生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 1096-1106.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.07.011
谢杰1,2( ), 陈院华1, 徐昌旭1, 杨涛1, 李建国1, 董爱琴1,*(
), 陈院华1, 徐昌旭1, 杨涛1, 李建国1, 董爱琴1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-08
出版日期:2024-07-18
发布日期:2024-09-04
通讯作者:
*董爱琴。E-mail: aiqin.dong@outlook.com作者简介:谢杰(1983年生),男,副研究员,博士,主要从事受污染耕地安全利用研究。E-mail: jerous.xie@outlook.com
基金资助:
XIE Jie1,2( ), CHEN Yuanhua1, XU Changxu1, YANG Tao1, LI Jianguo1, DONG Aiqin1,*(
), CHEN Yuanhua1, XU Changxu1, YANG Tao1, LI Jianguo1, DONG Aiqin1,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-08
Online:2024-07-18
Published:2024-09-04
摘要:
长期种植和翻压紫云英能够显著提高土壤中有机质(SOM)和水溶性有机物(DOM)的含量,影响土壤颗粒对重金属镉(Cd)的吸附行为和Cd在土壤中的形态,了解该条件下Cd在不同土层中的特征对紫云英的进一步推广种植具有重要意义。以余江区(YJ)、南昌县(NC)、丰城市(FC)3地长期种植和翻压紫云英处理(F+M)和化肥处理(F)的定位试验点为研究对象,测试了不同层次土壤中SOM、水溶性有机碳(DOC)含量、Cd总量和形态、DOM三维荧光,以期探明紫云英长期还田模式下不同土层中DOM成分的差异及其对Cd含量和形态影响。结果显示,NC和FC试验点F+M处理耕作层土壤(0-20cm)中SOM的含量显著高于F处理,分别提高16.8%和10.5%。同一土层中土壤Cd活性呈现F+M处理>F处理的趋势。紫云英DOM主要在耕作层和中层(20-40 cm)土壤中迁移,YJ、NC、FC试验点中,F+M处理耕作层土壤中DOC含量比F处理分别提高17.0%、58.1%和33.7%,中层土壤中DOC含量分别提高43.0%、36.7%和11.2%。种植和翻压紫云英降低了DOM中类蛋白质组分的占比,增加了类腐殖质组分的占比,耕作层、中层和深层土壤(40-60 cm)中,3个试验点F处理DOM中类蛋白质的平均占比分别为7.34%、16.7%、23.9%,占比分别是F+M处理的1.26、1.92和1.54倍。类蛋白质组分的深层迁移能力大于类腐殖质组分。逐步回归分析表明,有生物活性的Cd形态占比与土壤SOM、类色氨酸含量存在负相关关系,与类富里酸含量存在正相关关系,其系数分别为−2.170、−0.760和0.239。常年种植和翻压紫云英通过影响土壤SOM总量以及DOM组分对土壤Cd表现出一定的活化潜力。
中图分类号:
谢杰, 陈院华, 徐昌旭, 杨涛, 李建国, 董爱琴. 紫云英长期还田对稻田土壤DOM和Cd形态影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1096-1106.
XIE Jie, CHEN Yuanhua, XU Changxu, YANG Tao, LI Jianguo, DONG Aiqin. Effects of Long-term Returning of Astragalus sinicus L. on Content and Forms of DOM and Cd in Paddy Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(7): 1096-1106.
| 试验点 | F处理 | F+M处理 |
|---|---|---|
| YJ | 早稻: 尿素330 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾190 kg∙hm−2 晚稻: 尿素390 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 | 早稻: 翻压紫云英 (22500 kg∙hm−2), 化肥减为F处理的60% 晚稻: 同F处理 |
| NC | 早稻: 尿素330 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙375 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 晚稻: 尿素390 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙375 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 | 早稻: 翻压紫云英 (22500 kg∙hm−2), 化肥同F处理 晚稻: 同F处理 |
| FC | 早稻: 尿素330 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾190 kg∙hm−2 晚稻: 尿素390 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 | 早稻: 翻压紫云英 (22500 kg∙hm−2), 化肥减为F处理的60% 晚稻: 同F处理 |
表1 各定位试验点不同处理施肥详细信息
Table 1 Application of fertilizer in different treatments at each experimental site
| 试验点 | F处理 | F+M处理 |
|---|---|---|
| YJ | 早稻: 尿素330 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾190 kg∙hm−2 晚稻: 尿素390 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 | 早稻: 翻压紫云英 (22500 kg∙hm−2), 化肥减为F处理的60% 晚稻: 同F处理 |
| NC | 早稻: 尿素330 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙375 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 晚稻: 尿素390 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙375 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 | 早稻: 翻压紫云英 (22500 kg∙hm−2), 化肥同F处理 晚稻: 同F处理 |
| FC | 早稻: 尿素330 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾190 kg∙hm−2 晚稻: 尿素390 kg∙hm−2, 过磷酸钙470 kg∙hm−2, 氯化钾240 kg∙hm−2 | 早稻: 翻压紫云英 (22500 kg∙hm−2), 化肥减为F处理的60% 晚稻: 同F处理 |
| 试验点 | 处理 | w(OM)/(g∙kg−1) | w(DOC)/(mg∙kg−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | |||
| YJ | F | 28.4±1.19c | 12.8±2.88c | 5.31±1.15b | 310.1±10.8d | 121.1±17.6c | 75.3±13.5d | |
| F+M | 30.8±2.15c | 15.9±2.58bc | 5.72±0.63b | 362.9±16.6c | 173.1±24.0ab | 77.7±9.0d | ||
| NC | F | 36.9±1.69b | 17.1±2.40ab | 9.06±0.86a | 259.7±18.5e | 151.3±16.2bc | 108.8±11.2ab | |
| F+M | 43.1±3.03a | 21.0±2.47a | 10.6±1.65a | 410.8±11.7b | 206.9±17.8a | 118.8±15.6a | ||
| FC | F | 34.4±4.30c | 7.62±1.10d | 6.00±0.66b | 436.3±22.2b | 121.3±16.9c | 88.3±8.0bc | |
| F+M | 38.0±2.59b | 7.80±1.85d | 6.93±1.50b | 583.4±39.7a | 134.9±33.5bc | 95.2±6.2bc | ||
表2 不同深度处理土层中有机质和DOC含量
Table 2 Organic matter and DOC content in different soil layers between different treatments
| 试验点 | 处理 | w(OM)/(g∙kg−1) | w(DOC)/(mg∙kg−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | |||
| YJ | F | 28.4±1.19c | 12.8±2.88c | 5.31±1.15b | 310.1±10.8d | 121.1±17.6c | 75.3±13.5d | |
| F+M | 30.8±2.15c | 15.9±2.58bc | 5.72±0.63b | 362.9±16.6c | 173.1±24.0ab | 77.7±9.0d | ||
| NC | F | 36.9±1.69b | 17.1±2.40ab | 9.06±0.86a | 259.7±18.5e | 151.3±16.2bc | 108.8±11.2ab | |
| F+M | 43.1±3.03a | 21.0±2.47a | 10.6±1.65a | 410.8±11.7b | 206.9±17.8a | 118.8±15.6a | ||
| FC | F | 34.4±4.30c | 7.62±1.10d | 6.00±0.66b | 436.3±22.2b | 121.3±16.9c | 88.3±8.0bc | |
| F+M | 38.0±2.59b | 7.80±1.85d | 6.93±1.50b | 583.4±39.7a | 134.9±33.5bc | 95.2±6.2bc | ||
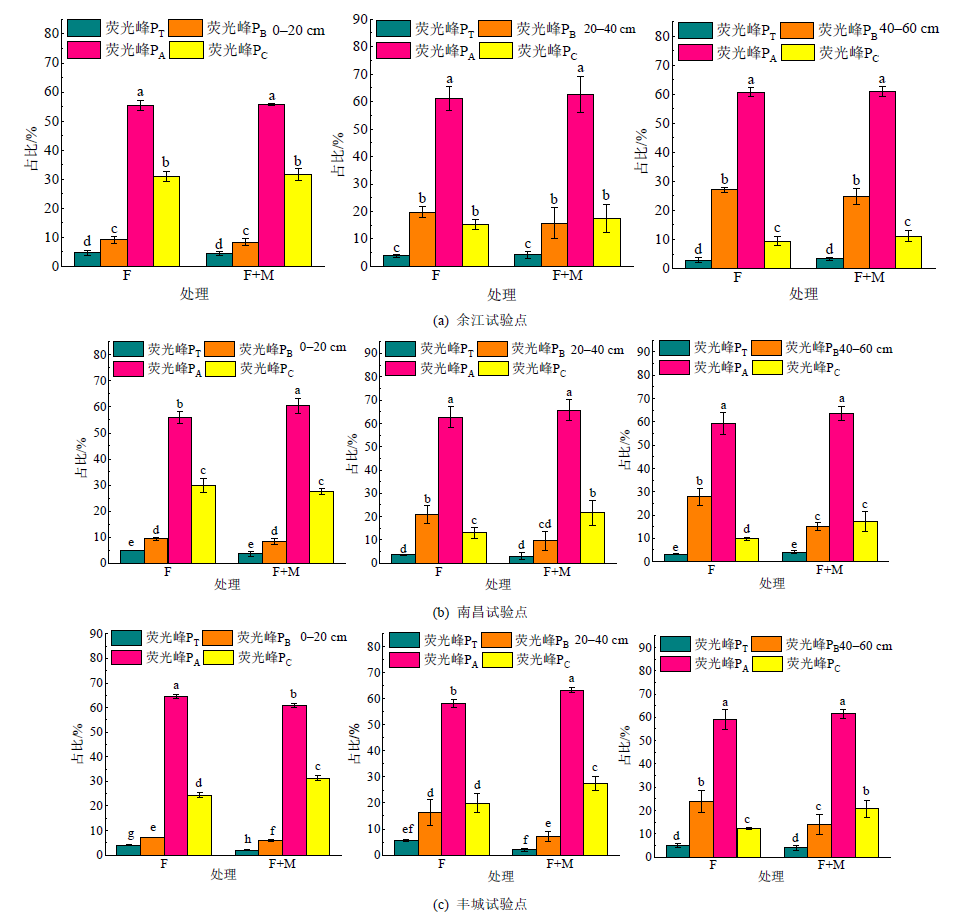
图3 各试验点不同深度土层中各荧光峰占比 不同小写字母表示同一处理不同荧光峰占比差异显著(p<0.05),n=3
Figure 3 Proportion of fluorescence peaks in differents soil depths in each experimental site
| 试验点 | 处理 | 类蛋白质组分 | 类腐殖质组分 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | |||
| YJ | F | 7.76±1.37ab | 16.6±3.04a | 23.8±2.00a | 92.2±1.37cd | 83.4±3.04c | 76.2±2.00b | |
| F+M | 6.99±1.24abc | 13.6±5.73ab | 22.9±3.77a | 93.0±1.24bcd | 86.4±5.73bc | 77.1±3.77b | ||
| NC | F | 8.32±0.37a | 19.2±3.40a | 26.5±3.65a | 91.7±0.37d | 80.8±3.40c | 73.5±3.65b | |
| F+M | 6.50±1.19bc | 7.47±3.98b | 12.2±1.21b | 93.5±1.19bc | 92.5±3.98ab | 87.8±1.21a | ||
| FC | F | 5.94±0.05c | 14.4±4.25ab | 21.4±4.40a | 94.1±0.05b | 85.6±4.25bc | 78.6±4.40b | |
| F+M | 3.97±0.24d | 5.05±1.61c | 11.4±3.95b | 96.0±0.24a | 94.9±1.61a | 88.6±3.95a | ||
表3 各试验点土层总类蛋白质组分和类腐殖质组分占比
Table 3 The proportion of protein-like and humic-like substances in different experiment sites and soil layers %
| 试验点 | 处理 | 类蛋白质组分 | 类腐殖质组分 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | |||
| YJ | F | 7.76±1.37ab | 16.6±3.04a | 23.8±2.00a | 92.2±1.37cd | 83.4±3.04c | 76.2±2.00b | |
| F+M | 6.99±1.24abc | 13.6±5.73ab | 22.9±3.77a | 93.0±1.24bcd | 86.4±5.73bc | 77.1±3.77b | ||
| NC | F | 8.32±0.37a | 19.2±3.40a | 26.5±3.65a | 91.7±0.37d | 80.8±3.40c | 73.5±3.65b | |
| F+M | 6.50±1.19bc | 7.47±3.98b | 12.2±1.21b | 93.5±1.19bc | 92.5±3.98ab | 87.8±1.21a | ||
| FC | F | 5.94±0.05c | 14.4±4.25ab | 21.4±4.40a | 94.1±0.05b | 85.6±4.25bc | 78.6±4.40b | |
| F+M | 3.97±0.24d | 5.05±1.61c | 11.4±3.95b | 96.0±0.24a | 94.9±1.61a | 88.6±3.95a | ||
| 组分 | 试验点 | 处理 | 土层 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | |||
| 类酪氨酸组分 | YJ | F | 14.7±3.24aAB | 4.66±1.25bAB | 2.08±0.15cC |
| F+M | 16.3±3.21aAB | 7.54±3.38bA | 2.52±0.14bBC | ||
| NC | F | 12.7±0.85aAB | 5.36±0.80bAB | 3.49±0.45cABC | |
| F+M | 14.8±4.30aAB | 6.19±2.90bAB | 4.77±0.98cA | ||
| FC | F | 17.6±1.41aA | 6.84±1.51bAB | 4.42±1.28bA | |
| F+M | 11.2±0.44aB | 2.87±1.65 bB | 3.75±0.79bAB | ||
| 类色氨酸组分 | YJ | F | 28.2±4.29aAB | 24.1±5.71 aAB | 20.3±3.15aB |
| F+M | 30.3±5.09aAB | 26.5±6.01abAB | 19.4±4.09bB | ||
| NC | F | 24.3±2.79aB | 31.1±2.49aA | 30.2±4.53aA | |
| F+M | 34.0±5.16aA | 19.4±7.35bB | 17.6±1.35bBC | ||
| FC | F | 31.1±0.81aAB | 19.6±5.73bB | 20.8±2.52bB | |
| F+M | 34.7±1.96aA | 20.0±5.14bB | 13.0±3.51bC | ||
| 类富里酸组分 | YJ | F | 171±7.76aE | 73.7±7.50bC | 45.8±8.87cC |
| F+M | 202±10.7aD | 108±17.1bB | 47.1±4.31cC | ||
| NC | F | 145±15.9aE | 95.2±15.6bBC | 64.5±8.47cAB | |
| F+M | 249±11.3aC | 136±11.8bA | 75.4±6.30cA | ||
| FC | F | 281±18.7aB | 70.5±6.43bC | 52.3±6.46cBC | |
| F+M | 355±20.2aA | 85.4±11.1bBC | 58.6±5.31cBC | ||
| 类胡敏酸组分 | YJ | F | 95.7±2.99aC | 18.7±4.52bB | 7.12±2.11cB |
| F+M | 114.2±4.42aB | 31.0±3.37bB | 8.69±1.93cB | ||
| NC | F | 77.4±3.64aD | 19.7±4.39bB | 10.7±1.49cB | |
| F+M | 113±5.80aB | 50.4±1.39bA | 21.0±8.03cA | ||
| FC | F | 106±1.59aBC | 24.4±6.49bB | 10.8±0.87cB | |
| F+M | 183±18.1aA | 36.6±5.97bB | 19.9±4.93cA | ||
表4 不同实验点、不同处理间土层DOM各组分质量分数
Table 4 The mass fraction of DOM substances in different soil layer between experimental sites and treatments mg?kg?1
| 组分 | 试验点 | 处理 | 土层 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒20 cm | 20‒40 cm | 40‒60 cm | |||
| 类酪氨酸组分 | YJ | F | 14.7±3.24aAB | 4.66±1.25bAB | 2.08±0.15cC |
| F+M | 16.3±3.21aAB | 7.54±3.38bA | 2.52±0.14bBC | ||
| NC | F | 12.7±0.85aAB | 5.36±0.80bAB | 3.49±0.45cABC | |
| F+M | 14.8±4.30aAB | 6.19±2.90bAB | 4.77±0.98cA | ||
| FC | F | 17.6±1.41aA | 6.84±1.51bAB | 4.42±1.28bA | |
| F+M | 11.2±0.44aB | 2.87±1.65 bB | 3.75±0.79bAB | ||
| 类色氨酸组分 | YJ | F | 28.2±4.29aAB | 24.1±5.71 aAB | 20.3±3.15aB |
| F+M | 30.3±5.09aAB | 26.5±6.01abAB | 19.4±4.09bB | ||
| NC | F | 24.3±2.79aB | 31.1±2.49aA | 30.2±4.53aA | |
| F+M | 34.0±5.16aA | 19.4±7.35bB | 17.6±1.35bBC | ||
| FC | F | 31.1±0.81aAB | 19.6±5.73bB | 20.8±2.52bB | |
| F+M | 34.7±1.96aA | 20.0±5.14bB | 13.0±3.51bC | ||
| 类富里酸组分 | YJ | F | 171±7.76aE | 73.7±7.50bC | 45.8±8.87cC |
| F+M | 202±10.7aD | 108±17.1bB | 47.1±4.31cC | ||
| NC | F | 145±15.9aE | 95.2±15.6bBC | 64.5±8.47cAB | |
| F+M | 249±11.3aC | 136±11.8bA | 75.4±6.30cA | ||
| FC | F | 281±18.7aB | 70.5±6.43bC | 52.3±6.46cBC | |
| F+M | 355±20.2aA | 85.4±11.1bBC | 58.6±5.31cBC | ||
| 类胡敏酸组分 | YJ | F | 95.7±2.99aC | 18.7±4.52bB | 7.12±2.11cB |
| F+M | 114.2±4.42aB | 31.0±3.37bB | 8.69±1.93cB | ||
| NC | F | 77.4±3.64aD | 19.7±4.39bB | 10.7±1.49cB | |
| F+M | 113±5.80aB | 50.4±1.39bA | 21.0±8.03cA | ||
| FC | F | 106±1.59aBC | 24.4±6.49bB | 10.8±0.87cB | |
| F+M | 183±18.1aA | 36.6±5.97bB | 19.9±4.93cA | ||
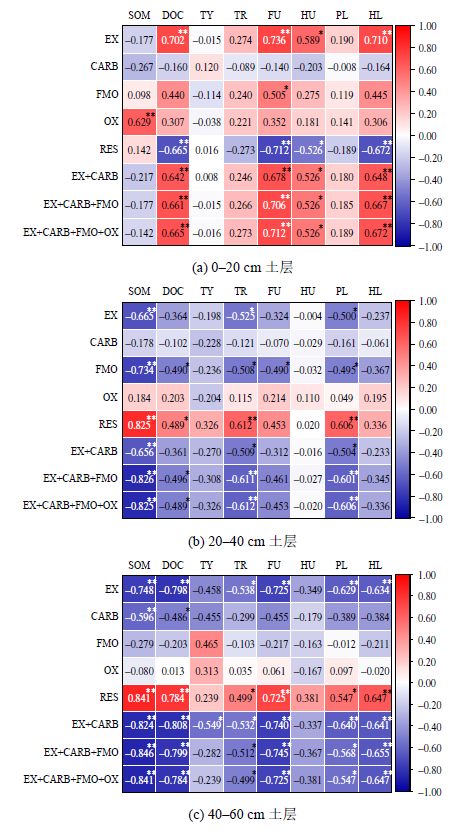
图4 不同土层深度中各形态Cd占比和累积占比与DOM组分含量、土壤有机质含量间的相关性 *和**分别表示显著相关(p<0.05)和极显著相关(p<0.01),n=3;SOM、DOC分别代表土壤中有机质含量和水溶性有机碳含量;TY、TR、FU、HU、PL、HL分别代表类酪氨酸、类色氨酸、类富里酸、类胡敏酸、类蛋白质和类腐殖质的占比,其中类蛋白质占比为类酪氨酸与类色氨酸占比之和,类腐殖质占比为类富里酸与类胡敏酸占比之和;EX、CAB、FMO、OX、RES分别代表可交换态Cd、碳酸盐结合态Cd、铁锰氧化物结合态Cd、有机结合态Cd和残渣态Cd占比
Figure 4 Correlation between individual and cumulative proportion of Cd forms and content of DOM components,soil organic matter, and DOC in different soil layers
| 模型 | 未标准化系数 | 标准化系数 | t | 显著性 | 共线性统计 | r | 调整后r2 | 德宾-沃森值 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 标准错误 | Beta | 容差 | VIF | ||||||||
| 1 | 常量 | 77.2 | 4.22 | 18.3 | 0.000 | 0.593 | 0.339 | |||||
| OM | −1.01 | 0.190 | −0.593 | −5.31 | 0.000 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| 2 | 常量 | 73.8 | 3.62 | 20.3 | 0.000 | 0.743 | 0.534 | |||||
| OM | −2.38 | 0.330 | −1.41 | −7.23 | 0.000 | 0.233 | 4.30 | |||||
| FU | 0.225 | 0.047 | 0.927 | 4.77 | 0.000 | 0.233 | 4.30 | |||||
| 3 | 常量 | 86.1 | 6.42 | 13.4 | 0.000 | 0.772 | 0.571 | 1.85 | ||||
| OM | −2.17 | 0.330 | −1.28 | −6.58 | 0.000 | 0.214 | 4.66 | |||||
| FU | 0.239 | 0.046 | 0.985 | 5.24 | 0.000 | 0.229 | 4.37 | |||||
| TR | −0.760 | 0.326 | −0.276 | −2.33 | 0.024 | 0.575 | 1.74 | |||||
表5 有生物活性的Cd形态占比与土壤有机物各因子回归方程模型摘要
Table 5 Summarization of the regression equation model of biologically active Cd forms proportion and soil organic matter factors
| 模型 | 未标准化系数 | 标准化系数 | t | 显著性 | 共线性统计 | r | 调整后r2 | 德宾-沃森值 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 标准错误 | Beta | 容差 | VIF | ||||||||
| 1 | 常量 | 77.2 | 4.22 | 18.3 | 0.000 | 0.593 | 0.339 | |||||
| OM | −1.01 | 0.190 | −0.593 | −5.31 | 0.000 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| 2 | 常量 | 73.8 | 3.62 | 20.3 | 0.000 | 0.743 | 0.534 | |||||
| OM | −2.38 | 0.330 | −1.41 | −7.23 | 0.000 | 0.233 | 4.30 | |||||
| FU | 0.225 | 0.047 | 0.927 | 4.77 | 0.000 | 0.233 | 4.30 | |||||
| 3 | 常量 | 86.1 | 6.42 | 13.4 | 0.000 | 0.772 | 0.571 | 1.85 | ||||
| OM | −2.17 | 0.330 | −1.28 | −6.58 | 0.000 | 0.214 | 4.66 | |||||
| FU | 0.239 | 0.046 | 0.985 | 5.24 | 0.000 | 0.229 | 4.37 | |||||
| TR | −0.760 | 0.326 | −0.276 | −2.33 | 0.024 | 0.575 | 1.74 | |||||
| [1] |
ALESSANDRO P, RICCARDO S, ANTONIO D M, et al., 2019. Soil washing with solutions of humic substances from manure compost removes heavy metal contaminants as a function of humic molecular composition[J]. Chemosphere, 225: 150-156.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | CERDÁN M, SÁNCHEZ-SÁNCHEZ A, JORDÁ J D, et al., 2016. Characterization of water dissolved organic matter under woody vegetation patches in semi-arid Mediterranean soils[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 553: 340-348. |
| [3] | CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al., 2003. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(24): 5701-5710. |
| [4] | CHOTPANTARAT S, CHUNHACHERDCHAI L, WIKINIYADHANEE R, et al., 2015. Effects of humic acid amendment on the mobility of heavy metals (Co, Cu, Cr, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn) in gold mine tailings in Thailand[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(9): 7589-7600. |
| [5] | COBLE P G, 1996. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry, 51(4): 325-346. |
| [6] | FELLMAN J B, HOOD E, SPENCER R G M, 2010. Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: A review[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(6): 2452-2462. |
| [7] | GUSIATIN Z M, KULIKOWSKA D, KLIK B, 2020. New-generation washing agents in remediation of metal-polluted soils and methods for washing effluent treatment: A review[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17): 6220. |
| [8] |
KALBITZ K, WENNRICH R, 1998. Mobilization of heavy metals and arsenic in polluted wetland soils and its dependence on dissolved organic matter[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 209(1): 27-39.
PMID |
| [9] | KLIK B, GUSIATIN Z M, KULIKOWSKA D, 2021. Quality of heavy metal-contaminated soil before and after column flushing with washing agents derived from municipal sewage sludge[J]. Scientific Reports, 11(1): 15773. |
| [10] | OHNO T, FERNANDEZ I J, HIRADATE S, et al., 2007. Effects of soil acidification and forest type on water soluble soil organic matter properties[J]. Geoderma, 140(1): 176-187. |
| [11] | RASHID I, MURTAZA G, DAR A A, et al., 2020. The influence of humic and fulvic acids on Cd bioavailability to wheat cultivars grown on sewage irrigated Cd-contaminated soils[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 205: 111347. |
| [12] | TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M, 1979. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7): 844-851. |
| [13] | WANG K, LIU Y H, SONG Z G, et al., 2019. Effects of biodegradable chelator combination on potentially toxic metals leaching efficiency in agricultural soils[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 182: 109399. |
| [14] | XIE J, DONG A Q, LIU J, et al., 2019. Relevance of dissolved organic matter generated from green manuring of Chinese milk vetch in relation to water-soluble cadmium[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(16): 16409-16421. |
| [15] | 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等, 2017. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| CAO W D, BAO X G, XU C X, et al., 2017. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| [16] | 陈丽瑶, 连泽阳, 宋卫锋, 等, 2024. 不同外源Cd(II)对Pseudomonas aeruginosa EPS的胁迫效应——产量、组分、吸附特性变化及其机制[J]. 中国环境科学, 44(1): 537-547. |
| CHEN L Y, LIAN Z Y, SONG W F, et al., 2024. Coercive effects of different exogenous Cd(II) on Pseudomonas aeruginosa EPS: Changes in yield, composition, adsorption characteristics and their mechanisms[J]. China Environmental Science, 44(1): 537-547. | |
| [17] | 邓朝阳, 朱霞萍, 郭兵, 等, 2012. 不同性质土壤中镉的形态特征及其影响因素[J]. 南昌大学学报(工科版), 34(4): 341-346. |
| DENG C Y, ZHU X P, GUO B, et al., 2012. Distribution and influence factors of Cd speciation on the soil with different properties[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Engineering & Technology), 34(4): 341-346. | |
| [18] | 丁昌璞, MARIA DE NOBILI, CECCANTI B, 1989. 绿肥分解产物中水溶性有机物质的伏安行为及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 26(3): 331-336. |
| DING C P, MARIA D N, CECCANTI B, 1989. Voltammetric behavior of water-soluble organic substances in decomposition products of green manures and its effecting factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 26(3): 331-336. | |
| [19] |
董爱琴, 陈院华, 杨涛, 等, 2024. 紫云英和石灰配施对水稻镉吸收的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 36(3): 600-612.
DOI |
|
DONG A Q, CHEN Y H, YANG T, et al., 2024. Effect of application of lime with Chinese milk vetch on the cadmium uptake in rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 36(3): 600-612.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 高洁, 江韬, 李璐璐, 等, 2015. 三峡库区消落带土壤中溶解性有机质 (DOM) 吸收及荧光光谱特征[J]. 环境科学, 36(1): 151-162. |
| GAO J, JIANG T, LI L L, et al., 2015. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) and fluorescence spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in soils of water-level fluctuation zones of the three gorges reservoir region[J]. Environmental Science, 36(1): 151-162. | |
| [21] | 国家环境保护局, 国家技术监督局,, 1997. 土壤质量铅、镉的测定石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法: GB/T 17141—1997[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| State Bureau of Environment Protection, National Bureau of Technical Supervision, 1997. Soil quality-determination of lead, cadmium-Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry: GB/T 17141—1997[S]. Beijing: Standards press of China. | |
| [22] | 胡梦淩, 曾和平, 2021. 不同来源腐殖质淋洗去除土壤中Cd、Pb的研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 43(1): 14-19. |
| HU M L, ZENG H P, 2021. The performance of different sources of humic substances for leaching removal of Cd and Pb from soils[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 43(1): 14-19. | |
| [23] | 季蒙蒙, 王星星, 马欢欢, 等, 2021. 磷酸氨基酸盐对Cd污染土壤的淋洗效果[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(2): 329-337 |
| JI M M, WANG X X, MA H H, et al., 2021. Removal of Cd from contaminated soil using amino acid salt[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(2): 329-337. | |
| [24] | 江智敏, 郑宏斌, 张仲文, 等, 2016. 绿肥在湘西烟田中的腐解和养分释放动态研究[J]. 烟草科技, 48(6): 13-18. |
| JIANG Z M, ZHENG H B, ZHANG Z W, et al., 2016. Dynamics of decomposition and nutrient release of green manures in tobacco fields in Xiangxi[J]. Tobacco Science & Technology, 48(6): 13-18. | |
| [25] | 李廷强, 杨肖娥, 2004. 土壤中水溶性有机质及其对重金属化学与生物行为的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 15(6): 1083-1087. |
| LI T Q, YANG X E, 2004. Soil dissolved organic matter and its effect on chemical and biological behaviors of soil heavy metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15(6): 1083-1087. | |
| [26] | 刘彩玲, 何春梅, 王飞, 等, 2024. 紫云英压青结合稻秸还田对水稻的节肥增效作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 30(2): 279-288. |
| LIU C L, HE C M, WANG F, et al., 2024. Co-incorporation of rice stubble and Chinese milk vetch saves fertilizer input and increases production efficiency of rice[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 30(2): 279-288. | |
| [27] | 柳夏艳, 曹浩轩, 缪闯和, 等, 2023. 长期施用堆肥处理下潮土剖面水溶性有机物的三维荧光光谱研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 43(3): 674-684. |
| LIU X Y, CAO H X, MIU C H, et al., 2023. Three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of dissolved organic matter in fluvo-aquic soil profile under long-term composting treatment[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 43(3): 674-684. | |
| [28] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 106-107. |
| LU R K, 2000. Methods for agrochemical analysis of soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 106-107. | |
| [29] | 宋莉, 韩上, 鲁剑巍, 等, 2015. 油菜秸秆、紫云英绿肥及其不同比例配施还田的腐解及养分释放规律研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (3): 100-104. |
| SONG L, HAN S, LU J W, et al., 2015. Study on characteristics of decomposing and nutrients releasing of different proportional mixture of rape straw and Chinese milk vetch in rice field[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (3): 100-104. | |
| [30] | 王艮梅, 周立祥, 占新华, 等, 2004. 水田土壤中水溶性有机物的产生动态及对土壤中重金属活性的影响: 田间微区试验[J]. 环境科学学报, 24(5): 858-864. |
| WANG G M, ZHOU L X, ZHAN X H, et al., 2004. Dynamics of dissolved organic matter and its effect on metal availability in paddy soil: Field micro-plot trials[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 24(5): 858-864. | |
| [31] | 王浩, 章明奎, 2009. 有机质积累和酸化对污染土壤重金属释放潜力的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 40(3): 538-541. |
| WANG H, ZHANG M K, 2009. Effects of Organic matter accumulation and acidification on release potential of heavy metals from polluted soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 40(3): 538-541. | |
| [32] | 王齐磊, 江韬, 赵铮, 等, 2016. 三峡库区典型农业小流域水体中溶解性有机质的光谱特征[J]. 环境科学, 37(6): 2082-2092. |
| WANG Q L, JIANG T, ZHAO Z, et al., 2016. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in waters of typical agricultural watershed of three gorges reservoir areas[J]. Environmental Science, 37(6): 2082-2092. | |
| [33] | 王胜, 季蒙蒙, 阮文权, 等, 2023. 沼渣腐殖质对Cd污染土壤的淋洗效果及性质影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 39(5): 1169-1178. |
| WANG S, JI M M, RUAN W Q, et al., 2023. Effects of biogas residue humus on the leaching efficiency and properties of Cd contaminated soil[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 39(5): 1169-1178. | |
| [34] |
吴浩杰, 周兴, 鲁艳红, 等, 2017. 紫云英翻压对稻田土壤镉有效性及水稻镉积累的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 33(16): 105-111.
DOI |
| WU H J, ZHOU X, LU Y H, et al., 2017. Effects of Astragalus smicus on cadmium effectiveness in paddy soil and cadmium accumulation in rice plant[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 33(16): 105-111. | |
| [35] | 夏海林, 康丽春, 王飞, 等, 2018. 江西绿肥紫云英的研究[J]. 草业科学, 35(11): 2711-2721. |
| XIA H L, KANG L C, WANG F, et al., 2018. The research status and prospect of Astragalus smicus as green manure in Jiangxi[J]. Pratacultural Science, 35(11): 2711-2721. | |
| [36] |
谢杰, 董爱琴, 徐昌旭, 等, 2019. 紫云英长期还田对稻田土壤Cd含量与形态的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 31(12): 2084-2094.
DOI |
| XIE J, DONG A Q, XU C X, et al., 2019. Impact of long-term returning of Astragalus sinicus L. on content and forms of Cd in different depths of paddy soils[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhengjiangensis, 31(12): 2084-2094. | |
| [37] | 颜志雷, 方宇, 陈济琛, 等, 2014. 连年翻压紫云英对稻田土壤养分和微生物学特性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20(5): 1151-1160. |
| YAN Z L, FANG Y, CHEN J C, et al., 2014. Effect of turning over Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) on soil nutrients and microbial properties in paddy fields[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 20(5): 1151-1160. | |
| [38] | 杨佳波, 曾希柏, 2007. 水溶性有机物在土壤中的化学行为及其对环境的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 15(5): 206-211. |
| YANG J B, ZENG X B, 2007. Behavior and environmental impact of soil dissolved organic matter[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 15(5): 206-211. | |
| [39] | 杨志斌, 杨忠芳, 冯海艳, 等, 2008. 四川成都经济区土壤腐殖质重金属元素含量特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 39(5): 1135-1139. |
| YANG Z B, YANG Z F, FENG H Y, et al., 2008. Content characteristic of heavy metal in soil humus of Chengdu economic area in Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 39(5): 1135-1139. | |
| [40] | 姚瑶, 张世熔, 王怡君, 等, 2018. 3种环保型淋洗剂对重金属污染土壤的淋洗效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 12(7): 2039-2046. |
| YAO Y, ZHANG S R, WANG Y J, et al., 2018. Effects of different environmentally friendly washing agents on removal of soil heavy metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 12(7): 2039-2046. | |
| [41] |
钟晓兰, 周生路, 黄明丽, 等, 2009. 土壤重金属的形态分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 18(4): 1266-1273.
DOI |
| ZHONG X L, ZHOU S L, HUANG M L, et al., 2009. Chemical form distribution characteristic of soil heavy metals and its influencing factors[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(4): 1266-1273. |
| [1] | 刘晨, 白雪冬, 赵海超, 黄智鸿, 刘松涛, 卢海博, 刘子刚, 刘雪玲. 寒旱区春玉米秸秆还田方式对土壤DOM光谱特征的影响机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1419-1432. |
| [2] | 梅闯, 蔡昆争, 黎紫珊, 徐美丽, 黄飞. 稻秆生物炭对稻田土壤Cd形态转化和微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 380-390. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
