生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 1959-1970.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.004
周徐平1,2( ), 唐录艳1, 何卓冀1, 王顺莉1, 黄丹1, 李大华3, 邓欣妍1, 侯梦丹1, 杨书林1, 彭涛1,*(
), 唐录艳1, 何卓冀1, 王顺莉1, 黄丹1, 李大华3, 邓欣妍1, 侯梦丹1, 杨书林1, 彭涛1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-10
出版日期:2022-10-18
发布日期:2022-12-09
通讯作者:
*彭涛(1977年生),男,副教授,博士,主要从事苔藓植物学、湿地生态学及生物多样性保护。E-mail: pengtao@gznu.edu.cn作者简介:周徐平(1997年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事苔藓植物学研究。E-mail: zhouxp9709@163.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Xuping1,2( ), TANG Luyan1, HE Zhuoji1, WANG Shunli1, HUANG Dan1, LI Dahua3, DENG Xinyan1, HOU Mengdan1, YANG Shulin1, PENG Tao1,*(
), TANG Luyan1, HE Zhuoji1, WANG Shunli1, HUANG Dan1, LI Dahua3, DENG Xinyan1, HOU Mengdan1, YANG Shulin1, PENG Tao1,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-10
Online:2022-10-18
Published:2022-12-09
摘要:
苔藓植物是生物多样性的重要组成部分,在水分平衡、侵蚀防治和氮收支等方面发挥着重要功能。为了揭示苔藓植物地理成分构成差异的影响因素,该研究基于19个省和2个直辖市内27个国家级自然保护区内的苔藓植物物种数据,以及中心地理坐标、气候因子、黏土含量和海拔等参数,利用中心经纬度坐标通过基于距离的Moran特征向量图(distance-based Moran’s eigenvector maps,dbMEM)构建空间变量,分析了空间因子和环境因子对苔藓植物地理成分分异的贡献。结果表明,(1)27个国家级自然保护区共有苔藓植物130科445属1962种(包含21个亚种和94个变种),其中有国家重点保护野生植物3种,受威胁物种62个。(2)分布区类型以温带分布为主。在纬度上,温带成分自南向北显著增加,东亚成分在中部达到最大值,热带成分和亚洲-澳大利亚-大洋洲成分均显著减少;在经度上,温带成分在中部处于最低值,东亚成分自西向东显著增加,热带成分和亚洲-澳大利亚-大洋洲成分在中部达到最大值。(3)变差分解显示由前向选择得到的最冷月最低温、年均温和黏土含量组成的环境因子(18.04%)的独自效应(unique effect)高于由前向选择得到的dbMEM1和dbMEM3组成的空间因子(3.30%),环境因子和空间因子的共同效应(common effect)为49.15%,表明环境因子和空间因子共同影响27个保护区间地理成分的相似性,并且环境因子的贡献要高于空间因子。该研究基于现代环境因素和空间距离,初步揭示了影响27个保护区间地理成分相似性的因素,为苔藓植物区系研究提供了一定的理论基础。
中图分类号:
周徐平, 唐录艳, 何卓冀, 王顺莉, 黄丹, 李大华, 邓欣妍, 侯梦丹, 杨书林, 彭涛. 中国27个国家级自然保护区苔藓植物地理成分构成差异与环境和空间因素的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1959-1970.
ZHOU Xuping, TANG Luyan, HE Zhuoji, WANG Shunli, HUANG Dan, LI Dahua, DENG Xinyan, HOU Mengdan, YANG Shulin, PENG Tao. Deviation in the Composition of Bryophytes Geographic Elements in Relation to Environmental and Spatial Factors among 27 National Nature Reserves in China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1959-1970.
| 国家级自然保护区 National nature reserve | 省级行政区 Provincial administrative region | 面积 Acreage/km2 | 中心点坐标 Coordinates of center | 海拔 Elevation/m | 苔藓植物物种数据来源 References of bryophytes species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 百花山 Baihua Mt. | 北京 | 217.43 | 39°56′N, 115°34′E | 2289 | 田晔林, |
| 白石砬子 Baishilazi | 辽宁 | 74.67 | 40°54′N, 124°49′E | 1253 | 陈玮等, |
| 大巴山 Daba Mt. | 重庆 | 1157.5 | 31°54′N, 108°55′E | 2679 | 刘艳等, |
| 大围山 Dawei Mt. | 云南 | 439.93 | 22°50′N, 103°47′E | 2342 | 翟德逞, |
| 戴云山 Daiyun Mt. | 福建 | 134.72 | 25°41′N, 118°12′E | 1833 | 张晓青, |
| 额尔古纳 Eerguna | 内蒙古 | 1260 | 51°48′N, 120°29′E | 1135 | 王挺杨等, |
| 佛坪 Foping | 陕西 | 292.4 | 33°38′N, 107°47′E | 2888 | 李粉霞, |
| 牯牛降 Guniujiang | 安徽 | 67.133 | 30°2′N, 117°29′E | 1733 | 师雪芹等, |
| 贺兰山 Helan Mt. | 内蒙古; 宁夏 | 2739.76 | 38°50′N, 106°12′E | 3537 | 王小明, |
| 尖峰岭 Jianfengling | 海南 | 201.7 | 18°49′N, 108°58′E | 1367 | 孙悦, |
| 九连山 Jiulian Mt. | 江西 | 134.12 | 24°34′N, 114°27′E | 1392 | 刘信中等, |
| 宽阔水 Kuankuoshui | 贵州 | 262.31 | 28°12′N, 107°8′E | 1748 | 喻理飞等, |
| 喀纳斯 Kanasi | 新疆 | 2201.62 | 48°47′N, 87°8′E | 3820 | 买买提明·苏来曼等, |
| 昆嵛山 Kunyu Mt. | 山东 | 154.17 | 37°15′N, 121°43′E | 909 | 任昭杰等, |
| 雷公山 Leigong Mt. | 贵州 | 473 | 26°22′N, 108°15′E | 2175 | 张华海等, |
| 连康山 Liankang Mt. | 河南 | 185 | 31°37′N, 114°48′E | 789 | 叶永忠等, |
| 庐山 Lu Mt. | 江西 | 305 | 29°33′N, 115°58′E | 1466 | 刘信中等, |
| 木林子 Mulinzi | 湖北 | 208.38 | 30°5′N, 110°8′E | 2080 | 洪柳等, |
| 庞泉沟 Pangquangou | 山西 | 104.66 | 37°52′N, 111°27′E | 2807 | 张二芳, |
| 清凉峰 Qingliangfeng | 浙江 | 108 | 30°5′N, 118°54′E | 1770 | 程丽媛, |
| 祁连山 Qilian Mt. | 甘肃 | 26530.23 | 38°17′N, 100°27′E | 5548 | 杨海英, |
| 齐云山 Qiyun Mt. | 江西 | 171.05 | 25°49′N, 114°1′E | 2046 | 何祖霞等, |
| 十万大山 Shiwanda Mt. | 广西 | 582.771 | 21°51′N, 107°51′E | 1450 | 唐艳雪, |
| 武夷山 Wuyi Mt. | 江西 | 160.07 | 27°54′N, 117°47′E | 2145 | 刘信中等, |
| 西天山 Xitian Mt. | 新疆 | 312.17 | 43°8′N, 82°54′E | 3515 | 熊嘉武, |
| 小寨子沟 Xiaozhaizigou | 四川 | 443.91 | 32°1′N, 103°53′E | 4722 | 胡进耀, |
| 阳际峰 Yangjifeng | 江西 | 109.46 | 27°55′N, 117°19′E | 1527 | 严雄梁, |
表1 27个国家级自然保护区的基本统计信息
Table 1 The basic information of 27 national nature reserves
| 国家级自然保护区 National nature reserve | 省级行政区 Provincial administrative region | 面积 Acreage/km2 | 中心点坐标 Coordinates of center | 海拔 Elevation/m | 苔藓植物物种数据来源 References of bryophytes species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 百花山 Baihua Mt. | 北京 | 217.43 | 39°56′N, 115°34′E | 2289 | 田晔林, |
| 白石砬子 Baishilazi | 辽宁 | 74.67 | 40°54′N, 124°49′E | 1253 | 陈玮等, |
| 大巴山 Daba Mt. | 重庆 | 1157.5 | 31°54′N, 108°55′E | 2679 | 刘艳等, |
| 大围山 Dawei Mt. | 云南 | 439.93 | 22°50′N, 103°47′E | 2342 | 翟德逞, |
| 戴云山 Daiyun Mt. | 福建 | 134.72 | 25°41′N, 118°12′E | 1833 | 张晓青, |
| 额尔古纳 Eerguna | 内蒙古 | 1260 | 51°48′N, 120°29′E | 1135 | 王挺杨等, |
| 佛坪 Foping | 陕西 | 292.4 | 33°38′N, 107°47′E | 2888 | 李粉霞, |
| 牯牛降 Guniujiang | 安徽 | 67.133 | 30°2′N, 117°29′E | 1733 | 师雪芹等, |
| 贺兰山 Helan Mt. | 内蒙古; 宁夏 | 2739.76 | 38°50′N, 106°12′E | 3537 | 王小明, |
| 尖峰岭 Jianfengling | 海南 | 201.7 | 18°49′N, 108°58′E | 1367 | 孙悦, |
| 九连山 Jiulian Mt. | 江西 | 134.12 | 24°34′N, 114°27′E | 1392 | 刘信中等, |
| 宽阔水 Kuankuoshui | 贵州 | 262.31 | 28°12′N, 107°8′E | 1748 | 喻理飞等, |
| 喀纳斯 Kanasi | 新疆 | 2201.62 | 48°47′N, 87°8′E | 3820 | 买买提明·苏来曼等, |
| 昆嵛山 Kunyu Mt. | 山东 | 154.17 | 37°15′N, 121°43′E | 909 | 任昭杰等, |
| 雷公山 Leigong Mt. | 贵州 | 473 | 26°22′N, 108°15′E | 2175 | 张华海等, |
| 连康山 Liankang Mt. | 河南 | 185 | 31°37′N, 114°48′E | 789 | 叶永忠等, |
| 庐山 Lu Mt. | 江西 | 305 | 29°33′N, 115°58′E | 1466 | 刘信中等, |
| 木林子 Mulinzi | 湖北 | 208.38 | 30°5′N, 110°8′E | 2080 | 洪柳等, |
| 庞泉沟 Pangquangou | 山西 | 104.66 | 37°52′N, 111°27′E | 2807 | 张二芳, |
| 清凉峰 Qingliangfeng | 浙江 | 108 | 30°5′N, 118°54′E | 1770 | 程丽媛, |
| 祁连山 Qilian Mt. | 甘肃 | 26530.23 | 38°17′N, 100°27′E | 5548 | 杨海英, |
| 齐云山 Qiyun Mt. | 江西 | 171.05 | 25°49′N, 114°1′E | 2046 | 何祖霞等, |
| 十万大山 Shiwanda Mt. | 广西 | 582.771 | 21°51′N, 107°51′E | 1450 | 唐艳雪, |
| 武夷山 Wuyi Mt. | 江西 | 160.07 | 27°54′N, 117°47′E | 2145 | 刘信中等, |
| 西天山 Xitian Mt. | 新疆 | 312.17 | 43°8′N, 82°54′E | 3515 | 熊嘉武, |
| 小寨子沟 Xiaozhaizigou | 四川 | 443.91 | 32°1′N, 103°53′E | 4722 | 胡进耀, |
| 阳际峰 Yangjifeng | 江西 | 109.46 | 27°55′N, 117°19′E | 1527 | 严雄梁, |
| 国家级自然保护区 National nature reserve | 苔藓植物分布区类型 Distribution types of bryophytes | 合计 Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 | T11 | T12 | T13 | T14 | ||
| 百花山 Baihua Mt. | 113 | 19 | 54 | 24 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 7 | 37 | 6 | 285 |
| 白石砬子 Baishilazi | 109 | 21 | 50 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 32 | 7 | 245 |
| 大巴山 Daba Mt. | 106 | 23 | 102 | 42 | 4 | 13 | 32 | 12 | 18 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 36 | 11 | 425 |
| 大围山 Dawei Mt. | 63 | 31 | 78 | 43 | 11 | 26 | 118 | 42 | 25 | 14 | 0 | 15 | 20 | 11 | 497 |
| 戴云山 Daiyun Mt. | 54 | 23 | 129 | 29 | 13 | 22 | 89 | 44 | 30 | 19 | 1 | 13 | 30 | 14 | 510 |
| 额尔古纳 Eerguna | 119 | 12 | 17 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 198 |
| 佛坪 Foping | 126 | 33 | 127 | 46 | 3 | 15 | 19 | 7 | 12 | 27 | 0 | 5 | 25 | 11 | 456 |
| 牯牛降 Guniujiang | 33 | 10 | 42 | 2 | 3 | 13 | 8 | 8 | 13 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 8 | 166 |
| 贺兰山 Helan Mt. | 108 | 11 | 23 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 34 | 6 | 202 |
| 尖峰岭 Jianfengling | 17 | 12 | 25 | 13 | 29 | 27 | 92 | 53 | 23 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 14 | 6 | 324 |
| 九连山 Jiulian Mt. | 59 | 16 | 44 | 5 | 8 | 17 | 20 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 0 | 7 | 25 | 7 | 253 |
| 宽阔水 Kuankuoshui | 93 | 21 | 90 | 31 | 11 | 15 | 48 | 8 | 26 | 18 | 1 | 10 | 30 | 10 | 412 |
| 喀纳斯 Kanasi | 95 | 12 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 30 | 8 | 160 |
| 昆嵛山 Kunyu Mt. | 100 | 23 | 71 | 20 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 15 | 14 | 2 | 8 | 35 | 12 | 315 |
| 雷公山 Leigong Mt. | 71 | 28 | 81 | 35 | 14 | 18 | 69 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 1 | 10 | 32 | 11 | 427 |
| 连康山 Liankang Mt. | 69 | 15 | 73 | 9 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 11 | 13 | 0 | 5 | 28 | 8 | 247 |
| 庐山 Lu Mt. | 96 | 17 | 74 | 18 | 4 | 15 | 17 | 9 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 6 | 28 | 12 | 336 |
| 木林子 Mulinzi | 65 | 19 | 52 | 13 | 10 | 14 | 27 | 11 | 21 | 14 | 0 | 7 | 28 | 7 | 288 |
| 庞泉沟 Pangquangou | 87 | 8 | 32 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 27 | 3 | 179 |
| 清凉峰 Qingliangfeng | 71 | 20 | 79 | 25 | 6 | 15 | 22 | 14 | 20 | 17 | 0 | 7 | 29 | 8 | 333 |
| 祁连山 Qilian Mt. | 149 | 18 | 51 | 16 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 41 | 7 | 307 |
| 齐云山 Qiyun Mt. | 26 | 12 | 33 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 29 | 15 | 15 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 14 | 8 | 189 |
| 十万大山 Shiwanda Mt. | 46 | 17 | 39 | 19 | 19 | 12 | 50 | 18 | 19 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 17 | 9 | 284 |
| 武夷山 Wuyi Mt. | 51 | 18 | 50 | 9 | 9 | 12 | 22 | 15 | 17 | 12 | 2 | 9 | 30 | 10 | 266 |
| 西天山 Xitian Mt. | 133 | 14 | 32 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 42 | 8 | 248 |
| 小寨子沟 Xiaozhaizigou | 40 | 13 | 26 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 25 | 5 | 140 |
| 阳际峰 Yangjifeng | 63 | 21 | 52 | 14 | 8 | 13 | 35 | 14 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 9 | 23 | 6 | 288 |
表2 各保护区的苔藓植物分布区类型构成
Table 2 The composition of bryophyte distribution types in each reserve
| 国家级自然保护区 National nature reserve | 苔藓植物分布区类型 Distribution types of bryophytes | 合计 Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 | T11 | T12 | T13 | T14 | ||
| 百花山 Baihua Mt. | 113 | 19 | 54 | 24 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 7 | 37 | 6 | 285 |
| 白石砬子 Baishilazi | 109 | 21 | 50 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 32 | 7 | 245 |
| 大巴山 Daba Mt. | 106 | 23 | 102 | 42 | 4 | 13 | 32 | 12 | 18 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 36 | 11 | 425 |
| 大围山 Dawei Mt. | 63 | 31 | 78 | 43 | 11 | 26 | 118 | 42 | 25 | 14 | 0 | 15 | 20 | 11 | 497 |
| 戴云山 Daiyun Mt. | 54 | 23 | 129 | 29 | 13 | 22 | 89 | 44 | 30 | 19 | 1 | 13 | 30 | 14 | 510 |
| 额尔古纳 Eerguna | 119 | 12 | 17 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 198 |
| 佛坪 Foping | 126 | 33 | 127 | 46 | 3 | 15 | 19 | 7 | 12 | 27 | 0 | 5 | 25 | 11 | 456 |
| 牯牛降 Guniujiang | 33 | 10 | 42 | 2 | 3 | 13 | 8 | 8 | 13 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 8 | 166 |
| 贺兰山 Helan Mt. | 108 | 11 | 23 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 34 | 6 | 202 |
| 尖峰岭 Jianfengling | 17 | 12 | 25 | 13 | 29 | 27 | 92 | 53 | 23 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 14 | 6 | 324 |
| 九连山 Jiulian Mt. | 59 | 16 | 44 | 5 | 8 | 17 | 20 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 0 | 7 | 25 | 7 | 253 |
| 宽阔水 Kuankuoshui | 93 | 21 | 90 | 31 | 11 | 15 | 48 | 8 | 26 | 18 | 1 | 10 | 30 | 10 | 412 |
| 喀纳斯 Kanasi | 95 | 12 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 30 | 8 | 160 |
| 昆嵛山 Kunyu Mt. | 100 | 23 | 71 | 20 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 15 | 14 | 2 | 8 | 35 | 12 | 315 |
| 雷公山 Leigong Mt. | 71 | 28 | 81 | 35 | 14 | 18 | 69 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 1 | 10 | 32 | 11 | 427 |
| 连康山 Liankang Mt. | 69 | 15 | 73 | 9 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 11 | 13 | 0 | 5 | 28 | 8 | 247 |
| 庐山 Lu Mt. | 96 | 17 | 74 | 18 | 4 | 15 | 17 | 9 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 6 | 28 | 12 | 336 |
| 木林子 Mulinzi | 65 | 19 | 52 | 13 | 10 | 14 | 27 | 11 | 21 | 14 | 0 | 7 | 28 | 7 | 288 |
| 庞泉沟 Pangquangou | 87 | 8 | 32 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 27 | 3 | 179 |
| 清凉峰 Qingliangfeng | 71 | 20 | 79 | 25 | 6 | 15 | 22 | 14 | 20 | 17 | 0 | 7 | 29 | 8 | 333 |
| 祁连山 Qilian Mt. | 149 | 18 | 51 | 16 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 41 | 7 | 307 |
| 齐云山 Qiyun Mt. | 26 | 12 | 33 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 29 | 15 | 15 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 14 | 8 | 189 |
| 十万大山 Shiwanda Mt. | 46 | 17 | 39 | 19 | 19 | 12 | 50 | 18 | 19 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 17 | 9 | 284 |
| 武夷山 Wuyi Mt. | 51 | 18 | 50 | 9 | 9 | 12 | 22 | 15 | 17 | 12 | 2 | 9 | 30 | 10 | 266 |
| 西天山 Xitian Mt. | 133 | 14 | 32 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 42 | 8 | 248 |
| 小寨子沟 Xiaozhaizigou | 40 | 13 | 26 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 25 | 5 | 140 |
| 阳际峰 Yangjifeng | 63 | 21 | 52 | 14 | 8 | 13 | 35 | 14 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 9 | 23 | 6 | 288 |
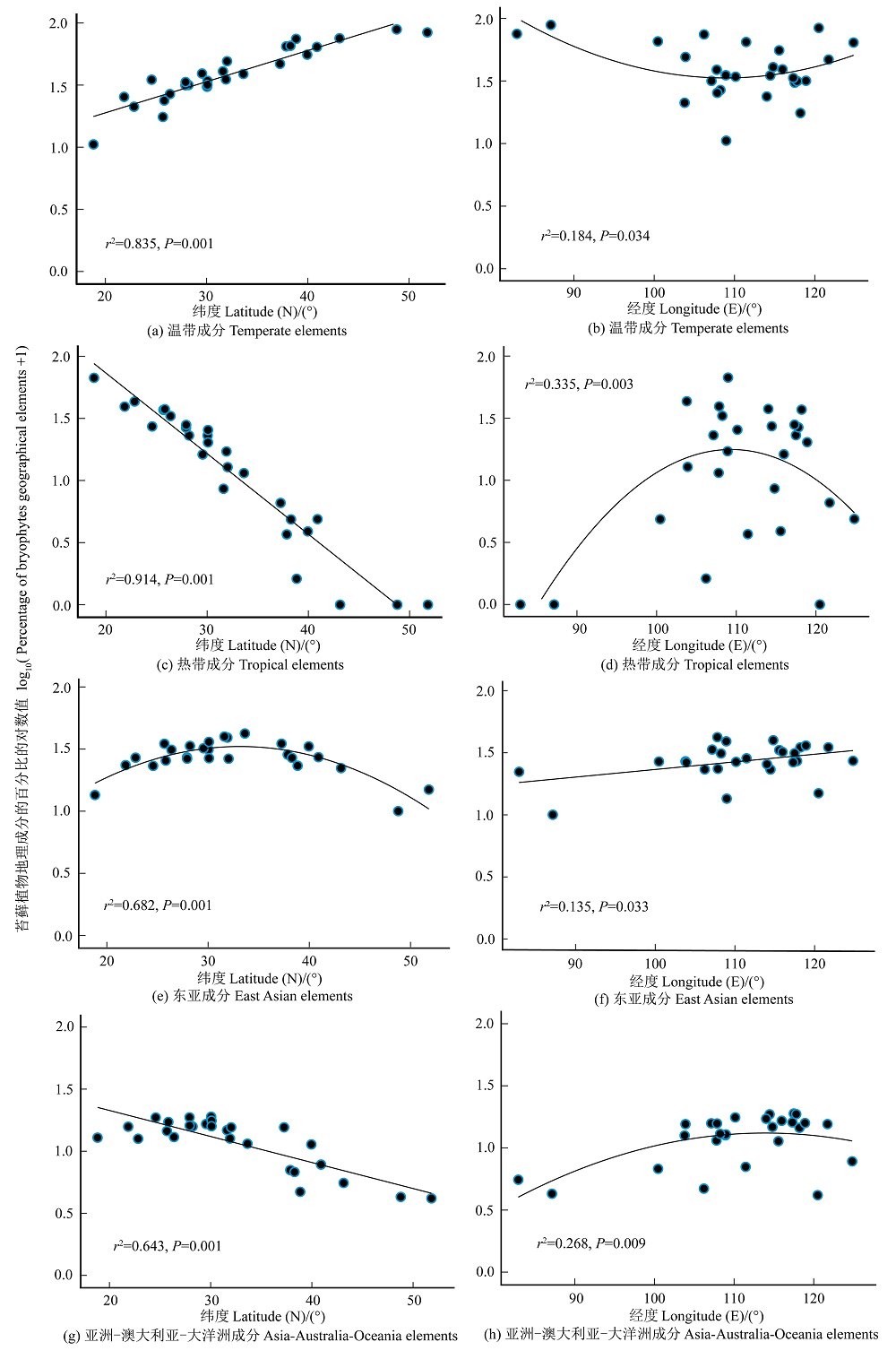
图1 27个国家级自然保护区苔藓植物不同地理成分沿纬度和经度的分布格局
Figure 1 The distribution patterns of different bryophytes geographical elements along latitude and longitude from 27 national nature reserves
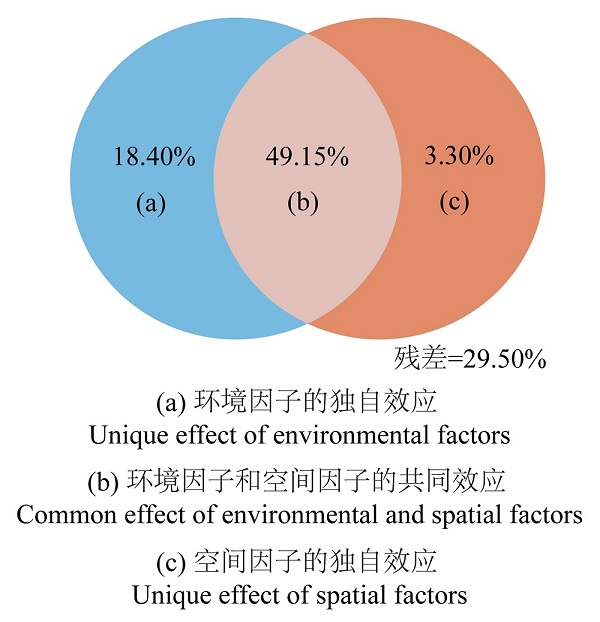
图2 27个国家级自然保护区苔藓植物地理成分与环境因子和空间因子的变差分解分析
Figure 2 Variation partitioning analysis of the geographical elements of bryophytes with environmental and spatial factors from 27 national nature reserves
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 单独效应 Individual effect/% | 独自效应 Unique effect/% |
|---|---|---|
| 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month | 16.27 | 1.49 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | 14.52 | 0.68 |
| 年均降水 Mean annual precipitation | 11.66 | — |
| 黏土占比 Clay percentage | 9.96 | 5.90 |
| 湿润指数 Moist index | 6.55 | — |
| 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month | 4.86 | — |
| 海拔 Elevation | 1.65 | 0.81 |
| 年均潜在蒸散量 Mean annual potential evapotranspiration | 1.42 | — |
| 年均太阳辐射 Mean annual solar radiation | 0.80 | — |
表3 27个国家级自然保护区苔藓植物地理成分与各环境因子的变差分解分析
Table 3 Variation partitioning analysis of the geographical elements of bryophytes with environmental factors from 27 national nature reserves
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 单独效应 Individual effect/% | 独自效应 Unique effect/% |
|---|---|---|
| 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month | 16.27 | 1.49 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | 14.52 | 0.68 |
| 年均降水 Mean annual precipitation | 11.66 | — |
| 黏土占比 Clay percentage | 9.96 | 5.90 |
| 湿润指数 Moist index | 6.55 | — |
| 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month | 4.86 | — |
| 海拔 Elevation | 1.65 | 0.81 |
| 年均潜在蒸散量 Mean annual potential evapotranspiration | 1.42 | — |
| 年均太阳辐射 Mean annual solar radiation | 0.80 | — |
| 地理成分 Geographical elements | Temp | Trop | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | ||
| EA | -0.372 | 0.056 | -0.112 | 0.577 | |
| AAO | -0.817 | 0.001 | 0.565 | 0.002 | |
表4 温带成分和热带成分与东亚成分和亚洲-澳大利亚-大洋洲成分间的pearson相关
Table 4 Pearson coefficients between Temperate elements, Tropical elements and East Asian elements, Asia-Australia-Oceania elements
| 地理成分 Geographical elements | Temp | Trop | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | ||
| EA | -0.372 | 0.056 | -0.112 | 0.577 | |
| AAO | -0.817 | 0.001 | 0.565 | 0.002 | |
| [1] |
ABAY G, GÜL E, URSAVAS S, et al., 2014. Substratum properties and mosses in semi-arid environments. A case study from north Turkey[J]. Cryptogamie Bryologie, 35(2): 181-196.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ANDERSON M J, CRIST T O, CHASE J M, et al., 2011. Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: a roadmap for the practicing ecologist[J]. Ecology Letters, 14(2): 19-28.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ASTORGA A, HEINO J, LUOTO M, et al., 2011. Freshwater biodiversity at regional extent: determinants of macroinvertebrate taxonomic richness inheadwater streams[J]. Ecography, 34(5): 705-713.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BLANCHET F G, LEGENDRE P, BORCARD D, 2008. Forward selection of explanatory variables[J]. Ecology, 89(9): 2623-2632.
PMID |
| [5] |
BOUFFORD D E, 1998. Eastern Asian-North American plant disjunctions: opportunities for further investigation[J]. Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy, 28(1): 49-61.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CAPINHA C, ESSL F, SEEBENS H, et al., 2015. The dispersal of alien species redefines biogeography in the Anthropocene[J]. Science, 348(6240): 1248-1251.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHAMIZO S, CANTÓN Y, MIRALLES I, et al., 2012. Biological soil crust development affects physicochemical characteristics of soil surface in semiarid ecosystems[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry. 49: 96-105.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN S B, SLIK J W F, GAO J, et al. 2015a, Latitudinal diversity gradients in bryophytes and woody plants: Roles of temperature and water availability[J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 53(6): 535-545.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CHEN S B, SLIK J W F, MAO L F, et al, 2015b. Spatial patterns and environmental correlates of bryophyte richness: sampling effort matters[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 24(3): 593-607.
DOI URL |
| [10] | GOFFINET B, SHAW A J, 2009. Bryophyte Biology[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 487-488. |
| [11] |
GÖTZENBERGER L, de BELLO F, BRÄTHEN K A, et al., 2012. Ecological assembly rules in plant communities—approaches, patterns and prospects[J]. Biological Reviews, 87(1): 111-127.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
HEWITT G M, 2000. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages[J]. Nature, 405(6789): 907-913.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KÖRNER C, 2007. The use of ‘altitude’ in ecological research[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22(11): 569-574.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LAI J S, ZOU Y, ZHANG J L et al., 2022. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 13(4): 782-788.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MA J Z, CHEN X, MALLIK A, et al., 2020. Environmental together with interspecific interactions determine bryophyte distribution in a protected mire of Northeast China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 8: 32.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MÖLS T, VELLAK K, VELLAK A, et al., 2013. Global gradients in moss and vascular plant diversity[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation 22(7): 1537-1551.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MUNOZ J, FELICISIMO A M, CABEZAS F, et al., 2004. Wind as a long-distance dispersal vehicle in the Southern Hemisphere[J]. Science, 304(5674): 1144-1147.
PMID |
| [18] |
NEKOLA J C, WHITE P S, 1999. The distance decay of similarity in biogeography and ecology[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 26(4): 867-878.
DOI URL |
| [19] | OKSANEN J, SIMPSON G L, BLANCHET F G, et al., 2022. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.6-2 [EB/OL]. [2022-05-09]. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf. |
| [20] |
PATIÑO J, VANDERPOOTEN A, 2018. Bryophyte Biogeography[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 37(2-3): 175-209.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
QIAN H, 1998. Large-scale biogeographic patterns of vascular plant richness in North America: An analysis at the generic level[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 25(5): 829-836.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
QIAN H, CHEN S B, 2016. Reinvestigation on species richness and environmental correlates of bryophytes at a regional scale in China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 9(6): 734-741.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
QIAO X J, LI Q X, JIANG Q H, et al., 2015. Beta diversity determinants in Badagongshan, a subtropical forest in central China[J]. Scientific Reports, 5(1): 17043.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SU D Y, YANG L X, SHI X, et al., 2021. Large-scale phylogenomic analyses reveal the monophyly of bryophytes and neoproterozoic origin of land plants[J]. Molecular biology and evolution, 38(8): 3332-3344.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
TONGNELLI M F, de ARELLANO P I R, MARQUET P A, 2008. How well do the existing and proposed reserve networks represent vertebrate species in Chile?[J]. Diversity and Distributions, 14(1): 148-158.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
TURETSKY M R, 2003. The role of bryophytes in carbon and nitrogen cycling[J]. The Bryologist, 106(3): 395-409.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WALTHER G R, POST E, CONVEY P, et al., 2002. Ecological responses to recent climate change[J]. Nature, 416(6879): 389-395.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
YU J, SHEN L, ZANG C, et al., 2019. Geographical, anthropogenic and climatic determinants of bryophyte species composition and richness in the Shengsi archipelago, East China Sea[J]. Journal of Bryology, 41(2): 107-120.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZANATTA F, ENGLER R, COLLART F, et al., 2020. Bryophytes are predicted to lag behind future climate change despite their high dispersal capacities[J]. Nature communications, 11: 5601.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
ZANATTA F, JAIRO P, LEBEAU F, et al., 2016. Measuring spore settling velocity for an improved assessment of dispersal rates in mosses[J]. Annals of Botany, 118(2): 197-206.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
ZHANG L, CORLETT R T, 2003. Phytogeography of Hong Kong bryophytes[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 30(9): 1329-1337.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHU H, 2016. Biogeographical evidences help revealing the origin of Hainan Island[J]. PLoS ONE 11(4): e0151941.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHU H, 2013. Geographical elements of seed plants suggest the boundary of the tropical zone in China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 386: 16-22.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 曹同, 郭水良, 高谦, 2000. 应用排序分析藓类植物分类群分布与气候因素的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 11(5): 680-686. |
| CAO T, GUO S L, GAO Q, 2000. Ordination analysis on relationship between bryophyte distribution and climatic factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 11(5): 680-686. | |
| [35] | 陈邦杰, 吴鹏程, 裘佩熹, 等, 1965. 黄山植物的研究: 苔藓、蕨类、种子植物的区系和地理[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社: 47-52. |
| CHEN B J, WU P C, QIU P X, et al., 1965. Study of plants in Huangshan Mountain: flora and geography of bryophytes, ferns, and seed plants[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: 47-52. | |
| [36] | 陈玮, 曲再春, 张粤, 2017. 辽宁白石砬子国家级自然保护区生物多样性[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁科学技术出版社: 125-143. |
| CHEN W, QU Z C, ZHANG Y, 2017. Biodiversity of Baishilazi National Nature Reserve, Liaoning Province[M]. Shengyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Publishing House: 125-143. | |
| [37] | 程丽媛, 2017. 浙江省清凉峰国家级自然保护区苔藓植物区系及地理分布研究上海[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学:61-94. |
| CHENG L Y, 2017. Study on flora and geographic distribution of bryophytes in Qingliangfeng National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province, China[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University:61-94. | |
| [38] | 冯建孟, 毛光权, 李珍贵, 2012a. 澜沧江流域 (云南段) 种子植物区系成分的纬度分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(12): 1928-1934. |
| FENG J M, MAO G Q, LI Z G, 2012a. Latitudinal patterns of floristic elements of seed plants in Lancang river in Yunnan, southwest China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(12): 1928-1934. | |
| [39] | 冯建孟, 徐成东, 2008. 植物区系平衡点及其生物地理意义[J]. 云南植物研究, 30(4): 400-404. |
|
FENG J M, XU C D, 2008. Floristic equilibrium point and its biogeographic significance[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 30(4): 400-404.
DOI URL |
|
| [40] | 冯建孟, 张钊, 南仁永, 2012b. 云南地区种子植物区系过渡性地理分布格局的群落尺度分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(1): 1-6. |
| FENG J M, ZHANG Z, NAN R Y, 2012b. Geographical patterns of flora transition of seed plants at community scale in Yunnan, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(1): 1-6. | |
| [41] | 韩博平, 李秋华, 徐玉萍, 等, 2022. 生物群落梯度分析方法的由来、发展及广义非相似性模拟方法与应用[J]. 贵州师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 40(2): 1-10, 132. |
| HAN B P, LI Q H, XU Y P, et al., 2022. Origin and development of gradient analysis for biological communities and the generalized dissimilarity modelling with its application[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 40(2): 1-10, 132. | |
| [42] | 何祖霞, 严岳鸿, 徐婧宇, 等, 2010. 江西齐云山自然保护区苔藓植物研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 18(1): 32-39. |
| HE Z X, YAN Y H, XU J Y, et al., 2010. Studies on the bryophtes of Qiyunshan Nature Reserve, Jiangxi[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 18(1): 32-39. | |
| [43] | 洪柳, 吴林, 牟利, 等, 2020. 木林子国家级自然保护区苔藓植物物种与区系研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 38(1): 68-76. |
| HONG L, WU L, MOU L, et al., 2020. Study on bryophyte species and flora in Mulinzi National Nature Reserve[J]. Plant Science Journal, 38(1): 68-76. | |
| [44] | 胡进耀, 2015. 四川小寨子沟国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社: 152-155. |
| HU J Y, 2015. A report of comprehensive survey on Xiaozhaizigou National Nature Reserve in Sichuan, China[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House: 152-155. | |
| [45] | 贾渝, 何思, 2013. 中国生物物种名录第1卷植物苔藓植物[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:1-417. |
| JIA Y, HE S, 2013. Species Catalogue of China Vol.1. Plants: Bryophytes[M]. Beijing: Science Press:1-417. | |
| [46] | 李粉霞, 2006. 佛坪国家自然保护区苔藓植物的物种及生态系统多样性[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. |
| LI F X, 2006. Species and ecosystem diversity of bryophyte in Foping Nature Reserve[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University. | |
| [47] |
李嵘, 孙航, 2017. 植物系统发育区系地理学研究: 以云南植物区系为例[J]. 生物多样性, 25(2): 195-203.
DOI |
|
LI R, SUN H, 2017. Phylofloristics: A case study from Yunnan, China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 25(2): 195-203.
DOI |
|
| [48] | 刘信中, 方福生, 2001. 江西武夷山自然保护区科学考察集[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社: 115-124. |
| LIU X Z, FANG F S, 2001. Scientific survey of the Wuyishan Nature Reserve in Jiangxi[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House: 115-124. | |
| [49] | 刘信中, 王琅, 2010. 江西省庐山自然保护区生物多样性考察与研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 529-533. |
| LI X Z, WANG L, 2010. Scientific survey and study of biodiversity on the Lushan Nature Reserve in Jiangxi Province[J]. Beijing: Science Press: 529-533. | |
| [50] | 刘信中, 肖忠优, 马建华, 2002. 江西九连山自然保护区科学考察集与森林生态系统系研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业出版社:166-171. |
| LIU X Z, XIAO Z Y, MA J H, 2002. Scientific survey and study on the forest ecosystem in Jiangxi Jiulianshan Nature Reserve[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House: 166-171. | |
| [51] |
刘艳, 皮春燕, 田尚,2016. 重庆大巴山国家级自然保护区苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 24(2): 244-247.
DOI |
|
LIU Y, PI C Y, TIAN S, 2016. Bryophyte biodiversity of the Dabashan National Nature Reserve in Chongqing[J]. Biodiversity Science, 24(2): 244-247.
DOI |
|
| [52] | 刘振生, 陈立杰, 2015. 内蒙古贺兰山国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告[M]. 银川: 宁夏人民出版社: 286-294. |
| LIU Z S, CHEN L J, 2015. A report of comprehensive survey on Helan Mountain National Nature Reserve in Inner Mongolia, China[M]. Yinchuan: Ningxia people Publishing House: 286-294. | |
| [53] | 马克平, 高贤明, 于顺利, 1995. 东灵山地区植物区系的基本特征与若干山区植物区系的关系[J]. 植物研究, 15(4): 501-515. |
| MA K P, GAO X M, YU S L, 1995. On the characteristics of the flora of Dongling Mountain area and its relationship with a number of other mountainous floras in China[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 15(4): 501-515. | |
| [54] | 买买提明·苏来曼, 赵建成, 索菲娅, 1999. 喀纳斯自然保护区苔藓植物区系[J]. 干旱区研究, 16(4): 19-24. |
| MAMTIMIN S, ZHAO J C, SOPHIA, 1999. A study of the bryoflora of the Kanas Nature Reserve, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 16(4): 19-24. | |
| [55] | 彭华, 1996. 无量山种子植物的区系平衡点[J]. 云南植物研究, 18(4): 385-397. |
| PENG H, 1996. The floristic equilibrium point of seed plants in Mt. Wuliangshan[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 18(4): 385-397. | |
| [56] |
覃海宁, 杨永, 董仕勇, 等, 2017. 中国高等植物受威胁物种名录[J]. 生物多样性, 25(7): 696-744.
DOI |
|
QIN H N, YANG Y, DONG S Y, et al., 2017. Threatened species list of China’s higher plants[J]. Biodiversity Science, 25(7): 696-744.
DOI URL |
|
| [57] | 任昭杰, 李林, 钟蓓, 等, 2014. 山东昆嵛山苔藓植物多样性及区系特征[J]. 植物科学学报, 32(4): 340-354. |
| REN Z J, LI L, ZHONG B, et al., 2014. Bryophyte diversity and florisitic characteristics of Mountain Kunyu, Shandong, China[J]. Plant Science Journal, 32(4): 340-354. | |
| [58] |
申琳, 于晶, 李丹丹, 等, 2019. 舟山群岛苔藓植物地理成分分析: 兼论苔藓植物地理成分的划分方法[J]. 植物研究, 39(6): 826-834
DOI |
|
SHEN L, YU J, LI D D, et al., 2019. Geographical elements of bryophytes recorded from Zhoushan Archipelago: discussion on methods of geographical element division of bryophytes[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 39(6): 826-834.
DOI |
|
| [59] |
沈泽昊, 杨明正, 冯建孟, 等, 2017. 中国高山植物区系地理格局与环境和空间因素的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 25(2): 182-194.
DOI |
|
SHEN Z H, YANG M Z, FENG J M, et al., 2017. Geographic patterns of alpine flora in China in relation to environmental and spatial factors[J]. Biodiversity Science, 25(2): 182-194.
DOI |
|
| [60] | 师雪芹, 王健, 2021. 安徽省苔藓植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 29(6): 798-804. |
|
SHI X Q, WANG J, 2021. Bryophyte checklist of Anhui Province, China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 29(6): 798-804.
DOI URL |
|
| [61] | 孙悦, 2011. 尖峰岭国家自然保护区苔藓植物物种多样性研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学:50-62. |
| SUN Y, 2011. Study on species diversity of bryophytes in Jianfengling Nature Reserve[D]. Haikou: Hainan University:50-62. | |
| [62] | 唐艳雪, 2014. 广西十万大山自然保护区苔藓植物区系及地理分布研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学: 60-75. |
| TANG Y X, 2014. Studies on flora and geographic distribution of bryophytes in Shiwandashan Natural Reserve, Guangxi Province, China[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University: 60-75. | |
| [63] | 田悦, 赵正武, 刘艳, 2022. 西藏东部高寒草甸苔藓植物群落数量分类与排序[J]. 生态学报, 42(2): 755-765. |
| TIAN Y, ZHAO Z W, LIU Y, 2022. Classification and ordination of bryophyte communities in alpine meadow of eastern Tibet[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(2): 755-765. | |
| [64] | 田晔林, 2010. 北京百花山自然保护区苔藓植物多样性研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| TIAN Y L, 2010. The biodiversity of bryophytes in Baihua Mountain Nature Reserve in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [65] | 王荷生, 1992. 植物区系地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:1-2. |
| WANG H S, 1992. Floristic Geography[M]. Beijing: Science Press:1-2. | |
| [66] | 王挺杨, 官飞荣, 周明, 等, 2015. 内蒙古额尔古纳国家自然保护区苔藓植物区系研究[J]. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 14(2): 183-190. |
| WANG T Y, GUAN F R, ZHOU M, et al., 2015. A floristic study on bryophytes of Eerguna National Nature Reserve in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 14(2): 183-190. | |
| [67] |
王伟, 辛利娟, 杜金鸿, 等, 2016. 自然保护地保护成效评估: 进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 24(10): 1177-1188.
DOI |
|
WANG W, XIN L J, DU J H, et al., 2016. Evaluating conservation effectiveness of protected areas: advances and new perspectives[J]. Biodiversity Science, 24(10): 1177-1188.
DOI |
|
| [68] | 王小明, 2011. 宁夏贺兰山国家自然保护区综合科学考察[M]. 银川: 阳光出版社: 290-301. |
| WANG X M, 2011. Comprehensive survey of Helan Mountain National Nature Reserve in Ningxia, China[M]. Yinchuan: Sunshine Press: 290-301. | |
| [69] | 吴鹏程, 1998. 苔藓植物生物学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 288-291. |
| WU P C, 1998. Bryological biology[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 288-291. | |
| [70] | 吴鹏程, 贾渝, 汪楣芝, 2001. 中国与北美苔藓植物区系关系的探讨[J]. 植物分类学报, 39(6): 526-539. |
| WU P C, JIA Y, WANG M Z, 2001. Phytogeographical relationships of the bryophytes between China and North America[J]. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 39(6): 526-539. | |
| [71] | 吴文英, 2012. 福建戴云山国家级自然保护区藓类植物区系研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 36-98. |
| WU W Y, 2012. Study on the moss flora of the Daiyunshan National Nature Reserve, Fujian Province[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 36-98. | |
| [72] | 吴征镒, 1991. 中国种子植物属的分布区类型[J]. 云南植物研究, 13(增刊IV): 1-139. |
| WU Z Y, 1991. The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 13(Suppl. IV): 1-139. | |
| [73] | 吴征镒, 孙航, 周浙昆, 等, 2010. 中国种子植物区系地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WU Z Y, SUN H, ZHOU Z K, et al., 2010. Floristic Geography of Seed Plants in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [74] | 吴征镒, 周浙昆, 孙航, 等, 2006. 种子植物分布区类型及其起源和分化[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社: 40-41. |
| WU Z Y, ZHOU Z K, SUN H, et al., 2006. The areal-types of seed plants and their origin and differentiation[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press: 40-41. | |
| [75] | 肖月娥, 2014. 东亚间断分布植物玉蝉花(Iris ensata)亲缘地理学及传粉互作对其后缘种群维持的作用[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 6-7. |
| XIAO Y E, 2014. Phylogeography of iris ensata (Iris daceae), a disjunct species in East Asia, and role of pollinators on the persistence of rear edge populations[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 6-7. | |
| [76] | 邢诗晨, 唐录艳, 戴尊, 等, 2022. 安徽石台县与青阳县苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 30(1): 1-8. |
| XING S C, TANG L Y, DAI Z, et al., 2022. Bryophyte diversity in Shitai County and Qingyang County, Anhui Province[J]. Biodiversity Science, 30(1): 1-8. | |
| [77] | 熊嘉武, 2017. 新疆天山西部山地综合科学考察[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社: 290-300. |
| XIONG J W, 2017. Comprehensive scientific investigation of the Western Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House: 290-300. | |
| [78] | 严雄梁, 2009. 阳际峰自然保护区苔藓植物分类及区系研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江林学院: 52-74. |
| YAN X L, 2009. The study on the bryoflora and its classification of Yangjifeng Nature Reserve[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Forestry University: 52-74. | |
| [79] | 杨海英, 2004. 祁连山苔藓植物分类及区系研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学: 60-96. |
| YANG H Y, 2004. A study on taxonomy and flora of bryophytes in Qilian Mountain[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University: 60-96. | |
| [80] | 杨丽琼, 2004. 云南屏边大围山自然保护区藓类植物区系研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 51-74. |
| YANG L Q, 2004. Moss flora of Daweishan Nature Reserve, Yunnan Pingbian County[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 51-74. | |
| [81] |
叶建飞, 陈之端, 刘冰, 等, 2012. 中国西南与台湾地区维管植物的间断分布格局及形成机制[J]. 生物多样性, 20(4): 482-494.
DOI |
|
YE J F, CHEN Z D, LIU B, et al., 2012. Disjunct distribution of vascular plants between southwestern area and Taiwan area in China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 20(4): 482-494.
DOI URL |
|
| [82] | 叶永忠, 瞿文元, 黄远超, 2002. 连康山自然保护区科学考察集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 72-85. |
| YE Y Z, QU W Y, HUANG Y C, 2002. A survey of Liankang Mountain Nature Reserve[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 72-85. | |
| [83] | 于晶, 曹同, 郭水良, 等, 2001. 医巫闾山自然保护区苔藓植物区系地理成分与地理分布特征研究[J]. 植物研究, 21(1): 38-41. |
| YU J, CAO T, GUO S L, et al., 2001. Floristics and geographical distribution of bryophytes in Yiwulu Mountain, Wilderness Area[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 21(1): 38-41. | |
| [84] | 喻理飞, 陈光平, 余登利, 2018. 贵州宽阔水国家级自然保护区生物多样性保护研究[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社:200-220. |
| YU L F, CHEN G P, YU D L, 2018, The biodiversity conservation in Kuankuanshui National Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House:200-220. | |
| [85] | 翟德逞, 2004. 云南大围山苔类植物区系及其常绿阔叶内苔藓植物生态分布的研究[D]. 上海: :华东师范大学: 50-63. |
| ZHAI D C, 2004. Study on the liverwort flora and ecological distribution of bryophytes in evergreen broadleaved forests of Daweishan Nature Reserve[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 50-63. | |
| [86] | 张二芳, 2008. 山西庞泉沟自然保护区苔藓植物区系研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学. |
| ZHANG E F, 2008. The study on the bryoflora of Pangquangou Nature Reserve of Shanxi Province[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University. | |
| [87] | 张宏达, 1980. 华夏植物区系的起源与发展[J]. 中山大学学报 (自然科学版), 19(1): 89-98. |
| ZHANG H D, 1980. Origin and development of flora in China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 19(1): 89-98. | |
| [88] | 张华海, 张旋, 2007. 雷公山国家级自然保护区生物多样性研究[M]. 贵阳: 贵州科技出版社. |
| ZHANG H H, ZHANG X, 2007. Study on biodiversity of Leigongshan National Nature Reserve[M]. Guiyang: Guizhou Science and Technology Publishing House. | |
| [89] | 张晓青, 2011. 福建戴云山自然保护区苔类和角苔类的物种多样性[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 58-112. |
| ZHANG X Q, 2011. Species diversity of liverworts and hornworts of Daiyunshan Nature Reserve, Fujian, China[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 58-112. | |
| [90] | 周徐平, 唐录艳, 夏红霞, 等, 2022. 六盘水娘娘山国家湿地公园的苔藓植物区系特点[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 30(1): 111-124. |
| ZHOU X P, TANG L Y, XIA H X, et al., 2022. Bryoflora characteristics in Niangniang Mountain National Wetland Park, Liupanshui, Guizhou[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 30(1): 111-124. |
| [1] | 李婷婷, 侯梦丹, 邓欣妍, 周徐平, 王顺莉, 黄丹, 曾芷若, 彭涛. 贵州习水国家级自然保护区4种植被类型树附生苔藓植物多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1556-1565. |
| [2] | 李聪, 吕晶花, 陆梅, 杨志东, 刘攀, 任玉连, 杜凡. 滇东南亚热带土壤细菌群落对植被垂直带变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| [3] | 董鑫, 郎嘉钰, 楚原梦冉, 赵姗姗, 张晋东, 白文科. 川金丝猴家域的季节性差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1342-1352. |
| [4] | 赵娜, 王俊博, 李少宁, 鲁绍伟, 徐晓天. 北京松山4种典型林分枯落物持水特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1139-1147. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
