Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1627-1633.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.009
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
KONG Pan( ), XIA Sujing, ZHANG Haiwei, ZHU Jianqiang*(
), XIA Sujing, ZHANG Haiwei, ZHU Jianqiang*( )
)
Received:2021-05-19
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
Contact:
ZHU Jianqiang
通讯作者:
朱建强
作者简介:孔盼(1994年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为作物栽培与耕作。E-mail: 1006282958@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
KONG Pan, XIA Sujing, ZHANG Haiwei, ZHU Jianqiang. Effects of Tillage Methods on Ammonia Volatilization of Early Season Rice-ratooning Rice Fields[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1627-1633.
孔盼, 夏苏敬, 张海维, 朱建强. 耕作方式对早稻-再生稻稻田氨挥发的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1627-1633.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.009
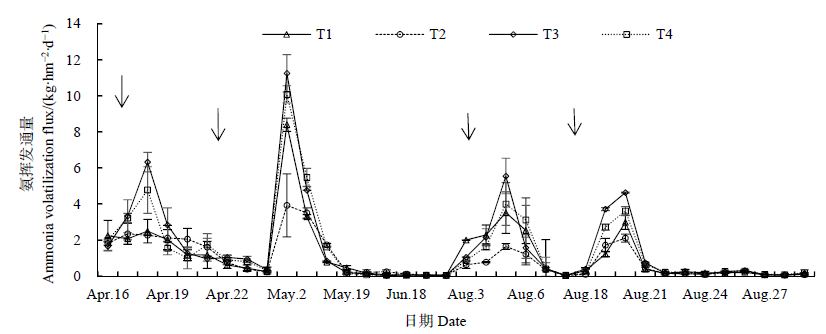
Fig. 2 Seasonal variation of ammonia volatilization flux in paddy fields under different tillage methods The downward arrows in the figure indicate the dates of application of basal fertilizer, tillering fertilizer, sprout accelerating fertilizer and seedling raising fertilizer in the field
| 处理 Treatment | 早稻施入基肥后2天 2 days after applying basal fertilizer to early rice | 早稻施入分蘖期后3天 3 days after applying tillering fertilizer to early rice | 再生稻施入促芽肥后2天 2 days after applying germination promoting fertilizer to ratooning rice | 再生稻施入提苗肥后2天 2 days after applying seedling raising fertilizer to ratooning rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 2.34±0.58c | 8.40±1.75b | 3.52±0.90abc | 2.98±0.07bc |
| T2 | 2.26±0.75c | 3.92±0.37c | 2.30±0.39c | 2.10±0.18c |
| T3 | 6.32±0.92a | 11.25±0.48a | 5.55±1.19a | 4.63±0.89a |
| T4 | 4.77±0.25b | 10.08±1.04ab | 4.00±0.59ab | 3.61±0.61ab |
Table 1 Peak value of ammonia volatilization flux after fertilization under different tillage methods kg∙hm-2∙d-1
| 处理 Treatment | 早稻施入基肥后2天 2 days after applying basal fertilizer to early rice | 早稻施入分蘖期后3天 3 days after applying tillering fertilizer to early rice | 再生稻施入促芽肥后2天 2 days after applying germination promoting fertilizer to ratooning rice | 再生稻施入提苗肥后2天 2 days after applying seedling raising fertilizer to ratooning rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 2.34±0.58c | 8.40±1.75b | 3.52±0.90abc | 2.98±0.07bc |
| T2 | 2.26±0.75c | 3.92±0.37c | 2.30±0.39c | 2.10±0.18c |
| T3 | 6.32±0.92a | 11.25±0.48a | 5.55±1.19a | 4.63±0.89a |
| T4 | 4.77±0.25b | 10.08±1.04ab | 4.00±0.59ab | 3.61±0.61ab |
| 处理 Treatment | 早稻季 In early rice season | 再生稻 In ratooning rice season | 全生育期 Whole growth period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基肥期 Base fertilizer period | 分蘖肥期 Tillering fertilizer period | 小计 Sub-total | 促芽肥期 Germination-promoting fertilizer period | 提苗肥期 Seedling raising fertilizer period | 小计 Sub-total | ||
| T1 | 13.45±0.12b | 12.04±2.33a | 25.49±2.44b | 10.38±4.85ab | 4.54±0.08bc | 14.92±4.82ab | 40.41±6.36b |
| T2 | 12.06±0.46b | 7.21±0.51b | 19.27±0.08c | 5.86±0.82b | 3.83±0.31c | 9.69±1.13b | 28.96±1.24c |
| T3 | 19.18±1.71a | 14.69±0.82a | 33.87±0.92a | 13.89±1.77a | 6.55±0.71a | 20.44±1.18a | 54.31±2.62a |
| T4 | 18.32±1.53a | 13.50±1.44a | 31.82±0.63a | 12.08±1.10a | 5.48±0.79ab | 17.56±1.79a | 49.38±3.74a |
Table 2 Cumulative volatilization of ammonia in paddy field after fertilization under different tillage methods kg∙hm-2
| 处理 Treatment | 早稻季 In early rice season | 再生稻 In ratooning rice season | 全生育期 Whole growth period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基肥期 Base fertilizer period | 分蘖肥期 Tillering fertilizer period | 小计 Sub-total | 促芽肥期 Germination-promoting fertilizer period | 提苗肥期 Seedling raising fertilizer period | 小计 Sub-total | ||
| T1 | 13.45±0.12b | 12.04±2.33a | 25.49±2.44b | 10.38±4.85ab | 4.54±0.08bc | 14.92±4.82ab | 40.41±6.36b |
| T2 | 12.06±0.46b | 7.21±0.51b | 19.27±0.08c | 5.86±0.82b | 3.83±0.31c | 9.69±1.13b | 28.96±1.24c |
| T3 | 19.18±1.71a | 14.69±0.82a | 33.87±0.92a | 13.89±1.77a | 6.55±0.71a | 20.44±1.18a | 54.31±2.62a |
| T4 | 18.32±1.53a | 13.50±1.44a | 31.82±0.63a | 12.08±1.10a | 5.48±0.79ab | 17.56±1.79a | 49.38±3.74a |
| 处理 Treatment | 早稻施入基肥后2天 2 days after applying basal fertilizer to early rice | 早稻施入分蘖期后3天 3 days after applying tillering fertilizer to early rice | 再生稻施入促芽肥后2天 2 days after applying germination promoting fertilizer to ratooning rice | 再生稻施入提苗肥后2天 2 days after applying seedling raising fertilizer to ratooning rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 26.31±0.71b | 31.24±3.74b | 41.37±5.53bc | 42.45±2.74b |
| T2 | 22.54±2.59b | 18.83±1.17c | 39.23±2.09c | 33.02±1.51c |
| T3 | 36.51±0.51a | 51.33±4.29a | 56.77±4.11a | 52.14±1.51a |
| T4 | 33.05±2.17a | 45.54±7.61a | 48.85±3.21ab | 46.39±3.06b |
Table 3 Peak value of NH4+-N in field water after fertilization under different tillage methods mg∙mL-1
| 处理 Treatment | 早稻施入基肥后2天 2 days after applying basal fertilizer to early rice | 早稻施入分蘖期后3天 3 days after applying tillering fertilizer to early rice | 再生稻施入促芽肥后2天 2 days after applying germination promoting fertilizer to ratooning rice | 再生稻施入提苗肥后2天 2 days after applying seedling raising fertilizer to ratooning rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 26.31±0.71b | 31.24±3.74b | 41.37±5.53bc | 42.45±2.74b |
| T2 | 22.54±2.59b | 18.83±1.17c | 39.23±2.09c | 33.02±1.51c |
| T3 | 36.51±0.51a | 51.33±4.29a | 56.77±4.11a | 52.14±1.51a |
| T4 | 33.05±2.17a | 45.54±7.61a | 48.85±3.21ab | 46.39±3.06b |
| 生长季 Growing season | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/ (kg∙hm-2) | 氮肥偏生产力 Partial productivity of nitrogen fertilizer/(kg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | T1 | 6800.00±529.15ab | 43.31±2.75ab |
| T2 | 7533.33±1006.64a | 47.98±5.24a | |
| T3 | 4833.33±208.17c | 30.79±1.08c | |
| T4 | 5200.00±137.07bc | 33.12±8.51bc | |
| 再生稻 Regenerated rice | T1 | 3533.33±1006.64a | 28.45±6.62a |
| T2 | 3800.00±1249.00a | 30.60±8.21a | |
| T3 | 2866.67±503.32a | 18.79±3.31a | |
| T4 | 3466.67±611.01a | 27.91±4.02a |
Table 4 Rice yield and partial productivity of nitrogen fertilizer under different tilliage methods
| 生长季 Growing season | 处理 Treatment | 产量 Yield/ (kg∙hm-2) | 氮肥偏生产力 Partial productivity of nitrogen fertilizer/(kg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | T1 | 6800.00±529.15ab | 43.31±2.75ab |
| T2 | 7533.33±1006.64a | 47.98±5.24a | |
| T3 | 4833.33±208.17c | 30.79±1.08c | |
| T4 | 5200.00±137.07bc | 33.12±8.51bc | |
| 再生稻 Regenerated rice | T1 | 3533.33±1006.64a | 28.45±6.62a |
| T2 | 3800.00±1249.00a | 30.60±8.21a | |
| T3 | 2866.67±503.32a | 18.79±3.31a | |
| T4 | 3466.67±611.01a | 27.91±4.02a |
| [1] | FAN X H, SONG Y S, LIN D X, 2006. Ammonia volatilization losses and 15N balance from urea applied to rice on a paddy soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 18(2): 299-303. |
| [2] | LIANG X Q, ZHANG H F, HE M M, et al., 2016. No-tillage effects on grain yield, N use efficiency, and nutrient runoff losses in paddy fields[J]. Environ-mental Science and Pollution Research, 23(21): 21451-21459. |
| [3] | MKHABELA M S, MADANI R A, GONDON D, et al., 2007. Gaseous and leaching nitrogen losses from no-tillage and conventional tillage systems following surface application of cattle manure[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 98(2): 187-199. |
| [4] | PHILPPE R, DENIS A, ANGERS, et al., 2008. Ammonia volatilization following surface application of urea to tilled and no-till soils: A laboratory comparison[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 103(2): 310-315. |
| [5] | ZHANG H, YANG Z L, LUO L G, et al., 2011. Study on the ammonia volatilization from paddy field in irrigation area of the Yellow River[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 17(5): 1131-1139. |
| [6] | 曹凑贵, 李成芳, 寇志奎, 等, 2010. 不同类型氮肥和耕作方式对稻田土壤氨挥发的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 32(5): 881-886. |
| CAO C G, LI C F, KOU Z K, et al., 2010. Effects of N source and tillage on NH3 volatilization from paddy soils[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis, 32(5): 881-886. | |
| [7] | 邓美华, 尹斌, 张绍林, 等, 2006. 不同施氮量和施氮方式对稻田氨挥发损失的影响[J]. 土壤, 38(3): 263-269. |
| DENG M H, YIN B, ZHANG S L, et al., 2006. Effects of rate and method of N application on ammonia volatilization in paddy fields[J]. Soils, 38(3): 263-269. | |
| [8] | 冯国禄, 杨仁斌, 2011. 耕作模式和滞水时间对稻田中氮磷动态变化的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 30(5): 917-924. |
| FENG G L, YANG R B, 2011. Effect of tillage models and water logging time on dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorus in paddy field[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(5): 917-924. | |
| [9] | 葛畅, 刘慧琳, 张世文, 等, 2018. 耕作方式和土壤类型对皖北旱作农田土壤紧实度的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(5): 89-94. |
| GE C, LIU H L, ZHANG S W, et al., 2018. Effects of tillage methods and soil types on characteristics of soil compaction in rainfed farmland in northern Anhui province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(5): 89-94. | |
| [10] | 黄进宝, 范晓晖, 张绍林. 2006. 太湖地区铁渗水耕人为土稻季上氮肥的氨挥发[J]. 土壤学报, (5):786-792. |
| HUANG J B, FAN X H, ZHANG S L, 2006. Ammonia volatilization from nttrogen fertilzer in the rice field of Fe-leachii-stagnic anthrosols in the Taihu Lake region[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, (5): 786-792. | |
| [11] | 刘世平, 陈文林, 聂新涛, 等, 2007. 麦稻两熟地区不同埋深对还田秸秆腐解进程的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 13(6): 1049-1053. |
| LIU S P, CHEN W L, NIE X T, et al., 2007. Effect of embedding depth on decomposition course of crop residues in rice-wheat system[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 13(6): 1049-1053. | |
| [12] | 刘骁蒨, 涂仕华, 孙锡发, 等, 2013. 秸秆还田与施肥对稻田土壤微生物生物量及固氮菌群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(17): 5210-5218. |
|
LIU X Q, TU S H, SUN X F, et al., 2013. Effect of different fertilizer combinations and straw return on microbial biomass and nitrogen-fixing bacteria community in a paddy soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(17): 5210-5218.
DOI URL |
|
| [13] | 马玉华, 刘兵, 张枝盛, 等, 2013. 免耕稻田氮肥运筹对土壤NH3挥发及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(18): 5556-5564. |
|
MA Y H, LIU B, ZHANG Z S, et al., 2013. Effects of nitrogen management on NH3 volatilization and nitrogen use efficiency under no-tillage paddy fields[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(18): 5556-5564.
DOI URL |
|
| [14] | 区惠平, 周柳强, 黄金生, 等, 2013. 不同施氮量对稻田氨挥发损失的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 44(11): 1851-1855. |
| QU H P, ZHOU L Q, HUANG J S, et al., 2013. Nitrogen application impact on ammonia volatilization in paddy field[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 44(11): 1851-1855. | |
| [15] | 宋勇生, 范晓晖, 2003. 稻田氨挥发研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 12(2): 240-244. |
| SONG Y S, FAN X H, 2003. Summanry of research on ammonia volatilization in paddy soil[J]. Ecology and Environmnet, 12(2): 240-244. | |
| [16] | 王朝辉, 刘学军, 巨晓棠, 等, 2002. 田间土壤氨挥发的原位测定通气法[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 8(2): 205-209. |
| WANG Z H, LIU X J, XIAO X P, et al., 2002. Field in situ determination of ammonia volatilization from soil: Venting method[J]. Plant Natrition and Fertilizen Science, 8(2): 205-209. | |
| [17] | 王大鹏, 杜玉赫, 罗雪华, 等, 2018. 橡胶林下砖红壤不同氮肥处理氨挥发特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(4): 685-691. |
| WANG D P, DU Y H, LUO X H, et al., 2018. Characteristics of ammonia volatilization under different nitrogen managements in red latosol of rubber plantation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(4): 685-691. | |
| [18] | 汪军, 王德建, 张刚, 等, 2013. 麦秸全量还田下太湖地区两种典型水稻土稻季氨挥发特性比较[J]. 环境科学, 34(1): 27-33. |
|
WANG J, WANG D J, ZHANG G, et al., 2013. Comparing the ammonia volatilization characteristic of two typical paddy soil with total wheat straw returning in Taihu Lake region[J]. Environmental Science, 34(1): 27-33.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] | 姚秀娟, 2007. 翻耕与旋耕作业对水稻生产的影响[J]. 现代化农业 (7): 27-28. |
| YAO X J, 2007. Effect of turning and rotary tillage on rice production[J]. Modernizing Agriculture (7): 27-28. | |
| [20] | 张大伟, 刘建, 王波, 等, 2009. 连续两年秸秆还田与不同耕作方式对直播稻田土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 江西农业学报, 21(8): 53-56. |
| ZHANG D W, LIU J, WANG B, et al., 2009. Effects of straw-returning and different tillage modes on physical and chemical properties of direct seeding paddy soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 21(8): 53-56. | |
| [21] | 朱兆良, 2000. 农田中氮肥的损失与对策[J]. 土壤与环境, 9(1): 1-6. |
| ZHANG Z L, 2000. Loss of fertilizer n from plants-soil system and the strategies and techniques for its reduction[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 9(1): 1-6. | |
| [22] | 张向前, 杨文飞, 徐云姬, 2019. 中国主要耕作方式对旱地土壤结构及养分和微生态环境影响的研究综述[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(12): 2464-2472. |
| ZHANG X Q, YANG W F, XU Y J, 2019. Effects of main tillage methods on soil structure, nutrients and micro-ecological environment of upland in China: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(12): 2464-2472. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
