生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2093-2099.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.016
茶丽娟1,2( ), 周丹丹1,2,*(
), 周丹丹1,2,*( ), 冯鸿娟1, 赵淑媛1, 冯凯萍1
), 冯鸿娟1, 赵淑媛1, 冯凯萍1
收稿日期:2021-04-22
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
通讯作者:
* 周丹丹,女,副教授。E-mail: 82066981@qq.com作者简介:茶丽娟(1987年生),女(彝族),实验师,博士研究生,主要研究方向为污染物环境行为。E-mail: 532064365@qq.com
基金资助:
CHA Lijuan1,2( ), ZHOU Dandan1,2,*(
), ZHOU Dandan1,2,*( ), FENG Hongjuan1, ZHAO Shuyuan1, FENG Kaiping1
), FENG Hongjuan1, ZHAO Shuyuan1, FENG Kaiping1
Received:2021-04-22
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
野生食用菌具有富集重金属的能力,据调查研究云南省的部分野生食用菌有重金属超标的情况,探讨野生食用菌对重金属的富集具有迫切意义。本文以鸡枞菌(Termitomyces albuminosus)和珊瑚菌(Ramaria botrytoides)为研究对象,采用ICP-MS测定鸡枞菌和珊瑚菌中Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb的含量,以及野生菌根际土壤和非根际土中重金属的总量和有效态含量。在此基础上,计算了两种野生食用菌根际与非根际土壤中重金属总量的比值,根际与非根际土壤中重金属有效态比值,以及鸡枞菌和珊瑚菌对土壤中重金属富集系数,还探讨了鸡枞菌、珊瑚菌重金属含量与根际土壤重金属总量的相关性。研究结果表明,(1)两种野生食用菌根际与非根际土壤中重金属总量的比值大于1。在鸡枞菌根际/非根际土壤中重金属含量比值高低顺序为:Cd>Pb>Zn>Cu,珊瑚菌根际/非根际土壤中重金属含量比值高低顺序为:Zn>Cd>Pb>Cu。(2)根际与非根际土壤中重金属有效态比值总体上大于1。由以上两点可见,鸡枞菌、珊瑚菌根系微环境有利于重金属元素(Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb)的富集。(3)鸡枞菌对Cd、Cu、Zn的BCF(Bioaccumulation factor,BCF)大于1,而珊瑚菌对Cd、Cu、Zn的BCF小于1。鸡枞菌和珊瑚菌对Cd、Cu和Zn的富集能力存在差异。鸡枞菌对重金属富集与根际土壤重金属含量无显著相关性,珊瑚菌对Cu的富集与根际土壤中的Cu呈显著正相关。对野生食用菌进行富集差异研究有利于合理利用云南野生食用菌资源,以及野生食用菌根际效应研究将为野生食用菌生长土壤的重金属环境风险评价提供依据。
中图分类号:
茶丽娟, 周丹丹, 冯鸿娟, 赵淑媛, 冯凯萍. 两种野生食用菌对土壤重金属的富集特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2093-2099.
CHA Lijuan, ZHOU Dandan, FENG Hongjuan, ZHAO Shuyuan, FENG Kaiping. Research on the Bioaccumulation Characteristics of Two Kinds of Wild Edible Fungi to Soil Heavy Metals[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2093-2099.
| 供试 土壤 Test soil | 野生食用菌 Wild edible Fungi | 采集地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | ||
| 1 | 鸡枞菌1 Termitomyces albuminosus | 100.1474°E | 25.0051°N | 1903±16 |
| 2 | 鸡枞菌2 Termitomyces albuminosus | 100.1463°E | 25.0103°N | 1895.92±16 |
| 3 | 鸡枞菌3 Termitomyces albuminosus | 100.1468°E | 25.0082°N | 1897.84±16 |
| 4 | 珊瑚菌1 Ramaria botrytoides | 100.1456°E | 25.0098°N | 1939.17±16 |
| 5 | 珊瑚菌2 Ramaria botrytoides | 100.1405°E | 25.0108°N | 1931.63±16 |
| 6 | 珊瑚菌3 Ramaria botrytoides | 100.1455°E | 25.112°N | 1938.25±12 |
表1 采样点位基本情况表
Table 1 Basic situation table of sampling points
| 供试 土壤 Test soil | 野生食用菌 Wild edible Fungi | 采集地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | ||
| 1 | 鸡枞菌1 Termitomyces albuminosus | 100.1474°E | 25.0051°N | 1903±16 |
| 2 | 鸡枞菌2 Termitomyces albuminosus | 100.1463°E | 25.0103°N | 1895.92±16 |
| 3 | 鸡枞菌3 Termitomyces albuminosus | 100.1468°E | 25.0082°N | 1897.84±16 |
| 4 | 珊瑚菌1 Ramaria botrytoides | 100.1456°E | 25.0098°N | 1939.17±16 |
| 5 | 珊瑚菌2 Ramaria botrytoides | 100.1405°E | 25.0108°N | 1931.63±16 |
| 6 | 珊瑚菌3 Ramaria botrytoides | 100.1455°E | 25.112°N | 1938.25±12 |
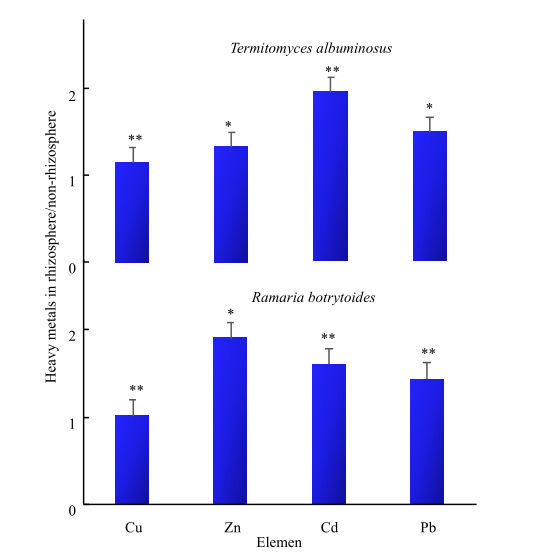
图2 两种野生食用菌对应根际土壤和非根际土壤中重金属总量的比值
Fig. 2 Two kinds of wild edible fungi correspond to the ratio of total heavy metals in rhizosphere soil and non-rhizosphere soil
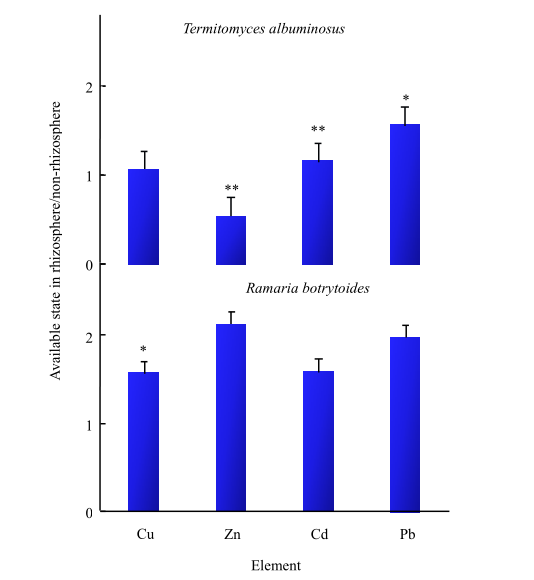
图3 两种野生食用菌对应根际土壤和非根际土壤中重金属有效态的比值
Fig. 3 Two kinds of wild edible fungi correspond to the ratio of available heavy metals in rhizosphere soil and non-rhizosphere soil
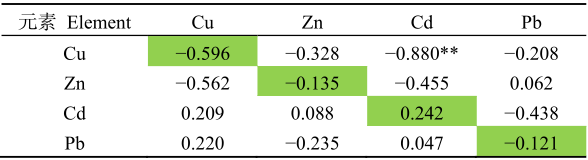 |
表2 鸡枞菌重金属含量与根际土壤重金属总量的相关系数
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between the content of heavy metals in Termitomyces albuminosus and the total amount of heavy metals in rhizosphere soil
 |
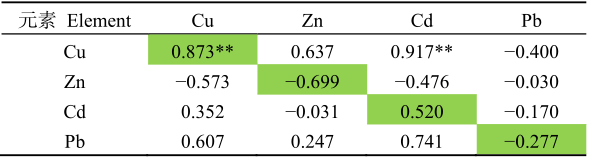 |
表3 珊瑚菌重金属含量与根际土壤重金属总量的相关系数
Table 3 Correlation coefficients between the content of heavy metals in Ramaria botrytoides and the total amount of heavy metals in rhizosphere soil
 |
| [1] |
BARCH R C, KLEMMEDSON J O, 1978. Shrubinduced spatial patterms of dry matter, nitrogen, and organic carbon[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42(5):804-809.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CUNNINNGHAM S D, 1995. Phytoremediation of contaminated soil[J]. Trend Biotechnol, 13(9):393-397.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FALANDYSZ J, DRYZAOWSKA A, SABA M, et al., 2014. Mercury in the fairy-ring of Gymnopus erythropus (Pers.) and Marasmius dryophilus (Bull.) P. Karst. mushrooms from the Gongga Mountain, Eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 104:18-22.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FERNÁNDEZ-FUEYO E, RUIZ-DUENAS F J, LOPEZ-LUCENDO M F, et al., 2016. A secretomic view of woody and nonwoody lignocellulose degradation by Pleurotus ostreatus[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, DOI: 10.1186/s13068-016-0462-9.
DOI |
| [5] |
GADD G M, 1993. Interactions of fungi with toxic metals[J]. New Phytologist, 124:25-60.
DOI URL |
| [6] | GARCÍA M A, ALONSO J, FERNÁNDEZ M I, et al., 1998. Lead content in edible wild mushrooms in northwest Spain as indicator of environmental contamination[J]. Architech Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 34(4):330-335. |
| [7] | HARLEY J L, SMITH S E, 1983. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. London [M]. New York: Acdemic Press: 2. |
| [8] |
JOHNSON R A, THOMAS R J, WOOD T G, et al., 1981. The inoculation of the fungus comb in newly founded colonies of some species of the Macrotermitinae (Isoptera) from Nigeria[J]. Journal of Natural History, 15(5):751-756.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
KOYYALAMUDI S R, JEONG S C, MANAVALAN S, et al., 2013. Micronutrient mineral content of the fruiting bodies of Australian cultivated Agaricus bisporus white button mushrooms[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 31(1):109-114.
DOI URL |
| [10] | MA B, ZHOU Z Y, ZHANG C P, et al., 2005. The character of phosphorus concentrations in rhizosphere soil of superxerophytic shrubs[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 14(3):106-110. |
| [11] |
MALINOWSKA E, SZEFER P, FALANDYSZ J, 2004. Metals bioaccumulation by bay bolete, Xerocomus badius: From selected sites in Poland[J]. Food Chemistry, 84(3):405-416.
DOI URL |
| [12] | MANDIC M L, GRGIC J, GRGIG Z, et al., 1992. The natural levels of aluminium, cadmium and lead in wild mush-rooms in Eastern Croatia[J]. Deutsche Lebensmittel-Rundschau, 88(3):76-77. |
| [13] | MOREL J L, MENCH M, GUCKERT A, 1986. Measurement of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ binding with mucilage exudatcs from maize (Zea mays L.) root[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils (2):29-34. |
| [14] |
MULLIGAN C N, YONG R N, GIBBS B F, et al., 1999. Metal removal from contaminated soil and sediments by the biosurfactant surfacetion[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(21):3812-3820.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
REDDY N G, PRASAD M N V, 1990. Heavy metal-binding proteins/ peptides: Occurrence, structure, synjournal and functions. A review[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 30(3):251-264.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
POSTA K, MARSCHNER H, RÖMHELD V, 1994. Manganese reduction in the rhizosphere of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal maize[J]. Mycorrhiza, 5:119-124.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG X M, ZHANG J, WU L H, et al., 2014. A mini-review of chemical composition and nutritional value of edible wild-grown mushroom from China[J]. Food Chemistry, 151:279-285.
DOI URL |
| [18] | ZHU F K, QU L, FAN W Q, et al., 2011. Assessment of heavy metals in some wild edible mushrooms collected from Yunnan province, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 179(1-4):191-199. |
| [19] | 茶丽娟, 赵淑媛, 冯鸿娟, 等, 2020. 野生菌生长土壤中重金属形态影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(12):2457-2464. |
| CHA L J, ZHAO S Y, FENG H J, et al., 2020. Study on influencing factors of heavy metal forms in wild fungi growth soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(12):2457-2464. | |
| [20] | 程扬, 刘子丹, 沈启斌, 等, 2018. 秸秆生物炭施用对玉米根际和非根际土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(10):1870-1877. |
| CHENG Y, LIU Z D, SHEN Q B, et al., 2018. The impact of straw biochar on corn rhizosphereic and non-rhizospheric soil microbial community structure[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(10):1870-1877. | |
| [21] | 窦晓兰, 2013. 珊瑚菌化学成分的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学:11. |
| DOU X L, 2013. Studies on the Compositions of Ramaria Botrytis[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology11. | |
| [22] | 高文慧, 郭宗昊, 高科, 等, 2021. 生物炭与炭基肥对大豆根际土壤细菌和真菌群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(1):205-212. |
| GAO W H, GUO Z H, GAO K, et al., 2021. Effects of biochar and biochar compound fertilizer on the soil bacterial and fungal community in the soybean rhizosphere[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(1):205-212. | |
| [23] | 顾济沧, 赵娟, 2010. 云南省土壤重金属污染现状及治理技术研究[J]. 环境科学刊, 29(5):68-71. |
| GU J C, ZHAO J, 2010. Status of Soil Contamination by Heavy Metals and Study on Remediation Techniques in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 29(5):68-71. | |
| [24] | 黄晨阳, 陈强, 赵永昌, 等, 2010. 云南省主要野生食用菌中重金属调查[J]. 中国农业科学, 43(6):1198-1203. |
| HUANG C Y, CHEN Q, ZHAO Y C, et al., 2010. Investigation on heavy metals of main wild edible mushrooms in Yunnan Province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 43(6):1198-1203. | |
| [25] | 黄瑞松, 陈广林, 吴祖军, 等, 2006. 广西产土垅大白蚁菌圃中几种重金属的含量测定[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 23(6):887-889. |
| HUANG R S, CHEN G L, WU Z J, et al., 2006. Determination of heavy metals in fungus gardens of Macrotermites annadalei in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Guangxi Medical University, 23(6):887-889. | |
| [26] | 雷敬敷, 杨德芬, 1990. 食用菌的重金属含量及食用菌对重金属富集作用的研究[J]. 中国食用菌, 9(6):14-17. |
| LEI J F, YANG D F, 1990. Research on the heavy metal content of edible fungi and the enrichment effect of edible fungi on heavy metals[J]. Edible Fungi of China, 9(6):14-17. | |
| [27] | 李丽, 蒋景龙, 季晓晖, 等, 2015. 野生食用菌中矿物质和重金属研究概况[J]. 食品工业科技, 36(16):395-400. |
| LI L, JIANG J L, JI X H, et al., 2015. A review of minerals and heavy metals in wild edible mushroom[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 36(16):395-400. | |
| [28] | 李泰辉, 宋斌, 2002. 中国食用牛肝菌的种类及其分布[J]. 食用菌学报, 9(2):22-30. |
| LI T H, SONG B, 2002. Species and distribution of Chinese edible boletus[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 9(2):22-30. | |
| [29] | 李艳, 谭文峰, 陈义, 等, 2018. 酶/蛋白质与土壤组分界面作用的研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(2):205-214. |
| LI Y, TAN W F, CHEN Y, et al., 2018. Advancement in the research of enzyme binding on the interfaces of soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(2):205-214. | |
| [30] | 刘剑飞, 胡留杰, 廖敦秀, 等, 2011. 食用菌生物修复重金属污染研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(2):543-548. |
| LIU J F, HU L J, LIAO D X, et al., 2011. Bioremediation of heavy metal pollution by edible fungi: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(2):543-548. | |
| [31] | 刘京伟, 李香真, 姚敏杰, 2020. 植物根际微生物群落构建的研究进展[EB/OL]. 微生物学报, https://doi.org/10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20200154. |
| LIU J W, LI X Z, YAO M J, 2020. Research Progress on Assembly of plant rhizosphere microbial community [EB/OL]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, https://doi.org/10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20200154. | |
| [32] | 刘朋虎, 雷锦桂, 王义祥, 等, 2017. 食用菌富集重金属主要特征与相关机制研究进展[J]. 热带作物学报, 38(12):2407-2414. |
| LIU P H, LEI J G, WANG Y X, et al., 2017. Advances in Research on Characteristics and Related Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Enrichment by Edible Fungi[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 38(12):2407-2414. | |
| [33] | 刘瑞霞, 汤鸿霄, 劳伟雄, 2002. 重金属的生物吸附机理及吸附平衡模式研究[J]. 化学进展, 14(2):87-92. |
| LIU R X, TANG H X, LAO W X, 2002. Advances in Biosorption Mechanism and Equilibrium Modeling for Heavy Metals on Biomaterials[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 14(2):87-92. | |
| [34] | 解楠, 冷桃花, 刘丁, 等, 2012. ICP-MS测定食用菌中重金属含量的研究[J]. 食品工业, 33(6):122-124. |
| XIE N, LENG T H, LIU D, et al., 2012. Determination of Heavy Metal Elements in Edible Mushrooms by ICP-MS[J]. Food Industry, 33(6):122-124. | |
| [35] | 邢增涛, 王晨光, 2000. 食 (药) 用菌中重金属的研究进展[J]. 食用菌学报, 7(2):58-64. |
| XING Z T, WANG C G, 2000. The progress in the research of the heavy metal elements contained in edible fungi[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 7(2):58-64. | |
| [36] | 徐丹先, 林佶, 万玉萍, 等, 2011. 云南省常见野生食用菌镉含量调查分析[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 21(3):705-706. |
| XU D X, LIN J, WAN Y P, et al., 2011. Detection and analysis of cadmium content in common wild edible fungi in Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 21(3):705-706. | |
| [37] | 徐柯, 2011. 矿质元素对平菇生理特性的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学: 3-6. |
| XU K, 2011. The effect of mineral elements on the physiological characteristics of Pleurotus ostreatus[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University: 3-6. | |
| [38] | 阎晓明, 何金柱, 2002. 重金属污染土壤的微生物修复机理及研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 30(6):877-879. |
| YAN X M, HE J Z, 2002. The mechanism and research progress of microbial remediation of soil contaminated by heavy metals[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 30(6):877-879. | |
| [39] | 杨天伟, 张霁, 李涛, 等, 2016. 云南野生食用牛肝菌中镉含量测定及食用安全评估[J]. 食品工业科技, 37(15):354-359. |
| YANG T W, ZHANG J, LI T, et al., 2016. Determination of content of cadmium and health risk assessment in wild-grown bolete mushrooms from Yunnan province[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 37(15):354-359. | |
| [40] | 袁静, 2012. 微波消解-ICP-MS测定土壤和底泥中的12种金属元素[J]. 中国环境监测, 28(5):96-98. |
| YUAN J, 2012. Determination of 12 Metals in Soil and Sediment by Microwave Digestion and ICP-MS[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 28(5):96-98. | |
| [41] | 张晓柠, 兰进, 2006. 食药用菌重金属富集机理及应用研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药, 17(12):2593-2594. |
| ZHANG X N, LAN J, 2006. Research progress on the enrichment mechanism and application of heavy metals in edible and medicinal fungi[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 17(12):2593-2594. | |
| [42] | 张玉金, 2012. 云南鸡枞菌与共生白蚁的系统发育和协同演化关系研究[D]. 昆明: 云南农业大学. |
| ZHANG Y J[D]. 2012. Molecular phylogeny and coevolution between Termitomcyes and fungus-growing termites in Yunnan[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Agricultural University | |
| [43] | 郑航, 2017. 云南省野生食用菌产业发展研究[D]. 昆明: 云南农业大学: 9. |
| ZHENG H, 2017. A Study on the Development of Wild Edible Fungi Industry in Yunnan Province[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Agricultural University:9. |
| [1] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [2] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [3] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [4] | 刘娣, 苏超, 张红, 秦冠宇. 典型煤炭产业聚集区土壤重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 391-399. |
| [5] | 他维媛, 康桢, 孟昭君, 金盛华, 杨幸, 郭龙飞, 赵东旭, 张馨. 秦岭典型停产关闭锌冶炼企业场地土壤重金属污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1513-1521. |
| [6] | 朱平, 崔姗姗, 李占彬, 朱雪铜, 何锦林, 谭红. 大气降水对贵州喀斯特地区高背景值土壤镉的释放影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2213-2222. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 129
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 213
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
