生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2195-2203.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.11.010
收稿日期:2021-06-11
出版日期:2021-11-18
发布日期:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
* 赵天宏(1972年生),男,教授,博士研究生导师,研究方向为农业生态学和生态经济。作者简介:周映彤(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为农业生态系统生态学。E-mail: 1121705386@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Yingtong( ), WANG Yan, SUN Mingyu, SAN Yu, YAO Xingzhou, ZHAO Tianhong
), WANG Yan, SUN Mingyu, SAN Yu, YAO Xingzhou, ZHAO Tianhong
Received:2021-06-11
Online:2021-11-18
Published:2021-12-29
摘要:
为探究臭氧胁迫对不同世代大豆(Glycine max)抗氧化能力的影响,以栽培大豆“铁丰29号”为试验材料,在开顶式气室(OTCs)中,采用盆栽试验方法,设置3个O3熏蒸体积分数梯度[CK:对照,45 nL∙L-1 O3;T1:(80±10) nL∙L-1 O3;T2:(120±10) nL∙L-1 O3],并将受胁迫后的子代复种,研究臭氧浓度升高条件下大豆亲代和子代抗氧化能力的差异。结果表明,(1)随着臭氧体积分数增加,开花期和结荚期亲子代大豆叶片相对电导率较CK显著增加(P<0.05);MDA含量均增加,且在分枝期和开花期的T2处理下,与CK之间达显著差异(P<0.05),其增加幅度分别为32.9%、37.0%。(2)随着臭氧体积分数增加,O2∙-产生速率加快,除分枝期T1条件的其他处理外,S1和S2较CK都表现出显著差异水平(P<0.05);H2O2含量增大,在分枝期和开花期的T2条件下,S1、S2较CK上升幅度显著,分别达到88.2%、92.4%(P<0.05)。(3)SOD、CAT活性逐渐减弱,POD活性逐步增强。与对照相比,亲子代在3个时期均有显著下降的趋势(P<0.05)。(4)在胁迫后期,子代大豆叶片的ROS含量、产生速率高于亲代,抗氧化酶活性低于亲代,且在T2处理下达到显著水平(P<0.05)。(5)亲、子代大豆的膜脂过氧化程度、活性氧含量和产生速率两两之间均呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与SOD、CAT活性均极显著负相关(P<0.01),与POD活性呈不相关关系(P>0.05)。试验表明,臭氧体积分数升高对亲子代大豆的抗氧化能力有明显的抑制作用,且对子代的抑制作用略强于亲代,说明同时受到了遗传因素的影响。
中图分类号:
周映彤, 王岩, 孙铭禹, 伞昱, 姚星州, 赵天宏. 近地层臭氧浓度升高对亲子代大豆叶片抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2195-2203.
ZHOU Yingtong, WANG Yan, SUN Mingyu, SAN Yu, YAO Xingzhou, ZHAO Tianhong. Effect of Ozone Concentration Increasing Near the Ground on Antioxidant System of Parent and Offspring Soybean Leaves[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2195-2203.
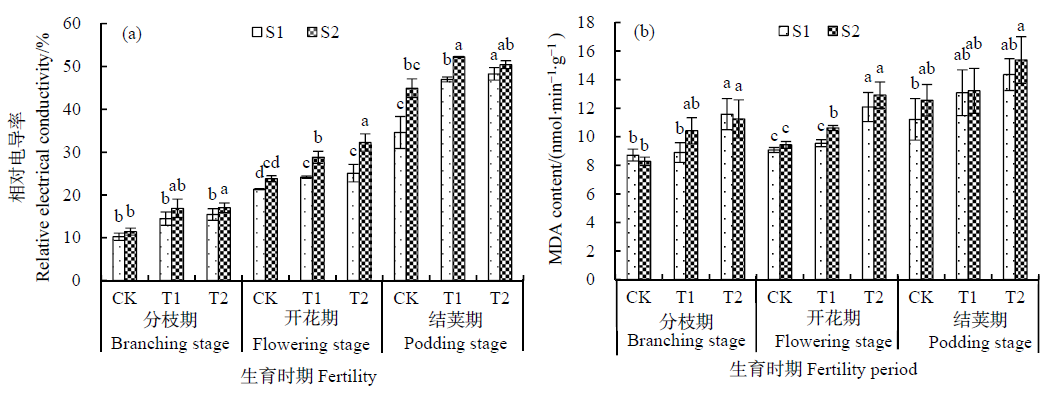
图1 不同臭氧体积分数处理下大豆亲子代叶片的外渗电导率和MDA含量 S1:大豆亲代;S2:大豆子代。图中不同小写字母分别表示不同处理间的差异达到P<0.05显著性水平。CK:臭氧体积分数为45 nL∙L-1;T1:臭氧体积分数为 (80±10) nL·L-1;T2:臭氧体积分数为 (120±10) nL·L-1,n=3,下同
Fig. 1 Variation of relative electrical conductivity and MDA content in parent and offspring soybean leaves under different ozone concentration S1: soybean parent; S0: soybean progeny. Different small letters in the rows show the significance of different treatments at P<0. 05 level, respectively. CK: ozone concentration: 45 nL·L-1; T1: ozone concentration :(80±10) nL·L-1; T2: ozone concentration: (120±10) nL·L-1. n=3,The same below
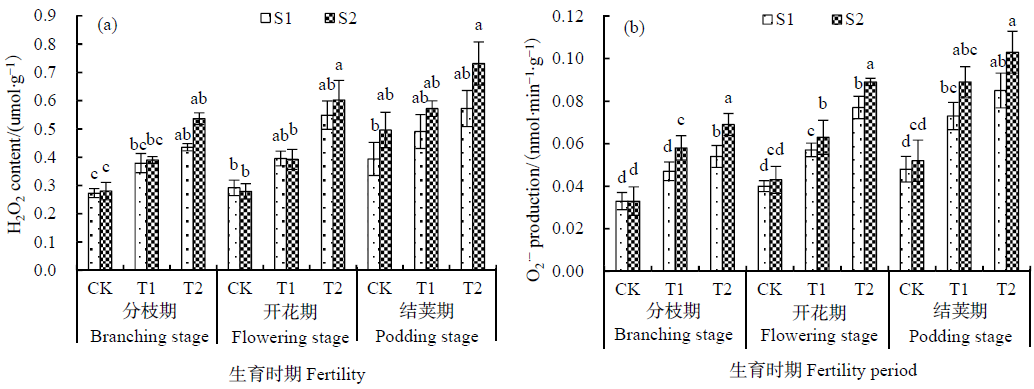
图2 不同臭氧体积分数处理下大豆亲子代叶片的H2O2含量和O2∙-产生速率
Fig. 2 Variation of H2O2 content and O2∙- production in parent and offspring soybean leaves under different ozone concentration
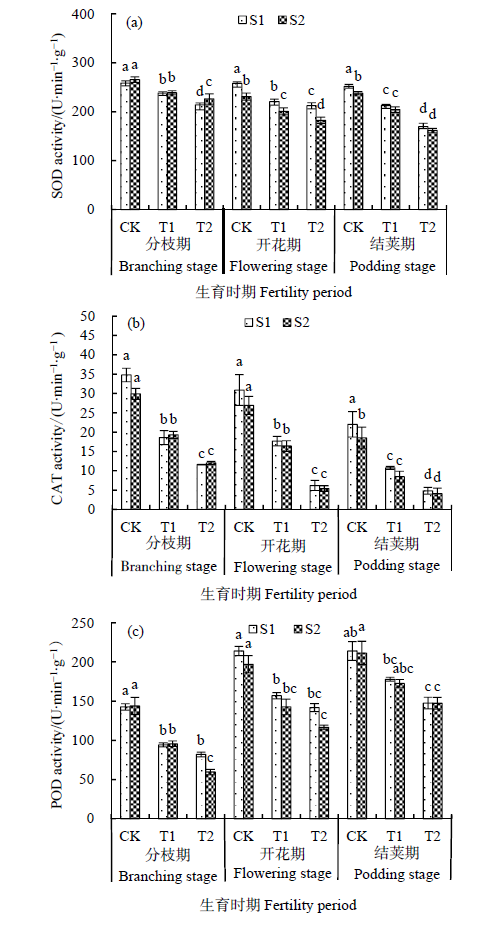
图3 不同臭氧体积分数处理下大豆亲子代叶片的抗氧化防御酶系统活性变化
Fig. 3 Variation of antioxidant enzyme system activity in parent and offspring soybean leaves under different ozone concentration
| 因素 Factor | 自由度 df | 显著性Significance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 外渗电导率Relative electrical conductivity | MDA含量 MDA content | H2O2含量H2O2 content | O2∙-产生速率O2∙- production | SOD活性 SOD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | POD活性 POD activity | ||
| O3 | 2 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Generation | 1 | <0.01 | 0.049 | 0.050 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.016 | 0.010 |
| Stage | 2 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| O3×Generation | 2 | 0.674 | 0.875 | 0.431 | 0.062 | 0.294 | 0.048 | 0.405 |
| O3×Stage | 4 | 0.023 | 0.981 | 0.764 | 0.059 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.696 |
| Generation×Stage | 2 | 0.010 | 0.818 | 0.279 | 0.439 | <0.01 | 0.878 | 0.238 |
| O3×Generation×Stage | 4 | 0.080 | 0.732 | 0.998 | 0.970 | 0.544 | 0.836 | 0.583 |
表1 三因素及其交互作用对大豆亲子代叶片各抗氧化指标的方差分析
Table 1 Variance analysis of three factors and their interaction on the antioxidant indexes of parent and offspring soybean leaves
| 因素 Factor | 自由度 df | 显著性Significance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 外渗电导率Relative electrical conductivity | MDA含量 MDA content | H2O2含量H2O2 content | O2∙-产生速率O2∙- production | SOD活性 SOD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | POD活性 POD activity | ||
| O3 | 2 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Generation | 1 | <0.01 | 0.049 | 0.050 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.016 | 0.010 |
| Stage | 2 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| O3×Generation | 2 | 0.674 | 0.875 | 0.431 | 0.062 | 0.294 | 0.048 | 0.405 |
| O3×Stage | 4 | 0.023 | 0.981 | 0.764 | 0.059 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.696 |
| Generation×Stage | 2 | 0.010 | 0.818 | 0.279 | 0.439 | <0.01 | 0.878 | 0.238 |
| O3×Generation×Stage | 4 | 0.080 | 0.732 | 0.998 | 0.970 | 0.544 | 0.836 | 0.583 |
| 指标 Index | 相关系数 (r) Correlation coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | MDA含量 MDA content | H2O2含量 H2O2 content | O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | SOD活性 SOD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | POD活性 POD activity | |
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | 1 | 0.667** | 0.584** | 0.660** | -0.636** | -0.533** | 0.412* |
| MDA含量 MDA content | 1 | 0.849** | 0.814** | -0.713** | -0.686** | 0.018 | |
| H2O2含量 H2O2 content | 1 | 0.837** | -0.807** | -0.851** | -0.134 | ||
| O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | 1 | -0.802** | -0.799** | -0.126 | |||
| SOD活性 SOD activity | 1 | 0.856** | 0.296 | ||||
| CAT活性 CAT activity | 1 | 0.285 | |||||
| POD活性 POD activity | 1 | ||||||
表2 亲代大豆抗氧化相关指标间的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between indexes of anti-oxidation in parent soybean leaves
| 指标 Index | 相关系数 (r) Correlation coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | MDA含量 MDA content | H2O2含量 H2O2 content | O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | SOD活性 SOD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | POD活性 POD activity | |
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | 1 | 0.667** | 0.584** | 0.660** | -0.636** | -0.533** | 0.412* |
| MDA含量 MDA content | 1 | 0.849** | 0.814** | -0.713** | -0.686** | 0.018 | |
| H2O2含量 H2O2 content | 1 | 0.837** | -0.807** | -0.851** | -0.134 | ||
| O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | 1 | -0.802** | -0.799** | -0.126 | |||
| SOD活性 SOD activity | 1 | 0.856** | 0.296 | ||||
| CAT活性 CAT activity | 1 | 0.285 | |||||
| POD活性 POD activity | 1 | ||||||
| 指标 Index | 相关系数 (r) Correlation coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | MDA含量 MDA content | H2O2含量 H2O2 content | O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | SOD活性 SOD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | POD活性 POD activity | |
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | 1 | 0.702** | 0.596** | 0.644** | -0.626** | -0.616** | 0.506* |
| MDA含量 MDA content | 1 | 0.723** | 0.724** | -0.671** | -0.743** | 0.047 | |
| H2O2含量 H2O2 content | 1 | 0.728** | -0.632** | -0.751** | -0.138 | ||
| O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | 1 | -0.848** | -0.892** | -0.206 | |||
| SOD活性 SOD activity | 1 | 0.825** | 0.056 | ||||
| CAT活性 CAT activity | 1 | 0.259 | |||||
| POD活性 POD activity | 1 | ||||||
表3 子代大豆抗氧化相关指标间的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between indexes of anti-oxidation in offspring soybean leaves
| 指标 Index | 相关系数 (r) Correlation coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | MDA含量 MDA content | H2O2含量 H2O2 content | O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | SOD活性 SOD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity | POD活性 POD activity | |
| 外渗电导率 Relative electrical conductivity | 1 | 0.702** | 0.596** | 0.644** | -0.626** | -0.616** | 0.506* |
| MDA含量 MDA content | 1 | 0.723** | 0.724** | -0.671** | -0.743** | 0.047 | |
| H2O2含量 H2O2 content | 1 | 0.728** | -0.632** | -0.751** | -0.138 | ||
| O2∙-产生速率 O2∙- production | 1 | -0.848** | -0.892** | -0.206 | |||
| SOD活性 SOD activity | 1 | 0.825** | 0.056 | ||||
| CAT活性 CAT activity | 1 | 0.259 | |||||
| POD活性 POD activity | 1 | ||||||
| [1] |
AGATHOKLEOUS E, SAITANIS C J, 2020. Plant susceptibility to ozone: A tower of babel?[J]. Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134962.
DOI |
| [2] |
ALESSANDRA C, LORENZO C, ELISA P, et al., 2018. Phenylpropanoids are key players in the antioxidant defense to ozone of European ash, Fraxinus excelsior[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(9): 8137-8147.
DOI URL |
| [3] | ALONSO R, ELVIRA S, CARTILLO F J, et al., 2001. Interactive effects of ozone and drought stress on pigments and activities of antioxidantive enzymes in Pinus halepensis[J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 24(9): 905-916. |
| [4] |
ALSCHER R G, ERTURK N, HEATH L S, 2002. Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53(372): 1331-1341.
DOI URL |
| [5] | ASADA K, 1999. The water- water cycle in chlorplasts: Scavenging of active oxygens and dissipation of excess photons[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiologyand Plant Molecular Biology, 50: 601-639. |
| [6] |
BASSIN S, VOLK M, FUHRER J, 2007. Factors affecting the ozone sensitivity of temperate European grasslands: An overview[J]. Environmental Pollution, 146(3): 678-691.
DOI URL |
| [7] | BERGMANN E, BENDER J, WEIGEL H J, et al., 2017. Impact of tropospheric ozone on terrestrial biodiversity: A literature analysis to identify ozone sensitive taxa[J]. Journal of Applied Botany and Food Quality, 90: 83-105. |
| [8] |
BETZELBERGER A M, YENDREK C R, MELLO T R, et al., 2012. Ozone Exposure Response for U.S. Soybean Cultivars: Linear Reductions in Photosynthetic Potential, Biomass, and Yield[J]. Plant Physiology, 160(4): 1827-1839.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CAKMAK I, HORST W J, 1991. Effect of aluminium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max)[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 83(3): 463-468.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CALATAYUD A, BARRENO E, 2001. Chlorophyll a fluorescence,antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in tomato in response to ozone and benomy[J]. Environmental Pollution, 115(2): 283-289.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHEN Z Y, ZHUANG Y, XIE X M, et al., 2019. Understanding long-term variations of meteorological influences on ground ozone concentrations in Beijing During 2006-2016 [J]. Environmental Pollution, 245: 29-37.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
DAVISON A W, BARNES J D, 1998. Effects of ozone on wild plants[J]. New Phytologist, 139(1): 135-151.
DOI URL |
| [13] | DE SOUZA I R, MACADAM J W, 2001. Gibberellic acid and dwarfism effects on the growth dynamics of B73 maize (Zea mays L.) leaf blades: A transient increase in apoplastic peroxidase activity precedes cessation of cell elongation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 52(361): 1673-1682. |
| [14] |
DUQUE L, POELMAN E H, STEFFAN-DEWENTER I, et al., 2021. Effects of ozone stress on flowering phenology, plant-pollinator interactions and plant reproductive success[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115953.
DOI |
| [15] |
ELISA P, ALICE T, ALESSANDRA C, et al., 2013. Signaling molecules and cell death in Melissa officinalis plants exposed to ozone[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 32(12): 1965-1980.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
FENG Z Z, SHANG B, LI Z Z, et al., 2019. Ozone will remain a threat for plants independently of nitrogen load[J]. Functional Ecology, 33(10): 1854-1870.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
FENG Z Z, AGATHOKLEOUS E, YUE X, et al., 2021. Emerging challenges of ozone impacts on asian plants: Actions are needed to protect ecosystem health[J]. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, DOI: 10.1080/20964129. 2021.1911602.
DOI |
| [18] | FISCUS E L, BOOKER F L, BURKEY K O, et al., 2005. Crop responses to ozone: Uptake, modes of action, carbon assimilation and partitioning[J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 28(8): 997-1011. |
| [19] |
ELINA H, FREIWALD V, JULKUNEN-TIITTO R, et al., 2009. Differences in leaf characteristics between ozone-sensitive and ozone-tolerant hybrid aspen (Populus tremula×Populus tremuloides) clones[J]. Tree Physiology, 29(1): 53-66.
DOI URL |
| [20] | HEATH R L, TAYLOR G E, 1997. Physiological processes and plant responses to ozone exposure[J]. Ecological Studies, 127: 317-368. |
| [21] |
KEUTGEN A J, PAWELZIK E, 2008. Apoplastic antioxidative system responses to ozone stress in strawberry leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 165(8): 868-875.
DOI URL |
| [22] | LEFFOHN A S, MALLEY C S, SMITH L, et al., 2018. Tropospheric ozone assessment report: Global ozone metrics for climate change, human health, and crop-ecosystem research[J]. Elementa: Science of the Anthropocene, 6(1): 28. |
| [23] |
LI P, CALATAYUD V, GAO F, et al., 2016. Differences in ozone sensitivity among woody species are related to leaf morphology and antioxidant levels[J]. Tree Physiology, 36(9): 1105-1116.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LIU R Y, MA Z W, LIU Y, et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal distributions of surface ozone levels in China from 2005 to 2017: A machine learning approach[J]. Environment International, DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2020. 105823.
DOI |
| [25] |
LOW P S, MERIDA J R, 1996. The oxidative burst in plant defense: Function and signal transduction[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 96(3): 533-542.
DOI URL |
| [26] | LU X, ZHANG L, WANG X L, et al., 2020. Rapid Increases in Warm-Season Surface Ozone and Resulting Health Impact in China Since 2013 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 7(4): 240-247. |
| [27] |
MILLS G, SHARPS K, DAVID S, et al., 2018. Closing the global ozone yield gap: Quantification and cobenefits for multistress tolerance[J]. Global Change Biology, 24(10): 4869-4893.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
OKSANEN E, MANNINEN S, VAPAAVUORI E, et al., 2009. Near-ambient ozone concentrations reduce the vigor of Betula and Populus species in Finland[J]. Ambio: A Journal of the Human Environment, 38(8): 413-417.
DOI URL |
| [29] | RANIERI A, NALI C, LORENZINI G, et al., 1996. Ozone stimulates apoplastic antioxidant systems in pumpkin leaves[J]. Physiol Plant, 97(2): 381-387. |
| [30] |
SAIRAM R K, SRIVASTAVA G C, 2002. Changes in antioxidant activity in sub cellular fractions of tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes in response to long term salt stress[J]. Plant Science, 162(6): 897-904.
DOI URL |
| [31] | SHARPS K, HAYES F, HARMENS H, et al., 2021. Ozone-induced effects on leaves in African crop species[J]. Environmental Pollution, 268 (Pt A): 115789. 1-115789.9. |
| [32] |
SILLMAN S, 1999. The relation between ozone, NOx and hydrocarbons in urban and polluted rural environments[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 33(12): 1821-1845.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
SUZUKI N, RIVERO R M, SHULAEV V, et al., 2014. Abiotic and biotic stress combinations[J]. New Phytol, 203(1): 32-43.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
TARASICK D, GALBALLY L E, COOPER O R, et al., 2019. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Tropospheric ozone from 1877 to 2016, observed levels, trends and uncertainties[J]. Elem Sci Anth, 7(1): 39.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
TRAINER M, PARRISH D D, GOLDAN P D, et al., 2000. Review of observation-based analysis of the regional factors influencing ozone concentrations[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 34(12-14): 2045-2061.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 贾桂霞, 杨俊明, 沈熙环, 2003. 落叶松种间交配结实力变异和自交衰退的研究[J]. 林业科学, 39(1): 62-68. |
| JIA G X, YANG J M, SHEN X H, 2003. Study on the mating strength variation and automating decline of the larch species[J]. Forestry Science, 39(1): 62-68. | |
| [37] | 姬东华, 薛亚东, 郑用琏, 等, 2013. 玉米初级作图群体的籽粒性状遗传效应分析[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 32(4): 1-5. |
| JI D H, XUE Y D, ZHENG Y L, et al., 2013. Genetic analysis of grain related traits of a maize primary mapping population[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 32(4): 1-5. | |
| [38] | 秦子晴, 徐胜, 齐淑艳, 等, 2020. 臭氧和增温对醉蝶花 (Cleome spinosa) 氧化伤害及抗氧化酶活的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(3): 830-837. |
| QIB Z Q, XU S, QI S Y, et al., 2020. Effect of Ozone and Temperature on oxidative injury and antioxidant enzyme activity of Drunken Butterfly Flower (Cleome spinosa)[J]. Journal of Ecology, 39 (3): 830-837. | |
| [39] | 阮亚男, 何兴元, 陈玮, 等, 2009. 臭氧浓度升高对油松抗氧化系统活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 20(5): 1032-1037. |
| RUAN Y N, HE X Y, CHEN W, et al., 2009. Effect of increased ozone concentration on the activity of oil pine antioxidant system[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 20(5): 1032-1037. | |
| [40] | 宋琎楠, 陆启环, 王中新, 等, 2018. 臭氧水浇灌对韭菜幼苗抗氧化酶活性及营养成分的影响[J]. 中国瓜菜, 31(4): 16-18. |
| SONG J N, LU Q H, WANG Z X, et al., 2018. Effect of Ozone Water Irrigation on Antioxidase Activity and Nutrients of Leek Seedlings[J]. Chinese Melon and Vegetables, 31(4): 16-18. | |
| [41] | 孙加伟, 赵天宏, 付宇, 等, 2008. 臭氧浓度升高对玉米活性氧代谢及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 27(5): 1929-1934. |
| SUN J W, ZHAO T H, FU Y, et al., 2008. Effect of elevated ozone concentration on reactive oxygen metabolism and antioxidase activity of corn[J]. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences, 27(5): 1929-1934. | |
| [42] | 王俊力, 陈桂发, 刘福兴, 等, 2016. 臭氧氧化猪场处理尾水对苦草 (Vallisneria spiralis) 抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(12): 2299-2305. |
| WANG J L, CHEN G F, LIU F X, et al., 2016. Effect of Ozone Oxidation Pig Farm Handling Tailing Water on Bitter Grass (Vallisneria spiralis) antioxidant System[J]. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences, 35(12): 2299-2305. | |
| [43] | 王俊力, 王岩, 赵天宏, 等, 2011. 臭氧胁迫对大豆叶片抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环的影响[J]. 生态学报, 31(8): 2068-2075. |
| WANG J L, WANG Y, ZHAO T H, et al., 2011. Effect of Ozone Stress on ascorbate-glutathione circulation in soybean leaves[J]. Journal of Ecology, 31(8): 2068-2075. | |
| [44] | 王浩, 2013. 自交衰退新解[J]. 分子植物育种, 11(5): 630-637. |
| WANG H, 2013. New solution to the self-surrender recession[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 11(5): 630-637. | |
| [45] | 徐玲, 赵天宏, 胡莹莹, 等, 2008. 高浓度臭氧对春小麦膜脂过氧化和抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 26(2): 74-78. |
| XU L, ZHAO T H, HU Y Y, et al., 2008. Effect of high concentration ozone on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant system in spring wheat[J]. Agricultural Studies in Arid Areas, 26(2): 74-78. | |
| [46] | 徐雁飞, 陈发棣, 滕年军, 等, 2009. 菊花自交衰退现象初步研究[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 18(4): 28-32. |
| XU Y F, CHEN F D, TENG N J, et al., 2009. Preliminary study on inbreeding depression of Dendranthema morifolium[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 18(4): 28-32. | |
| [47] | 杨舒贻, 陈晓阳, 惠文凯, 等, 2016. 逆境胁迫下植物抗氧化酶系统响应研究进展[J]. 福建农林大学学报: 自然科学版, 45(5): 481-489. |
| YANG S Y, CHEN X Y, HUI W K, et al., 2016. Progress in responses of antioxidant enzyme systems in plant to environmental stresses[J]. Journal of Fu-jian Agriculture and Forestry University: Natural Science Edition, 45(5): 481-489. | |
| [48] | 于涛, 2010. 臭氧浓度升高对银杏抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 现代农业科技 (10): 186, 192. |
| YU T, 2010. Effect of increased ozone concentration on the antioxidant capacity of ginkgo[J]. Modern Agricultural Technology (10): 186, 192. | |
| [49] | 张国范, 刘述锡, 刘晓, 等, 2003. 海湾扇贝自交家系的建立和自交效应[J]. 中国水产科学, 10(6): 441-445. |
| ZHANG G F, LIU S X, LIU X, et al., 2003. Self-fertilization family establishment and its depression in bay scallop Argopecten irradians[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 10(6): 441-445. | |
| [50] |
张巍巍, 郑飞翔, 王效科, 等, 2009. 臭氧对水稻根系活力、可溶性蛋白含量与抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 33(3): 425-432.
DOI |
| ZHANG W W, ZHENG F X, WANG X K, et al., 2009. Effect of Ozone on Root Vitality, soluble Protein Content and antioxidant System in Rice[J]. Botanical Ecology, 33(3): 425-432. | |
| [51] | 赵天宏, 金东艳, 王岩, 等, 2011. 臭氧胁迫对大豆酚类化合物含量和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 44(4): 708-715. |
| ZHAO T H, JIN D Y, WANG Y, et al., 2011. Effect of Ozone stress on the content and antioxidant capacity of soybean phenolic compounds[J]. China Agricultural Science, 44(4): 708-715. | |
| [52] | 郑有飞, 胡程达, 吴荣军, 等, 2010. 臭氧胁迫对冬小麦光合作用、膜脂过氧化和抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 环境科学, 31(7): 1643-1651. |
| ZHENG Y F, HU C D, WU R J, et al., 2010. Effect of Ozone Stress on Photosynthesis, Membrane Fat Peroxidation, and Antioxidant Systems in Winter Wheat[J]. Environmental Sciences, 31(7): 1643-1651. | |
| [53] | 周慧敏, 李品, 高峰, 等, 2018. 臭氧和干旱交互作用对杨树叶片抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 39(9): 4359-4365. |
| ZHOU H M, LI P, GAO F, et al., 2018. Effect of ozone and drought interaction on antioxidase activity of poplar leaves[J]. Environmental Sciences, 39(9): 4359-4365. |
| [1] | 李程程, 张子蕤, 宋晓萱, 孔娟娟, 韩阳, 阮亚男. 臭氧胁迫对大豆抗氧化代谢与生殖生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1383-1392. |
| [2] | 刘江, 朱丽杰, 张开, 王晓明, 王立为, 高西宁. 不同生育期干旱胁迫/复水对大豆光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 286-296. |
| [3] | 张鹏, 刘玮, 王铁杆, 钟晨辉, 陶月良. 无机砷短期胁迫对铜藻幼苗氧化损伤、抗氧化酶及抗氧化物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1034-1041. |
| [4] | 张晋龙, 黄颖, 吴丽芳, 龚云辉, 刘云根, 王妍, 杨思林. 砷胁迫对狭叶香蒲生理生态及砷亚细胞分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1042-1050. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 88
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 172
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
