生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 297-306.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.010
黄巧义1( ), 于俊红1, 黄建凤1, 黄旭1, 李苹1, 付弘婷1, 唐拴虎1, 刘一锋2,*(
), 于俊红1, 黄建凤1, 黄旭1, 李苹1, 付弘婷1, 唐拴虎1, 刘一锋2,*( ), 徐培智1,*(
), 徐培智1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-06
出版日期:2022-02-18
发布日期:2022-04-14
通讯作者:
刘一锋(1985年生),男,高级农艺师,主要从事耕地土壤质量保护提升研究。E-mail: 109279800@qq.com作者简介:黄巧义(1985年生),男,副研究员,博士,主要耕地质量提升与植物营养方面的研究。E-mail: huangqiaoyi@gdaas.cn
基金资助:
HUANG Qiaoyi1( ), YU Junhong1, HUANG Jianfeng1, HUANG Xu1, LI Ping1, FU Hongting1, TANG Shuanhu1, LIU Yifeng2,*(
), YU Junhong1, HUANG Jianfeng1, HUANG Xu1, LI Ping1, FU Hongting1, TANG Shuanhu1, LIU Yifeng2,*( ), XU Peizhi1,*(
), XU Peizhi1,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-06
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-04-14
摘要:
合理利用秸秆养分资源可替代部分化肥使用,是种植业减肥增效并促进农业绿色发展的重要途径之一,探明广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及其替代化肥潜力,对于全省化肥减施增效、农业绿色生产具有重要意义。该研究以广东省主要农作物水稻(Oryza sativa L.)、玉米(Zea mays L.)、薯类(Dioscorea esculenta (Lour.) Burkill)、甘蔗(Saccharum officinarum L.)、花生(Arachis hypogaea Linn.)和大豆(Glycine max (Linn.) Merr.)为研究对象,通过查阅广东省统计数据和公开发表的文献资料,对2019年广东省主要农作物秸秆数量、养分资源量及区域分布情况进行估算,并根据不同作物推荐养分用量计算各地区的养分需求量,分析秸秆养分资源替代化肥的潜力。结果表明,2019年广东省主要农作物秸秆资源量为1951.00 ×104 t,其中粤西秸秆资源量最大,其次是粤北,珠三角地区最少。全省秸秆的氮(N)、磷(P2O5)、钾(K2O)养分资源总量分别达到19.26×104、4.51×104、33.51×104 t,其中水稻的秸秆养分资源量最大,占全省农作物秸秆养分资源总量的63%;其次是甘蔗秸秆养分资源,占18%;第三大秸秆养分资源是花生,占10%。湛江市的秸秆养分资源最大,占全省秸秆养分资源总量的25%,其中甘蔗和水稻秸秆的贡献率最大;其次为茂名市和肇庆市,占11%和8%,以水稻秸秆养分资源为主。广东省2019年主要农作物播种面积为265.91×104 hm2,理论上养分需求量为46.18×104 t N、15.78×104 t P2O5、40.41×104 t K2O,秸秆养分资源替代化肥的潜力为N 22%、P2O5 19%、K2O 70%。不同种植制度下秸秆替代化肥的潜力不同,其中,水稻和甘蔗秸秆替代钾肥潜力最大,大豆秸秆替代氮肥潜力最大,而薯类秸秆替代化肥潜力最低。不同地区的秸秆养分资源替代化肥潜力不同,其中湛江市和广州市秸秆替代氮肥的潜力最高,分别达30%和29%;珠海市和梅州市秸秆替代磷肥的潜力较高,分别达26%和24%;梅州市秸秆替代钾肥的潜力最高,达78%以上。
中图分类号:
黄巧义, 于俊红, 黄建凤, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 唐拴虎, 刘一锋, 徐培智. 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 297-306.
HUANG Qiaoyi, YU Junhong, HUANG Jianfeng, HUANG Xu, LI Ping, FU Hongting, TANG Shuanhu, LIU Yifeng, XU Peizhi. Nutrient Resources of Main Crop Straw and Its Potential of Substituting for Chemical Fertilizer in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 297-306.
| 作物 Crop | 草/谷比 Straw/grain | 秸秆养分质量分数 w(nutrient in straw)/% | 养分当季释放率 Rate of in-season nutrient release from straw/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| 水稻 Rice | 1.06 | 0.83 | 0.27 | 2.06 | 47.19 | 66.69 | 84.91 |
| 玉米 Maize | 1.32 | 0.87 | 0.31 | 1.345 | 54.04 | 73.03 | 84.43 |
| 薯类 Potato | 0.58 | 1.97 | 0.43 | 1.93 | 74.38 | 81.00 | 76.90 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 1.02 | 56.21 | 49.39 | 86.74 |
| 花生 Peanut | 1.65 | 1.64 | 0.15 | 1.56 | 51.61 | 66.50 | 85.82 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 1.60 | 1.63 | 0.39 | 1.27 | 52.06 | 54.41 | 84.30 |
表1 广东省主要农作物的草谷比、秸秆养分质量分数(风干基)和养分当季释放率
Table 1 Ratio of straw to grain, nutrient contents in straws (air-dried base) and rate of in-season nutrient release from different crops straw
| 作物 Crop | 草/谷比 Straw/grain | 秸秆养分质量分数 w(nutrient in straw)/% | 养分当季释放率 Rate of in-season nutrient release from straw/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| 水稻 Rice | 1.06 | 0.83 | 0.27 | 2.06 | 47.19 | 66.69 | 84.91 |
| 玉米 Maize | 1.32 | 0.87 | 0.31 | 1.345 | 54.04 | 73.03 | 84.43 |
| 薯类 Potato | 0.58 | 1.97 | 0.43 | 1.93 | 74.38 | 81.00 | 76.90 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 1.02 | 56.21 | 49.39 | 86.74 |
| 花生 Peanut | 1.65 | 1.64 | 0.15 | 1.56 | 51.61 | 66.50 | 85.82 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 1.60 | 1.63 | 0.39 | 1.27 | 52.06 | 54.41 | 84.30 |
| 作物Crop | 播种面积 Sown area/ (104 hm2) | 总产量 Total yields/ (104 t) | 理论秸秆资源量 Theoretical straw resources/(104 t) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 Rice | 179.37 | 1075.05 | 1139.55 |
| 玉米 Maize | 12.01 | 55.59 | 73.38 |
| 薯类 Potato | 20.25 | 97.41 | 56.50 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 16.97 | 1434.65 | 487.78 |
| 花生 Peanut | 34.05 | 108.69 | 179.33 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 3.26 | 9.04 | 14.46 |
| 合计 Total | 265.91 | 2780.42 | 1951.00 |
表2 广东省主要农作物的播种面积、产量及秸秆资源量估算
Table 2 Sown area, yields and theoretical straw resources of major crops in Guangdong Province
| 作物Crop | 播种面积 Sown area/ (104 hm2) | 总产量 Total yields/ (104 t) | 理论秸秆资源量 Theoretical straw resources/(104 t) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 Rice | 179.37 | 1075.05 | 1139.55 |
| 玉米 Maize | 12.01 | 55.59 | 73.38 |
| 薯类 Potato | 20.25 | 97.41 | 56.50 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 16.97 | 1434.65 | 487.78 |
| 花生 Peanut | 34.05 | 108.69 | 179.33 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 3.26 | 9.04 | 14.46 |
| 合计 Total | 265.91 | 2780.42 | 1951.00 |
| 区域 Region | 城市 City | 秸秆 Straw | 秸秆养分量 Straw nutrient/(104 t) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 Yield/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| 珠三角地区 Pearl river delta | 广州 | 38.47 | 1.97 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.53 |
| 深圳 | 0.99 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| 佛山 | 5.00 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.09 | |
| 东莞 | 0.70 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 中山 | 2.32 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| 珠海 | 2.91 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| 江门 | 113.86 | 5.84 | 1.04 | 0.29 | 2.18 | |
| 肇庆 | 139.23 | 7.14 | 1.33 | 0.37 | 2.71 | |
| 惠州 | 73.45 | 3.76 | 0.73 | 0.19 | 1.36 | |
| 粤东地区 Eastern Guangdong | 汕头 | 44.46 | 2.28 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 0.88 |
| 潮州 | 28.95 | 1.48 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.57 | |
| 揭阳 | 81.15 | 4.16 | 0.91 | 0.24 | 1.58 | |
| 汕尾 | 48.340 | 2.48 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 0.95 | |
| 粤西 Western Guangdong | 湛江 | 584.92 | 29.98 | 5.91 | 1.00 | 7.65 |
| 茂名 | 198.16 | 10.16 | 1.95 | 0.49 | 3.69 | |
| 阳江 | 75.16 | 3.85 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 1.45 | |
| 云浮 | 75.50 | 3.87 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 1.47 | |
| 粤北 Northern Guangdong | 韶关 | 109.04 | 5.59 | 1.12 | 0.26 | 1.99 |
| 清远 | 105.18 | 5.39 | 1.08 | 0.25 | 1.87 | |
| 河源 | 99.61 | 5.11 | 0.95 | 0.25 | 1.93 | |
| 梅州 | 123.61 | 6.34 | 1.11 | 0.33 | 2.46 | |
表3 广东省不同地区主要农作物秸秆及其养分资源分布
Table 3 Distribution of straws and their nutrients resources of crops in different regions of Guangdong Province
| 区域 Region | 城市 City | 秸秆 Straw | 秸秆养分量 Straw nutrient/(104 t) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 Yield/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| 珠三角地区 Pearl river delta | 广州 | 38.47 | 1.97 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.53 |
| 深圳 | 0.99 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| 佛山 | 5.00 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.09 | |
| 东莞 | 0.70 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| 中山 | 2.32 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 | |
| 珠海 | 2.91 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| 江门 | 113.86 | 5.84 | 1.04 | 0.29 | 2.18 | |
| 肇庆 | 139.23 | 7.14 | 1.33 | 0.37 | 2.71 | |
| 惠州 | 73.45 | 3.76 | 0.73 | 0.19 | 1.36 | |
| 粤东地区 Eastern Guangdong | 汕头 | 44.46 | 2.28 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 0.88 |
| 潮州 | 28.95 | 1.48 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.57 | |
| 揭阳 | 81.15 | 4.16 | 0.91 | 0.24 | 1.58 | |
| 汕尾 | 48.340 | 2.48 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 0.95 | |
| 粤西 Western Guangdong | 湛江 | 584.92 | 29.98 | 5.91 | 1.00 | 7.65 |
| 茂名 | 198.16 | 10.16 | 1.95 | 0.49 | 3.69 | |
| 阳江 | 75.16 | 3.85 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 1.45 | |
| 云浮 | 75.50 | 3.87 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 1.47 | |
| 粤北 Northern Guangdong | 韶关 | 109.04 | 5.59 | 1.12 | 0.26 | 1.99 |
| 清远 | 105.18 | 5.39 | 1.08 | 0.25 | 1.87 | |
| 河源 | 99.61 | 5.11 | 0.95 | 0.25 | 1.93 | |
| 梅州 | 123.61 | 6.34 | 1.11 | 0.33 | 2.46 | |
| 作物 Crop | N | P2O5 | K2O | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 资源量 Amount/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | 资源量 Amount/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | 资源量 Amount/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | |
| 水稻 Rice | 9.46 | 49.10 | 3.08 | 68.27 | 23.47 | 70.06 |
| 玉米 Maize | 0.64 | 3.31 | 0.23 | 5.05 | 0.99 | 2.95 |
| 薯类 Potato | 1.11 | 5.78 | 0.24 | 5.39 | 1.09 | 3.25 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 4.88 | 25.32 | 0.63 | 14.07 | 4.98 | 14.85 |
| 花生 Peanut | 2.94 | 15.27 | 0.27 | 5.97 | 2.80 | 8.35 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 0.24 | 1.22 | 0.06 | 1.25 | 0.18 | 0.55 |
| 合计 Total | 19.26 | 100.00 | 4.51 | 100.00 | 33.51 | 100.00 |
表4 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及其在全部秸秆中的占比
Table 4 Nutrients quantities of crop straw and their percentages in the whole straw yields in Guangdong Province
| 作物 Crop | N | P2O5 | K2O | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 资源量 Amount/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | 资源量 Amount/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | 资源量 Amount/(104 t) | 占比 Percentage/% | |
| 水稻 Rice | 9.46 | 49.10 | 3.08 | 68.27 | 23.47 | 70.06 |
| 玉米 Maize | 0.64 | 3.31 | 0.23 | 5.05 | 0.99 | 2.95 |
| 薯类 Potato | 1.11 | 5.78 | 0.24 | 5.39 | 1.09 | 3.25 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 4.88 | 25.32 | 0.63 | 14.07 | 4.98 | 14.85 |
| 花生 Peanut | 2.94 | 15.27 | 0.27 | 5.97 | 2.80 | 8.35 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 0.24 | 1.22 | 0.06 | 1.25 | 0.18 | 0.55 |
| 合计 Total | 19.26 | 100.00 | 4.51 | 100.00 | 33.51 | 100.00 |
| 作物 Crop | 推荐施肥量 Optimum nutrient rate/(kg∙hm-2) | 秸秆有效养分量 Available nutrients from straw/(kg∙hm-2) | 秸秆还田率 Ratio of straw to farmland/ % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| 水稻 Rice | 150.00 | 37.5.00 | 120.00 | 24.88 | 11.44 | 111.13 | 80.57 |
| 玉米 Maize | 300.00 | 90.00 | 210.00 | 28.71 | 13.83 | 69.35 | 49.83 |
| 薯类 Potato | 225.00 | 120.00 | 330.00 | 40.88 | 9.72 | 41.41 | 54.97 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 400.00 | 120.00 | 270.00 | 161.59 | 18.46 | 254.34 | 64.74 |
| 花生 Peanut | 120.00 | 96.00 | 144.00 | 44.58 | 5.25 | 70.51 | 61.42 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 75.50 | 74.00 | 59.90 | 37.68 | 9.42 | 47.54 | 59.54 |
表5 广东省主要农作物推荐施肥量、秸秆有效养分量和直接还田率
Table 5 Optimum fertilizer rates of different main crops, available nutrients from straw and ratio of direct straw returning from major crops to farmland in Guangdong province
| 作物 Crop | 推荐施肥量 Optimum nutrient rate/(kg∙hm-2) | 秸秆有效养分量 Available nutrients from straw/(kg∙hm-2) | 秸秆还田率 Ratio of straw to farmland/ % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| 水稻 Rice | 150.00 | 37.5.00 | 120.00 | 24.88 | 11.44 | 111.13 | 80.57 |
| 玉米 Maize | 300.00 | 90.00 | 210.00 | 28.71 | 13.83 | 69.35 | 49.83 |
| 薯类 Potato | 225.00 | 120.00 | 330.00 | 40.88 | 9.72 | 41.41 | 54.97 |
| 甘蔗 Sugarcane | 400.00 | 120.00 | 270.00 | 161.59 | 18.46 | 254.34 | 64.74 |
| 花生 Peanut | 120.00 | 96.00 | 144.00 | 44.58 | 5.25 | 70.51 | 61.42 |
| 大豆 Soybean | 75.50 | 74.00 | 59.90 | 37.68 | 9.42 | 47.54 | 59.54 |
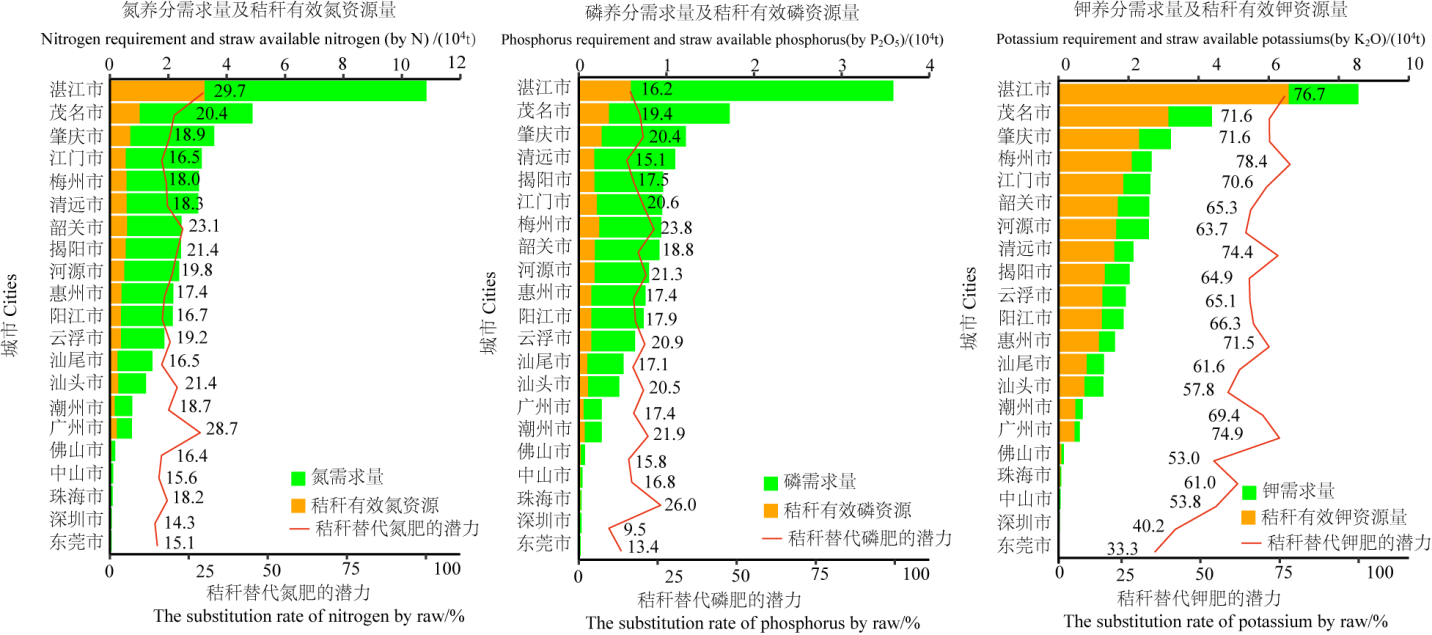
图3 广东省各个地级市主要农作物秸秆氮、磷、钾养分需求量及秸秆替代氮肥潜力
Figure 3 The nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium requirement of crop straw and how much could be substituted by straw in different cities of Guangdong province
| [1] |
ALVA A K, COLLINS H P, BOYDSTON R A, 2002. Corn, wheat, and potato crop residue decomposition and nitrogen mineralization in sandy soils under an irrigated potato rotation[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 33(15-18): 2643-2651.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAI Y C, CHANG Y Y, HUSSAIN M, et al., 2020. Soil chemical and microbiological properties are changed by long-term chemical fertilizers that limit ecosystem functioning[J]. Microorganisms, 8(5): 694.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CONLEY D J, PAERL H W, HOWARTH R W, et al., 2009. Controlling Eutrophication: Nitrogen and Phosphorus[J]. Science, 323(5917): 1014-1015.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZOLAHCHI Z, JALALI M, 2012. Kinetics of nutrient release from different organic residues using a laboratory system[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 58(9): 1013-1031.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 毕于运, 高春雨, 王亚静, 等, 2009. 中国秸秆资源数量估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 25(12): 211-217. |
| BI Y Y, GAO C Y, WANG Y J, et al., 2009. Estimation of straw resources in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 25(12): 211-217. | |
| [6] | 柴如山, 徐悦, 程启鹏, 等, 2021. 安徽省主要作物秸秆养分资源量及还田利用潜力[J]. 中国农业科学, 54(1): 95-109. |
| CAI R S, XU Y, CHENG Q P, et al., 2021. Nutrient resource quantity of main crop straw and utilization potential under straw returning in Anhui Province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 54(1): 95-109. | |
| [7] | 程文龙, 韩上, 武际, 等, 2019. 连续秸秆还田替代钾肥对作物产量及土壤钾素平衡的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 72-78. |
| CHENG W L, HAN S, WU J, et al., 2019. Effect of continuous straw incorporation substitute for K-fertilizer on crop yield and soil potassium balance[J]. Soil and Fertilizers Sciences in China (5): 72-78. | |
| [8] | 程文龙, 韩上, 李敏, 等, 2020. 主要农作物秸秆养分资源现状及其肥料替代潜力分析--以安徽省为例[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 28(11): 1789-1798. |
| CHENG W L, HAN S, LI M, et al., 2020. Current situation of the main crop straw nutrient resources and the substitute potential of crop straw for chemical fertilizer: A case study of Anhui Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 28(11): 1789-1798. | |
| [9] | 代文才, 高明, 兰木羚, 等, 2017. 不同作物秸秆在旱地和水田中的腐解特性及养分释放规律[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 25(2): 188-199. |
| DAI W C, GAO M, LAN M L, et al., 2017. Nutrient release patterns and decomposition characteristics of different crop straws in drylands and paddy fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 25(2): 188-199. | |
| [10] | 房静静, 丁维婷, 武雪萍, 等, 2020. 长期秸秆配施化肥对土壤养分及小麦产量、品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 141-146. |
| FANG J J, DING W T, WU X P, et al., 2020. Effects of long-term straw and fertilizer combined application on soil nutrient, wheat yield and quality[J]. Soil and Fertilizers in China (5): 141-146. | |
| [11] | 付浩然, 李婷玉, 曹寒冰, 等, 2020. 我国化肥减量增效的驱动因素探究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(3): 561-580. |
| FU H R, LI T Y, CAO H B, et al., Research on the driving factors of fertilizer reduction in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(3): 561-580. | |
| [12] | 高洪军, 朱平, 彭畅, 等, 2015. 等氮条件下长期有机无机配施对春玉米的氮素吸收利用和土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21(2): 318-325. |
| GAO H J, ZHU P, PENG C, et al., 2015. Effects of partially replacement of inorganic N with organic materials on nitrogen efficiency of spring maize and soil inorganic nitrogen content under the same N input[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 21(2): 318-325. | |
| [13] | 高利伟, 马林, 张卫峰, 等, 2009. 中国作物秸秆养分资源数量估算及其利用状况[J]. 农业工程学报, 25(7): 173-179. |
| GAO L W, MA L, ZHANG W F, et al., 2009. Estimation of nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its utilization situation in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 25(7): 173-179. | |
| [14] | 韩冰, 王效科, 逯非, 等, 2008. 中国农田土壤生态系统固碳现状和潜力[J]. 生态学报, 28(2): 612-619. |
| HAN B, WANG X K, LU F, et al., 2008. Soil carbon sequestration and its potential by cropland ecosystems in China[J]. Acta Ecology Sinica, 28(2): 612-619. | |
| [15] | 侯云鹏, 刘志全, 尹彩侠, 等, 2020. 长期秸秆还田下基于东北水稻高产和钾素平衡的钾肥用量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(11): 2020-2031. |
| HOU Y P, LIU Z Q, YIN C X, et al., 2020. Optimum amount of potassium fertilizer based on high yield and soil potassium balance under straw return in rice production region of northeast China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(11): 2020-2031. | |
| [16] | 胡蓉, 郑露, 刘浩, 等, 2020. 秸秆还田对水稻根际微生物多样性和水稻纹枯病发生的影响[J]. 植物保护学报, 47(6): 1261-1269. |
| HU R, ZHENG L, LIU H, et al., 2020. Effects of straw returning on microbial diversity in rice rhizosphere and occurrence of rice sheath blight[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 47(6): 1261-1269. | |
| [17] | 黄继川, 彭智平, 徐培智, 等, 2017. 华南区域秸秆和畜禽粪便有机钾资源调查分析[J]. 广东农业科学, 44(4): 83-89. |
| HUANG J C, PENG Z P, XU P Z, et al., 2017. Investigation and analysis of organic potassium resources from straw and livestock manure in South China[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 44(4): 83-89. | |
| [18] | 解文艳, 周怀平, 杨振兴, 等, 2015. 秸秆还田方式对褐土钾素平衡与钾库容量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21(4): 936-942. |
| JIE W Y, ZHOU H P, YANG Z X, et al., 2015. Effect of different straw return modes on potassium balance and potassium pool in cinnamon soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 21(4): 936-942. | |
| [19] | 李昌明, 王晓玥, 孙波, 2017. 不同气候和土壤条件下秸秆腐解过程中养分的释放特征及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 54(5): 1206-1217. |
| LI C M, WANG X Y, SUN B, et al., 2017. Characteristics of Nutrient Release and Its Affecting Factors during Plant Residue Decomposition under Different Climate and Soil Conditions[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 54(5): 1206-1217. | |
| [20] | 李红莉, 张卫峰, 张福锁, 等, 2010. 中国主要粮食作物化肥施用量与效率变化分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 16(5): 1136-1143. |
| LI H L, ZHANG W F, ZHANG F S, et al., 2010. Chemical fertilizer use and efficiency change of main grain crops in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 16(5): 1136-1143. | |
| [21] | 李胜男, 纪雄辉, 邓凯, 等, 2020. 区域秸秆资源分布及全量化利用潜力分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 36(12): 221-228. |
| LI S N, JI X H, DENG K, et al., 2020. Analysis of regional distribution patterns and full utilization potential of crop straw resources[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 36(12): 221-228. | |
| [22] | 李廷亮, 王嘉豪, 王宇峰, 等, 2020. 我国主要粮食作物秸秆还田养分资源量及其对小麦化肥减施的启示[J]. 中国农业科学, 53(23): 4835-4854. |
| LI T L, WANG J H, WANG Y F, et al., 2020. Nutrient resource quantity from main grain crop straw incorporation and its enlightenment on chemical fertilizer reduction in wheat production in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 53(23): 4835-4854. | |
| [23] | 李一, 王秋兵, 2020. 我国秸秆资源养分还田利用潜力及技术分析[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (1): 119-126. |
| LI Y, WANG Q B, 2020. Study on potential of straw resource nutrient return to field and application technology in China[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (1): 119-126. | |
| [24] | 林日强, 宋丹丽, 2002. 广东省作物秸秆的利用现状与问题[J]. 土壤与环境, 11(1): 110. |
| LIN R Q, SONG D L, 2002. Utilization status and problems of crop straw in Guangdong Province[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 11(1): 110. | |
| [25] | 刘晓永, 李书田, 2017. 中国秸秆养分资源及还田的时空分布特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 33(21): 1-19. |
| LIU X Y, LI S T, 2017. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of crop straw nutrient resources and returning to farmland in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 33(21): 1-19. | |
| [26] | 刘晓永, 2018. 中国农业生产中的养分平衡与需求研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院. |
| LIU X Y, 2018. Study on nutrients balance and requirement in agricultural production in China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. | |
| [27] | 罗文丽, 2014. 广西主要作物秸秆腐解特征研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学. |
| LUO W L, 2014. Decomposing characteristics of main crop straws in Guangxi[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University. | |
| [28] | 麻坤, 刁钢, 2018. 化肥对中国粮食产量变化贡献率的研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(4): 1113-1120. |
| MA K, DIAO G, 2018. Research on the contribution rate of fertilizer to grain yield in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 24(4): 1113-1120. | |
| [29] | 马文奇, 马林, 张建杰, 等, 2020. 农业绿色发展理论框架和实现路径的思考[J]. 中国生态农业学报 (中英文), 28(8): 1103-1112. |
| MA W Q, MA L, ZHANG J J, et al., 2020. Theoretical framework and realization pathway of agricultural green development[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 28(8): 1103-1112. | |
| [30] | 马想, 徐明岗, 赵惠丽, 等, 2019. 我国典型农田土壤中有机物料腐解特征及驱动因子[J]. 中国农业科学, 52(9): 1564-1573. |
| MA X, XU M G, ZHAO H L, et al., 2019. Decomposition characteristics and driving factors of organic materials in typical farmland soils in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 52(9): 1564-1573. | |
| [31] | 牛新胜, 巨晓棠, 2017. 我国有机肥料资源及利用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23(6): 1462-1479. |
| NIU X S, JU X T, 2017. Organic fertilizer resources and utilization in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 23(6): 1462-1479. | |
| [32] | 区惠平, 周柳强, 黄金生, 等, 2018. 长期不同施肥对甘蔗产量稳定性、肥料贡献率及养分流失的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 51(10): 1931-1939. |
| OU H P, ZHOU L Q, HUANG J S, et al., 2018. Effects of long-term different fertilization on sugarcane yield stability, fertilizer contribution rate and nutrition loss[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 51(10): 1931-1939. | |
| [33] | 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 1999. 中国有机肥料资源[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| National Agricultural Technology Extension Service Center of China, 1999. Organic fertilizer nutrition records of China[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [34] | 宋大利, 侯胜鹏, 王秀斌, 等, 2018. 中国秸秆养分资源数量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(1): 1-21. |
| SONG D L, HOU S P, WANG X B, et al., 2018. Nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its potential of substituting[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 24(1): 1-21. | |
| [35] | 谭宏伟, 周柳强, 谢如林, 等, 2014. 甘蔗实现减量施肥的理论与实践[J]. 广西糖业 (6): 9-11. |
| TAN H W, ZHOU L Q, XIE R L, et al., 2014. Theory and practice of reducing fertilizer on Sugarcane[J]. Guangxi Sugar Industry (6): 9-11. | |
| [36] | 王碧胜, 于维水, 武雪萍, 等, 2021. 不同耕作措施下添加秸秆对土壤有机碳及其相关因素的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 54(6): 1176-1187. |
| WANG B S, YU W S, WU X P, et al., 2021. Effects of Straw Addition on Soil Organic Carbon and Related Factors Under Different Tillage Practices[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 54(6): 1176-1187. | |
| [37] | 王金洲, 卢昌艾, 张文菊, 等, 2016. 中国农田土壤中有机物料腐解特征的整合分析[J]. 土壤学报, 53(1): 16-27. |
| WANG J Z, LU C A, ZHANG W J, et al., 2016. Minggang decomposition of organic materials in cropland soils across China: A meta-analysis[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 53(1): 16-27. | |
| [38] | 王昆昆, 廖世鹏, 任涛, 等, 2020. 连续秸秆还田对油菜水稻轮作土壤磷素有效性及作物磷素利用效率的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 53(1): 94-104. |
| WANG K K, LIAO S P, REN T, et al., 2020. Effect of continuous straw returning on soil phosphorus availability and crop phosphorus utilization efficiency of oilseed rape-rice rotation[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 53(1): 94-104. | |
| [39] | 王如芳, 张吉旺, 董树亭, 等, 2011. 我国玉米主产区秸秆资源利用现状及其效果[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(6): 1504-1510. |
| WANG R F, ZHANG J W, DONG S T, et al., 2011. Present situation of maize straw resource utilization and its effect in main maize production regions of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(6): 1504-1510. | |
| [40] | 王亚静, 毕于运, 高春雨, 2010. 中国秸秆资源可收集利用量及其适宜性评价[J]. 中国农业科学, 43(9): 1852-1859. |
| WANG Y J, BI Y Y, GAO C Y, et al., 2010. Collectable Amounts and Suitability Evaluation of Straw Resource in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 43(9): 1852-1859. | |
| [41] | 魏文良, 刘路, 仇恒浩, 2020. 有机无机肥配施对我国主要粮食作物产量和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(8): 1384-1394. |
| WEI W L, LIU L, QIU HH, 2020. Effects of different organic resources application combined with chemical fertilizer on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of main grain crops in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(8): 1384-1394. | |
| [42] | 吴多广, 吴建涛, 谢静, 等, 2017. 中国甘蔗生产发展趋势分析[J]. 广东农业科学, 44(7): 154-160. |
| WU D G, WU J T, XIE J, et al., 2017. Development trend of sugarcane production in China[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 44(7): 154-160. | |
| [43] | 熊娜, 宋洪玲, 刘文武, 等, 2019. 广西主要农作物秸秆资源估算及其空间分布[J]. 西南农业学报, 32(6): 1404-1411. |
| XIONG N, SONG H L, LIU W W, et al., 2019. Estimation and spatial distribution of main crop straw resources in Guangxi[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 32(6): 1404-1411. | |
| [44] | 徐奔奔, 范萌, 陈良富, 等, 2020. 2013-2017年主要农业区秸秆焚烧时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 遥感学报, 24(10): 1221-1232. |
| XU B B, FAN M, CHEN L F, et al., 2020. Analysis of temporal and spatial characteristics and Influencing Factors of crop residue burning in major agricultural areas from 2013 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(10): 1221-1232. | |
| [45] | 杨竣皓, 骆永丽, 陈金, 等, 2020. 秸秆还田对我国主要粮食作物产量效应的整合 (Meta) 分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 53(21): 4415-4429. |
| YANG J H, LUO Y L, CHEN J, et al., 2020. Effects of Main Food Yield Under Straw Return in China: A Meta-Analysis[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 53(21): 4415-4429. | |
| [46] | 杨夏捷, 马远帆, 鞠园华, 等, 2018. 华南农产品主产区2005-2014年秸秆露天燃烧污染物排放估算及时空分布[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(2): 358-368. |
| YANG X J, MA Y F, JU Y H, et al., 2018. Temporal and spatial distribution of air pollutants emitted from field burning of straw crops in Southern China during 2005-2014 [J]. Journal of Agro-environment Science, 37(2): 358-368. | |
| [47] | 叶延琼, 汪晶, 章家恩, 等, 2019. 广东省水稻秸秆露天焚烧大气污染物排放的时空分布特征[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 40(4): 52-60. |
| YE Y Q, WANG J, ZHANG J E, et al., 2019. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of air pollutants from open burning of rice straw in Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 40(4): 52-60. | |
| [48] | 张鑫, 周卫, 艾超, 等, 2020. 秸秆还田下氮肥运筹对夏玉米不同时期土壤酶活性及细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(2): 295-306. |
| ZHANG X, ZHOU W, AI C, et al., 2020. Effects of nitrogen management on soil enzyme activities and bacterial community structure in summer maize growing stages under straw incorporation[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(2): 295-306. |
| [1] | 王晨茜, 张琼锐, 张若琪, 孙学超, 徐颂军. 广东省珠江流域景观格局对水质净化服务的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1425-1433. |
| [2] | 刘香华, 王秀明, 刘谞承, 张音波, 刘飘. 基于外溢生态系统服务价值的广东省生态补偿机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1024-1031. |
| [3] | 陈瑶瑶, 廖彤, 汪宇, 沈劲, 翟宇虹, 叶斯琪, 陈多宏, 陈靖扬. 2016—2020年广东省臭氧污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2374-2381. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
