生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 1633-1643.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.10.013
王安侯1( ), 谢志宜1, 陈多宏1, 王博瑾1, 黄莹2, 逯颖3, 王玉3, 杨行健2,*(
), 谢志宜1, 陈多宏1, 王博瑾1, 黄莹2, 逯颖3, 王玉3, 杨行健2,*( ), 李永涛2,*(
), 李永涛2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-01
出版日期:2025-10-18
发布日期:2025-09-26
通讯作者:
E-mail: 作者简介:王安侯(1992年生),男,工程师,硕士,从事生态环境监测工作。E-mail: wang92925@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Anhou1( ), XIE Zhiyi1, CHEN Duohong1, WANG Bojin1, HUANG Ying2, LU Ying3, WANG Yu3, YANG Xingjian2,*(
), XIE Zhiyi1, CHEN Duohong1, WANG Bojin1, HUANG Ying2, LU Ying3, WANG Yu3, YANG Xingjian2,*( ), LI Yongtao2,*(
), LI Yongtao2,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-01
Online:2025-10-18
Published:2025-09-26
摘要:
农业面源污染监测对于保障水环境安全和推动农业可持续发展至关重要。以广州市增城区典型监测区为对象,系统分析了2023年降雨期间出入口水质的时空变化特征及潜在影响因素。结果表明,监测区水质主要为III类至V类,其中V类水质占比最大(37.9%),其次为IV类(31.0%)。监测区内水质指标呈现明显的逐月波动趋势。总磷、磷酸盐和可溶性磷酸盐浓度随月份逐渐降低,这可能与农业活动、降雨、气温和农村污水排放相关。总氮、氨氮和硝酸盐氮大致呈现波动下降而后逐渐上升趋势,这可能与降雨稀释以及较强的氮素迁移能力相关。相关性分析显示,总磷和磷酸盐的出入口月度降雨期间污染物平均瞬时通量差值与降雨量呈高度正相关(r=0.89-0.93,p=0.021-0.043),说明降雨径流对监测区水体磷素污染有显著影响。在降雨产流初期和中期,总磷、磷酸盐、可溶性磷酸盐与流量呈显著正相关(r=0.46-0.57,p=0.001-0.008),而在降雨产流后期,更多指标与流量产生相关性(r=0.43-0.68,p=0.001-0.012)。以上结果表明,初期降雨径流冲刷作用微弱,对水质影响较小,而中期大量污染物随降雨径流汇入,导致后期相关性增强。该研究为农业面源污染防控与区域水污染攻坚提供了科学依据。
中图分类号:
王安侯, 谢志宜, 陈多宏, 王博瑾, 黄莹, 逯颖, 王玉, 杨行健, 李永涛. 广州市典型小流域降雨时期农业面源污染特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(10): 1633-1643.
WANG Anhou, XIE Zhiyi, CHEN Duohong, WANG Bojin, HUANG Ying, LU Ying, WANG Yu, YANG Xingjian, LI Yongtao. Characterizing Agricultural Non-point Source Pollution in Representative Small Watershed of Guangzhou under Rainfall Conditions[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(10): 1633-1643.
| 点位 | 项目 | 总氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 氨氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 硝酸盐氮质量 浓度/(mg·L−1) | 总磷质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 磷酸盐质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 可溶性磷酸盐质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | 化学需氧量/ (mg·L−1) | 流量/ (m3·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i-01 | 最大值 | 4.12 | 2.93 | 2.04 | 0.54 | 0.27 | 0.254 | 38 | 0.12759 |
| 最小值 | 1.07 | 0.170 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.040 | ND | 0.00953 | |
| 均值 | 2.37 | 1.16 | 0.61 | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.113 | 17 | 0.04970 | |
| i-02 | 最大值 | 2.98 | 0.522 | 0.83 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.080 | 34 | 0.00679 |
| 最小值 | 0.21 | 0.027 | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.00001 | |
| 均值 | 0.73 | 0.202 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.008 | 14 | 0.00163 | |
| o-01 | 最大值 | 4.49 | 1.79 | 1.62 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.372 | 36 | 0.31344 |
| 最小值 | 0.36 | 0.185 | 0.09 | ND | ND | ND | 6 | 0.04392 | |
| 均值 | 1.88 | 0.702 | 0.59 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.096 | 21 | 0.10642 | |
| 整体 情况 | 最大值 | 4.49 | 2.93 | 2.04 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.372 | 38 | 0.31344 |
| 最小值 | 0.21 | 0.027 | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.00001 | |
| 均值 | 1.66 | 0.688 | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.073 | 18 | 0.05258 |
表1 监测区出入口各指标统计结果
Table 1 Statistical results of various indicators at inlet and outlet of the monitoring area
| 点位 | 项目 | 总氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 氨氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 硝酸盐氮质量 浓度/(mg·L−1) | 总磷质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 磷酸盐质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 可溶性磷酸盐质量浓度/(mg·L−1) | 化学需氧量/ (mg·L−1) | 流量/ (m3·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i-01 | 最大值 | 4.12 | 2.93 | 2.04 | 0.54 | 0.27 | 0.254 | 38 | 0.12759 |
| 最小值 | 1.07 | 0.170 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.040 | ND | 0.00953 | |
| 均值 | 2.37 | 1.16 | 0.61 | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.113 | 17 | 0.04970 | |
| i-02 | 最大值 | 2.98 | 0.522 | 0.83 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.080 | 34 | 0.00679 |
| 最小值 | 0.21 | 0.027 | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.00001 | |
| 均值 | 0.73 | 0.202 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.008 | 14 | 0.00163 | |
| o-01 | 最大值 | 4.49 | 1.79 | 1.62 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.372 | 36 | 0.31344 |
| 最小值 | 0.36 | 0.185 | 0.09 | ND | ND | ND | 6 | 0.04392 | |
| 均值 | 1.88 | 0.702 | 0.59 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.096 | 21 | 0.10642 | |
| 整体 情况 | 最大值 | 4.49 | 2.93 | 2.04 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.372 | 38 | 0.31344 |
| 最小值 | 0.21 | 0.027 | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.00001 | |
| 均值 | 1.66 | 0.688 | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.073 | 18 | 0.05258 |
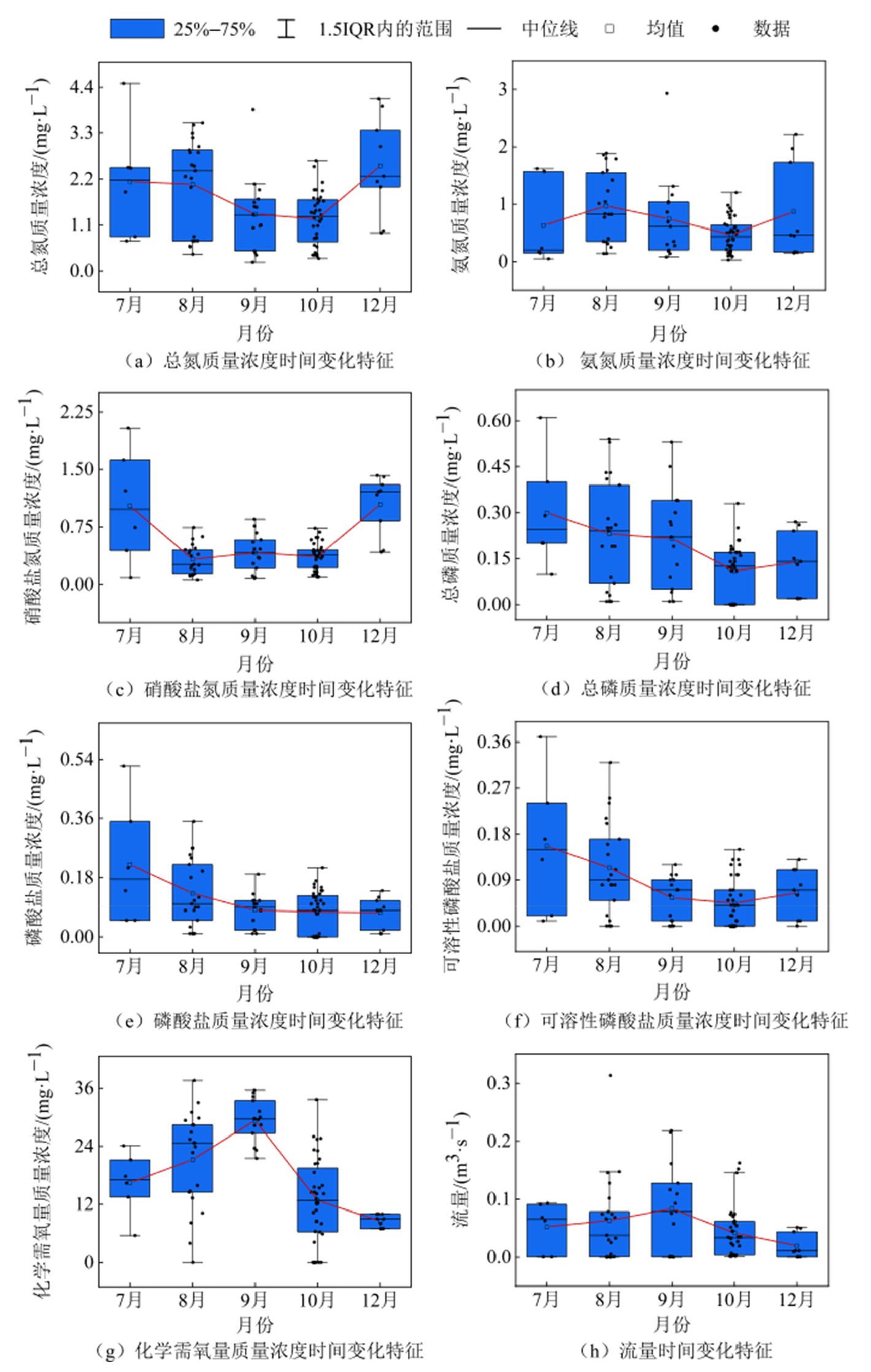
图3 监测区各指标时间变化特征 低于检出限数值以0计;n(7月)=6、n(8月)=21、n(9月)=15、n(10月)=36、n(12月)=9
Figure 3 Temporal variation characteristics of various indicators in the monitoring area
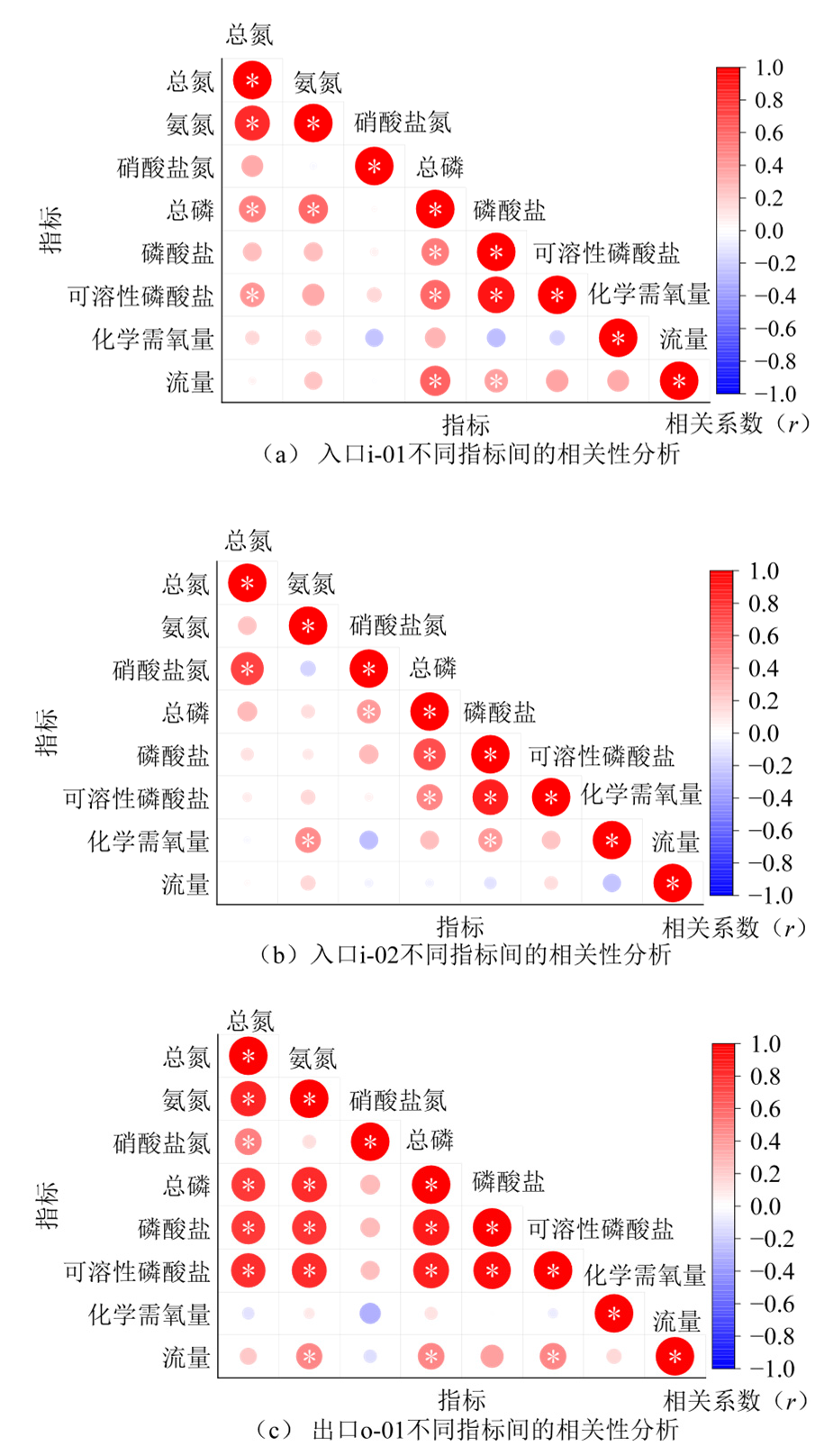
图4 监测区出入口不同指标间的相关性分析 红色表示正相关,蓝色表示负相关,颜色深浅表示相关性强弱,*表示p<0.05
Figure 4 Correlation analysis of different indicators at the inlet and outlet of the monitoring area
| 指标 | 总氮 | 氨氮 | 硝酸盐氮 | 总磷 | 磷酸盐 | 可溶性磷酸盐 | 化学需氧量 | 降雨量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氮 | 1 | |||||||
| 氨氮 | 0.865 | 1 | ||||||
| 硝酸盐氮 | −0.497 | −0.849 | 1 | |||||
| 总磷 | 0.748 | 0.945* | −0.859 | 1 | ||||
| 磷酸盐 | 0.816 | 0.965* | −0.831 | 0.994* | 1 | |||
| 可溶性磷酸盐 | 0.902* | 0.959* | −0.743 | 0.958* | 0.983* | 1 | ||
| 化学需氧量 | −0.179 | −0.243 | 0.219 | 0.038 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 1 | |
| 降雨量 | 0.480 | 0.771 | −0.803 | 0.932* | 0.891* | 0.809 | 0.261 | 1 |
表2 降雨量和出口与入口月度污染物平均瞬时通量差值的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of rainfall and difference of monthly average instantaneous flux of pollutants between export and import
| 指标 | 总氮 | 氨氮 | 硝酸盐氮 | 总磷 | 磷酸盐 | 可溶性磷酸盐 | 化学需氧量 | 降雨量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氮 | 1 | |||||||
| 氨氮 | 0.865 | 1 | ||||||
| 硝酸盐氮 | −0.497 | −0.849 | 1 | |||||
| 总磷 | 0.748 | 0.945* | −0.859 | 1 | ||||
| 磷酸盐 | 0.816 | 0.965* | −0.831 | 0.994* | 1 | |||
| 可溶性磷酸盐 | 0.902* | 0.959* | −0.743 | 0.958* | 0.983* | 1 | ||
| 化学需氧量 | −0.179 | −0.243 | 0.219 | 0.038 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 1 | |
| 降雨量 | 0.480 | 0.771 | −0.803 | 0.932* | 0.891* | 0.809 | 0.261 | 1 |

图7 降雨不同产流阶段各指标间的相关性分析 椭圆越扁,表示相关系数的绝对值较大;椭圆长轴的方向表示相关系数的正负,右上-左下方向对应正值,左上-右下方向对应负值,*表示p<0.05
Figure 7 Correlation analysis of various indicators at different runoff generation stages
| [1] | DUPAS R, FAUCHEUX M, SENGA KIESSÉ T, et al., 2024. High-intensity rainfall following drought triggers extreme nutrient concentrations in a small agricultural catchment[J]. Water Research, 264: 122108. |
| [2] | HUANG X, ZHU Y, LIN H, et al., 2024. High-frequency monitoring during rainstorm events reveals nitrogen sources and transport in a rural catchment[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 362: 121308. |
| [3] | JI X L, SHU L L, CHEN W L, et al., 2022. Nitrate pollution source apportionment, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis across a rural-urban river network based on δ15N/δ18O-NO3- isotopes and SIAR modeling[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 438: 129480. |
| [4] | JUNG H J, LEE J H, YOO J S, et al., 2024. Improving the accuracy of nitrogen estimates from nonpoint source in a river catchment with multi-isotope tracers[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 921: 171016. |
| [5] | LE F, RUAN X H, WEI Z, et al., 2024. Tracing phosphorus sources in the river-lake system using the oxygen isotope of phosphate[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 949: 175022. |
| [6] | LI Y, MI W J, JI L, et al., 2023. Urbanization and agriculture intensification jointly enlarge the spatial inequality of river water quality[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 878: 162559. |
| [7] | LIU X, YUE F, WONG WW, et al., 2024. Unravelling nitrate transformation mechanisms in karst catchments through the coupling of high-frequency sensor data and machine learning[J]. Water Research, 267: 122507. |
| [8] | QIAO J, WANG J, ZHAO D, et al., 2022. Effect of continuous N fertilizer reduction on N losses and wheat yield in the Taihu Lake Region, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 364: 132475. |
| [9] | QIN B Q, DENG J M, SHI K, et al., 2021. extreme climate anomalies enhancing cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic lake Taihu, China[J]. Water Resources Research, 57(7): e2020WR029371. |
| [10] | TONG Y D, ZHANG W, WANG X J, et al., 2017. Decline in Chinese lake phosphorus concentration accompanied by shift in sources since 2006[J]. Nature Geoscience, 10(7): 507-511. |
| [11] |
WANG Y Y, XU H, ZHAO X C, et al., 2025. Rainfall impacts on nonpoint nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in an agricultural river in subtropical montane reservoir region of southeast China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 149: 551-563.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | YAN L, XUE L H, PETROPOULOS E, et al., 2021. Nutrient loss by runoff from rice-wheat rotation during the wheat season is dictated by rainfall duration[J]. Environmental Pollution, 285: 117382. |
| [13] | 安志装, 索琳娜, 刘宝存, 2024. 我国农业面源污染研究与展望[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 30(7): 1422-1436. |
| AN Z Z, SUO L N, LIU B C, 2024. Prospect and research on agricultural non-point source pollution in China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 30(7): 1422-1436. | |
| [14] | 曹佳霖, 胡茂川, 贺凯, 等, 2023. 广东省农业面源污染现状及变化的多尺度评价[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 39(7): 924-933. |
| CAO J L, HU M C, HE K, et al., 2023. Multi-scale assessment of agricultural non-point source pollution loadings and its changing characteristics in Guangdong province[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 39(7): 924-933. | |
| [15] | 车蕊, 林澍, 范中亚, 等, 2019. 连续极端降雨对东江流域水质影响分析[J]. 环境科学, 40(10): 4440-4449. |
| CHE R, LIN S, FAN Z Y, et al., 2019. Effects of continuous extreme rainfall on water quality of the Dongjiang river basin[J]. Environmental Science, 40(10): 4440-4449. | |
| [16] | 葛成军, 唐文浩, 陈淼, 等, 2015. 海南岛典型农业土壤产流与面源污染特征分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 36(8): 1469-1474. |
| GE C J, TANG W H, CHEN M, et al., 2015. Runoff characteristics of agricultural non-point source pollutants in typical soils in hainan island[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 36(8): 1469-1474. | |
| [17] | 国家环境保护总局, 2002. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 第四版增补版.北京: 中国环境出版社: 93-274. |
| State Environmental Protection Agency, 2002. Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater[M]. 4th Edition, Supplementary Edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 93-274. | |
| [18] | 焦云飞, 李强, 高洪军, 等, 2021. 降雨对吉林省黑土区雨养春玉米农田氮磷淋溶的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 29(1): 19-28. |
| JIAO Y F, LI Q, GAO H J, et al., 2021. Effects of rainfall on nitrogen and phosphorus leaching in rainfed spring maize black soil farmland in Jilin Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29(1): 19-28. | |
| [19] |
林兰稳, 朱立安, 曾清苹, 2020. 广东省农业面源污染时空变化及其防控对策[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(6): 1245-1250.
DOI |
|
LIN L W, ZHU L A, ZENG Q P, 2020. Spatial and temporal changes of Agricultural non-point source pollution in Guangdong province and its prevention and control measures[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 29(6): 1245-1250.
DOI |
|
| [20] |
苗慧, 沈峥, 蒋豫, 等, 2017. 巢湖表层沉积物氮、磷、有机质的分布及污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(12): 2120-2125.
DOI |
| MIAO H, SHEN Z, JIANG Y, et al., 2017. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in surface sediments of Chaohu lake[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 26(12): 2120-2125. | |
| [21] | 王登超, 李发东, 李曹乐, 等, 2025. 降雨对河流水质影响及污染源解析: 以鉴江茂名段为例[J]. 环境科学, 46(4): 2165-2178. |
| WANG D C, LI F D, LI C L, et al., 2025. Impact of rainfall on river water quality and source identification: an example in the Maoming section of the Jianjiang river[J]. Environmental Science, 46(4): 2165-2178. | |
| [22] | 王萌, 周丽丽, 耿润哲, 2020. 农业面源污染治理的技术与政策研究进展[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 45(1): 98-103. |
| WANG M, ZHOU L L, GENG R Z, 2020. A review: The technology and policy design of agricultural non-point source pollution management[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 45(1): 98-103. | |
| [23] | 王甜, 肖文发, 黄志霖, 等, 2022. 三峡库区紫色土坡地典型暴雨径流氮磷流失特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 38(3): 367-374. |
| WANG T, XIAO W F, HUANG Z L, et al., 2022. Characteristics of typical rainstorm-runoff nitrogen and phosphorus loss on purple soil slope in three gorges reservoir area[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 38(3): 367-374. | |
| [24] | 王永壮, 陈欣, 史奕, 2013. 农田土壤中磷素有效性及影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(1): 260-268. |
| WANG Y Z, CHEN X, SHI Y, 2013. Phosphorus availability in cropland soils of China and related affecting factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(1): 260-268. | |
| [25] | 吴道铭, 傅友强, 于智卫, 等, 2013. 我国南方红壤酸化和铝毒现状及防治[J]. 土壤, 45(4): 577-584. |
| WU D M, FU Y Q, YU Z W, et al., 2013. Status of red soil acidification and aluminum toxicity in south China and prevention[J]. Soils, 45(4): 577-584. | |
| [26] | 徐垦, 张芊芊, 张思毅, 等, 2024. 粤西典型村域次降雨条件下非点源氮素排放特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 37(8): 1725-1735. |
| XU K, ZHANG Q Q, ZHANG S Y, et al., 2024. Characteristics of non-point source nitrogen emissions under individual rainfall events in a typical village area in western Guangdong, China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 37(8): 1725-1735. | |
| [27] | 严磊, 吴田乡, 赵素雅, 等, 2022. 雨强及播栽方式对太湖地区麦田径流氮磷流失的影响[J]. 土壤, 54(2): 358-364. |
| YAN L, WU T X, ZHAO S Y, et al., 2022. Effects of rainfall intensity and sowing method on nitrogen and phosphorus losses by surface runoff from wheat field in Taihu lake region[J]. Soils, 54(2): 358-364. | |
| [28] | 张运林, 杨龙元, 秦伯强, 等, 2008. 太湖北部湖区COD浓度空间分布及与其它要素的相关性研究[J]. 环境科学, 29(6): 1457-1462. |
| ZHANG Y L, YANG L Y, QIN B Q, et al., 2008. Spatial distribution of COD and the correlations with other parameters in the northern region of lake Taihu[J]. Environmental Science, 29(6): 1457-1462. | |
| [29] | 赵越, 梁新强, 傅朝栋, 等, 2015. 磷肥输入对稻田土壤剖面胶体磷含量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 35(24): 8251-8257. |
| ZHAO Y, LIANG X Q, FU C D, et al., 2015. Effects of phosphorus addition on soil colloidal phosphorus content in a paddy soil profile[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(24): 8251-8257. | |
| [30] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 1989. 水质总磷的测定钼酸铵分光光度法: GB/T 11893—1989[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 1989. Water quality-Determination of total phosphorus-Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometric method: GB/T 11893—1989[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [31] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2009a. 水质氨氮的测定纳氏试剂分光光度法: HJ 535—2009[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2009a. Water quality-Determination of ammonia nitrogen-Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry: HJ 535—2009[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [32] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2009b. 水质采样技术指导: HJ 494—2009[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2009b. Water quality—Guidance on sampling techniques: HJ 494—2009b[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [33] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2009c. 水质样品的保存和管理技术规定: HJ 493—2009[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2009c. Water quality -Technical regulation of the preservation and handling of samples:HJ 493—2009c[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [34] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2012a. 水质总氮的测定碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法: HJ 636—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2012a. Water quality-Determination of total nitrogen-Alkaline potassium persulfate digestion UV spectrophotometric method:HJ 636—2012a[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [35] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2012b. 土壤氨氮、亚硝酸盐氮、硝酸盐氮的测定氯化钾溶液提取-分光光度法: HJ 634—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2012b. Soil-Determination of ammonium, nitrite and nitrate by extraction with potassium chloride solution -spectrophotometric methods:HJ 634—2012b[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [36] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2013. 水质磷酸盐的测定离子色谱法: HJ 669—2013[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2013. Water quality-Determination of phosphate-Ion chromatography: HJ 669—2013[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [37] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2017. 水质化学需氧量的测定重铬酸盐法: HJ 828—2017[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2017. Water quality-Determination of the chemical oxygen demand-Dichromate method: HJ 828—2017[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [38] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2020. 水质pH值的测定电极法: HJ 1147—2020[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2020. Water quality—Determination of pH—Electrode method: HJ 1147—2020[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [39] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2022. 地表水环境质量监测技术规范: HJ 91.2—2022[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2022. Technical specifications for surface water environmental quality monitoring: HJ 91.2—2022[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [40] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 2015. 河流流量测验规范: GB 50179—2015[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, 2015. Code for liquid flow measurement in open channels: GB 50179—2015[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press. |
| [1] | 任宸剑, 郝瑞霞, 张杨, 韩丽娟, 魏煜星, 柴璐. 水动力作用下河道底泥氨氮释放特性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 931-940. |
| [2] | 王弋, 严茂泽, 肖倩, 张思毅, 郝贝贝. 广东省农村生活污水处理现状及建议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(5): 819-830. |
| [3] | 王斌, 曾兆荷, 董璐, 岳林. 内梅罗指数法在地下水水质评价中的修正探讨与实践效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 293-301. |
| [4] | 陈鑫怡, 毛雅若, 宋靓颖, 王童瑶, 李启权. 四川盆地耕地土壤全磷空间分布特征及其主控因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(10): 1569-1578. |
| [5] | 张宝东, 王彪, 吴艳兰, 孟玉, 徐升, 钱贞兵, 秦军. 安徽省农村黑臭水体特征分析及识别[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1257-1268. |
| [6] | 潘家响, 朱明飞, 秦念慈, 肖晶, 刘晨, 李秋华. 贵州高原车田河浮游植物功能群时空特征及水环境质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 935-945. |
| [7] | 肖扬岚, 沈惠柔, 许一涵, 尤添革, 郑艺婧, 谢候展, 宁静. 基于GBDT-LSTM的闽江流域水质预测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 597-606. |
| [8] | 高尧峰, 段艳平, 陈昱如, 涂耀仁, 高峻. 长江流域氧氟沙星和金霉素的人体健康水质基准研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 92-100. |
| [9] | 鲁言波, 陈湛峰, 李晓芳. 基于粒子群优化的GRU广东省跨境断面水质预测模型研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1673-1681. |
| [10] | 王源哲, 华春林, 赵丽, 樊敏, 梁晓盈, 周乐乐, 蔡璨, 姚婧. 山地城市主要河流水质评价及预测研究——以四川省绵阳市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1465-1477. |
| [11] | 何贝贝, 范珊珊, 洪念, 刘安. 不同储存方式下屋顶雨水水质特性变化规律研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 567-578. |
| [12] | 钱海铭, 张运林, 李娜, 王玮佳, 孙晓, 张毅博, 施坤, 冯胜, 高阳辉. 典型降雨过程中河流饮用水源地水质高频监测研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 579-589. |
| [13] | 程鹏, 孙明东, 郝韶楠. 基于最简水质综合评价指数的官厅水库上游河流水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 372-380. |
| [14] | 鲁言波, 陈湛峰, 李彤. 基于改进TOPSIS模型的广东省主要湖库水质特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2194-2206. |
| [15] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
