生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 819-830.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.05.015
• 综述 •
上一篇
王弋1( ), 严茂泽1, 肖倩1, 张思毅2, 郝贝贝2,*(
), 严茂泽1, 肖倩1, 张思毅2, 郝贝贝2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-14
出版日期:2025-05-18
发布日期:2025-05-16
通讯作者:
*郝贝贝。E-mail: 作者简介:王弋(1977年生),女,教授,博士,主要研究方向为水生态和水环境。E-mail: wangyi28@ncepu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Yi1( ), YAN Maoze1, XIAO Qian1, ZHANG Siyi2, HAO Beibei2,*(
), YAN Maoze1, XIAO Qian1, ZHANG Siyi2, HAO Beibei2,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-14
Online:2025-05-18
Published:2025-05-16
摘要:
农村生活污水治理是改善人居环境和实施乡村振兴战略的重要环节,分析农村生活污水处理设施的出水水质,对于解析污水处理现状和提高设施处理水平非常必要。收集了广东省2021-2023年期间农村生活污水处理设施出水的水质数据,并使用水质单因子评价法、双因素方差分析法和层次分析法对广东省不同地区和不同处理技术下污水处理设施的处理效果和影响进行了综合性分析与评价,为农村生活污水的处理和生态环境保护提供科学支撑。结果表明,1)广东省农村生活污水的主要污染物为氨氮、化学需氧量、悬浮物和总磷;粤西和粤北地区农村生活污水的污染情况总体上比珠三角和粤东地区更严重,其中粤西地区的水质指标平均浓度最高,粤东地区的主要污染物平均超标倍数最大,超标倍数最大的污染物为氨氮;处理技术上,使用厌氧池+人工湿地和化粪池技术的污水处理设施的出水水质超标率较高。2)农村生活污水处理设施出水的水质情况在不同地区和处理技术间存在显著差异,而处理技术的选择则需要综合考虑多方因素。3)整体综合性评价结果显示,经济较发达的农村地区得分最高的处理技术为缺氧好氧/厌氧缺氧好氧工艺(AO/AAO);经济欠发达地区得分最高的处理技术为厌氧池+人工湿地。建议广东省农村地区优化污水处理工艺,灵活调整运行策略,增强处理设施中微生物群落稳定性;加大粤西地区的污水治理投入;提高处理设施的设计、管理和维护水平,并根据地区特点选择合适的处理技术。
中图分类号:
王弋, 严茂泽, 肖倩, 张思毅, 郝贝贝. 广东省农村生活污水处理现状及建议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(5): 819-830.
WANG Yi, YAN Maoze, XIAO Qian, ZHANG Siyi, HAO Beibei. Current Status and Recommendations for Rural Domestic Sewage Treatment in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(5): 819-830.
| 村庄类别 | 小型村庄 | 中型村庄 | 大型村庄 | 特大型村庄 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量占比 | 25.5% | 54.4% | 11.2% | 9.0% |
| 设计日处理能力/t | 20-30 | 30-60 | 60-110 | >110 |
| 主要处理工艺 | 厌氧池+人工湿地 化粪池 | 厌氧池+人工湿地 AO/AAO 生物接触氧化 | AO/AAO MBR/MBBR 航天ANAO | AO/AAO MBR/MBBR SBR 一体化设备 |
表1 农村类型占比、污水处理规模及主要处理工艺
Table 1 Proportion of rural types, sewage treatment scale and main treatment processes
| 村庄类别 | 小型村庄 | 中型村庄 | 大型村庄 | 特大型村庄 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量占比 | 25.5% | 54.4% | 11.2% | 9.0% |
| 设计日处理能力/t | 20-30 | 30-60 | 60-110 | >110 |
| 主要处理工艺 | 厌氧池+人工湿地 化粪池 | 厌氧池+人工湿地 AO/AAO 生物接触氧化 | AO/AAO MBR/MBBR 航天ANAO | AO/AAO MBR/MBBR SBR 一体化设备 |
| 标准号 | 执行标准名称 | 执行几级 标准 | 水温/ ℃ | 化学需 氧量/ (mg·L−1) | 氨氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | pH | 五日生化需氧量/ (mg·L−1) | 悬浮物质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 总磷质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 粪大肠 菌群/(ind·L−1) | 总氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 动植物油质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 一级 | >12 | 60 | 8 | 6-9 | - | 20 | 1 | - | 20 | 3 |
| 1 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 一级 | ≤12 | 60 | 15 | 6-9 | - | 20 | 1 | - | 20 | 3 |
| 2 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 二级 | - | 70 | 15 | 6-9 | - | 30 | - | - | - | 5 |
| 3 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 三级 | - | 100 | 25 | 6-9 | - | 50 | - | - | - | 5 |
| 4 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | >12 | 50 | 5 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 4 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | ≤12 | 50 | 8 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 5 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | >12 | 50 | 5 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 5 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | ≤12 | 50 | 8 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 6 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | >12 | 60 | 8 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1.5 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 6 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | ≤12 | 60 | 15 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1.5 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 7 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | >12 | 60 | 8 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 7 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | ≤12 | 60 | 15 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 10 | 农田灌溉水质标准 (GB 5084—2021) | 水田作物 | 35 | 150 | - | 5.5-8.5 | 60 | 80 | - | 40000 | - | - |
| 11 | 农田灌溉水质标准 (GB 5084—2021) | 旱地作物 | 35 | 200 | - | 5.5-8.5 | 100 | 100 | - | 40000 | - | - |
| 12 | 农田灌溉水质标准 (GB 5084—2021) | 蔬菜 | 35 | 100 | - | 5.5-8.5 | 40 | 60 | - | 20000 | - | - |
| 16 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) 水污染物排放限值 (DB44/ 26—2001) | 一级A 第二时段一级较严值 | >12 | 40 | 8 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 16 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) 水污染物排放限值 (DB44/ 26—2001) | 一级A 第二时段一级较严值 | ≤12 | 40 | 5 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
表2 广东省农村生活污水排放地方执行标准表
Table 2 Local implementation standards for rural domestic sewage discharge in Guangdong Province
| 标准号 | 执行标准名称 | 执行几级 标准 | 水温/ ℃ | 化学需 氧量/ (mg·L−1) | 氨氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | pH | 五日生化需氧量/ (mg·L−1) | 悬浮物质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 总磷质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 粪大肠 菌群/(ind·L−1) | 总氮质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) | 动植物油质量浓度/ (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 一级 | >12 | 60 | 8 | 6-9 | - | 20 | 1 | - | 20 | 3 |
| 1 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 一级 | ≤12 | 60 | 15 | 6-9 | - | 20 | 1 | - | 20 | 3 |
| 2 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 二级 | - | 70 | 15 | 6-9 | - | 30 | - | - | - | 5 |
| 3 | 农村生活污水处理排放标准 (DB 44/2208—2019) | 三级 | - | 100 | 25 | 6-9 | - | 50 | - | - | - | 5 |
| 4 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | >12 | 50 | 5 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 4 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | ≤12 | 50 | 8 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 5 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | >12 | 50 | 5 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 5 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级A | ≤12 | 50 | 8 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 6 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | >12 | 60 | 8 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1.5 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 6 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | ≤12 | 60 | 15 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1.5 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 7 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | >12 | 60 | 8 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 7 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) | 一级B | ≤12 | 60 | 15 | 6-9 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 10000 | 20 | 3 |
| 10 | 农田灌溉水质标准 (GB 5084—2021) | 水田作物 | 35 | 150 | - | 5.5-8.5 | 60 | 80 | - | 40000 | - | - |
| 11 | 农田灌溉水质标准 (GB 5084—2021) | 旱地作物 | 35 | 200 | - | 5.5-8.5 | 100 | 100 | - | 40000 | - | - |
| 12 | 农田灌溉水质标准 (GB 5084—2021) | 蔬菜 | 35 | 100 | - | 5.5-8.5 | 40 | 60 | - | 20000 | - | - |
| 16 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) 水污染物排放限值 (DB44/ 26—2001) | 一级A 第二时段一级较严值 | >12 | 40 | 8 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| 16 | 城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918—2002) 水污染物排放限值 (DB44/ 26—2001) | 一级A 第二时段一级较严值 | ≤12 | 40 | 5 | 6-9 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 1000 | 15 | 1 |
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | 0 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.89 | 1.12 | 1.26 | 1.34 | 1.41 | 1.46 |
表3 随机一致性指标(D)
Table 3 Random consistency index (D)
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | 0 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.89 | 1.12 | 1.26 | 1.34 | 1.41 | 1.46 |
| 项目 | 水温 | COD | 氨氮 | pH | BOD5 | SS | 总磷 | FCB | 总氮 | 动植物油 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 超标率 | 0.01 | 1.66 | 6.75 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
表4 不同指标水质超标率
Table 4 Water quality exceeding standard rate of different indicators %
| 项目 | 水温 | COD | 氨氮 | pH | BOD5 | SS | 总磷 | FCB | 总氮 | 动植物油 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 超标率 | 0.01 | 1.66 | 6.75 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| 地区 | 超标倍数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化学需氧量 | 氨氮 | 悬浮物 | 总磷 | 平均 | |
| 珠三角 | 0.37 | 1.5 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| 粤东 | 0.29 | 2.03 | 0.36 | 1.5 | 1.05 |
| 粤西 | 0.54 | 0.88 | 0.51 | 1.33 | 0.82 |
| 粤北 | 0.63 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.84 |
| 平均 | 0.46 | 1.35 | 0.65 | 1.17 | - |
表5 不同地区主要污染指标超标倍数
Table 5 Excessive multiples of key pollution indicators in different regions
| 地区 | 超标倍数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化学需氧量 | 氨氮 | 悬浮物 | 总磷 | 平均 | |
| 珠三角 | 0.37 | 1.5 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| 粤东 | 0.29 | 2.03 | 0.36 | 1.5 | 1.05 |
| 粤西 | 0.54 | 0.88 | 0.51 | 1.33 | 0.82 |
| 粤北 | 0.63 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.84 |
| 平均 | 0.46 | 1.35 | 0.65 | 1.17 | - |
| 水质指标 | 处理技术 | 区域 | 处理技术×区域 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自由度 | F值 | p值 | 自由度 | F值 | p值 | 自由度 | F值 | p值 | |
| ρ(NH3-N) | 5 | 69.798 | <0.001 | 3 | 15.319 | <0.001 | 15 | 11.906 | <0.001 |
| ρ(COD) | 5 | 33.962 | <0.001 | 3 | 20.013 | <0.001 | 15 | 16.566 | <0.001 |
| ρ(SS) | 5 | 3.504 | 0.004 | 3 | 3.520 | 0.014 | 15 | 2.218 | 0.006 |
| ρ(TP) | 5 | 1.891 | 0.092 | 3 | 11.984 | <0.001 | 15 | 2.463 | 0.002 |
表6 不同处理设施、不同区域水质指标方差分析结果
Table 6 Variance analysis results of water quality indicators in different treatment facilities and different regions
| 水质指标 | 处理技术 | 区域 | 处理技术×区域 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自由度 | F值 | p值 | 自由度 | F值 | p值 | 自由度 | F值 | p值 | |
| ρ(NH3-N) | 5 | 69.798 | <0.001 | 3 | 15.319 | <0.001 | 15 | 11.906 | <0.001 |
| ρ(COD) | 5 | 33.962 | <0.001 | 3 | 20.013 | <0.001 | 15 | 16.566 | <0.001 |
| ρ(SS) | 5 | 3.504 | 0.004 | 3 | 3.520 | 0.014 | 15 | 2.218 | 0.006 |
| ρ(TP) | 5 | 1.891 | 0.092 | 3 | 11.984 | <0.001 | 15 | 2.463 | 0.002 |
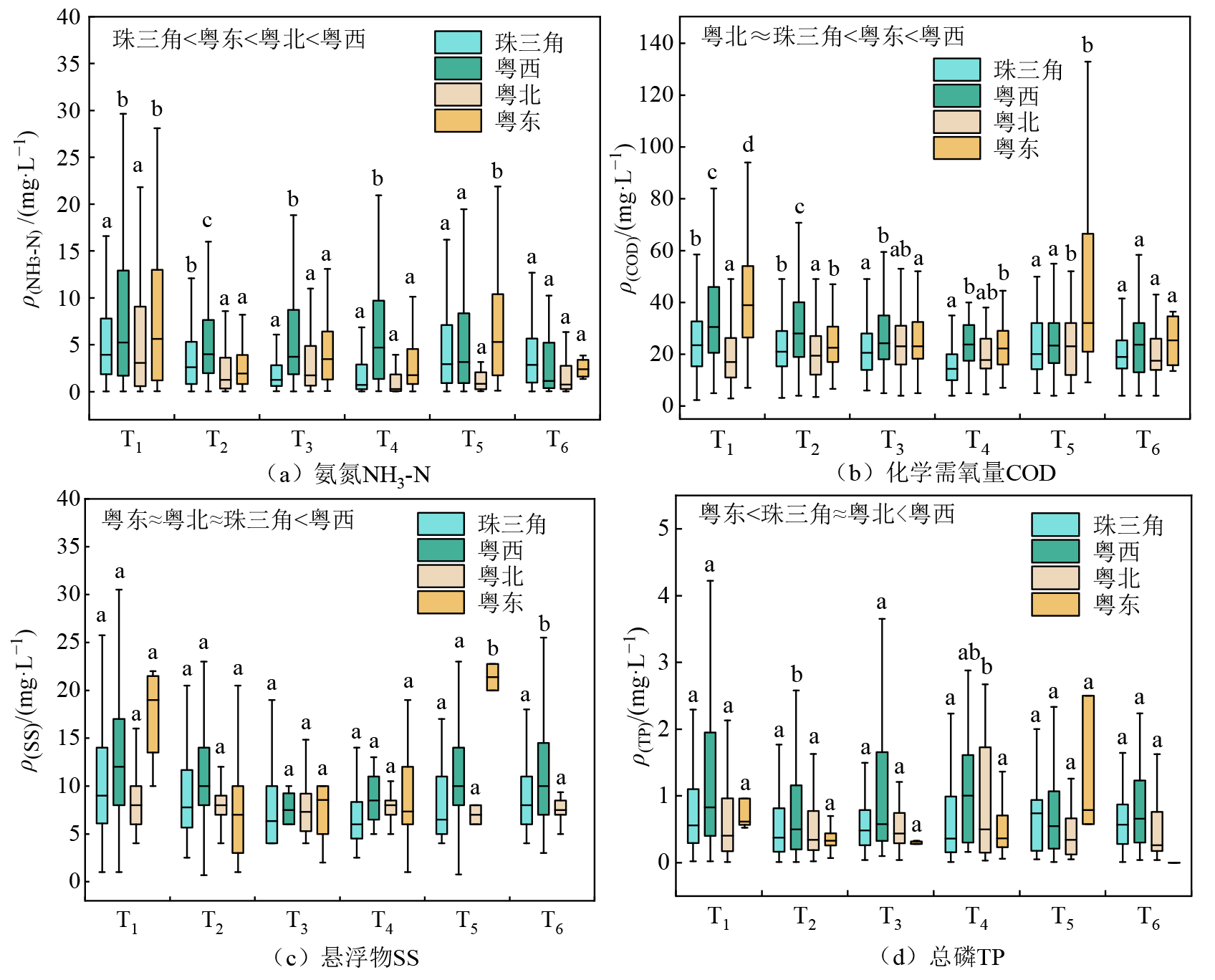
图6 广东省不同地区农村生活污水处理设施出水水质比较 图左上角表示水质指标浓度在4个区域间存在显著差异,p<0.05;图中不同小写字母表示同一处理技术的水质浓度在4个区域存在显著差异,p<0.05;T1-厌氧池+人工湿地;T2-AO/AAO;T3-生物接触氧化法;T4-MBR/MBBR;T5-化粪池;T6-其他
Figure 6 Comparison of effluent quality from rural domestic sewage treatment facilities in different regions of Guangdong Province
| 指标 | 要素及权重 | C层总排序 权重 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | ||
| 0.0960 | 0.6530 | 0.2510 | ||
| C1 | 0.2649 | - | - | 0.0254 |
| C2 | 0.3074 | - | - | 0.0295 |
| C3 | 0.4277 | - | - | 0.0411 |
| C4 | - | 0.2615 | - | 0.1707 |
| C5 | - | 0.3802 | - | 0.2483 |
| C6 | - | 0.2024 | - | 0.1018 |
| C7 | - | 0.1559 | - | 0.1322 |
| C8 | - | - | 0.2487 | 0.0624 |
| C9 | - | - | 0.3255 | 0.0817 |
| C10 | - | - | 0.4258 | 0.1069 |
表7 经济较发达农村地区指标层C对目标层A的权重
Table 7 The weight of indicator layer C to target layer A in economically developed rural areas
| 指标 | 要素及权重 | C层总排序 权重 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | ||
| 0.0960 | 0.6530 | 0.2510 | ||
| C1 | 0.2649 | - | - | 0.0254 |
| C2 | 0.3074 | - | - | 0.0295 |
| C3 | 0.4277 | - | - | 0.0411 |
| C4 | - | 0.2615 | - | 0.1707 |
| C5 | - | 0.3802 | - | 0.2483 |
| C6 | - | 0.2024 | - | 0.1018 |
| C7 | - | 0.1559 | - | 0.1322 |
| C8 | - | - | 0.2487 | 0.0624 |
| C9 | - | - | 0.3255 | 0.0817 |
| C10 | - | - | 0.4258 | 0.1069 |
| 指标 | 要素及权重 | C层总排序 权重 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | ||
| 0.5390 | 0.2973 | 0.1638 | ||
| C1 | 0.4387 | - | - | 0.2365 |
| C2 | 0.3132 | - | - | 0.1688 |
| C3 | 0.2480 | - | - | 0.1337 |
| C4 | - | 0.2800 | - | 0.0832 |
| C5 | - | 0.4687 | - | 0.1393 |
| C6 | - | 0.1152 | - | 0.0343 |
| C7 | - | 0.1361 | - | 0.0405 |
| C8 | - | - | 0.3255 | 0.0533 |
| C9 | - | - | 0.4258 | 0.0697 |
| C10 | - | - | 0.2487 | 0.0407 |
表8 经济欠发达农村地区指标层C对目标层A的权重
Table 8 Weight of indicator layer C to target layer A in economically underdeveloped rural areas
| 指标 | 要素及权重 | C层总排序 权重 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | ||
| 0.5390 | 0.2973 | 0.1638 | ||
| C1 | 0.4387 | - | - | 0.2365 |
| C2 | 0.3132 | - | - | 0.1688 |
| C3 | 0.2480 | - | - | 0.1337 |
| C4 | - | 0.2800 | - | 0.0832 |
| C5 | - | 0.4687 | - | 0.1393 |
| C6 | - | 0.1152 | - | 0.0343 |
| C7 | - | 0.1361 | - | 0.0405 |
| C8 | - | - | 0.3255 | 0.0533 |
| C9 | - | - | 0.4258 | 0.0697 |
| C10 | - | - | 0.2487 | 0.0407 |
| 不同处理技术 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经济较发达农村地区 | 0.367 | 0.754 | 0.699 | 0.640 | 0.385 |
| 经济欠发达农村地区 | 0.606 | 0.468 | 0.397 | 0.322 | 0.604 |
表9 不同地区不同处理技术评价得分
Table 9 Evaluation scores of different treatment technologies in different regions
| 不同处理技术 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经济较发达农村地区 | 0.367 | 0.754 | 0.699 | 0.640 | 0.385 |
| 经济欠发达农村地区 | 0.606 | 0.468 | 0.397 | 0.322 | 0.604 |
| [1] | BI X, GUO L, 2020. Treatment process of rural domestic sewage based on small purification tank technology[C]// IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing, 450(1): 012110. |
| [2] | CHEN P Z, ZHAO W J, CHEN D K, et al., 2022. Research progress on integrated treatment technologies of rural domestic sewage: A review[J]. Water, 14(15): 2439. |
| [3] | CHENG P P, JIN Q, 2022. Performance evaluation of the emerging rural sewage treatment facilities in China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(34): 51623-51634. |
| [4] | LI M T, CHEN Z P, ZHOU D, et al., 2024. Coagulation pretreatment coupled with indigenous microalgal-bacterial consortium system for on-site treatment of rural black wastewater[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 913: 169728. |
| [5] | PANT S, KUMAR A, RAM M, et al., 2022. Consistency indices in analytic hierarchy process: A review[J]. Mathematics, 10(8): 1206. |
| [6] | YANG P, HOU R R, LI D P, et al., 2022. Nitrogen removal from rural domestic wastewater by subsurface wastewater infiltration system: A review[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 159: 309-322. |
| [7] | 宾津佑, 唐小兵, 白福臣, 2021. 广东省经济发展的区域差异及其时空格局演变[J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 44(4): 62-70. |
| BIN J Y, TANG X B, BAI F C, 2021. The regional differences and the evolution of spatial-temporal patterns of economic development in Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 44(4): 62-70. | |
| [8] | 车璐璐, 何军, 王夏晖, 等, 2024. 我国农村生活污水治理问题研究[J]. 环境保护, 52(1): 39-43. |
| CHE L L, HE J, WANG X H, et al., 2024. Research on rural domestic sewage governance in China[J]. Environmental Protection, 52(1): 39-43. | |
| [9] | 董龙周, 王清涛, 2024. 农村生活污水治理现状及治理技术探讨[J]. 河北农业 (1): 26-27. |
| DONG L Z, WANG Q T, 2024. Current status of rural domestic sewage treatment and discussion on treatment technologies[J]. Hebei Agriculture (1): 26-27. | |
| [10] | 谷雨, 2020. 污水处理中硝化细菌生存的影响因素分析[J]. 江西化工 (3): 130-132. |
| GU Y, 2020. Analysis of influencing factors of the survival of nitrifying bacteria in sewage treatment[J]. Jiangxi Chemical Industry (3): 130-132. | |
| [11] | 广东省统计局国家统计局广东调查总队, 2024. 2023年广东省国民经济和社会发展统计公报[N]. 南方日报, A06. |
| Guangdong Provincial bureau of statistics, 2024. National bureau of statistics Guangdong investigation team, 2023 Statistical bulletin on the national economic and social development of Guangdong Province[N]. Southern Daily, A06. | |
| [12] | 贺玉晓, 杨璐, 任玉芬, 等, 2023. 农村生活污水治理存在问题及对策[J]. 市政技术, 41(10): 7-15. |
| HE Y X, YANG L, REN Y F, et al., 2023. Problems and countermeasures of rural domestic sewage treatment[J]. Journal of Municipal Technology, 41(10): 7-15. | |
| [13] |
黄国锋, 贺斌, 谢志宜, 等, 2023. 广东省农业源污染对水环境的影响及其空间分异格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(12): 2207-2215.
DOI |
| HUANG G F, HE B, XIE Z Y, et al., 2023. Impact of agricultural pollution on water environment and its spatial differentiation pattern in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 32(12): 2207-2215. | |
| [14] | 李鹏峰, 孙永利, 隋克俭, 等, 2021. 我国农村污水处理现状问题分析及治理模式探讨[J]. 给水排水, 57(12): 65-71. |
| LI P F, SUN Y L, SUI K J, et al., 2021. Analysis on the present situation and discussion on its treatment modeof rural sewage treatment in China[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 57(12): 65-71. | |
| [15] | 李志刚, 2021. 发达国家农村污水治理经验及启示[J]. 净水技术, 40(9): 71-77. |
| LI Z G, 2021. Experiences and the enlightenment of rural sewage treatment in developed countries[J]. Water Purification Technology, 40(9): 71-77. | |
| [16] | 刘蕾, 于丽, 张秀丽, 2023. 农村生活污水治理存在的问题及建议[J]. 环境与发展, 35(3): 1-5, 11. |
| LIU L, YU L, ZHANG X L, 2023. Problems and optimization measures of rural domestic sewage treatment[J]. Environment and Development, 35(3): 1-5, 11. | |
| [17] | 刘晓永, 吴启堂, 曹姝文, 2020. “厌氧+人工湿地” 在粤北农村生活污水处理工程上的应用[J]. 水利规划与设计 (6): 120-124, 132. |
| LIU X Y, WU Q T, CAO S W, 2020. Application of “Anaerobic+ Constructed Wetland” in rural domestic sewage treatment projects in Northern Guangdong[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design (6): 120-124, 132. | |
| [18] | 刘智晓, 吴凡松, 2024. 污水生化处理工艺发展阶段化技术特征及未来趋势[J]. 给水排水, 60(4): 12-22. |
| LIU Z X, WU F S, 2024. Technical characteristics and development trend of different stages of wastewater biological treatment process[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 60(4): 12-22. | |
| [19] | 罗韦, 牛忠磊, 吕婉莹, 2024. 加强农村生活污水处理设施建设管理[N]. 人民政协报, 004. |
| LUO W, NIU Z L, LÜ W Y, 2024. Strengthen the construction and management of rural domestic sewage treatment facilities[N]. The Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference Journal, 004. | |
| [20] | 潘振东, 莫小堂, 邱鸿荣, 等, 2023. 广州市增城区农村生活污水设施运维分析[J]. 给水排水, 59(8): 24-30. |
| PAN Z D, MO X T, QIU H R, et al., 2023. Investigation and analysis of technological treatment effect of rural domestic sewage facilities in Zengcheng district of Guangzhou city[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 59(8): 24-30. | |
| [21] | 任婧文, 2012. 农村生活污水处理设施综合技术应用研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学. |
| REN J W, 2012. A Study of Integrated Technology applications for rural sewage treatment facilities[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology. | |
| [22] |
任毅, 肖许沐, 伍峥, 等, 2023. 厌氧池处理农村生活污水效能提升对策研究[J]. 水处理技术, 49(12): 65-68.
DOI |
|
REN Y, XIAO X M, WU Z, et al., 2023. Research on strategies for enhancing the efficiency of anaerobic ponds in treating rural domestic sewage[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 49(12): 65-68.
DOI |
|
| [23] | 孙兴旺, 马友华, 王桂苓, 等, 2010. 中国重点流域农村生活污水处理现状及其技术研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 26(18): 384-388. |
|
SUN X W, MA Y H, WANG G L, et al., 2010. Research on current treatment status and technologies of rural domestic wastewater in China major basins[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 26(18): 384-388.
DOI |
|
| [24] | 陶小婷, 刘妙彤, 2022. 乡村振兴战略下粤西农村生活污水治理困境与应对策略[J]. 广东水利电力职业技术学院学报, 20(1): 31-36. |
| TAO X T, LIU M T, 2022. Challenges and response strategies for rural domestic sewage treatment in Western Guangdong under the rural revitalization strategy[J]. Journal of Guangdong Polytechnic of Water Resources and Electric Engineering, 20(1): 31-36. | |
| [25] | 田娇, 王玉军, 梁小萌, 等, 2010. 农村污水处理技术现状及发展前景[J]. 环境科学与管理, 35(5): 83-85, 142. |
| TIAN J, WANG Y J, LIANG X M, et al., 2010. The treament technology situation and development prospects for the rural sewage[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 35(5): 83-85, 142. | |
| [26] | 温凯茵, 林彰文, 卢欢亮, 2021. 广东省农村生活污水治理存在问题及对策研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 49(11): 85-87, 131. |
| WEN K Y, LIN Z W, LU H L, 2021. Problems and Countermeasures for the treatment of rural domestic sewage of Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 49(11): 85-87, 131. | |
| [27] | 熊锐, 曹锟生, 1992. 多目标决策的层次分析法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, (6): 58-62. |
| XIONG R, CAO K S, 1992. Hierarchical analysis of multiple criteria decision making[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, (6): 58-62. | |
| [28] | 肖艳蕾, 2023. 粤北某区农村生活污水治理问题研究[J]. 资源节约与环保 (10): 145-148. |
| XIAO Y L, 2023. Research on issues in rural domestic sewage treatment in a certain district of Northern Guangdong[J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection (10): 145-148. | |
| [29] | 于振江, 王大扬, 戴同威, 等, 2023. 广东省农村生活污水资源化路径分析与优化[J]. 给水排水, 59(S2): 112-117. |
| YU Z J, WANG D Y, DAI T W, et al., 2023. Path analysis and optimization strategy of rural domestic sewage resource utilization in Guangdong province[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 59(S2): 112-117. | |
| [30] | 中国环境保护产业协会水污染治理委员会, 2020. 水污染治理行业2019年发展报告[C]//中国环境保护产业发展报告(2020): 16-29. |
| Water pollution control committee, China Environmental Protection Industry Association, 2019. Water pollution control industry development report 2019[C]//China environmental protection industry development report (2020): 16-29. |
| [1] | 王斌, 曾兆荷, 董璐, 岳林. 内梅罗指数法在地下水水质评价中的修正探讨与实践效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 293-301. |
| [2] | 潘家响, 朱明飞, 秦念慈, 肖晶, 刘晨, 李秋华. 贵州高原车田河浮游植物功能群时空特征及水环境质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 935-945. |
| [3] | 肖扬岚, 沈惠柔, 许一涵, 尤添革, 郑艺婧, 谢候展, 宁静. 基于GBDT-LSTM的闽江流域水质预测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 597-606. |
| [4] | 王源哲, 华春林, 赵丽, 樊敏, 梁晓盈, 周乐乐, 蔡璨, 姚婧. 山地城市主要河流水质评价及预测研究——以四川省绵阳市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1465-1477. |
| [5] | 程鹏, 孙明东, 郝韶楠. 基于最简水质综合评价指数的官厅水库上游河流水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 372-380. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
