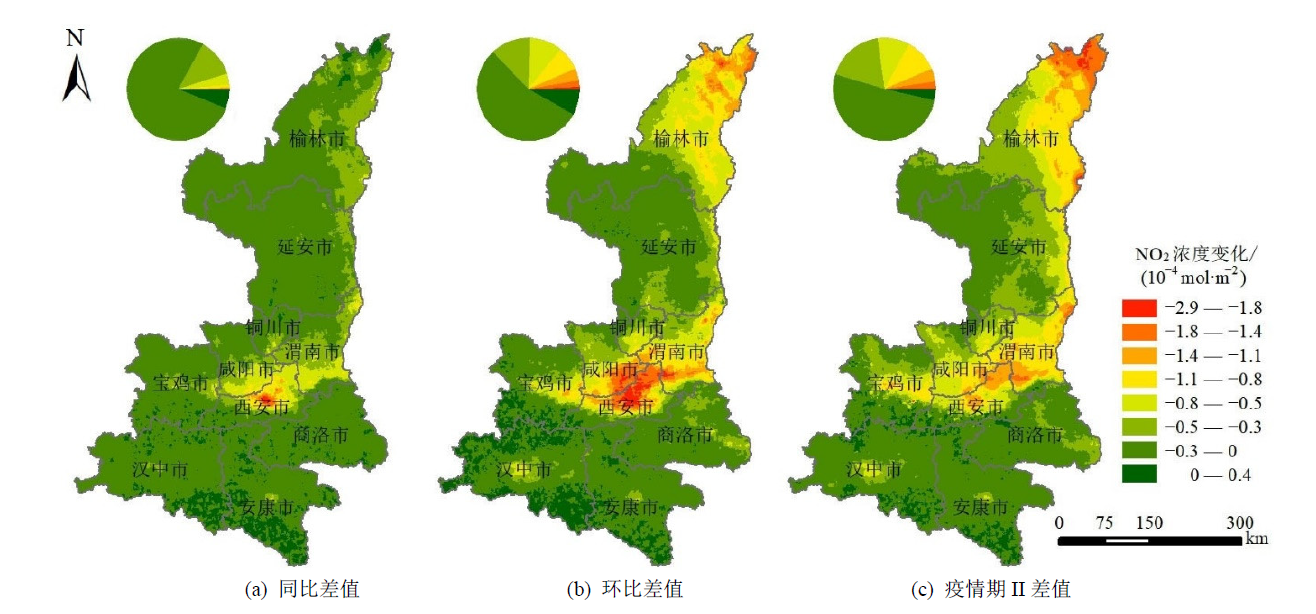
Figure 6 Spatial distribution of tropospheric NO2 column concentration during epidemic period I compared with the year-on-year period, the sequential period and the epidemic period II in Shaanxi province
| 阶段 | 估算柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 实际柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排估算 柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排量占实际柱浓度比重/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疫情期I | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 18.44 |
| 疫情期II | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 2.41 |
Table 1 Comparison between the estimated and actual tropospheric NO2 column concentration in Shaanxi Province
| 阶段 | 估算柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 实际柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排估算 柱浓度/ (10-4 mol∙m-2) | 减排量占实际柱浓度比重/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疫情期I | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 18.44 |
| 疫情期II | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.02 | 2.41 |
| [1] |
BURROWS J P, WEBER M, BUCHWITZ M, et al., 1999. The global ozone monitoring experiment (GOME): Mission concept and first scientific results[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 56(2): 151-175.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHU B, ZHANG S, LIU J, et al., 2021. Significant concurrent decrease in PM2.5 and NO2 concentrations in China during COVID-19 epidemic[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 99(1): 346-353.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JUDD L M, AL-SAADI J A, SZYKMAN J J, et al., 2020. Evaluating Sentinel-5P TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 column densities with airborne and Pandora spectrometers near New York City and Long Island Sound[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 13(11): 6113-6140.
DOI URL |
| [4] | KROTKOV N A, MCLINDEN C A, LI C, et al., 2016. Aura OMI observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16(7): 4605-4629. |
| [5] | SHOWSTACK R, 2014. Sentinel Satellites Initiate New Era in Earth Observation[J]. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 95(26): 239-240. |
| [6] | STEINFELD J I, 1998. Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change[J]. Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development, 40(7): 26-26. |
| [7] |
STOLARSKI R S, BLOOMFIELD P, MCPETERS R D, et al., 1991. Total ozone trends deduced from Nimbus 7 TOMS data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 18(6): 1015-1018.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHANG R, ZHANG Y, LIN H, et al., 2020. NOx emission reduction and recovery during COVID-19 in East China[J]. Atmosphere, 11(4): 433-448.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHENG B. Zhang Q, Geng G et al., 2021. Changes in China's anthropogenic emissions and air quality during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020[J]. Earth System Science Data, 13(6): 2895-2907.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHENG Z H, YANG Z W, WU Z F, et al., 2019. Spatial variation of NO2 and its impact factors in China: An application of sentinel-5P products[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(16): 1939-1962.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 蔡晓斌, 任永鹏, 张媛, 等, 2020. 利用卫星遥感NO2监测结果分析COVID-19疫情对我国社会经济活动的短期影响[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 54(6): 1045-1050. |
| CAI X B, REN Y P, ZHANG Y, et al., 2020. The short-term impact estimate of COVID-19 epidemic on social-economic activity of China by using remotely sensed NO2 observations[J]. Journal of Central Normal University, 54(6): 1045-1050. | |
| [12] | 陈罕立, 王金南, 2005. 关于我国NOx排放总量控制的探讨[J]. 环境科学研究, 18(5): 107-110. |
| CHEN H L, WANG J N, 2005. Exploring the total emission control of nitrogen oxides in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 18(5): 107-110. | |
| [13] | 江文华, 马建中, 颜鹏, 等, 2006. 利用GOME卫星资料分析北京大气NO2污染变化[J]. 应用气象学报, 17(1): 67-72. |
| JIANG W H, MA J Z, YAN P, et al., 2006. Characterization of NO2 pollution changes in beijjing Using GOME satellite data[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 17(1): 67-72. | |
| [14] | 李令军, 王英, 2011. 基于卫星遥感与地面监测分析北京大气NO2污染特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 31(12): 2762-2768. |
| LI L J, WANG Y, 2011. The characterization of NO2 pollution in Beijing based on satellite and conventional observation data[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 31(12): 2762-2768. | |
| [15] |
李龙, 施润和, 陈圆圆, 等, 2013. 基于OMI数据的中国NO2时空分布与人类影响分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 15(5): 688-694.
DOI |
| LI L, SHI R H, CHEN Y Y, et al., 2013. Spatio-temporal characteristics of NO2 in China and the anthropogenic influences analysis based on OMI data[J]. Journal of Geo-information Sciences, 15(5): 688-694. | |
| [16] | 李鹏, 肖致美, 陈魁, 等, 2016. 基于OMI数据天津市NO2浓度分布特征及其适用性[J]. 环境科学与技术, 39(1): 183-186, 204. |
| LI P, XIAO Z M, CHEN K, et al., 2016. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of tropospheric NO2 and its adaptability in Tianjin using OMI satellite remote sensing data[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(1): 183-186, 204. | |
| [17] | 李旭文, 张悦, 姜晟, 等, 2019. “哨兵-5P” 卫星TROPOMI传感器在江苏省域大气污染监测中的初步应用[J]. 环境监控与预警, 11(2): 10-16. |
| LI X W, ZHANG Y, JIANG S, et al., 2019. Preliminary Application of Atmospheric Pollution Monitoring in Jiangsu Province with TROPOMI Sensor Onboard Sentinel - 5P Satellite[J]. Environment Monitoring and Forewarning, 11(2): 10-16. | |
| [18] | 刘文清, 陈臻懿, 刘建国, 2016. 我国大气环境立体监测技术及应用[J]. 科学通报, 61(30): 3196-3207. |
| LIU W Q, CHEN Z Y, LIU J G, 2016. Stereoscopic monitoring technology and applications for the atmospheric environment in China[J]. Science China Press, 61(30): 3196-3207. | |
| [19] | 刘跃斌, 张远, 张逸冰, 等, 2021. 邯郸市新冠疫情前后空气质量指数(AQI)对比与疫情防控期间大气污染特征分析[J]. 环境化学, 40(12): 3743-3754. |
| LIU Y B, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y B, et al., 2021. Comparison of air quality index (AQI) before and after COVID-19 in Handan City and analysis of air pollution characteristics during COVID-19 prevention and control[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 40(12): 3743-3754. | |
| [20] | 秦臻, 张明, 张月莹, 等, 2021. COVID-19疫情对河南省空气质量及社会经济活动短期影响[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(6): 221-228. |
| QIN Z, ZHANG M, ZHANG Y Y, et al., 2021. Short term impact of COVID-19 on Air quality and social economic activities in Henan province[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 37(6): 221-228. | |
| [21] | 陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队, 2020. 陕西统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社:52- 53. |
| Shaanxi Bureau of Statistics, Shaanxi Survey Team of National Bureau of Statistics, 2019. Shaanxi statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press:52- 53. | |
| [22] | 陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队, 2021. 陕西统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社:52- 53. |
| Shaanxi Bureau of Statistics, Shaanxi Survey Team of National Bureau of Statistics, 2020. Shaanxi statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press:52- 53. | |
| [23] | 陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队, 2022. 陕西统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社:52- 53. |
| Shaanxi Bureau of Statistics, Shaanxi Survey Team of National Bureau of Statistics, 2021. Shaanxi statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press:52- 53. | |
| [24] | 陶金花, 王子峰, 韩冬, 等, 2009. 华北地区秸秆禁烧前后的NO2卫星遥感监测分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 29(10): 1016-1020. |
| TAO J H, WANG Z F, HAN D, et al., 2009. Analysis of crop residue burning and tropospheric NO2 vertical column density retrieved from satellite remote sensing in North China.[J]. China Environmental Science, 29(10): 1016-1020. | |
| [25] | 陶金花, 范萌, 顾坚斌, 等, 2020. 新冠病毒疫情期间复工复产卫星遥感监测[J]. 遥感学报, 24(7): 824-836. |
| TAO J H, FAN M, GU J B, et al., 2020. Satellite observations of the return-to- work over China during the period of COVID-19[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(7): 824-836. | |
| [26] | 王厚俊, 陈志芳, 吴莹, 等, 2022. 基于TROPOMI的扬州市对流层甲醛和二氧化氮时空分布特征分析[J]. 环境监控与预警, 14(3): 70-75, 94. |
| WANG H J, CHEN Z F, WU Y, et al., 2022. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of formaldehyde and nitrogen dioxide in troposphere in Yangzhou city based on TROPOMI[J]. Environment Monitoring and Forewarning, 14(3): 70-75, 94. | |
| [27] | 姚凌, 吕宁, 师华定, 2012. 利用SCIAMACHY遥感资料研究我国NO2柱浓度及其时空分布[J]. 环境科学研究, 25(4): 419-424. |
| YAO L, LÜ N, SHI H D, 2012. Study on spatial-temporal variations in total NO2 column amounts over China using SCIAMACHY data[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 25(4): 419-424. | |
| [28] | 乐旭, 雷亚栋, 周浩, 等, 2020. 新冠肺炎疫情期间中国人为碳排放和大气污染物的变化[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(2): 265-274. |
| YUE X, LI Y D, ZHOU H, et al., 2020. Changes of anthropogenic carbon emissions and air pollutants during the COVID-19 epidemic in China[J]. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 43(2): 265-274. | |
| [29] | 张晗, 余超, 苏林, 等, 2017. MODIS和OMI数据评估阅兵期间北京市大气减排成效[J]. 遥感学报, 21(4): 622-632. |
| ZHAN H, YU C, SU L, et al., 2017. Emission control effects observed from space during the military parade 2015 in Beijing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(4): 622-632. | |
| [30] | 张连华, 周春艳, 厉青, 等, 2019. 2016-2018年汾渭平原对流层NO2柱浓度时空变化遥感监测[J]. 环境生态学, 1(4): 67-73. |
| ZHANG L H, ZHOU C Y, LI Q, et al., 2019. Remote sensing monitoring of spatiotemporal changes of tropospheric NO2 column concentration of Fen-Wei Plain in the year of 2016-2018[J]. Environmental Ecology, 1(4): 67-73. | |
| [31] |
张岳军, 朱凌云, 郭伟, 等, 2020. 汾渭平原大气SO2和NO2时空变化特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(6): 1147-1156.
DOI |
| ZHANG Y J, ZHU L Y, GUO W, et al., 2020. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of atmospheric SO2 and NO2 in Fenwei Plain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(6): 1147-1156. | |
| [32] | 赵金环, 蔡坤, 李莘莘, 等, 2021. 新冠疫情对我国NO2排放影响的时空分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(1): 56-62. |
| ZHAO J H, CAI K, LI S S, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal analysis on the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on NO2 emission in China[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(1): 56-62. | |
| [33] | 郑晓霞, 李令军, 赵文吉, 等, 2014. 京津冀地区大气NO2污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(12):1938-1945. |
| ZHENG X X, LI L J, ZHAO W J, et al., 2014. Spatial and temporal characteristics of atmospheric NO2 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(12): 1938-1945. | |
| [34] | 郑子豪, 吴志峰, 陈颖彪, 等, 2021. 基于Sentinel-5P的粤港澳大湾区NO2污染物时空变化分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(1): 63-72. |
| ZHENG Z H, WU Z F, CHEN Y B, et al., 2021. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of NO2 pollutants in Guangdong Hong Kong Macao Greater Bay Area based on Sentinel -5P satellite data[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(1): 63-72. | |
| [35] | 周春艳, 厉青, 王中挺, 等, 2016. 2005年-2014年京津冀对流层NO2 柱浓度时空变化及影响因素[J]. 遥感学报, 20(3): 468-480. |
| ZHOU C Y, LI Q, WANG Z T, et al., 2016. Spatio-temporal trend and changing factors of tropospheric NO2 column density in Bijing Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 20(3): 468-480. | |
| [36] | 周黎, 胡海涛, 王晓峰, 2022. 利用哨兵5P卫星数据初探攀枝花市域大气遥感监测[J]. 环保科技, 28(2): 40-44. |
| ZHOU L, HU H T, WANG X F, 2022. A preliminary study on the atmospheric remote sensing monitoring in Panzhihua City using Sentinel 5 P satellite data[J]. Environmental Technology, 28(2): 40-44. |
| [1] | LEI ShePing, FAN YanXiang, XIE JianCang. Analysis of Urban Industrial Sewage Discharge Decoupling and Driving Effect Decomposition on the Loess Plateau: A Case Study of Shaanxi Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 351-360. |
| [2] | LI Dengke, WANG Zhao. Quantitative Analysis of the Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation NPP in Shaanxi Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1071-1079. |
| [3] | YI Jiahui, HE Chao, YANG Lu, YE Zhixiang, TIAN Ya, KE Biqin, MU Hang, TU Peiyue, HAN Chaoran, HONG Song. Spatial Correlation between Changes in Global Temperature and Major Air Pollutants during the COVID-19 Pandemic [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 740-749. |
| [4] | WANG Wei, CHENG Xinyue, HU Chun, XIA Sihan, WANG Tian. Spatio-temporal Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 and Air Quality Evaluation in Urban Street Canyons: Take Changhuai Street in Hefei as An Example [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2157-2164. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
