生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1952-1963.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.11.006
许明( ), 张馥颖, 孙露露, 周增幸, 林超霸, 朱雪竹*(
), 张馥颖, 孙露露, 周增幸, 林超霸, 朱雪竹*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-24
出版日期:2023-11-18
发布日期:2024-01-17
通讯作者:
* 朱雪竹。E-mail: zhuxuezhu@njau.edu.cn作者简介:许明(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境污染控制与生物修复研究。E-mail: 3220225213@bit.edu.cn
基金资助:
XU Ming( ), ZHANG Fuying, SUN Lulu, ZHOU Zengxing, LIN Chaoba, ZHU Xuezhu*(
), ZHANG Fuying, SUN Lulu, ZHOU Zengxing, LIN Chaoba, ZHU Xuezhu*( )
)
Received:2022-03-24
Online:2023-11-18
Published:2024-01-17
摘要:
调查京津冀地区工业土壤污染的状况及其与土壤生物因子的相互关系,为后续环境监测及修复提供参考。在京津冀地区代表性工业园区采集土壤样品,分析其中半挥发有机污染和土壤生物状况。土壤采集点周边的工业产业涵盖了金属冶炼及压延加工业,石油加工业、炼焦及核燃料加工业,交通运输设备制造业,化学原料及化学制品制造业等北方地区典型重工业产业。结果表明,芘(Pyrene,Pyr)、荧蒽(Fluoranthene,Flu)、邻苯二甲酸二(2-二乙基己基)酯(Bis(2-diethylhexyl) Phthalate,DEHP)检出排名前3,分别有98.4%、98.4%、96.9%的点位浓度高于检出限,其最高质量分数分别为2.84、2.79、5.72 mg∙kg−1。土壤中多环芳烃(Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons,PAHs)以4-6环PAHs为主,∑16PAHs质量分数中位值为0.67 mg∙kg−1,约有90.6%的样品中苯并[a]芘(Benzo[a]pyrene,BaP)的浓度高于检出限。荧蒽、芘、苯并[a]蒽(Benzo[a]anthracene,BaA)、䓛(Chrysene,Chr)、苯并[b]荧蒽(Benzo[b]fluoranthene,BbF)、苯并[k]荧蒽(Benzo[k]fluoranthene,BkF)、BaP对土壤中PAHs污染方差的贡献率高达52.9%。结合特征比值法与主成分分析法得出液体化石燃料燃烧产生的PAHs占土壤PAHs来源的79.7%。微生物量碳(Microbial Biomass Carbon,MBC)、微生物量氮(Microbial Biomass Nitrogen,MBN)在0-20 cm处与2-3环和∑16PAHs呈显著负相关(r= −0.4,P=0.023),在20-40 cm土壤中蔗糖酶活性与LMW-PAHs(r=0.51,P=0.006)和HMW-PAHs(r=0.53,P=0.005)呈显著正相关。研究成果可为评估土壤有机污染环境归趋提供依据。
中图分类号:
许明, 张馥颖, 孙露露, 周增幸, 林超霸, 朱雪竹. 京津冀地区工业区土壤中多环芳烃的污染特征、源解析及生物因子相关性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1952-1963.
XU Ming, ZHANG Fuying, SUN Lulu, ZHOU Zengxing, LIN Chaoba, ZHU Xuezhu. Pollution Characteristics, Source Analysis and Correlation of Biological Factors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soils of Industrial Areas in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1952-1963.
| 特征比值 | 比值范围 | 指示污染物 |
|---|---|---|
| m(An)/m(An+Phe) | <0.1 | 石油源 |
| >0.1 | 燃烧源 | |
| <0.4 | 石油源 | |
| m(Flu)/m(Flu+Pry) | 0.4‒0.5 | 液体化石燃料燃烧 |
| >0.5 | 煤、生物质燃烧 | |
| <0.2 | 石油源 | |
| m(InP)/m(InP+BgP) | 0.2‒0.4 | 液体化石燃料燃烧 |
| >0.4 | 煤、生物质燃烧 | |
| <0.2 | 石油源 | |
| m(BaA)/m(BaA+Chr) | 0.2‒0.5 | 液体化石燃料燃烧 |
| >0.5 | 煤、生物质燃烧 |
表1 特征比值和排放源的关系
Table 1 Relationship between characteristic ratio and emission source
| 特征比值 | 比值范围 | 指示污染物 |
|---|---|---|
| m(An)/m(An+Phe) | <0.1 | 石油源 |
| >0.1 | 燃烧源 | |
| <0.4 | 石油源 | |
| m(Flu)/m(Flu+Pry) | 0.4‒0.5 | 液体化石燃料燃烧 |
| >0.5 | 煤、生物质燃烧 | |
| <0.2 | 石油源 | |
| m(InP)/m(InP+BgP) | 0.2‒0.4 | 液体化石燃料燃烧 |
| >0.4 | 煤、生物质燃烧 | |
| <0.2 | 石油源 | |
| m(BaA)/m(BaA+Chr) | 0.2‒0.5 | 液体化石燃料燃烧 |
| >0.5 | 煤、生物质燃烧 |
| 行业类型 | 污染物高于检出限的点位占比 | BaP高于检出 限的点位占比 | 质量分数最高的污染物 | 污染指数最高的污染物 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 名称 | w/(mg∙kg−1) | 名称 | 污染指数 | ||||
| 金属冶炼及压延加工制造业 | 100 | 84.21 | BgP | 2.16 | BaP | 0.40 | |
| 石油加工、炼焦及核燃料加工制造业 | 100 | 92.86 | BgP | 18.92 | BaP | 1.48 | |
| 交通运输设备制造业 | 100 | 88.89 | BbF | 6.12 | BaP | 2.99 | |
| 化学原料和化学制品制造业 | 100 | 100 | DEHP | 5.72 | BaP | 1.36 | |
表2 各行业周边土壤污染状况
Table 2 Pollutants in the soil around different industries
| 行业类型 | 污染物高于检出限的点位占比 | BaP高于检出 限的点位占比 | 质量分数最高的污染物 | 污染指数最高的污染物 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 名称 | w/(mg∙kg−1) | 名称 | 污染指数 | ||||
| 金属冶炼及压延加工制造业 | 100 | 84.21 | BgP | 2.16 | BaP | 0.40 | |
| 石油加工、炼焦及核燃料加工制造业 | 100 | 92.86 | BgP | 18.92 | BaP | 1.48 | |
| 交通运输设备制造业 | 100 | 88.89 | BbF | 6.12 | BaP | 2.99 | |
| 化学原料和化学制品制造业 | 100 | 100 | DEHP | 5.72 | BaP | 1.36 | |
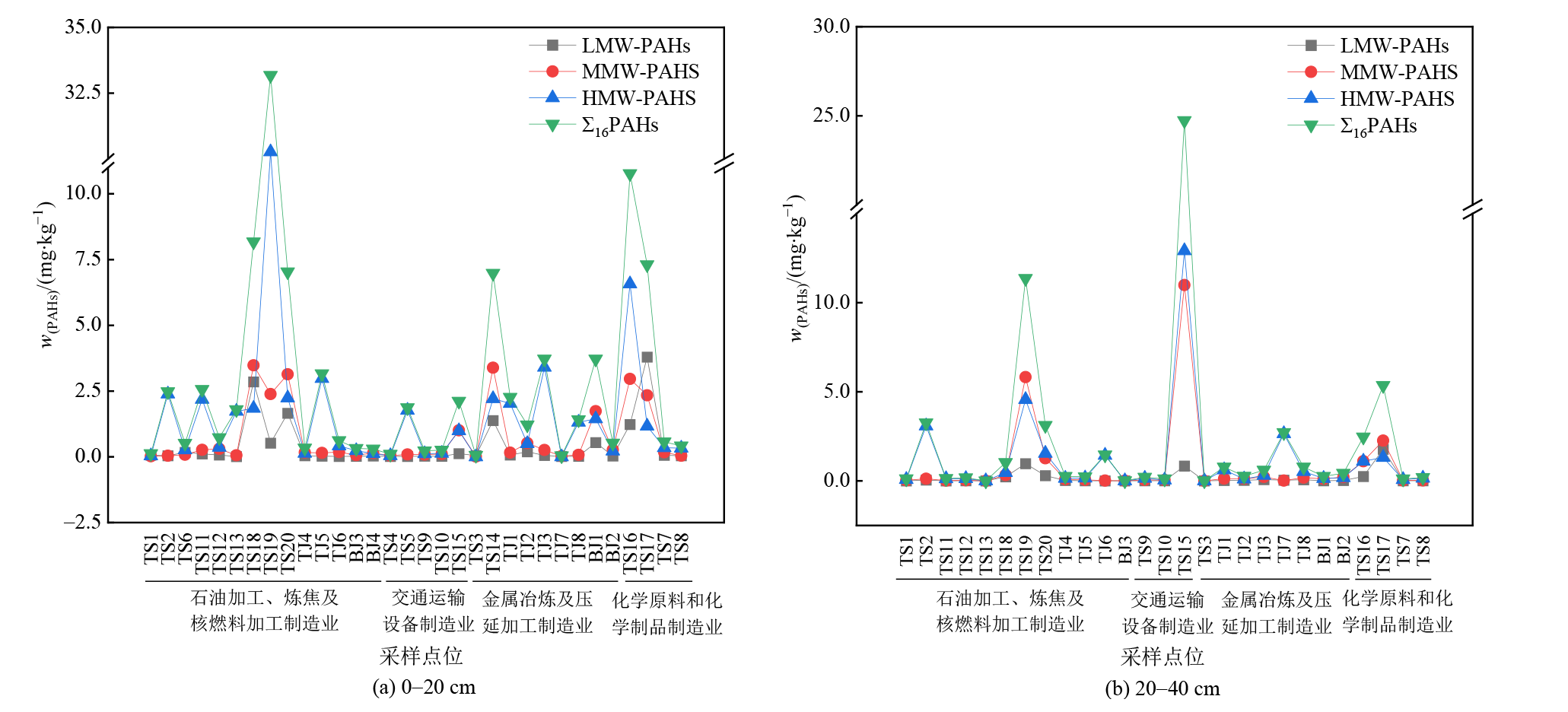
图2 各采样点土壤中PAHs污染 将16种PAHs分成三类:低分子量PAHs为(Low Molecular Weight Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons,LMW-PAHs),包含2环和3环;中分子量PAHs为(Medium Molecular Weight Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons,MMW-PAHs),为4环;高分子量PAHs为(High Molecular Weight Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons,HMW-PAHs),包含5环和6环(Wang et al.,2020)
Figure 2 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution in the soil of the industrial park
| PAHs | 荷兰最大允许质量分数 | 均值 | 毒性当量因子 | 超标率/% | 最大超标倍数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 0.14 | 0.037 | 0.001 | 3.1 | 11.31 |
| Phe | 0.51 | 0.178 | 0.001 | 12.5 | 3.56 |
| An | 0.12 | 0.027 | 0.01 | 9.4 | 2.88 |
| Flu | 2.6 | 0.249 | 0.001 | 1.6 | 1.07 |
| BaA | 0.25 | 0.138 | 0.1 | 17.2 | 9.55 |
| Chr | 10.7 | 0.180 | 0.01 | 0 | - |
| BkF | 2.4 | 0.123 | 0.1 | 0 | - |
| BaP | 0.26 | 0.242 | 1 | 20.3 | 17.26 |
| InP | 7.5 | 0.284 | 0.1 | 0 | - |
| BgP | 5.9 | 0.894 | 0.01 | 3.1 | 3.21 |
| ∑10PAHs | - | 2.337 | - | - | - |
| TEQ(BaP)10 | 0.033 | 0.308 | - | 65.6 | 150.48 |
表3 工业区周边土壤PAH10质量分数及BaP毒性当量质量分数
Table 3 Mass fraction of PAH10 and BaP toxic equivalent concentration in the surrounding soil of the industrial area mg?kg?1
| PAHs | 荷兰最大允许质量分数 | 均值 | 毒性当量因子 | 超标率/% | 最大超标倍数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 0.14 | 0.037 | 0.001 | 3.1 | 11.31 |
| Phe | 0.51 | 0.178 | 0.001 | 12.5 | 3.56 |
| An | 0.12 | 0.027 | 0.01 | 9.4 | 2.88 |
| Flu | 2.6 | 0.249 | 0.001 | 1.6 | 1.07 |
| BaA | 0.25 | 0.138 | 0.1 | 17.2 | 9.55 |
| Chr | 10.7 | 0.180 | 0.01 | 0 | - |
| BkF | 2.4 | 0.123 | 0.1 | 0 | - |
| BaP | 0.26 | 0.242 | 1 | 20.3 | 17.26 |
| InP | 7.5 | 0.284 | 0.1 | 0 | - |
| BgP | 5.9 | 0.894 | 0.01 | 3.1 | 3.21 |
| ∑10PAHs | - | 2.337 | - | - | - |
| TEQ(BaP)10 | 0.033 | 0.308 | - | 65.6 | 150.48 |
| PAHs | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | −0.073 | 0.698 | 0.006 |
| Ace | 0.185 | 0.951 | −0.055 |
| Acy | 0.24 | 0.882 | −0.044 |
| Fl | 0.161 | 0.955 | −0.021 |
| Phe | 0.409 | 0.878 | −0.034 |
| An | 0.475 | 0.748 | −0.033 |
| Flu | 0.872 | 0.423 | −0.033 |
| Pyr | 0.947 | 0.229 | −0.028 |
| BaA | 0.962 | 0.177 | −0.048 |
| Chr | 0.937 | 0.264 | −0.056 |
| BbF | 0.952 | 0.14 | 0.181 |
| BkF | 0.965 | 0.1 | 0.161 |
| BaP | 0.972 | 0.056 | 0.143 |
| Inp | 0.072 | −0.036 | 0.995 |
| DBA | 0.058 | −0.041 | 0.996 |
| BgP | 0.053 | −0.038 | 0.994 |
| 特征值 | 8.463 | 3.550 | 2.608 |
| 方差贡献率/% | 52.893 | 22.186 | 16.297 |
| 累积方差贡献率/% | 52.893 | 75.080 | 91.377 |
表4 土壤中PAHs主成分方差贡献率
Table 4 Principal component variance contribution rate
| PAHs | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | −0.073 | 0.698 | 0.006 |
| Ace | 0.185 | 0.951 | −0.055 |
| Acy | 0.24 | 0.882 | −0.044 |
| Fl | 0.161 | 0.955 | −0.021 |
| Phe | 0.409 | 0.878 | −0.034 |
| An | 0.475 | 0.748 | −0.033 |
| Flu | 0.872 | 0.423 | −0.033 |
| Pyr | 0.947 | 0.229 | −0.028 |
| BaA | 0.962 | 0.177 | −0.048 |
| Chr | 0.937 | 0.264 | −0.056 |
| BbF | 0.952 | 0.14 | 0.181 |
| BkF | 0.965 | 0.1 | 0.161 |
| BaP | 0.972 | 0.056 | 0.143 |
| Inp | 0.072 | −0.036 | 0.995 |
| DBA | 0.058 | −0.041 | 0.996 |
| BgP | 0.053 | −0.038 | 0.994 |
| 特征值 | 8.463 | 3.550 | 2.608 |
| 方差贡献率/% | 52.893 | 22.186 | 16.297 |
| 累积方差贡献率/% | 52.893 | 75.080 | 91.377 |
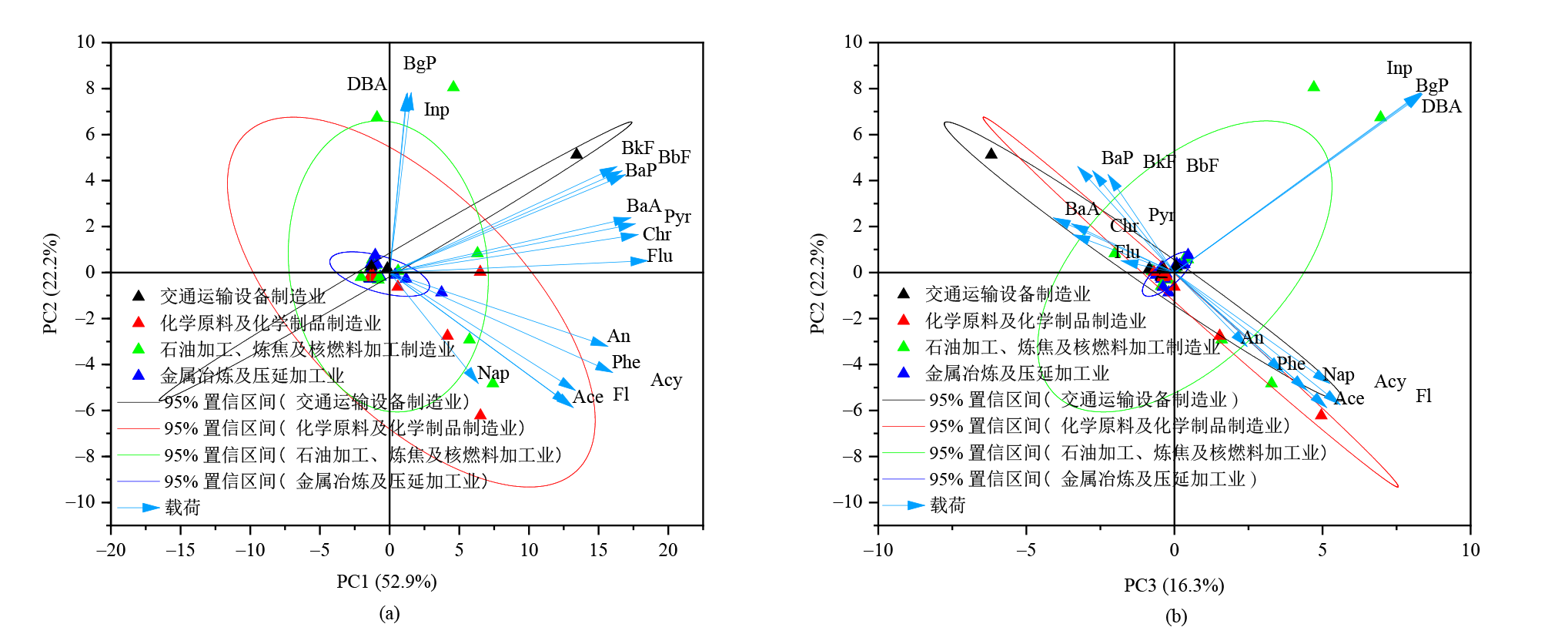
图5 主成分分析法分析土壤PAHs来源 用KMO和巴特利特球形度检验描述相关性矩阵,最大收敛迭代次数为25,提取特征值大于1的数值,并进行方差最大正交旋转。正交旋转后结果KMO取样适切性量数为0.703,巴特利特球形度检验显著性为0.000
Figure 5 Source analysis of PAHs in soils by principal component analysis method
| [1] |
ALSBOU E, ZAITOUN M A, ALASOUFI A M, et al., 2019. Concentration and source assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the street soil of Ma’an City, Jordan[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77(4): 619-630.
DOI |
| [2] |
BAO H Y, HOU S W, NIU H, et al., 2018. Status, sources, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of Xi’an, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(19): 18947-18959.
DOI |
| [3] |
BOENTE C, BARAGAÑO D, GALLEGO J R, 2020. Benzo[a]pyrene sourcing and abundance in a coal region in transition reveals historical pollution, rendering soil screening levels impractical[J]. Environmental Pollution, 266(Pat 1): 115341.
DOI URL |
| [4] | BYSZCZARZ S, LASOTA J, STASZEL K, et al., 2021. Effect of forest and agricultural land use on the accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in relation to soil properties and possible pollution sources[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 495: 119105. |
| [5] |
CERQUEIRA M, MATOS J, 2019. A one-year record of particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at an urban background site in Lisbon Metropolitan Area, Portugal[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 658: 34-41.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DAI J L, LI S J, ZHANG Y L, et al., 2008. Distributions, sources and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in topsoil at Ji’nan city, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 147(1-3): 317-326.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GALARNEAU E, 2008. Source specificity and atmospheric processing of airborne PAHs: Implications for source apportionment[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 42(35): 8139-8149.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GOLOBOČANIN D D, AKRBIĆ B D, MILJEVIĆ N R, 2004a. Principal component analysis for soil contamination with PAHs[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 72(2): 219-223.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HONG W J, LI Y F, LI W L, et al., 2020. Soil concentrations and soil-air exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in five Asian countries[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 711: 135223.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HU J, CHEN W P, ZHAO Z Q, et al., 2022. Source tracing of potentially toxic elements in soils around a typical coking plant in an industrial area in northern China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 807(Part2): 151091.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JIANG Y F, YVES U J, SUN H, et al., 2016. Distribution, compositional pattern and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of an industrial city, Lanzhou, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 126: 154-162.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
KALF D F, CROMMENTUIJN T, VAN DE PLASSCHE E J, 1997. Environmental quality objectives for 10 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[J]. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 36(1): 89-97.
PMID |
| [13] |
KULSHRESTHA M J, SINGH R, OJHA V N, 2019. Trends and source attribution of PAHs in fine particulate matter at an urban and a rural site in Indo-Gangetic plain[J]. Urban Climate, 29: 100485.
DOI URL |
| [14] | KWON H O, CHOI S D, 2014. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils from a multi-industrial city, South Korea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 470-471: 1494-1501. |
| [15] |
LI C T, MI H H, LEE W J, et al., 1999. PAH emission from the industrial boilers[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 69(1): 1-11.
PMID |
| [16] |
LIU M, GUO C, ZHU C, et al., 2021. Vertical profile and assessment of soil pollution from a typical coking plant by suspect screening and non-target screening using GC/QTOF-MS[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 810: 151278.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LIU W J, WANG Y L, CHEN Y C, et al., 2017. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air, surface soil and wheat grain near a large steel-smelting manufacturer in northern China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 57(7): 93-103.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LUO Y M, ZHOU D Y, TIAN Y Y, et al., 2021. Spatial and temporal characteristics of different types of pollution-intensive industries in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China by using land use data[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 329: 129601.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
MAHARJAN L, KANG S, TRIPATHEE L, et al., 2022. Atmospheric particle-bound polycyclic aromatic compounds over two distinct sites in Pakistan: Characteristics, sources and health risk assessment[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 112: 1-15.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
OMORES R A, WEWERS F, IKHIDE P O, et al., 2017. Spatio-temporal distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils in cape town, South Africa[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 11(2): 189-196.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
RUSSELL C A, VORONRY R P, 2017. Carbon dioxide efflux from the floor of a boreal aspen forest. I. Relationship to environmental variables and estimates of C respired[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 78(2): 301-310.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SELVARAJ S, GAONKAR O, KUMAR B, et al., 2021. Legacy persistent organochlorine pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface soil from the industrial corridor of South India: occurrence, sources and risk assessment[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(5): 2105-2120.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
SHI R G, LI X H, YANG Y Y, et al., 2021. Contamination and human health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soils from Tianjin coastal new region, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 268(Pt B): 115938
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SINGH D P, GADI R, MANDAL T K, 2012. Levels, sources, and toxic potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soil of Delhi, India[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 18(2): 393-411.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SIKORA L J, MCCOY J L, 1990. Attempts to determine available carbon in soils[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 9(1): 19-24.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
TANG L, TANG X Y, ZHU Y G, et al., 2005. Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils in Beijing, China[J]. Environment International, 31(6): 822-828.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
TSAI P J, SHIH T S, CHEN H L, et al., 2004. Assessing and predicting the exposures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their carcinogenic potencies from vehicle engine exhausts to highway toll station workers[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 38(2): 333-343.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
TSAI P, SHIEH H, HSIEH L, et al., 2001. The fate of PAHs in the carbon black manufacturing process[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 35(20): 3495-3501.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG F, DONG W Y, ZHAO Z L, et al., 2020. Spatial and vertical distribution, composition profiles, sources, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon residues in the sediments of an urban tributary: A case study of the Songgang River, Shenzhen, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 266(Part1): 115360.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WANG L C, WANG I C, CHANG J E, et al., 2007. Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from the liquid injection incineration of petrochemical industrial wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148(1-2): 296-302.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WANG L J, ZHANG P Q, WANG L, et al., 2018. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soil in the semi-arid city of Xi’an, northwest China: Composition, distribution, sources, and relationships with soil properties[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 75(3): 351-366.
DOI |
| [32] |
XING X L, MAO Y, HU T P, et al., 2020. Spatial distribution, possible sources and health risks of PAHs and OCPs in surface soils from Dajiuhu Sub-alpine Wetland, central China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 208:106393.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
XU B L, LIU F, ALFARO D, et al., 2022. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fine road dust from a coal-utilization city: Spatial distribution, source diagnosis and risk assessment[J]. Chemosphere, 286(Part1): 131555.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
XU X Y, JIANG Z Y, WANG J H, et al., 2012. Distribution and characterizing sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of surface water from Jialing River[J]. Journal of Central South University, 19(3): 850-854.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YAN Z, 2020. A preliminary study on pollution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil around a thermal power plant of Xi’an city[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, 204(6): 01012.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
YU H Y, LI T J, LIU Y, et al., 2019. Spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in urban soil of China[J]. Chemosphere, 230: 498-509.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | ZHANG M N, TANG Z W, YIN H M, et al., 2021. Concentrations, distribution and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from seven major river basins in China over the past 20 years[J]. Journal of Environment Management, 280: 111717. |
| [38] | 白莉, 荆钰童, 2020. 多环芳烃源解析方法对比[J]. 吉林建筑大学学报, 37(1): 45-50. |
| BAI L, JING Y T, 2020. Comparison of source apportionment methods for PAHs[J]. Journal of Jilin Jianzhu University, 37(1): 45-50. | |
| [39] | 国家统计局, 2021. 2020中国统计年鉴[J]. 统计理论与实践 (1): 2. |
| National Bureau of Statistics, 2021. 2020 China statistical yearbook[J]. Statistics Theory and Practice (1): 2. | |
| [40] | 韩煦, 陈洁, 孙守钧, 等, 2021. 染料厂遗留场地中氯仿和苯并(a)芘的污染特征与健康风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 39(8): 211-216. |
| HAN X, CHEN J, SUN S J, et al., 2021. Pollution analysis and spatial distribution of health risk in the residual site of dye factory[J]. Environmental Engineering, 39(8): 211-216. | |
| [41] | 环境保护部, 国土资源部, 2014. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[J]. 中国环保产业 (8): 26-29. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the PRC, Ministry of Natural Resources of the PRC, 2014. Report on the national general survey of soil contamination[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry (8): 26-29. | |
| [42] |
姜永海, 韦尚正, 席北斗, 等, 2009. PAHs在我国土壤中的污染现状及其研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 18(3): 1176-1181.
DOI |
| JIANG Y H, WEI S Z, XI B D, et al., 2009. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) pollution in soils in China: Recent advances and future prospects[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(3): 1176-1181. | |
| [43] | 李爽, 刘殷佐, 刘入瑜, 等, 2019. 浑河沈抚段多环芳烃的污染特征及风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(4): 1551-1559. |
| LI S, LIU Y Z, LIU R Y, et al., 2019. The pollution characteristics and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of Shen-Fu section of the Hun River Basin[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(4): 1551-1559. | |
| [44] | 林超霸, 张馥颖, 朱雪竹, 等, 2021. 我国农业土壤及农作物中多环芳烃污染特征与来源[J]. 生物加工过程, 19(4): 440-447. |
| LIN C B, ZHANG F Y, ZHU X Z, et al., 2021. Characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminations in agricultural soils and crops in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 19(4): 440-447. | |
| [45] | 鲁垠涛, 王雪雯, 张士超, 等, 2019. 黄河全流域岸边表层土壤中PAHs的分布、来源及风险评估[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(5): 2078-2085. |
| LU Y T, WANG X W, ZHANG S C, et al., 2019. Distribution, source and risk assessment of PAHs in surface soil of the Yellow River Basin[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(5): 2078-2085. | |
| [46] | 孟祥帅, 吴萌萌, 陈鸿汉, 等, 2020. 某焦化场地非均质包气带中多环芳烃 (PAHs) 来源及垂向分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 41(1): 377-384. |
| MENG X S, WU M M, CHEN H H, et al., 2020. Vertical pollution characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a heterogeneous unsaturated zone under a coking plant[J]. Environmental Science, 41(1): 377-384. | |
| [47] | 庞欣, 张福锁, 王敬国, 2000. 不同供氮水平对根际微生物量氮及微生物活度的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 6(4): 476-480. |
| PANG X, ZHANG F S, WANG J G, 2000. Effect of different nitrogen levels on SMB-N and microbial activity[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 6(4): 476-480. | |
| [48] | 生态环境部南京环境科学研究所, 中国环境科学研究院, 2018. 土壤环境质量建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)[S]. |
| Nanjing Institute of Environmental Sciences, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences, 2018. Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of development land[S]. | |
| [49] | 石钰婷, 何江涛, 金爱芳, 2011. 北京市东南郊不同灌区表层土壤中PAHs来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 25(2): 393-400. |
| SHI Y T, HE J T, JIN A F, 2011. Sources apportionment of PAHs in the surface soil of different irrigation areas in southeast suburb of Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 25(2): 393-400. | |
| [50] | 万云洋, 朱迎佳, 费佳佳, 等, 2017. 环境中的多环芳烃结构及其危害[J]. 油气田环境保护, 27(6): 23-26. |
| WAN Y Y, ZHU Y J, FEI J J, et al., 2017. The structure of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its danger in the environment[J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gasfields, 27(6): 23-26. | |
| [51] |
王洪, 李海波, 孙铁珩, 等, 2011. 生物修复PAHs污染土壤对酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(4): 691-695.
DOI |
| WANG H, LI H B, SUN T H, et al., 2011. Bioremediation of PAHs contaminated soil and its impacts on soil enzyme activity[J]. Ecology and Environment, 20(4): 691-695. | |
| [52] | 王芸, 韩宾, 史忠强, 等, 2006. 保护性耕作对土壤微生物特性及酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 20(4): 120-122. |
| WANG Y, HAN B, SHI Z Q, et al., 2006. Effects of conservati on tillageon soil microbial characters and soil enzyme activities[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(4): 120-122. | |
| [53] | 吴志远, 张丽娜, 夏天翔, 等, 2020. 基于土壤重金属及PAHs来源的人体健康风险定量评价: 以北京某工业污染场地为例[J]. 环境科学, 41(9): 4180-4196. |
|
WU Z Y, ZHANG L N, XIA T X, et al., 2020. Quantitative assessment of human health risks based on soil heavy metals and PAHs sources: Take a polluted industrial site of Beijing as an example[J]. Environmental Science, 41(9): 4180-4196.
DOI URL |
|
| [54] | 魏书精, 罗碧珍, 孙龙, 等, 2013. 森林生态系统土壤呼吸时空异质性及影响因子研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(04): 689-704. |
| WEI S J, LUO B Z, SUN L, et al., 2013. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity and effect factors of soil respiration in forest ecosystems: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(04): 689-704. | |
| [55] | 王启兰, 曹广民, 王长庭, 等, 2007. 高寒草甸不同植被土壤微生物数量及微生物生物量的特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 26(07): 1002-1008. |
| WANG Q L, CAO G M, WANG C T, et al., 2007. Quantitative characters of soil microbes a nd microbial biomass under different vegetations in alpine meadow[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(07): 1002-1008. | |
| [56] | 夏子书, 王玉玉, 钟艳霞, 等, 2020. 基于GIS和PMF模型的石嘴山市土壤多环芳烃空间分布及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 41(12): 5656-5667. |
| XIA Z S, WANG Y Y, ZHONG Y X, et al., 2020. Spatial distribution characteristics and source apportionment of soil PAHs in Shizuishan city based on GIS and PMF model[J]. Environmental Science, 41(12): 5656-5667. | |
| [57] | 闫广新, 田一茗, 孟美杉, 等, 2021. 某化工场地土壤与地下水中多环芳烃的分布特征及迁移规律[J]. 城市地质, 16(2): 156-162. |
| YAN G X, TIAN Y M, MENG M S, et al., 2021. Distribution and migration of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in soil and groundwater of a chemical site[J]. Brban Geology, 16(2): 156-162. | |
| [58] | 杨秀虹, 李适宇, 李岚, 等, 2008. 广州市工业、交通区表层土壤中多环芳烃分布特征初探[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 47(1): 93-97. |
| YANG X H, LI S Y, LI L, et al., 2008. Preliminary study on the composition characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soils of industrial sites and traffic in Guangzhou[J]. Acta ScientIarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatsebi, 47(1): 93-97. | |
| [59] | 叶凯, 孙玉川, 朱琳跃, 等, 2021. 典型岩溶槽谷区不同地表覆被土壤中多环芳烃的运移特征和来源解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(12): 5127-5136. |
| YE K, SUN Y C, ZHU L Y, et al., 2021. Migration characteristic and source analysis of PAHs in soils with different surface cover in typical Karst trough Valley Area[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(12): 5127-5136. | |
| [60] | 张鸿龄, 孙丽娜, 孙铁珩, 等, 2013. 浑河水环境中多环芳烃 (PAHs) 污染来源解析[J]. 沈阳大学学报(自然科学版), 25(2): 87-91. |
| ZHANG H L, SUN L N, SUN T H, et al., 2013. Sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface water from Hunhe River[J]. Journal of Shenyang University (Natural Science), 25(2): 87-91. | |
| [61] | 张金良, 张晗, 邹天森, 等, 2019. 某生物质电厂周边农田土壤中多环芳烃污染特征及生态安全评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 39(5): 1655-1663. |
| ZHANG J L, ZHANG H, ZOU T S, et al., 2019. Pollution characteristics and evaluation safety of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) pollution in surface soil of farmland around the biomass power plant[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(5): 1655-1663. | |
| [62] | 张旭, 卢双, 裴晋, 等, 2016. 长江湖北段表层土中多环芳烃分布、来源及风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(12): 4531-4536. |
| ZHANG X, LU S, PEI J, et al., 2016. Distribution, sources, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface soil from Yangtze River in Hubei[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(12): 4531-4536. | |
| [63] | 张希, 杨静, 刘敏, 等, 2019. 上海交通沿线农田土壤中PAHs分布特征及源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(2): 741-749. |
| ZHANG X, YANG J, LIU M, et al., 2019. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of PAHs in farmland soils along Shanghai traffic artery[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(2): 741-749. | |
| [64] | 张雪英, 李莲, 祝佩茹, 等, 2020. 生物纳米FeS和磁性炭对Klebsiella sp. LZ6降解芘效果的影响[J]. 南京工业大学学报, 42(6): 804-813. |
| ZHANG X Y, LI L, ZHU P R, et al., 2020. Effects of bio-nano FeS and magnetic carbon on pyrene degradation by Klebsiella sp. LZ6[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University, 42(6): 804-813. | |
| [65] |
张枝焕, 卢另, 贺光秀, 等, 2011. 北京地区表层土壤中多环芳烃的分布特征及污染源分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(4): 668-675.
DOI |
| ZHANG Z H, LU L, HE G X, et al., 2011. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compounds in topsoil of Beijing, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(4): 668-675. | |
| [66] | 赵宝中, 韩天熙, 郝向荣, 等, 2004. 多环芳烃水中溶解度的理论计算[J]. 分子科学学报, 20(2): 1-4. |
|
ZHAO B Z, HAN T X, HAO X R, et al., 2004. Theoretical calculation of the solubility for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Journal of Molecular Science, 20(2): 1-4.
DOI URL |
|
| [67] | 中国科学院亚热带农业生态研究所, 湖南永清环保研究院有限责任公司, 中国科学院南京土壤研究所, 等, 2020. 土壤微生物生物量的测定熏蒸提取法: GB/T 39228—2020 [S]. 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. |
| Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hunan Yongqing Environmental Protection Research Institute Co. LTD, Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, et al., 2020. Determination of soil microbial biomass Fumigation extraction method: GB/T 39228—2020 [S]. State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration. | |
| [68] | 钟名誉, 李慧颖, 贾晓洋, 等, 2021. 不同焦化厂土壤中多环芳烃污染特征比较研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 37(5): 627-635. |
| ZHONG M Y, LI H Y, JIA X Y, et al., 2021. A comparative study on the pollution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the soil of different coking plants[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37(5): 627-635. | |
| [69] | 周礼恺, 张志明, 1980. 土壤酶活性的测定方法[J]. 土壤通报, 11(5): 37-38. |
| ZHOU L K, ZHANG Z M, 1980. Determination of soil enzyme activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 11(5): 37-38. | |
| [70] | 左谦, 刘文新, 陶澍, 等, 2007. 环渤海西部地区表层土壤中的多环芳烃[J]. 环境科学学报, 27(4): 667-671. |
| ZUO Q, LIU W X, TAO S, et al., 2007. PAHs in surface soils from the western watershed of Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantie, 27(4): 667-671. |
| [1] | 夏美君, 李健, 闫永蚕. 京津冀城市群生态福利绩效时空格局及演进特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 814-824. |
| [2] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [3] | 孙正, 曹亚非, 王德彩, 刘峰, 宋效东, 张甘霖, 吴华勇. 近30年京津冀电镀场地时空演变特征及趋势预测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 183-194. |
| [4] | 王金杰, 赵安周, 胡小枫. 京津冀植被净初级生产力时空分布及自然驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1158-1167. |
| [5] | 王瑞娟, 彭文英, 刘丹丹. 共建共治共享视角下京津冀城市生态补偿研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1103-1110. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
