Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1706-1715.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.017
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Ping( ), FANG Chun, ZHU Sihan, HAN Song, LI Kai, WANG Zhikang*(
), FANG Chun, ZHU Sihan, HAN Song, LI Kai, WANG Zhikang*( )
)
Received:2021-05-10
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
Contact:
WANG Zhikang
通讯作者:
王志康
作者简介:张萍(1990年生),女,讲师,博士研究生,研究方向为污水处理技术与理论。E-mail: zhangping890511@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Ping, FANG Chun, ZHU Sihan, HAN Song, LI Kai, WANG Zhikang. Optimization of Microalgae Species and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Conversion for Domestic Sewage Treatment[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1706-1715.
张萍, 方淳, 朱思涵, 韩松, 李凯, 王志康. 生活污水处理中微藻的优选及氮、磷转化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1706-1715.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.017
| 成分 Component | 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 高质量浓度 High mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K2HPO4∙3H2O | 18.4 | 55.25 | 110.5 |
| NH4Cl | 57.3 | 114.6 | 229.3 |
| C6H12O6 | 94.32 | 235.8 | 471.7 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| CaCl2∙2H2O | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| C6H8FeNO7 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| EDTA-Na2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H3BO3 | 2.86 | 2.86 | 2.86 |
| MnCl2∙4H2O | 1.86 | 1.86 | 1.86 |
| ZnSO4∙7H2O | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| CuSO4∙5H2O | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Na2MoO4∙2H2O | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| Co(NO3)2∙6H2O | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Table 1 Simulated domestic sewage composition
| 成分 Component | 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) | 高质量浓度 High mass concentration/ (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K2HPO4∙3H2O | 18.4 | 55.25 | 110.5 |
| NH4Cl | 57.3 | 114.6 | 229.3 |
| C6H12O6 | 94.32 | 235.8 | 471.7 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| CaCl2∙2H2O | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| C6H8FeNO7 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| EDTA-Na2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| H3BO3 | 2.86 | 2.86 | 2.86 |
| MnCl2∙4H2O | 1.86 | 1.86 | 1.86 |
| ZnSO4∙7H2O | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| CuSO4∙5H2O | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Na2MoO4∙2H2O | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| Co(NO3)2∙6H2O | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
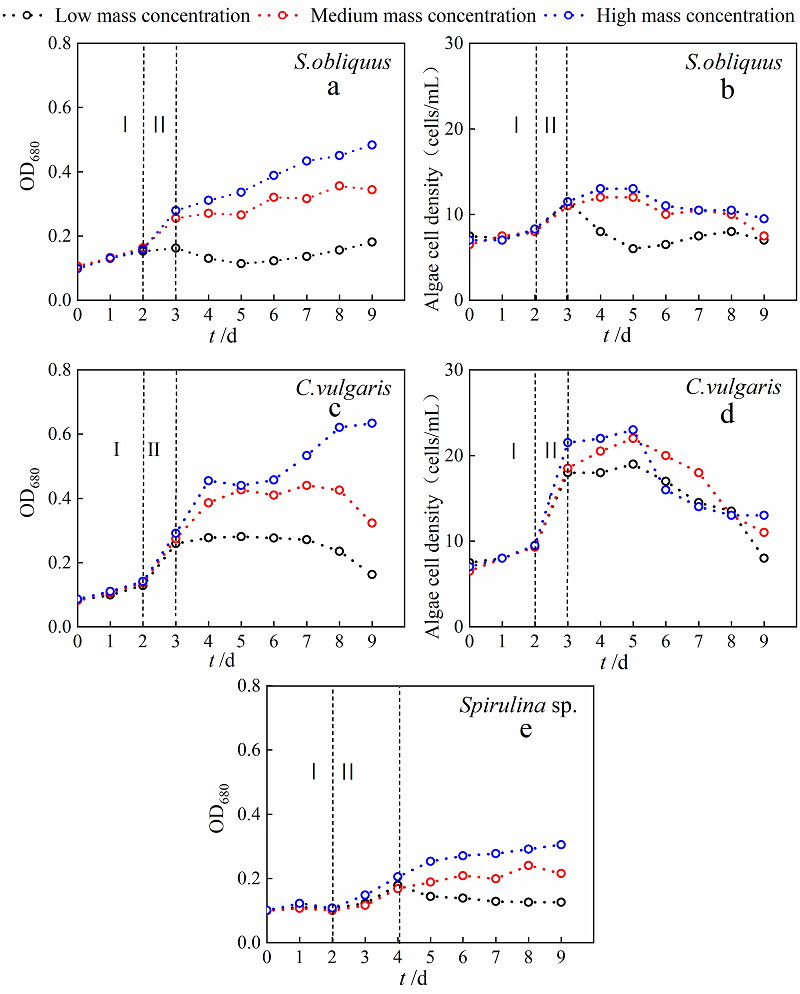
Fig. 1 Changes of microalgae biomass in simulated domestic sewage with different mass concentrations over time Ⅰ refer to adaptation phase, Ⅱ refer to logarithmic growth phase; a, c and e refer to algae cell OD680, b and d refer to algae cell density
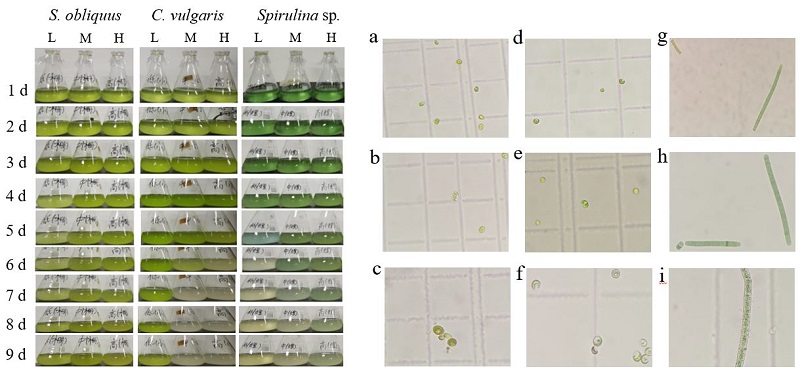
Fig. 2 Growth of various microalgae in low, medium and high mass concentration simulated domestic sewage ×400 microscope field of view: L, M, H refer to low mass concentration, medium mass concentration, and high mass concentration; a-c refer to S. obliquus, d-f refer to C. vulgaris, g-i refer to Spirulina sp.
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | SRP 去除率 SRP removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 31.53 | 44.02 | 45.69 | 66.51 | 74.01 | 82.34 | 76.51 | 74.01 | 75.68 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 29.86 | 35.69 | 55.68 | 74.84 | 78.18 | 84.84 | 85.67 | 78.18 | 78.18 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 31.53 | 27.36 | 49.85 | 53.19 | 53.19 | 56.52 | 54.85 | 49.02 | 47.35 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 19.42 | 20.81 | 27.47 | 35.80 | 41.91 | 54.68 | 51.63 | 52.19 | 52.74 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 18.31 | 23.86 | 28.86 | 36.91 | 36.36 | 45.24 | 50.80 | 51.63 | 49.41 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 17.20 | 18.59 | 25.53 | 33.30 | 33.30 | 40.25 | 38.30 | 38.30 | 36.36 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 14.45 | 16.95 | 23.34 | 29.17 | 29.17 | 36.80 | 39.02 | 40.69 | 44.58 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 17.23 | 18.48 | 21.67 | 27.08 | 27.50 | 36.94 | 35.70 | 38.61 | 40.97 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 14.87 | 18.34 | 21.53 | 25.14 | 22.50 | 22.36 | 28.06 | 27.50 | 30.97 | ||
Table 2 Removal efficiency of SRP from simulated domestic sewage with different mass concentrations by three microalgae
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | SRP 去除率 SRP removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 31.53 | 44.02 | 45.69 | 66.51 | 74.01 | 82.34 | 76.51 | 74.01 | 75.68 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 29.86 | 35.69 | 55.68 | 74.84 | 78.18 | 84.84 | 85.67 | 78.18 | 78.18 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 31.53 | 27.36 | 49.85 | 53.19 | 53.19 | 56.52 | 54.85 | 49.02 | 47.35 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 19.42 | 20.81 | 27.47 | 35.80 | 41.91 | 54.68 | 51.63 | 52.19 | 52.74 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 18.31 | 23.86 | 28.86 | 36.91 | 36.36 | 45.24 | 50.80 | 51.63 | 49.41 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 17.20 | 18.59 | 25.53 | 33.30 | 33.30 | 40.25 | 38.30 | 38.30 | 36.36 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 14.45 | 16.95 | 23.34 | 29.17 | 29.17 | 36.80 | 39.02 | 40.69 | 44.58 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 17.23 | 18.48 | 21.67 | 27.08 | 27.50 | 36.94 | 35.70 | 38.61 | 40.97 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 14.87 | 18.34 | 21.53 | 25.14 | 22.50 | 22.36 | 28.06 | 27.50 | 30.97 | ||
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | NH4+-N去除率 NH4+-N removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 17.82 | 19.84 | 29.54 | 33.98 | 46.10 | 52.16 | 49.74 | 44.08 | 47.72 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 15.80 | 7.31 | 45.70 | 56.20 | 61.86 | 60.24 | 56.20 | 30.34 | 46.51 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 12.16 | -8.44 | 6.91 | 33.17 | 27.52 | 36.00 | 26.30 | 24.69 | 20.24 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -38.67 | -24.73 | -13.82 | -6.95 | 5.17 | 16.89 | 14.26 | 9.01 | 10.42 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.77 | -36.24 | -10.99 | -0.89 | -5.13 | 8.61 | 22.55 | 14.67 | 7.39 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -34.42 | -34.83 | -30.99 | -4.32 | -5.33 | 2.55 | 1.13 | 5.37 | -0.08 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -30.85 | -28.02 | -15.49 | -12.46 | -2.97 | 0.97 | -0.65 | 11.27 | 9.25 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.53 | -35.90 | -17.62 | -7.41 | -5.29 | -3.68 | 1.88 | 8.34 | 12.79 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -42.77 | -36.10 | -24.59 | -13.37 | -18.12 | -17.82 | -10.85 | -9.33 | -2.67 | ||
Table 3 Removal efficiency of NH4+-N from simulated domestic sewage with different mass concentrations by three microalgae
| 污水类型 Type of wastewater | 藻种 Algae species | NH4+-N去除率 NH4+-N removal efficiency/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 d | 6 d | 7 d | 8 d | 9 d | |||
| 低质量浓度 Low mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | 17.82 | 19.84 | 29.54 | 33.98 | 46.10 | 52.16 | 49.74 | 44.08 | 47.72 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | 15.80 | 7.31 | 45.70 | 56.20 | 61.86 | 60.24 | 56.20 | 30.34 | 46.51 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | 12.16 | -8.44 | 6.91 | 33.17 | 27.52 | 36.00 | 26.30 | 24.69 | 20.24 | ||
| 中质量浓度 Medium mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -38.67 | -24.73 | -13.82 | -6.95 | 5.17 | 16.89 | 14.26 | 9.01 | 10.42 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.77 | -36.24 | -10.99 | -0.89 | -5.13 | 8.61 | 22.55 | 14.67 | 7.39 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -34.42 | -34.83 | -30.99 | -4.32 | -5.33 | 2.55 | 1.13 | 5.37 | -0.08 | ||
| 高质量浓度 High mass concentration | 斜生栅藻 S. obliquus | -30.85 | -28.02 | -15.49 | -12.46 | -2.97 | 0.97 | -0.65 | 11.27 | 9.25 | |
| 普通小球藻 C. vulgaris | -28.53 | -35.90 | -17.62 | -7.41 | -5.29 | -3.68 | 1.88 | 8.34 | 12.79 | ||
| 螺旋藻 Spirulina sp. | -42.77 | -36.10 | -24.59 | -13.37 | -18.12 | -17.82 | -10.85 | -9.33 | -2.67 | ||
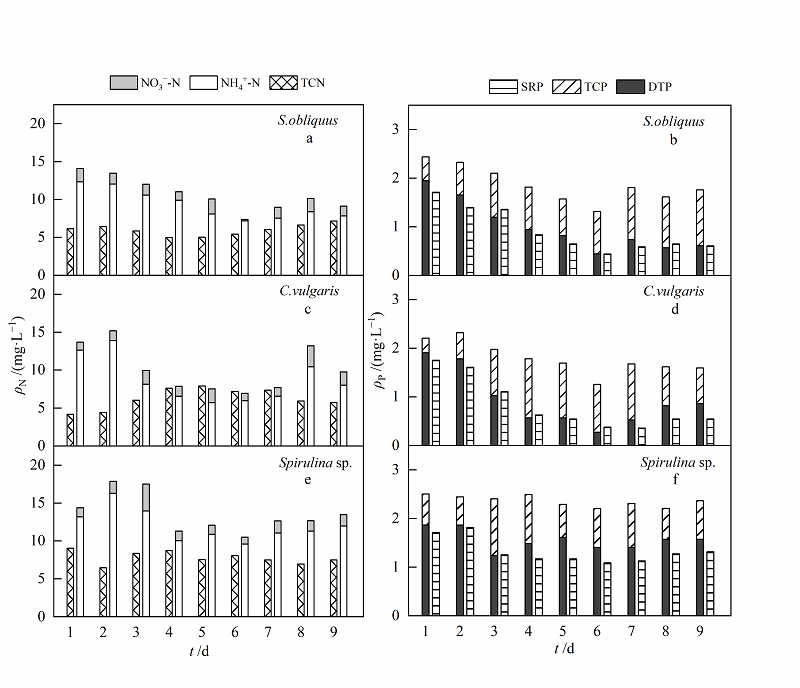
Fig. 4 Transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus form in low mass concentration simulated domestic sewage a, c and e refer to different forms of nitrogen mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.;figure b, d and f refer to different forms of phosphorus mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.
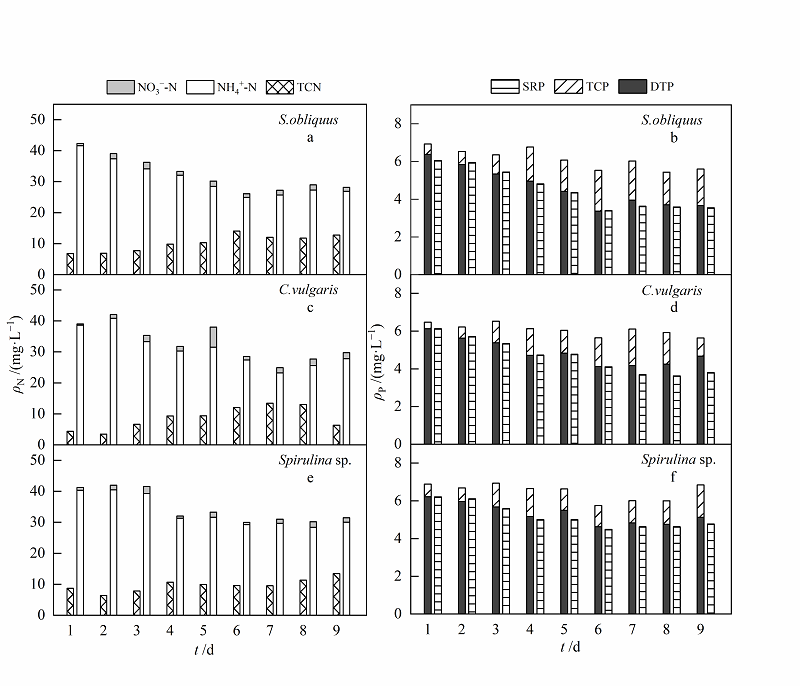
Fig. 5 Transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus form in medium mass concentration simulated domestic sewage a, c and e refer to different forms of nitrogen mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.;figure b, d and f refer to different forms of phosphorus mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.
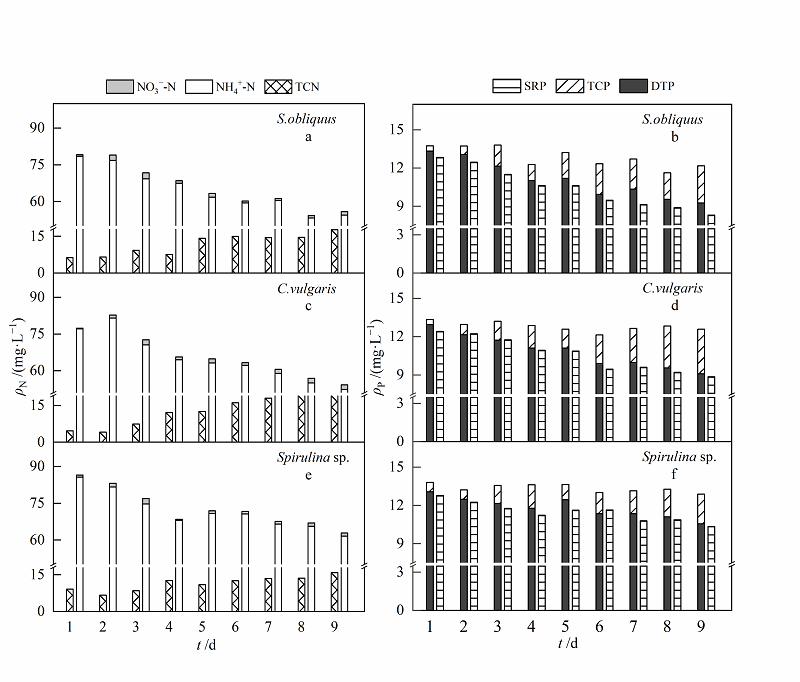
Fig. 6 Transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus form in high mass concentration simulated domestic sewage a, c and e refer to different forms of nitrogen mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.;figure b, d and f refer to different forms of phosphorus mass concentration in wastewater treated by S. obliquus, C. vulgaris and Spirulina sp.
| [1] | ALEJANDRO R M, MENDOZA-ESPINOSA L G, TOM S, 2010. Growth and nutrient removal in free and immobilized green algae in batch and semi-continuous cultures treating real wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 10(1): 58-64. |
| [2] |
ASLAN S, KAPDAN I K, 2006. Batch kinetics of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from synthetic wastewater by algae[J]. Ecological Engineering, 28(1): 64-70.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BEUCKELS A, SMOLDERS E, MUYLAERT K, 2015. Nitrogen availability influences phosphorus removal in microalgae-based wastewater treatment[J]. Water Research, 77: 98-106.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHAI W S, TAN W G, SITI H M H, et al., 2021. Multifaceted roles of microalgae in the application of wastewater biotreatment: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116236.
DOI |
| [5] |
CHEN H, WANG Q, 2020. Microalgae-based nitrogen bioremediation[J]. Algal Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.algal.2019.101775.
DOI |
| [6] |
CUELLAR-BERMUDEZ S P, ALEMAN-NAVA G S, CHANDRA R, et al., 2017. Nutrients utilization and contaminants removal. A review of two approaches of algae and cyanobacteria in wastewater[J]. Algal Research, 24: 438-449.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FEFFER A, NELSON Y, WOERTZ I, et al., 2009. Algae Grown on Dairy and Municipal Wastewater for Simultaneous Nutrient Removal and Lipid Production for Biofuel Feedstock[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 135(11): 1115-1122.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
FRANCHINO M, COMINO E, BONA F, et al., 2013. Growth of three microalgae strains and nutrient removal from an agro-zootechnical digestate[J]. Chemosphere, 92(6): 738-744.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI X, HU H Y, GAN K, et al., 2010. Growth and nutrient removal properties of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. LX1 under different kinds of nitrogen sources[J]. Ecological Engineering, 36(4): 379-381.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIANG Z J, LIU Y, GE F, et al., 2013. Efficiency assessment and pH effect in removing nitrogen and phosphorus by algae-bacteria combined system of Chlorella vulgaris and Bacillus licheniformis[J]. Chemosphere, 92(10): 1383-1389.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LU Q, ZHOU W G, MIN M, et al., 2015. Growing Chlorella sp. On meat processing wastewater for nutrient removal and biomass production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 198: 189-197.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MALIHE B, SADEGH H M, SAEED A, 2021. Direct brackish water desalination using Chlorella vulgaris microalgae[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 148: 237-248.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
OLGUÍN E J, 2003. Phycoremediation: key issues for cost-effective nutrient removal processes[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 22(1-2): 81-91.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ÓRPEZ R, MARTÍNEZ M E, HODAIFA G, et al., 2008. Growth of the microalga Botryococcus braunii in secondarily treated sewage[J]. Desalination, 246(1-3): 625-630.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PEREZ-GARCIA O, ESCALANTE F M E, DE-BASHAN L E, et al., 2011. Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: Metabolism and potential products[J]. Water Research, 45(1): 11-36.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PRANDINI J M, DA SILVA M L B, MEZZARI M P, et al., 2016. Enhancement of nutrient removal from swine wastewater digestate coupled to biogas purification by microalgae Scenedesmus spp.[J]. Bioresource Technology, 202: 67-75.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
REN H, TUO J, ADDY M M, et al., 2017. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris in a pilot-scale photobioreactor using real centrate wastewater with waste glycerol for improving microalgae biomass production and wastewater nutrients removal[J]. Bioresource Technology, 245: 1130-1138.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SANTOS-BALLARDO D U, ROSSI S, HERNÁNDEZ V, et al., 2015. A simple spectrophotometric method for biomass measurement of important microalgae species in aquaculture[J]. Aquaculture, 448: 87-92.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SU Y, MENNERICH A, URBAN B, 2011. Municipal wastewater treatment and biomass accumulation with a wastewater-born and settleable algal-bacterial culture[J]. Water Research, 45(11): 3351-3358.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG J, ZHOU W, YANG H, et al., 2015. Trophic mode conversion and nitrogen deprivation of microalgae for high ammonium removal from synthetic wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 196: 668-676.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 常婷, 许智慧, 程鹏飞, 等, 2019. 不同氨氮浓度对4株常见藻株生长及酶活性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(8): 3642-3649. |
| CHANG T, XU Z H, CHENG P F, et al., 2019. Effects of Different Concentrations of Ammonia Nitrogen on the Growth and Enzyme Activity of Four Common Algae Strains[J]. Environmental Science, 40(8): 3642-3649. | |
| [22] | 邓祥元, 丁婉婉, 樊玲波, 等, 2013. 2种微藻去除氮、磷能力的比较[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 35(6): 694-698, 726. |
| DENG X Y, DING W W, FAN L B, et al., 2013. Comparative Study on N and P Removal Ability of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 35(6): 694-698, 726. | |
| [23] | 苟尧, 2018. 菌藻生物反应器处理模拟生活污水的性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学: 23-25. |
| GOU Y, 2018. Performance of using algal-bacterial bioreactors for synthetic domestic wastewater treatment[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University: 23-25. | |
| [24] | 国家环境保护局水和污水监测分析方法编委会, 1997. 水和污水监测分析方法[M]. 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Editorial board of water and waste water monitoring and analysis methods of State Environmental Protection Administration, 1997. Water and waste water monitoring and analysis methods[M]. Fourth Edition. Beijing: China Environmental Press. | |
| [25] | 韩佩, 2018. 螺旋藻协同沸石高效处理高氨氮废水的研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学: 27. |
| HAN P, 2018. Study on effective treatment of high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater by combination of spirulina and zeolite[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University: 27. | |
| [26] | 郝晓地, 靳景宜, 罗玉琪, 等, 2020. 可沉微藻转化油脂潜力及PHB合成试验研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 36(7): 1-6. |
| HAO X D, JIN J Y, LUO Y Q, et al., 2020. Lipids Conversion Potential and PHB Synthesis of Settleable Microalgae[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 36(7): 1-6. | |
| [27] | 胡洪营, 李鑫, 杨佳, 2009. 基于微藻细胞培养的水质深度净化与高价值生物质生产耦合技术[J]. 生态环境学报, 18(3): 1122-1127. |
| HU H Y, LI X, YANG J, 2009. Coupling of wastewater deep purification and high quality biomass production based on microalgae cultivation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(3): 1122-1127. | |
| [28] | 胡鸿钧, 魏印心, 2006. 中国淡水藻类-系统、分类及生态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 7. |
| HU H J, WEI Y X, 2006. The Freshwater Algae of China systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 7. | |
| [29] | 黄静依, 张皓驰, 李先宁, 2020. 水产养殖废水处理的菌藻共生系统中藻种优选及氮、磷转化特性[J]. 净水技术, 39(9): 57-66, 84. |
| HUANG J Y, ZHANG H C, LI X N, 2020. Optimization of Microalgae Species and Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Conversion in Algae-Bacteria Symbiotic System for Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment[J]. Water Purification Technology, 39(9): 57-66, 84. | |
| [30] | 黄添浩, 林磊, 王趁义, 等, 2019. 吸氮除磷材料的研究和应用现状[J]. 化工新型材料, 47(3): 39-42, 46. |
| HUANG T H, LIN L, WANG C Y, et al., 2019. Research and application of nitrogen and phosphorus removal material[J]. New Chemical Materials, 47(3): 39-42, 46. | |
| [31] | 贾纬, 聂毅磊, 陈宏, 等, 2021. 水产养殖废水脱氮除磷微藻的筛选[J]. 福建农业学报, 36(2): 1-6. |
| JIA W, NIE Y L, CHEN H, et al., 2021. Microalgae for Effective Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal from aquaculture Effluence[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 36(2): 1-6. | |
| [32] | 江红霞, 郑怡, 2003. 微藻的药用, 保健价值及研究开发现状 (综述)[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 32(1): 68-72. |
| JIANG H X, ZHENG Y. 2003. A review of pharmaceutical and health care value of microalgae and their current status of research and development[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 32(1): 68-72. | |
| [33] | 姜红鹰, 周玉玲, 张桂敏, 等, 2017. 普通小球藻对养殖污水脱氮除磷的效果研究[J]. 生物资源, 39(3): 204-210. |
| JIANG H Y, ZHOU Y L, ZHANG G M, et al., 2017. Effect of Chlorella vulgaris on nitrogen and phosphorus removal from breeding wastewater[J]. Biotic Resources, 39(3): 204-210. | |
| [34] | 李扬, 2020. 微藻处理污水研究进展[J]. 水资源开发与管理, 8(4): 13-18. |
| LI Y, 2020. Research progress on treatment of sewage by microalgae[J]. Water Resources Development and Management, 8(4): 13-18. | |
| [35] | 梁芳, 鸭乔, 杜伟春, 等, 2014. 微藻光密度与细胞密度及生物质的关系[J]. 生态学报, 34(21): 6156-6163. |
| LIANG F, YA Q, DU W C, et al., 2014. The relationships between optical density, cell number, and biomass of four microalgae[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(21): 6156-6163. | |
| [36] | 刘磊, 杨雪薇, 陈朋宇, 等, 2014. 3种微藻对人工污水中氮磷去除效果的研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 41(11): 172-176, 201. |
| LIU L, YANG X W, CHEN P Y, et al., 2014. Efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from artificial wastewater by three kinds of microalgae[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 41(11): 172-176, 201. | |
| [37] | 刘淑坡, 李飞, 2012. 固定化核蛋白小球藻对人工废水中不同形态氮和磷的去除[J]. 山东理工大学学报 (自然科学版), 26(4): 43-47. |
| LIU S P, LI F, 2012. Removal of different forms nitrogen and phosphorus in artificial wastewater by immobilized Chlorella pyrenoidosa[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 26(4): 43-47. | |
| [38] | 刘伟, 2006. 雨生红球藻规模化培养工艺的构建及相关生物学特性的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所: 1. |
| LIU W, 2006. Technological assembly and related biological study in a pilot scale culture of Haematococcus pluvialis[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1. | |
| [39] | 罗龙皂, 林小爱, 朱峰, 等, 2019. 曝二氧化碳气体对近具刺链带藻在高氨氮废水中生长的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 31(9): 1541-1548. |
| LUO L Z, LIN X A, ZHU F, et al., 2019. Effect of aeration with carbon dioxide on growth of Desmodesmus sp. CHX1 in wastewater with high concentration of ammonium nitrogen[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 31(9): 1541-1548. | |
| [40] | 皮永蕊, 吕永红, 柳莹, 等, 2019. 微藻-细菌共生体系在废水处理中的应用[J]. 微生物学报, 59(6): 1188-1196. |
| PI Y R, LV Y H, LIU Y, et al., 2019. Application of microalgae-bacteria symbiosis system in wastewater treatment[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 59(6): 1188-1196. | |
| [41] | 秦乐乐, 李菊芳, 徐微, 等, 2020. 好氧接触氧化-混凝沉淀-人工湿地处理洗涤废水[J]. 中国给水排水, 36(2): 89-92. |
| QIN L L, LI J F, XU W, et al., 2020. Treatment of washing wastewater by aerobic contact oxidation/coagulation precipitation/constructed wetland process[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 36(2): 89-92. | |
| [42] | 脱金华, 任洪艳, 刘方舟, 等, 2019. 利用实际市政污水培养小球藻及优化外加碳源[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(1): 184-190. |
| TUO J H, REN H Y, LIU F Z, et al., 2019. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using real municipal wastewater and optimization of external carbon source[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 25(1): 184-190. | |
| [43] | 王海英, 牟晓庆, 2011. 城市污水培养富油蛋白小球藻的研究[J]. 中南民族大学学报 (自然科学版), 30(3): 38-41. |
| WANG H Y, MU X Q, 2011. Cultivation of high oil content Chlorella pyrenoidosa on urban sewage[J]. Journal of South-Central University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 30(3): 38-41. | |
| [44] | 王璐瑶, 桑敏, 李爱芬, 等, 2012. 不同缺氮营养水平对金色奥杜藻生长及光合生理的影响[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 32(6): 48-56. |
| WANG L Y, SANG M, LI A F, et al., 2012. Effects of Different Nitrogen Nutrition Level on the Growth and Photosynthetic Physiology of Odontella aurita[J]. China Biotechnology, 32(6): 48-56. | |
| [45] | 徐凯, 2015. 微藻脂肪酸积累的调控优化研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛农业大学: 4-5. |
| XU K, 2015. Optimization of regulation on fatty acid accumulation in microalgae[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao Agricultural University: 4-5. | |
| [46] | 杨福利, 李秀辰, 白晓磊, 等, 2014. 小球藻脱氮除磷及其生物量增殖潜力的研究[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 29(2): 193-197. |
| YANG F L, LI X C, BAI X C, et al., 2014. The removal efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus wastes and multiplication in biomass in green alga Chlorella vulgaris[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 29(2): 193-197. | |
| [47] | 于殿江, 施定基, 何培民, 等, 2021. 微藻规模化培养研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 61(2): 333-345. |
| YU D J, SHI D J, HE P M, et al., 2021. Progress in large-scale culture of microalgae[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 61(2): 333-345. | |
| [48] | 于茜, 朱元荣, 王焕华, 等, 2016. 铜绿微囊藻培养过程中氨基酸的释放特征及其对水体有机质的贡献[J]. 环境科学研究, 29(3): 360-367. |
| YU X, ZHU Y R, WANG H H, et al., 2016. Release of Amino Acids from Microcystis aeruginosa and its contributions to organic matter[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 29(3): 360-367. | |
| [49] | 于媛, 刘艳, 韩芸芸, 等, 2006. 小球藻去除水产加工废水中氨态氮的初步研究[J]. 生物技术, 16(5): 73-74. |
| YU Y, LIU Y, HAN Y Y, et al., 2006. The Primary Studies on Ammonia-nitrogen Removal from Fisheries Process Wastewater by Chlorella vulgaris[J]. Biotechnology, 16(5): 73-74. | |
| [50] | 余江, 陶红群, 王亚婷, 等, 2019. 磷受控对酿酒废水-微藻培育耦合体系的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 54(3): 655-662. |
| YU J, TAO H Q, WANG Y T, et al., 2019. Influence of Phosphorus Control on Coupling System of Winery Wastewater and Microalgae Cultivation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 54(3): 655-662. | |
| [51] | 张军晓, 李绪录, 许春玲, 等, 2017. 深圳湾及邻近水域溶解有机磷的分布和来源及其生物利用率[J]. 环境科学研究, 30(2): 232-239. |
| ZHANG J X, LI X L, XU C L, et al., 2017. Distributions sources and bioavailability of dissolved organic phosphorus in Shenzhen Bay and adjacent coastal waters[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 30(2): 232-239. | |
| [52] | 章斐, 陈秀荣, 江子建, 等, 2015. 不同氮磷浓度下2种无毒微藻的生长特性和脱氮除磷效能[J]. 环境工程学报, 9(2): 559-566. |
| ZHANG F, CHEN X R, JIANG Z J, et al., 2015. Growth characteristics and removal efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus of two kinds of non-toxic microalgae under different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 9(2): 559-566. | |
| [53] | 赵秀侠, 杨坤, 方婷, 等, 2018. 3种微藻在龟鳖养殖废水中的生长与脱氮除磷特性[J]. 水资源保护, 34(1): 83-87, 94. |
| ZHAO X X, YANG K, FANG T, et al., 2018. Growth feature and nitrogen and phosphorus removal characteristics of three microalgae in turtle breeding wastewaterr[J]. Water Resources Protection, 34(1): 83-87, 94. | |
| [54] | 周海东, 轩玉梅, 胡涛, 等, 2020. 氮磷形态对铜绿微囊藻的生长影响[J]. 能源研究与信息, 36(1): 1-8. |
| ZHOU H D, XUAN Y M, HU T, et al., 2020. Influences of nitrogen and phosphorus species on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Energy Research and Information, 36(1): 1-8. |
| [1] | YUAN Linjiang, LI Mengbo, LENG Gang, ZHONG Bingbing, XIA Dapeng, WANG Jinghua. Synergistic Effect of Sulfate Reduction and Ammonia Oxidation in Anaerobic Environment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
