生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 1214-1226.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.08.006
王聪聪1,2( ), 张小玲1,3,*(
), 张小玲1,3,*( ), 雷雨1, 黄小娟1,4, 王婧怡1, 尹黎昊1, 王传扬1
), 雷雨1, 黄小娟1,4, 王婧怡1, 尹黎昊1, 王传扬1
收稿日期:2023-10-18
出版日期:2024-08-18
发布日期:2024-09-25
通讯作者:
*张小玲。E-mail: xlzhang@ium.cn作者简介:王聪聪(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事大气物理学与大气环境研究。E-mail: 529890272@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Congcong1,2( ), ZHANG Xiaoling1,3,*(
), ZHANG Xiaoling1,3,*( ), LEI Yu1, HUANG Xiaojuan1,4, WANG Jingyi1, YIN Lihao1, WANG Chuanyang1
), LEI Yu1, HUANG Xiaojuan1,4, WANG Jingyi1, YIN Lihao1, WANG Chuanyang1
Received:2023-10-18
Online:2024-08-18
Published:2024-09-25
摘要:
为探究四川盆地典型城市PM2.5组分的污染特征及其与大气氧化性的关系,利用WRF-CMAQ模型对2020年春季一次持续O3污染过程中PM2.5组分进行模拟分析,并将O3, max作为光化学活性指标,划分出轻、低、中3种光化学水平,对不同光化学水平下PM2.5主要组分及贡献的变化特征。结果表明,四川盆地发生O3污染期间,高空为稳定的天气形势或下沉气流,海平面气压场为高压,对应晴好天气,有利于光化学反应及O3和二次气溶胶的生成。污染热点区域主要集中在成都平原和重庆西部,PM2.5和NO2的高浓度区与O3污染发生的区域相吻合。污染前期,OC和NO3−对PM2.5的贡献较大;污染后期,OC和SO42−对PM2.5的贡献较大。达州的NO3−和NH4+等离子在低光化学水平下浓度最高,光化学水平再升高反而出现下降的趋势。OC和SO42−与光化学水平呈较好的正相关关系。对于平均日变化情况,O3和PM2.5与光化学水平呈正相关,EC、NO2和NO3−的日变化情况均与PM2.5类似,自贡夜间
中图分类号:
王聪聪, 张小玲, 雷雨, 黄小娟, 王婧怡, 尹黎昊, 王传扬. 基于WRF-CMAQ模型的四川盆地春季持续臭氧污染过程中PM2.5组分解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1214-1226.
WANG Congcong, ZHANG Xiaoling, LEI Yu, HUANG Xiaojuan, WANG Jingyi, YIN Lihao, WANG Chuanyang. Analysis of PM2.5 Components During Continuous Spring Pollution in Sichuan Basin Based on WRF-CMAQ Model[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1214-1226.

图1 模式模拟区域和四川盆地18个城市分布以及海拔高度 中国地图依据自然资源部标准底图(审图号:GS (2019) 1697号)绘制而成
Figure 1 Model simulation area and distribution and elevation of 18 cities in Sichuan Basin

图2 2020年4月20日-5月10日4个城市逐时O3质量浓度观测(黑线)和模拟(红线)结果
Figure 2 Results of hourly O3 concentration observation (black line) and simulation (red line) in four cities from April 20 to May 10, 2020
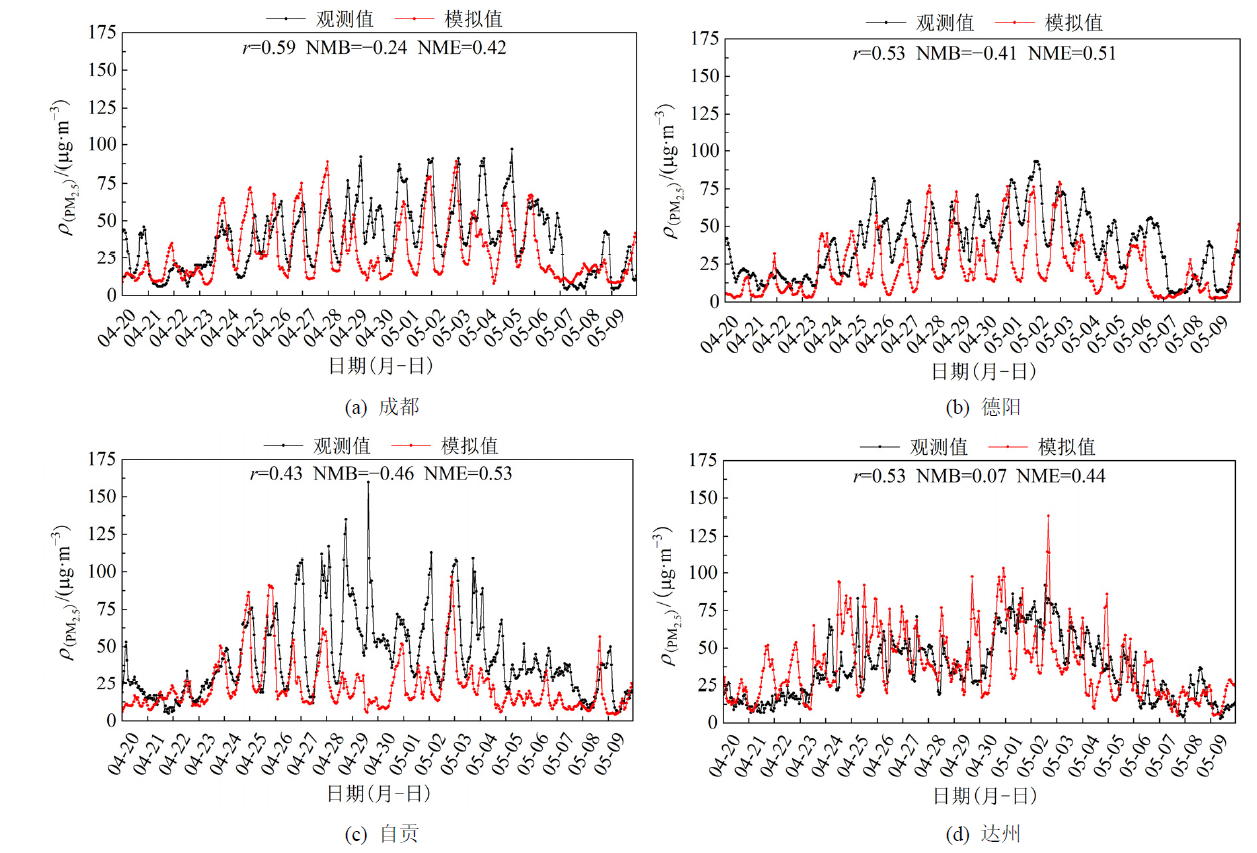
图3 2020年4月20日-5月10日4个城市逐时PM2.5质量浓度观测(黑线)和模拟(红线)结果
Figure 3 Results of hourly PM2.5 concentration observation (black line) and simulation (red line) in four cities from April 20 to May 10, 2020
| 光化学水平 | OC/EC的比值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 成都 | 德阳 | 自贡 | 达州 | |
| 轻 | 3.12 | 2.19 | 0.77 | |
| 低 | 1.97 | 3.28 | 3.21 | 1.45 |
| 中 | 2.48 | 3.08 | 3.07 | 2.60 |
表1 4个城市不同光化学水平下OC/EC的比值
Table 1 Ratio of OC/EC at different photochemical levels in four cities
| 光化学水平 | OC/EC的比值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 成都 | 德阳 | 自贡 | 达州 | |
| 轻 | 3.12 | 2.19 | 0.77 | |
| 低 | 1.97 | 3.28 | 3.21 | 1.45 |
| 中 | 2.48 | 3.08 | 3.07 | 2.60 |
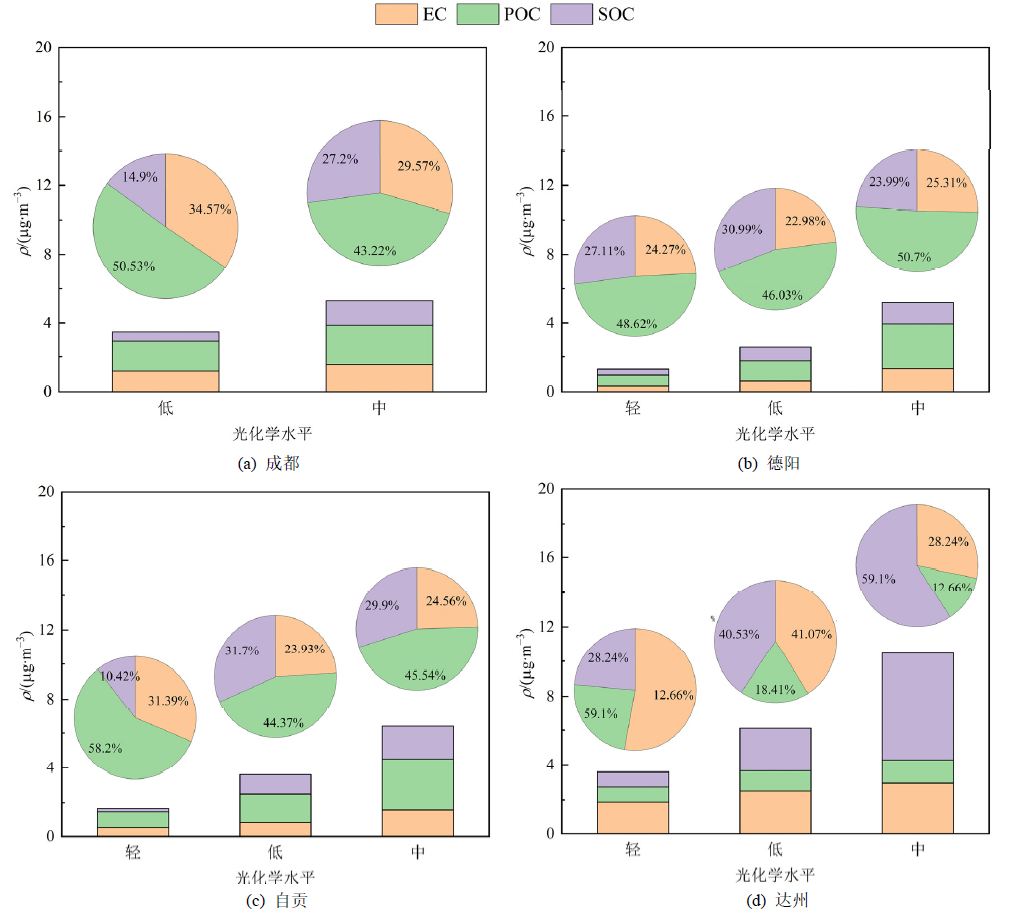
图8 4个城市不同光化学水平下PM2.5的碳组分(EC、POC、SOC)质量浓度及占比特征
Figure 8 The concentration and proportion characteristics of PM2.5 carbon components (EC, POC, SOC) at different photochemical levels in four cities
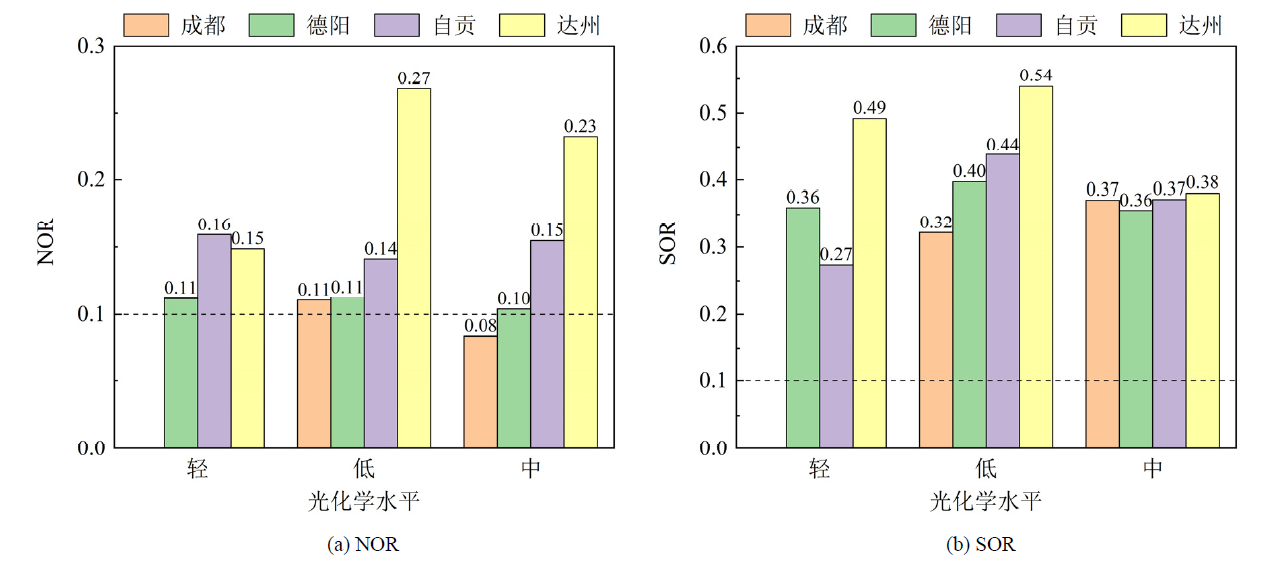
图9 4个城市不同光化学水平下氮氧化率(NOR)和硫氧化率(SOR)的特征
Figure 9 Characteristics of nitrogen oxidation rate (NOR) and sulfur oxidation rate (SOR) at different photochemical levels in four cities
| [1] | PIO C, CERQUEIRA M, HARRISON R M, et al., 2011. OC/EC ratio observations in Europe: Re-thinking the approach for apportionment between primary and secondary organic carbon[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(34): 6121-6132. |
| [2] | CASTRO L M, PIO C A, HARRISON R M, et al., 1999. Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 33(17): 2771-2781. |
| [3] | CHEN Y J, ZHI G R, FENG Y L, et al., 2006. Measurements of emission factors for primary carbonaceous particles from residential raw‐coal combustion in China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(20): 20815-1-20815-4. |
| [4] | CHU B W, MA Q X, LIU J, et al., 2020. Air pollutant correlations in China: Secondary air pollutant responses to NOx and SO2 control[J]. Environmental Science and Technology Letters, 7(10): 695-700. |
| [5] | CHUANG M T, CHEN Y C, LEE C T, et al., 2016. Apportionment of the sources of high fine particulate matter concentration events in a developing aerotropolis in Taoyuan, Taiwan[J]. Environmental Pollution, 214: 273-281. |
| [6] | DAI H B, LIAO H, LI K, et al., 2023. Composited analyses of the chemical and physical characteristics of co-polluted days by ozone and PM2.5 over 2013-2020 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 23(1): 23-39. |
| [7] | DESHMUKH D K, DEB M K, MKOMA S L., 2013. Size distribution and seasonal variation of size-segregated particulate matter in the ambient air of Raipur city, India[J]. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 6(1): 259-276. |
| [8] | FU J S, HSU N C, GAO Y, et al., 2012. Evaluating the influences of biomass burning during 2006 BASE-ASIA: A regional chemical transport modeling[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(9): 3837-3855. |
| [9] | HORNE J R, DONALD D., 2017. Impact of global climate change on ozone, particulate matter, and secondary organic aerosol concentrations in California: A model perturbation analysis[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 153: 1-17. |
| [10] | HU J L, CHEN J J, YING Q, et al., 2016. One-year simulation of ozone and particulate matter in China using WRF/CMAQ modeling system[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16(16): 10333-10350. |
| [11] | HUANG R J, ZHANG Y L, CARLO B, et al., 2014. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China[J]. Nature, 514(7521): 218-222. |
| [12] | LEI Y, WU K, ZHANG X L, et al., 2023. Role of meteorology-driven regional transport on O3 pollution over the Chengdu Plain, southwestern China[J]. Atmospheric Research, 285: 106619. |
| [13] | LI K, JACOB D J, LIAO H, et al., 2019. A two-pollutant strategy for improving ozone and particulate air quality in China[J]. Nature Geoscience, 12(11): 906-910. |
| [14] | LI X R, WANG L L, JI D S, et al., 2013. Characterization of the size-segregated water-soluble inorganic ions in the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration: Spatial/temporal variability, size distribution and sources[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 77: 250-259. |
| [15] | LI X R, WANG Y S, GUO X Q, et al., 2013. Seasonal variation and source apportionment of organic and inorganic compounds in PM2.5 and PM10 particulates in Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(4): 741-750. |
| [16] |
LU K, FUCHS H, HOFZUMAHAUS A, et al., 2019. Fast photochemistry in wintertime haze: Consequences for pollution mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(18): 10676-10684.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | MA J Z, XU X B, ZHAO C S, et al., 2012. A review of atmospheric chemistry research in China: Photochemical smog, haze pollution, and gas-aerosol interactions[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 29(5): 1006-1026. |
| [18] | PANDIS S N, HARLEY R A, CASS G R, et al., 1992. Secondary organic aerosol formation and transport[J]. Atmospheric Environment. Part A. General Topics, 26(13): 2269-2282. |
| [19] | QIN Y, LI J Y, GONG K J, et al., 2021. Double high pollution events in the Yangtze River Delta from 2015 to 2019: Characteristics, trends, and meteorological situations[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 792: 148349. |
| [20] | SCHAUER J J, KLEEMAN M J, CASS G R, et al., 2002. Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources 5 C1 - C32 organic compounds from gasoline-powered motor vehicles[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(6): 1169-1180. |
| [21] | TIE X X, GENG F H, PENG L, et al., 2009. Measurement and modeling of O3 variability in Shanghai, China: Application of the WRF-Chem model[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 43(28): 4289-4302. |
| [22] | TURPIN B J, HUNTZICKER J J, 1995. Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 29(23): 3527-3544. |
| [23] | WANG J D, ZHAO B, WANG S X, et al., 2017. Particulate matter pollution over China and the effects of control policies[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 584-585: 426-447. |
| [24] | WANG Y, ZHUANG G S, TANG A H, et al., 2005. The ion chemistry and the source of PM2.5 aerosol in Beijing[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 39(21): 3771-3784. |
| [25] | WIOLETTA R K, KRZYSZTOF K, PATRYCJA R K, et al., 2012. A Study on the Seasonal Mass Closure of Ambient Fine and Coarse Dusts in Zabrze, Poland[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 88(5): 722-729. |
| [26] | WU B, LIU C Q, ZHANG J, et al., 2021. The multifractal evaluation of PM2.5-O3 coordinated control capability in China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 129: 107877. |
| [27] | XIU G L, ZHANG D N, CHEN J Z, et al., 2004. Characterization of major water-soluble inorganic ions in size-fractionated particulate matters in Shanghai campus ambient air[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 38(2): 227-236. |
| [28] | YANG L X, ZHOU X H, WANG Z, et al., 2012. Airborne fine particulate pollution in Jinan, China: Concentrations, chemical compositions and influence on visibility impairment[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 55: 506-514. |
| [29] | YANG X Y, WU K, LU Y Q, et al., 2021. Origin of regional springtime ozone episodes in the Sichuan Basin, China: Role of synoptic forcing and regional transport[J]. Environmental Pollution, 278: 116845. |
| [30] | ZHANG X Y, ZHAO X, JI G X, et al., 2019. Seasonal variations and source apportionment of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 in Nanjing, a megacity in southeastern China[J]. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 76(1): 73-88. |
| [31] | ZHENG B, ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al., 2015. Heterogeneous chemistry: A mechanism missing in current models to explain secondary inorganic aerosol formation during the January 2013 haze episode in North China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(4): 2031-2049. |
| [32] | ZHENG Y X, TAO X, QIANG Z, et al., 2017. Air quality improvements and health benefits from China's clean air action since 2013[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 12(11): 114020. |
| [33] | ZHU J, CHEN L, LIAO H, et al., 2019. Correlations between PM2.5 and ozone over China and associated underlying reasons[J]. Atmosphere, 10(7): 352. |
| [34] | 曹庭伟, 吴锴, 康平, 等, 2018. 成渝城市群臭氧污染特征及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(4): 1275-1284. |
| CAO T W, WU K, KANG P, et al., 2018. Ozone pollution characteristics and influencing factors in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 38(4): 1275-1284. | |
| [35] |
陈瑶瑶, 廖彤, 汪宇, 等, 2022. 2016-2020年广东省臭氧污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(12): 2374-2381.
DOI |
| CHEN Y Y, LIAO T, WANG Y, et al., 2022. Characteristics of ozone pollution in Guangdong province from 2016 to 2020[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(12): 2374-2381. | |
| [36] | 高丽波, 王体健, 崔金梦, 等, 2019. 2016年夏季南京大气污染特征观测分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(1): 1-12. |
| GAO L B, WANG T J, CUI J M, et al., 2019. Observation and analysis of air pollution characteristics over Nanjing in summer 2016[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(1): 1-12. | |
| [37] | 环境保护部, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2012. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, 2012. Ambient air quality standards: GB 3095-2012[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Press. | |
| [38] | 贾海鹰, 李矛, 程兵芬, 等, 2017. 长沙市城区臭氧浓度特征研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(2): 168-173. |
| JIA H Y, LI M, CHENG B F, et al., 2017. Study on the characteristics of ozone concentration in the urban area of Changsha city[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(2): 168-173 | |
| [39] | 康平, 侯静雯, 冯浩鹏, 等, 2022. 成都市PM2.5和O3复合污染特征及相互作用研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 42(10): 80-90. |
| KANG P, HOU J W, FENG H P, et al., 2022. Study on the characteristics and interaction of PM2.5 and O3 combined pollution in Chengdu[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42(10): 80-90. | |
| [40] | 赖安琪, 陈晓阳, 刘一鸣, 等, 2017. 珠江三角洲PM2.5和O3复合污染过程的数值模拟[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(11): 4022-4031. |
| LAI A Q, CHEN X Y, LIU Y M, et al., 2017. Numerical simulation of PM2.5 and O3 combined pollution processes in the Pearl River Delta[J]. China Environmental Science, 37(11): 4022-4031. | |
| [41] | 赖安琪, 陈晓阳, 刘一鸣, 等, 2018. 珠江三角洲高质量浓度PM2.5和O3复合污染特征[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 57(4): 30-36. |
| LAI A Q, CHEN X Y, LIU Y M, et al., 2018. Characteristics of high mass concentration PM2.5 and O3 combined pollution in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis SunYatseni, 57(4): 30-36. | |
| [42] | 雷雨, 张小玲, 杨凯晴, 等, 2021. 川南城市群空气污染特征及气象影响因素分析[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 36(1): 101-109. |
| LEI Y, ZHANG X L, YANG K Q, et al., 2021. Air pollution characteristics and meteorological influencing factors in southern Sichuan urban agglomeration[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Information Technology, 36(1): 101-109. | |
| [43] | 李红丽, 王杨君, 黄凌, 等, 2020. 中国典型城市臭氧与二次气溶胶的协同增长作用分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(12): 4368-4379. |
| LI H L, WANG Y J, HUANG L, et al., 2020. Analysis of synergistic growth of ozone and secondary aerosols in typical cities in China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(12): 4368-4379. | |
| [44] | 李雪梅, 牟玲, 田妹, 等, 2020. 山西大学城PM2.5中元素特征、来源及健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 41(11): 4825-4831. |
| LI X M, MOU L, TIAN M, et al., 2020. Characteristics, sources and health risk assessment of PM2.5 in Shanxi University Town[J]. Environmental Science, 41(11): 4825-4831. | |
| [45] | 罗琼, 冯淼, 宋丹林, 等, 2022. 成都春季复合污染下PM2.5的化学消光贡献[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 17(1): 148-159. |
| LUO Q, FENG M, SONG D L, et al., 2022. Chemical extinction contribution of PM2.5 under combined pollution in Chengdu in spring[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 17(1): 148-159. | |
| [46] | 彭颖蓓, 刘国彬, 田霄, 等, 2019. 典型城市PM2.5的污染特征、来源及影响因素分析[C]// 《环境工程》2019年全国学术年会论文集. 中国北京: 171-174. |
| PENG Y B, LIU G B, TIAN X, et al., 2019. Analysis of pollution characteristics, sources and influencing factors of PM2.5 in typical cities[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 National Academic Conference of Environmental Engineering. Beijing, China: 171-174. | |
| [47] | 秦思达, 王帆, 王堃, 等, 2021. 基于WRF-CMAQ模型的辽宁中部城市群PM2.5化学组分特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 34(6): 1277-1286. |
| QIN S D, WANG F, WANG K, et al., 2021. Chemical composition characteristics of PM2.5 in urban agglomeration of Central Liaoning Province based on WRF-CMAQ model[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 34(6): 1277-1286. | |
| [48] | 任秀龙, 胡伟, 吴春苗, 等, 2022. 华北南部重污染城市周边区域二次气溶胶的化学特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 43(3): 1159-1169. |
| REN X L, HU W, WU C M, et al., 2022. Chemical characteristics and source analysis of secondary aerosols in the vicinity of heavily polluted cities in southern north China[J]. Environmental Science, 43(3): 1159-1169. | |
| [49] |
石慧斌, 黄艺, 程馨, 等, 2021. 成都市冬季PM2.5中碳组分污染特征及来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(7): 1420-1427.
DOI |
| SHI H B, HUANG Y, CHENG X, et al., 2021. Pollution characteristics and sources of carbonaceous components in PM2.5 during winter in Chengdu[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(7): 1420-1427. | |
| [50] | 田赐, 何军, 张巍, 等, 2023. 2020年自贡市主城区PM2.5污染特征及来源解析[J]. 四川环境, 42(1): 75-79. |
| TIAN C, HE J, ZHANG W, et al., 2023. Characteristics and sources of PM2.5 pollution in Zigong City in 2020[J]. Sichuan Environment, 42(1): 75-79. | |
| [51] | 王聪聪, 张小玲, 卢宁生, 2023. 2019-2021年四川盆地污染天气客观分型及典型污染个例研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 43(5): 2182-2197. |
| WANG C C, ZHANG X L, LU N S, 2019. Objective classification of pollution weather and typical pollution cases in Sichuan Basin from 2019 to 2021[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Sciences, 43(5): 2182-2197. | |
| [52] | 王君悦, 刘朝顺, 2022. 基于WRF-Chem的长三角地区PM2.5和O3污染协同控制研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 42(7): 32-42. |
| WANG J Y, LIU C S, 2022. Study on coordinated control of PM2.5 and O3 pollution in Yangtze River Delta based on WRF-Chem[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42(7): 32-42. | |
| [53] | 王文兴, 柴发合, 任阵海, 等, 2019. 新中国成立70年来我国大气污染防治历程、成就与经验[J]. 环境科学研究, 32(10): 1621-1635. |
| WANG W X, CHAI F H, REN Z H, et al., 2019. History, achievements and experience of air pollution control in China since the founding of New China 70 years ago[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32(10): 1621-1635. | |
| [54] | 王鑫, 安俊琳, 苏筱倩, 等, 2020. 南京北郊水溶性离子污染特征及其光学特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(2): 506-512. |
| WANG X, AN J L, SU X Q, et al., 2020. Characteristics and optical properties of water-soluble ion pollution in the northern suburbs of Nanjing[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(2): 506-512. | |
| [55] | 吴锴, 康平, 王占山, 等, 2017. 成都市臭氧污染特征及气象成因研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(11): 4241-4252. |
| WU K, KANG P, WANG Z S, et al., 2017. Characteristics and meteorological causes of ozone pollution in Chengdu[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(11): 4241-4252. | |
| [56] | 吴明, 吴丹, 夏俊荣, 等, 2019. 成都冬季PM2.5化学组分污染特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 40(1): 76-85. |
| WU M, WU D, XIA J R, et al., 2019. Pollution characteristics and sources of PM2.5 chemical components in Chengdu in winter[J]. Environmental Science, 40(1): 76-85. | |
| [57] | 肖伟, 何友江, 孟凡, 等, 2018. 空气质量模型中大气化学机理的发展与比较[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 8(1): 12-22. |
| XIAO W, HE Y J, MENG F, et al., 2018. Development and comparison of atmospheric chemical mechanisms in air quality models[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 8(1): 12-22. | |
| [58] | 赵云卿, 陈善莉, 朱彬, 等, 2018. 南京北郊早春霾污染过程及硫酸盐形成研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(7): 2438-2444. |
| ZHAO Y Q, CHEN S L, ZHU B, et al., 2018. Study on haze pollution process and sulfate formation in early spring in northern suburbs of Nanjing[J]. China Environmental Science, 38(7): 2438-2444. |
| [1] | 王薇, 伍君奇. 公共建筑入口形式对室内气溶胶扩散的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1227-1235. |
| [2] | 何沐全, 石艳军, 王晨茜, 罗祖红, 张少通. 广东省植被生态质量演变与气象条件贡献分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 679-688. |
| [3] | 王传扬, 张小玲, 兰琳惠, 潘婕. 2022年夏季高温干旱对四川盆地污染物浓度变化的影响分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 80-91. |
| [4] | 蒋伯琪, 浮天, 程昳璇, 苏枞枞, 沈建东, 于谨铖, 于兴娜. 沈阳市臭氧污染特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 72-79. |
| [5] | 王薇, 代萌萌. 基于颗粒物时空分布的街道峡谷空间形态研究——以合肥市同安街道为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1632-1643. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
