生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 320-330.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.02.012
林昕1,2,3( ), 段焜瑀1, 郭弘4, 蒋冬升5, 纪晓婷6, 王宏3,7,*(
), 段焜瑀1, 郭弘4, 蒋冬升5, 纪晓婷6, 王宏3,7,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-14
出版日期:2023-02-18
发布日期:2023-05-11
通讯作者:
*王宏(1976年生),女,研究员,从事大气环境研究。E-mail: wh1575@163.com作者简介:林昕(1993年生),女,助理工程师,硕士,从事大气环境研究与天气预报工作。E-mail: 313159287@qq.com
基金资助:
LIN Xin1,2,3( ), DUAN Kunyu1, GUO Hong4, JIANG Dongsheng5, JI Xiaoting6, WANG Hong3,7,*(
), DUAN Kunyu1, GUO Hong4, JIANG Dongsheng5, JI Xiaoting6, WANG Hong3,7,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-14
Online:2023-02-18
Published:2023-05-11
摘要:
2022年7月中下旬,福建省出现了1次大范围、持续性的高温过程,24日福州市日最高气温达41.9 ℃,打破1961年以来的历史记录。与此同时,福建省沿海地区出现了2次臭氧(O3)污染过程(7月11-17日和7月22-31日),省会福州市在第1个污染过程中出现4 d O3超标,在第2个过程中因重大社会活动保障期间实施了2 d二级和3 d一级的管控措施,但O3质量浓度仍维持在高位并出现1 d超标。利用环境监测、气象观测及气象再分析资料等,采用合成对比、天气学诊断、相关分析、后向轨迹模拟等方法,详细分析了2022年7月中下旬福州市O3质量浓度异常升高及其影响因素,以期为进一步开展中国东南沿海区域夏季O3污染防治、预警预报及与周边地区联防联控提供技术支撑。结果表明:2022年7月中下旬福州市O3日最大8 h滑动平均值异常升高达到141.2 μg·m-3是多年平均值(84.8 μg·m-3)的1.7倍。O3质量浓度小时值较多年平均值明显偏高且在12-17时出现了一段“峰顶平直”现象,并在17时前后达到第2个峰值(“翘尾”现象);后向轨迹分析表明,污染时段的影响气流主要来自福建省中部和南部地区,外来输送的O3及其前体物叠加本地O3的累积是“翘尾”现象发生的重要原因。O3污染过程持续发展的最直接原因是在中部型拉尼娜(La Niña)事件的气候背景下,副热带高压面积持续偏大、强度偏强导致极端高温长时间维持,这有利于O3的本地生成;副热带高压热穹顶和边界层O3垂直下沉动力输送、上游区域午后O3水平输送、不利的气象条件等多种因素都对O3污染的发生都有着重要影响。
中图分类号:
林昕, 段焜瑀, 郭弘, 蒋冬升, 纪晓婷, 王宏. 极端高温形势下福州市臭氧浓度异常升高及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 320-330.
LIN Xin, DUAN Kunyu, GUO Hong, JIANG Dongsheng, JI Xiaoting, WANG Hong. The Causes of the Abnormal Increase of Ozone in Fuzhou City under Extreme High Temperature[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 320-330.
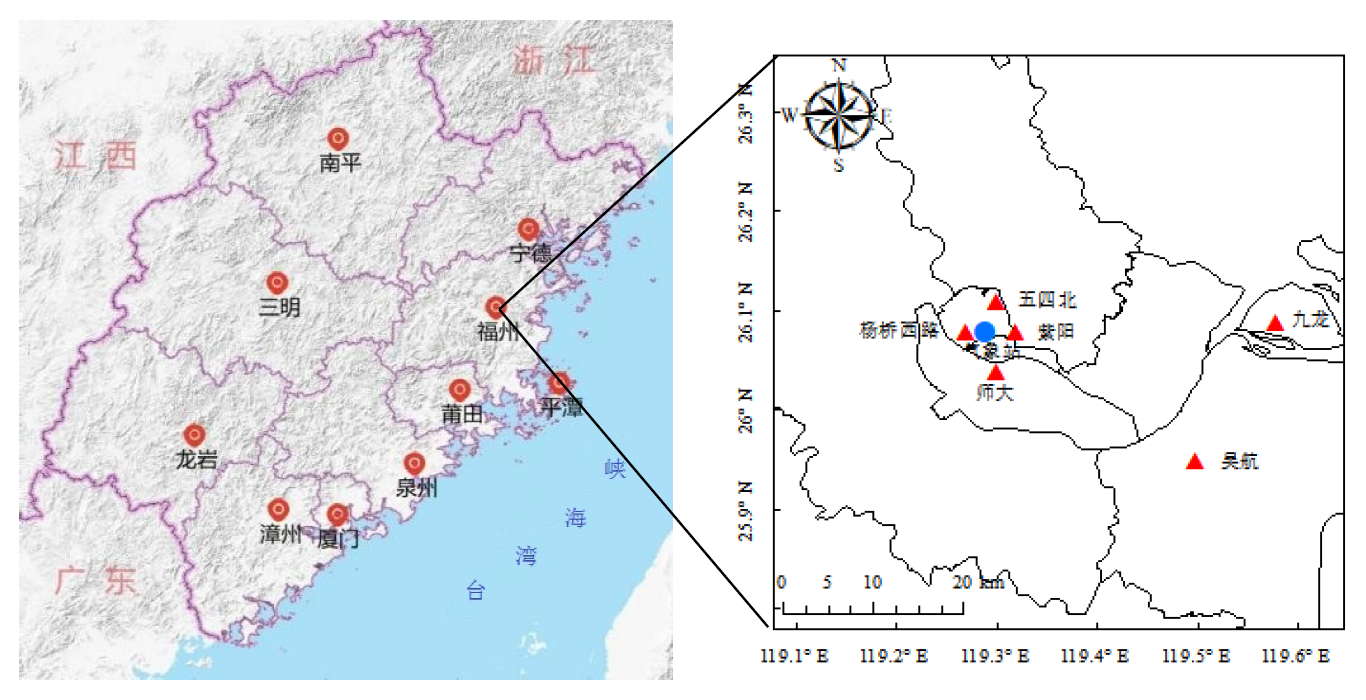
图1 福州市6个环境空气质量国控监测站(红色▲)和福州国家基本气象站(蓝色●)位置示意图
Figure 1 Distribution of national-controlling ambient air quality monitoring sites (red ▲) and meteorological station (blue ●) in Fuzhou City
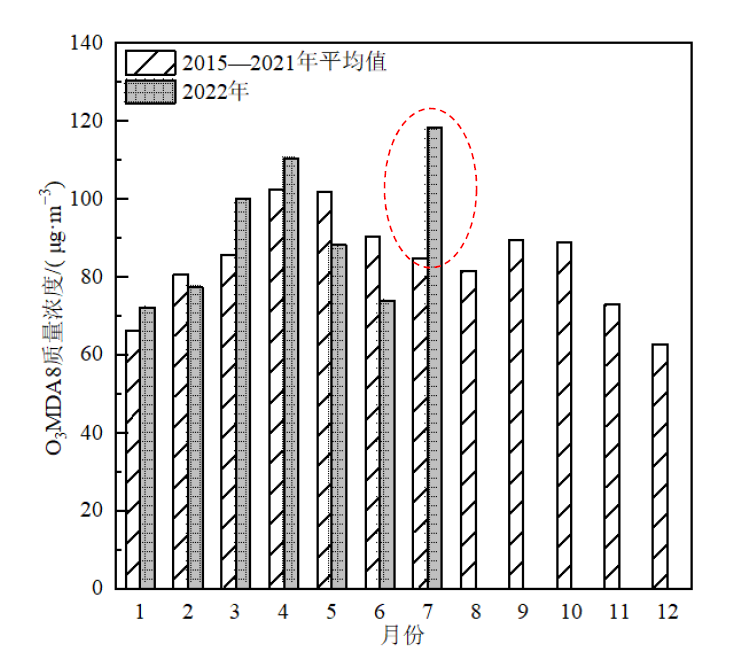
图2 福州市2022年O3MDA8质量浓度月均值及与2015-2021年平均值的对比图
Figure 2 Monthly mean value of O3MDA8 mass concentration in Fuzhou City in 2022 and contrast to monthly mean value (2015-2021)
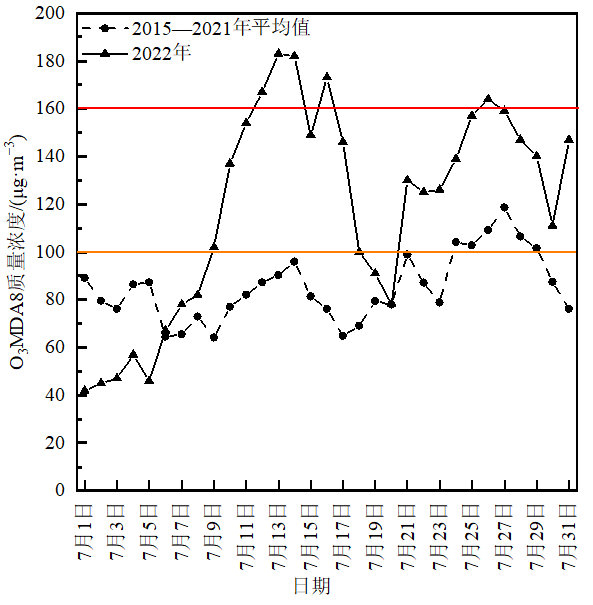
图3 福州市2022年7月O3MDA8质量浓度的逐日变化及与2015-2021年平均值的对比图
Figure 3 Day to day of O3MDA8 mass concentration in Fuzhou City in July, 2022 and contrast to mean value (2015-2021)
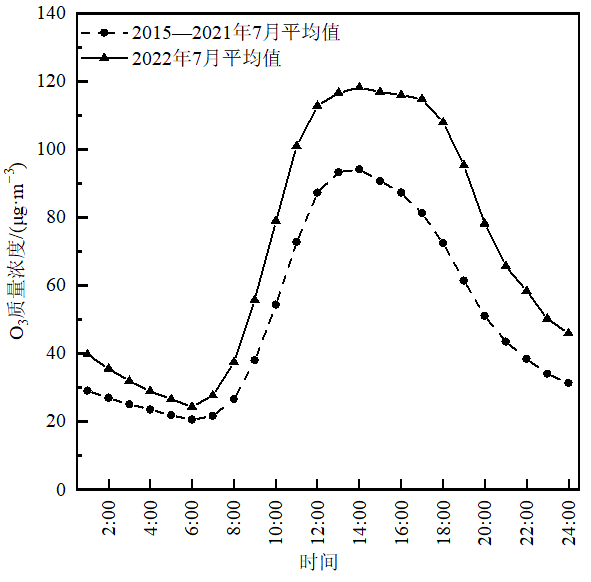
图4 福州市2022年7月O3质量浓度小时均值日变化及与2015-2021年7月平均值的对比图
Figure 4 Diurnal variation of O3 mass concentration in Fuzhou City in July, 2022 and contrast to mean value
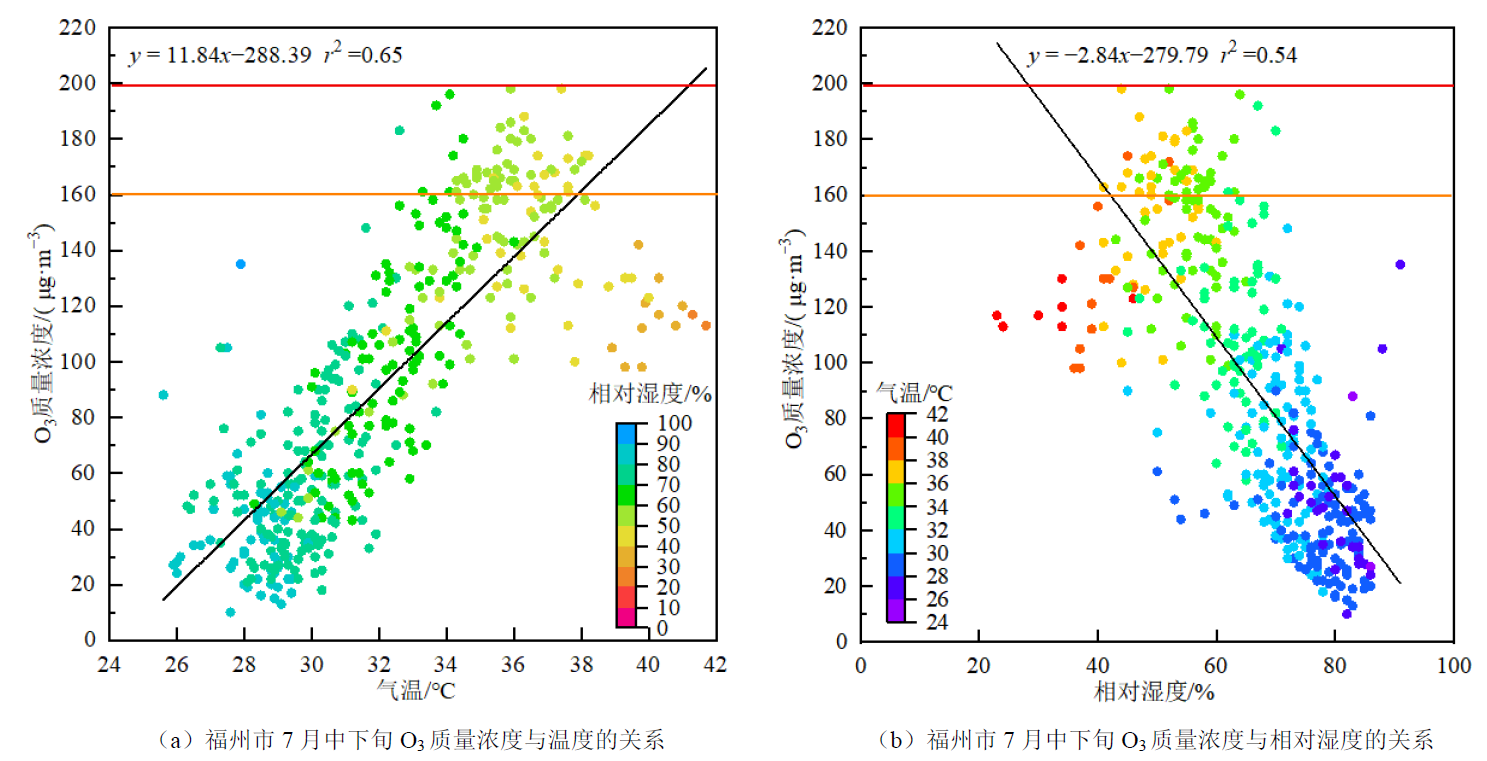
图7 7月中下旬O3质量浓度与温度、相对湿度的关系
Figure 7 Correlation between O3 mass concentration and temperature, relative humidity in Fuzhou city during mid-to-late July, 2022
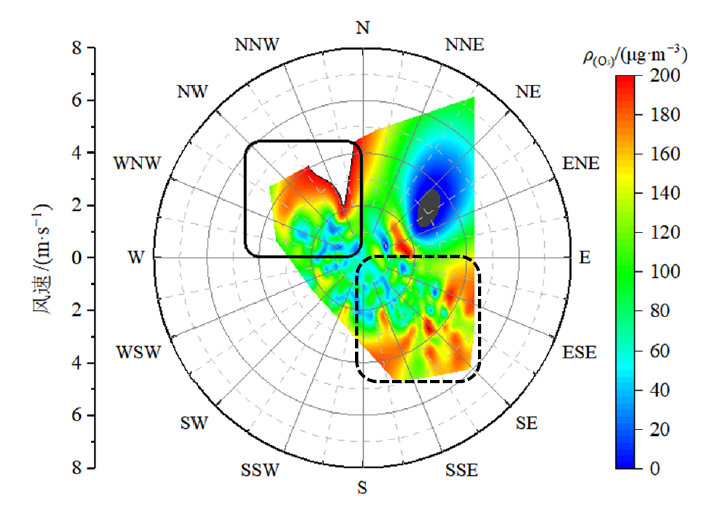
图9 2022年7月11-17日和22-31日O3质量浓度随风向风速的变化 灰色为缺测值
Figure 9 O3 mass concentration corresponding with wind speed,wind direction in Fuzhou city during July 11-17 and July 22-31, 2022
| 时间 | 2021年12月-2022年2月 | 2022年月份 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 2-4 | 3-5 | 4-6 | 5-7 | 6-8 | ||
| 平均值 | -0.9 | -0.9 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -0.9 | -0.9 | -1.0 |
表1 2022年1-7月Niño综合指数3个月滑动平均值
Table 1 Three month moving average of Niño Index from January to July, 2022 ℃
| 时间 | 2021年12月-2022年2月 | 2022年月份 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 2-4 | 3-5 | 4-6 | 5-7 | 6-8 | ||
| 平均值 | -0.9 | -0.9 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -0.9 | -0.9 | -1.0 |
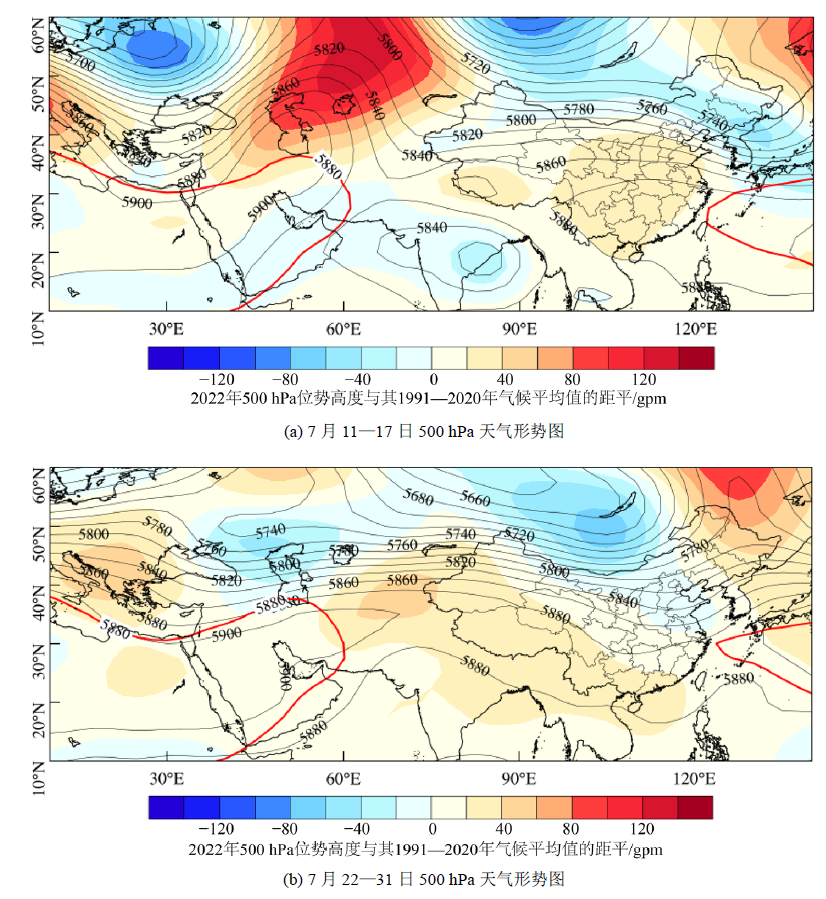
图10 2022年7月中下旬500 hPa天气形势图 红色实线为5880 gpm 1991-2020年的气候平均值,黑色实线为2022年对应时段500 hPa位势高度的平均值
Figure 10 Distribution of 500 hPa geopotential height during mid-to-late July, 2022
| [1] |
AVNERY S, MAUZERALL D L, LIU J F, et al., 2011. Global crop yield reductions due to surface ozone exposure: 1 Year 2000 crop production losses and economic damage[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(13): 2284-2296.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BLACK E, BLACKBURN M, HARRISON G, et al., 2004. Factors contributing to the summer 2003 European heatwave[J]. Weather, 59(8): 217-223.
DOI URL |
| [3] | GVOZDIC V, KOVAC-ANDRIC E, BRANA J, 2011. Influence of meteorological factors NO2, SO2, CO and PM10 on the concentration of O3 in the urban atmosphere of Eastern Croatia[J]. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 16(5): 491-501. |
| [4] |
HE J J, GONG S L, YU Y, et al., 2017. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014-2015 in major Chinese cities[J]. Environmental Pollution, 223: 484-496.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
JIN X M, HOLLOWAY T, 2015. Spatial and temporal variability of ozone sensitivity over China observed from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 120(14): 7229-7246.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KAVASSALIS S C, MURPHY J G, 2017. Understanding ozone- meteorology correlations: A role for dry deposition[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(6): 2922-2931.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI K, DANIEL J J, LU S, et al., 2020. Increases in surface ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2019: Anthropogenic and meteorological influences[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physic, 20(19): 11423-11433.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI Q Q, SU G J, LI C Q, et al., 2020. An investigation into the role of VOCs in SOA and ozone production in Beijing, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 720: 137536.
DOI URL |
| [9] | LIAO Z H, LING Z H, GAO M, et al., 2020. Tropospheric ozone variability over Hong Kong based on recent 20 years (2000-2019) ozonesonde observation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 126(3): 33-54. |
| [10] |
LIU H, LIU S, XUE B R, et al., 2018. Ground-level ozone pollution and its health impacts in China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 173: 223-230.
DOI URL |
| [11] | LU X, ZHANG L, WANG X L, et al., 2020. Rapid increases in warm-season surface ozone and resulting health impact in China since 2013[J]. Environmental Scienc & Technology, 7(4): 240-247. |
| [12] |
MATYSSEK R, KAMOSKY D F, WIESER G, et al., 2010. Advances in understanding ozone impact on forest trees: Messages from novel phytotron and free-air fumigation studies[J]. Environmental Pollution, 158(6): 1990-2006.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | MENG F, QIN M, TANG K, et al., 2020. High-resolution vertical distribution and sources of HONO and NO2 in the nocturnal boundary layer in urban Beijing, China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 20(8): 5071-5092 |
| [14] |
NEUMAN J A, GAO R S, FAHEY D W, et al., 2001. In situ measurements of HNO3, NOy, NO, and O3 in the lower stratosphere and upper troposphere[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 35(33): 5789-5797.
DOI URL |
| [15] | RAMAMURTHY P, GONZALEZ L, ORTIZ M, et al., 2017. Impact of heatwave on a megacity: An observational analysis of New York City during July 2016[J]. Environ mental Research Letters, 12: 054011. |
| [16] | WILLIAM T B, ALSING J, MORTLOCK D J, et al., 2018. Evidence for a continuous decline in lower stratospheric ozone offsetting ozone layer recovery[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(2): 1-36. |
| [17] | YU S J, SU F C, YIN S S, et al., 2021. Characterization of ambient volatile organic compounds,source apportionment,and the ozone-NOx-VOC sensitivities in a heavily polluted megacity of central China: Effect of sporting events and emission reductions[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 21(19): 15239-15257. |
| [18] |
ZHOU B, ZHAO T Y, MA J, et al., 2022. Characterization of VOCs during nonheating and heating periods in the typical suburban area of Beijing, China: Sources and health assessment[J]. Atmosphere, 13(4): 560.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
邓慧颖, 陈立新, 余永江, 等, 2021. 武夷山市臭氧分布特征及其与气象要素关系分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(7): 1428-1435.
DOI |
| DENG H Y, CHEN L X, YU Y J, et al., 2021. Characteristics of ozone pollution distribution and its correlation analysis with meteorological factors in Wuyishan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(7): 1428-1435. | |
| [20] |
符传博, 丹利, 刘丽君, 等, 2022. 2019年秋季三亚市一次典型臭氧污染个例气象成因解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(1): 89-99.
DOI |
| FU C B, DAN L, LIU L J, et al., 2022. Characteristics of a typical ozone pollution event and its meteorological reason in Sanya city in autumn 2019[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(1): 89-99. | |
| [21] | 福州市气象局, 2022. 2022年7月福州市气候影响评价[R]. 福州: 福州市气象局 (7): 2. |
| Fuzhou Meteorological Office, 2022. Fuzhou climate impact assessment in July, 2022[R]. Fuzhou: Fuzhou Meteorological Office (7): 2. | |
| [22] | 关茜妍, 陆克定, 张宁宁, 等, 2021. 西安市大气臭氧污染光化学特征与敏感性分析[J]. 科学通报, 66(35): 4561-4573. |
| GUAN X Y, LU K D, ZHANG N N, et al., 2021. Analysis of the photochemical characteristics and sensitivity of ozone pollution in Xi’an[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 66(35): 4561-4573. | |
| [23] | 洪莹莹, 翁佳烽, 谭浩波, 等, 2021. 珠江三角洲秋季典型O3污染的气象条件及贡献量化[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(1): 1-10. |
| HONG Y Y, WENG J F, TAN H B, et al., 2021. Meteorological conditions and contribution quantification of typical ozone pollution during autumn in Pearl River Delta[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(1): 1-10. | |
| [24] | 刘宏举, 郑有飞, 吴荣军, 等, 2009. 地表臭氧浓度增加对南京地区冬小麦生长和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 30(2): 195-200. |
| LIU H J, ZHENG Y F, WU H J, et al., 2009. Impacts of increasing surface Ozone on growth and yield of winter wheat in Nanjing area[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 30(2): 195-200. | |
| [25] | 漏嗣佳, 朱彬, 廖宏, 2010. 中国地区臭氧前体物对地面臭氧的影响[J]. 大气科学学报, 33(4): 451-459. |
| LOU S J, ZHU B, LIAO H, 2010. Impacts of O3 precursor on surface O3 concentration over China[J]. Transactions Atmospheric Sciences, 33(4): 451-459. | |
| [26] | 史文彬, 屈坤, 严宇, 等, 2022. 成都市夏季臭氧污染的环流分型与来源分析[J]. 北京大学学报 (自然科学版), 58(3): 565-574. |
| SHI W B, QU K, YAN Y, et al., 2022. Circulation classification and source analysis of summer ozone pollution in Chengdu[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 58(3): 565-574. | |
| [27] | 孙博, 王会军, 黄艳艳, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季中国高温干旱气候特征及成因探讨[J/OL]. 大气科学学报, 10.13878/j.cnki.dqkxxb.20220916003. |
| SUN B, WANG H J, HUANG Y Y, et al., 2022. Characteristics and causes of the hot-dry climate anomalies in China during summer of 2022[J/OL]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 10.13878/j.cnki.dqkxxb.20220916003. | |
| [28] | 王宏, 陈晓秋, 余永江, 等, 2012. 福州近地层臭氧分布及其与气象要素的相关性[J]. 自然灾害学报, 21(4): 175-181. |
| WANG H, CHEN X Q, YU Y J, et al., 2012. Distribution of ozone in land surface layer in Fuzhou and its relationship with meteorological factors[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 21(4): 175-181. | |
| [29] | 王宏, 郑秋萍, 温珍治, 等, 2021. ENSO循环对福建省近地层臭氧浓度变化的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(2): 145-153. |
| WANG H, ZHENG Q P, WEN Z Z, et al., 2021. Influence of ENSO cycle on change of ozone concentrantion near surface in Fujian province[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 37(2): 145-153. | |
| [30] |
王文, 许金萍, 蔡晓军, 等, 2017. 2013年夏季长江中下游地区高温干旱的大气环流特征及成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 36(6): 1595-1607.
DOI |
| WANG W, XU J P, CAI X J, et al., 2017. Analysis of atmospheric circulation characteristics and mechanism of heat wave and drought in summer of 2013 over the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River Basin[J]. Plateau Meteor, 36(6): 1595-1607. | |
| [31] | 王占山, 李云婷, 安欣欣, 等, 2018. 2006-2015年北京市不同地区O3浓度变化[J]. 环境科学, 39(1): 1-8. |
| WANG Z S, LI Y T, AN X X, et al., 2018. Variation of O3 concentration in different regions of Beijing from 2006-2015[J]. Environmental Science, 39(1): 1-8. | |
| [32] | 徐健, 2011. 天津市医院门诊就诊人次与大气污染的相关性研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学:14-30. |
| XU J, 2011. Association of air pollution with daily outpatient visits to hospital in Tianjin[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China:14-30. | |
| [33] | 严茹莎, 陈敏东, 高庆先, 等, 2013. 北京夏季典型臭氧污染分布特征及影响因子[J]. 环境科学研究, 26(1): 43-49. |
| YAN R S, CHEN M D, GAO Q X, et al., 2013. Characteristics of typical ozone pollution distribution and impact factors in Beijing in summer[J]. Research of Environmental, 26(1): 43-49. | |
| [34] |
严晓瑜, 缑晓辉, 杨婧, 等, 2020. 中国典型城市臭氧变化特征及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 高原气象, 39(2): 416-430.
DOI |
|
YAN X Y, HOU X H, YANG J, et al., 2020. The variety of ozone and its relationship with meteorological conditions in typical cities in China[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 39(2): 416-430.
DOI |
|
| [35] | 杨显玉, 吕雅琼, 王禹润, 等, 2021. 天气形势对四川盆地区域性臭氧污染的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(6): 14. |
| YANG X Y, LÜ Y Q, WANG Y R, et al., 2021. Impact of synoptic patterns on regional ozone pollution in Sichuan Basin[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(6): 14. | |
| [36] | 杨允凌, 郝巨飞, 杨丽娜, 等, 2020. 一次连续臭氧污染过程的气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 38(3): 448-456. |
| YANG Y L, HAO J F, YANG L N, et al., 2020. Analysis of meteorological conditions of a continuous ozone pollution process in Xingtai of Hebei province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 38(3): 448-456. | |
| [37] | 赵伟, 高博, 刘明, 等, 2019. 气象因素对香港地区臭氧污染的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(1): 55-66. |
| ZHAO W, GAO B, LIU M, et al., 2019. Impact of meteorological factors on the ozone pollution in Hong Kong[J]. Environmental Science, 40(1): 55-66. | |
| [38] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2012. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095-2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2012. Ambient air quality standards: GB 3095-2012[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. |
| [1] | 陈漾, 张金谱, 邱晓暖, 琚鸿, 黄俊. 2021年广州市臭氧污染特征及气象因子影响分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2028-2038. |
| [2] | 符传博, 丹利, 刘丽君, 佟金鹤. 2019年秋季三亚市一次典型臭氧污染个例气象成因解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 89-99. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
