生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 1773-1782.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.09.007
冯永霞1( ), 尚鹤1, 曹吉鑫2, 倪秀雅1, 陈展1,*(
), 尚鹤1, 曹吉鑫2, 倪秀雅1, 陈展1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-04
出版日期:2022-09-18
发布日期:2022-11-07
通讯作者:
*E-mail: chenzhan0508@126.com作者简介:冯永霞(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为森林生态学。E-mail: fengyongxia18@163.com
基金资助:
FENG Yongxia1( ), SHANG He1, CAO Jixin2, NI Xiuya1, CHEN Zhan1,*(
), SHANG He1, CAO Jixin2, NI Xiuya1, CHEN Zhan1,*( )
)
Received:2022-05-04
Online:2022-09-18
Published:2022-11-07
摘要:
CO2浓度升高与氮(N)沉降增加的交互作用对陆地生态系统的影响已成为全球变化研究的热点。大量研究报道了CO2浓度升高和氮沉降对生态系统的影响,但关于高浓度CO2以及N肥对木本植物的影响研究还很少。该研究拟探讨高浓度CO2和N添加对木荷(Schima superba)幼苗生理特性的影响,以了解木荷幼苗生理生态对未来气候变化的响应机制。利用开顶室气室(open top chambers,OTC)组成的CO2浓度自动调控平台,以一年生木荷幼苗为研究材料,根据联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会(Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Chang,IPCC)第五次评估报告预测的未来CO2浓度升高情景,设置550、750、1000 μmol∙mol-1共3个CO2熏气处理,以自然大气CO2浓度(约400 μmol∙mol-1,CK)为对照,在每个OTC内设置不施氮(低氮,0 g∙m-2∙a-1)和施氮(高氮,10 g∙m-2∙a-1)2个氮肥处理水平,研究CO2浓度升高和施用氮肥及其交互作用对木荷幼苗生理生态特征的影响。结果表明,(1)除1000 μmol∙mol-1 CO2处理外,其他CO2处理水平下高氮处理后木荷幼苗叶片光合色素含量较低氮处理显著增加(P<0.05)。(2)CO2浓度和施氮对丙二酮(MDA)活力无显著影响,但施氮却抑制了超氧化物岐化酶(SOD)活力(P<0.001)。(3)CO2浓度增加对脱落酸(ABA)含量无显著影响,但对生长素(IAA)含量有促进作用(P=0.003),施氮对玉米素(ZR)、赤霉素(GA3)有抑制作用(P<0.001)。(4)施氮和CO2浓度升高对植物的总生物量有促进作用。高氮条件下,1000 μmol∙mol-1 CO2处理木荷幼苗的总生物量较CK处理增加了52.79%(P=0.044)。1000 μmol∙mol-1 CO2处理下,高氮与低氮处理相比,木荷生物量增加了106.38%(P=0.003)。大气CO2浓度升高和施氮处理对木荷幼苗叶片的色素、抗氧化系统、激素含量的交互作用不显著,而施氮能显著提高光合色素含量,并显著提高IAA含量,降低ZR含量,且高氮处理下CO2摩尔分数达到1000 μmol∙mol-1时木荷幼苗生物量显著提高。
中图分类号:
冯永霞, 尚鹤, 曹吉鑫, 倪秀雅, 陈展. CO2升高和施氮互作对木荷幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1773-1782.
FENG Yongxia, SHANG He, CAO Jixin, NI Xiuya, CHEN Zhan. Interactive Effects of Elevated CO2 and Nitrogen Fertilization on Physiological Characteristics of Schima superba Seedings[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1773-1782.
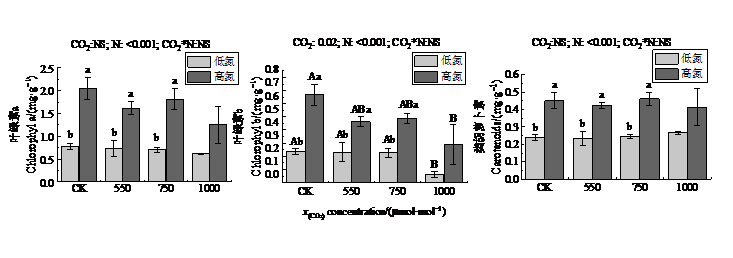
图1 不同CO2和氮肥水平对木荷幼苗光合色素的影响 平均值±标准误,n=6。图中柱子上的不同大写字母表示在同一N肥处理下,不同CO2浓度处理之间差异显著(P<0.05);小写字母表示相同CO2浓度处理下,不同氮处理存在显著差异性(P<0.05)。图上部显示的是多因素方差分析的结果,CO2表示不同CO2浓度的影响,N表示不同施氮处理的影响,CO2*N表示CO2和N肥的交互作用;NS表示影响不显著。下同
Figure 1 Different effects of elevated CO2 and N fertilization on photosynthetic pigments in Schima superba seedlings Mean±SE, n=6. Different capital letters on the columns in the figure indicate that under the same N fertilizer treatment, there are significant differences between treatments with different CO2 concentrations (P<0.05); lowercase letters indicate that under the same CO2 concentration treatments, there are significant differences between different nitrogen treatments (P<0.05). The upper part of the figure shows the results of multi-factor ANOVA, CO2 represents the effect of different CO2 concentrations, N represents the effect of different nitrogen fertilization treatments, CO2*N represents the interaction between CO2 and N fertilizer; NS means that the effect is not significant. The same below
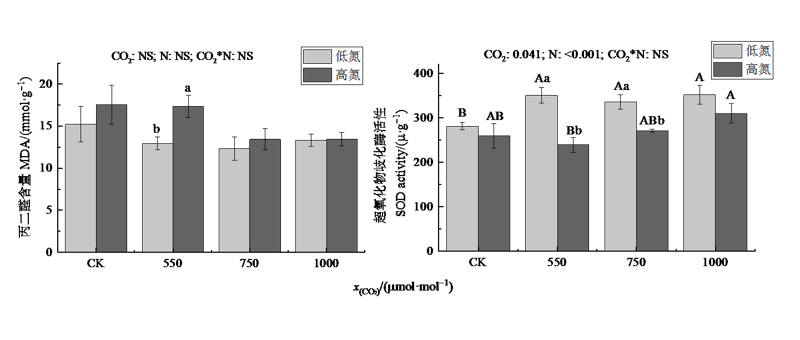
图2 不同CO2和氮肥水平对木荷幼苗丙二醛和超氧化物歧化酶活力的影响
Figure 2 Effects of different CO2 and N fertilization on the activities of malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase in Schima superba seedlings
| CO2处理/(µmol∙mol-1) | 低氮 Low nitrogen | 高氮 High nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| CK(400) | 18.3±2.7 | 25.7±3.6B |
| 550 | 16.0±2.6 | 26.6±2.8AB |
| 750 | 16.8±1.4 | 36.3±6.5AB |
| 1000 | 19.05±3.0b | 39.3±1.3Aa |
| CO2 | NS | |
| N | P<0.001 | |
| CO2*N | NS | |
表1 不同CO2和氮肥水平对木荷幼苗总生物量的影响
Table 1 Effects of elevated CO2 and N fertilizationon plant biomass g∙plant-1
| CO2处理/(µmol∙mol-1) | 低氮 Low nitrogen | 高氮 High nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| CK(400) | 18.3±2.7 | 25.7±3.6B |
| 550 | 16.0±2.6 | 26.6±2.8AB |
| 750 | 16.8±1.4 | 36.3±6.5AB |
| 1000 | 19.05±3.0b | 39.3±1.3Aa |
| CO2 | NS | |
| N | P<0.001 | |
| CO2*N | NS | |
| [1] |
CHANDRA A, DUBEY A, 2007. Evaluation of genus Cenchrus based on malondialdehyde, proline content, specific leaf area and carbon isotope discrimination for drought tolerance and divergence of species at DNA level[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 30(1): 53-61.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHATER C, PENG K, MOVAHEDI M, et al., 2015. Elevated CO2-induced responses in stomata require ABA and ABA signaling[J]. Current Biology, 25(20): 2709-2716.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | CHEN Z, YE S Y, CAO J X, et al., 2021. Nitrogen fertilization modified the responses of Schima superba seedlings to elevated CO2 in subtropical China[J]. Plants (Basel), 10(2): 383. |
| [4] | DENAXA N K, DAMVAKARIS T, ROUSSOS P A, 2020. Antioxidant defense system in young olive plants against drought stress and mitigation of adverse effects through external application of alleviating products[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 259: 108812. |
| [5] | FORSMARK B, NORDIN A, ROSENSTOCK N P, et al., 2021. Anthropogenic nitrogen enrichment increased the efficiency of belowground biomass production in a boreal forest[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 155: 108154. |
| [6] |
GAO P J, ZUO Z J, ZHANG R M, et al., 2016. Optimum nitrogen fertilization for phyllostachys edulis productivity and photosynthetic respone[J]. Agronomy Journal, 108(1): 448-458.
DOI URL |
| [7] | IPCC, 2014. Synthesis Report[C]// Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. |
| [8] |
KUNALAN S, PALANIVELU K, 2022. Polymeric composite membranes in carbon dioxide capture process: A review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(26): 38735-38767.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU X J, ZHANG Y, HAN W X, et al., 2013. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China[J]. Nature, 494: 459-462.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LÜ R L, MABROUK E, TAKETO O, et al., 2021. Changes of photosynthetic pigments and phytol content at different levels of nitrogen fertilizer in Italian ryegrass fresh herbage and hay[J]. Grassland Science, 68(1): 53-59.
DOI URL |
| [11] | PEI J M, LI J Q, FANG C M, et al., 2020. Different responses of root exudates to biochar application under elevated CO2[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 301: 107061. |
| [12] |
RODRIGUES W P, MARTINS M Q, FORTUNATO A S, et al., 2016. Long-term elevated air CO2 strengthens photosynthetic functioning and mitigates the impact of supra-optimal temperatures in tropical Coffea arabica and C. canephora species[J]. Global Change Biology, 22(1): 415-431.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SCHWEDE D B, SIMPSON D, TAN J N, et al., 2018. Spatial variation of modelled total, dry and wet nitrogen deposition to forests at global scale[J]. Environmental Pollution, 243(Part B): 1287-1301.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | SOFO A, VITTI A, NUZZACI M, et al., 2013. Correlation between hormonal homeostasis and morphogenic responses in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings growing in a Cd/Cu/Zn multi-pollution context[J]. Physiol Plant, 149(4): 487-498. |
| [15] |
SUN X C, CHEN F J, YUAN L X, et al., 2020. The physiological mechanism underlying root elongation in response to nitrogen deficiency in crop plants[J]. Planta, 251(84): 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WANG C Y, ZHOU J W, LIU J, et al., 2017. Differences in functional traits between invasive and native Amaranthus species under different forms of N deposition[J]. Naturwissenschaften, 104(7-8): 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG Y, DU S T, LI L L, et al., 2009. Effect of CO2 elevation on root growth and its relationship with indole acetic acid and ethylene in Tomato Seedlings[J]. Pedosphere, 19(5): 570-576.
DOI URL |
| [18] | XU W, LUO X S, PAN Y P et al., 2015. Quantifying atmospheric nitrogen deposition through a nationwide monitoring network across China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(21): 12345-12360. |
| [19] | YE D H, SHEN Q W, GUO Y, et al., 2021. Sufficient nitrogen promoted high phosphorus tolerance and phosphorus-accumulating capability of Polygonum hydropiper in relation to changes of phytohormones and phenols[J]. 278: 130318. |
| [20] |
YI Z H, CUI J J, FU Y M, et al., 2020. Effect of different light intensity on physiology, antioxidant capacity and photosynthetic characteristics on wheat seedlings under high CO2 concentration in a closed artificial ecosystem[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 144(1): 23-34.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG Z H, CAO B L, CHEN Z J, et al., 2022. Grafting enhances the photosynthesis and nitrogen absorption of tomato plants under low-nitrogen stress[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 41(4): 1714-1725.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 常宏, 杨洪国, 赵广东, 等, 2019. 施氮和减水对中亚热带壳斗科三种幼树生物量及其分配的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(18): 6753-6761. |
| CHANG H, YANG G H, ZHAO G D, et al., 2019. Effects of nitrogen application and rainfall exclusion on biomass and biomass allocation in saplings from three species of the Fagaceae family in the midsubtropical region of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(18): 6753-6761. | |
| [23] | 陈晓娜, 李清河, 段娜, 等, 2020. 干旱胁迫下氮添加对白刺根系形态和内源激素的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 33(2): 279-283. |
| CHEN X N, LI Q H, DUAN N, et al., 2020. Effects of nitrogen addition on root morphology endogenous hormones of Nitraria tangutorum under drought stress[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 33(2): 279-283. | |
| [24] | 陈雨娇, 李汛, 田兴军, 等. 2020, CO2浓度与氮磷供应水平对黄瓜根系生长及各组织矿质养分含量的影响[J]. 土壤, 52(6): 1129-1138. |
| CHEN Y J, LI X, TIAN X J, et al., 2020. Effects of atmospheric CO2 concentration, nitrogen and phosphorus levels on root growth and mineral nutrient concentrations in different organs of Cucumber[J]. Soils, 52(6): 1129-1138. | |
| [25] | 杜启燃, 雷静品, 刘建锋, 等, 2014. CO2浓度增加和施氮对栓皮栎幼苗生理生态特征的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(1): 24-30. |
| DU Q R, LEI J P, LIU J F, et al., 2014. Eco-physiological response of Quercus variabilis seedlings to increased atmospheric CO2 and N supply[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(1): 24-30. | |
| [26] | 范金杰, 俞杨浏, 左强, 等, 2020. 大气CO2浓度升高对小麦蒸腾耗水与根系吸水的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 36(3): 92-98. |
| FAN J J, YU Y L, ZUO Q, et al., 2020. Effects of elevated CO2concentration on transpiration and root-water-uptake of wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 36(3): 92-98. | |
| [27] | 高培军, 2013. 氮素施肥对毛竹光合能力与光谱特性的影响[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| GAO P J, 2013. Effects nitrogen fertilization on photosynthetic capacity and spectral properties of Phyllostachys pubescens[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [28] | 郭文琦, 陈兵林, 刘瑞显, 等, 2010. 施氮量对花铃期短期渍水棉花叶片抗氧化酶活性和内源激素含量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 21(1): 53-60. |
| GUO W Q, CHEN B L, LIU R X, et al., 2010. Effects of nitrogen application rate on cotton leaf antioxidant enzyme activities and endogenous hormone contents under short-term waterlogging at flowering and boll-forming stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(1): 53-60. | |
| [29] | 何梅, 章金辉, 王再花, 等, 2020. CO2倍增对铁皮石斛光合特性和生长的影响[J]. 广东农业科学, 47(2): 17-23. |
| HE M, ZHANG J H, WANG Z H, et al., 2020. Effects of doubling the CO2 concentration on photosynthetic characteristics and growth of dendrobium officinale[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 47(2): 17-23. | |
| [30] | 洪凯, 李茂, 许珊珊, 等, 2020. CO2浓度升高对杉木幼苗生长及其光合特性和养分含量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 40(6): 1011-1021. |
| HONG K, LI S, XU S S, et al., 2020. Effect of elevated on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and nutrient concenteration of Cunninghamia lanceolata seedings[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali- Occidentalia Sinica, 40(6): 1011-1021. | |
| [31] | 姜帅, 居辉, 刘勤, 2013. CO2浓度升高对作物生理影响研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 29(18): 11-15. |
| JIANG S, JU H, LIU Q, 2013. The effects of CO2 concentration enrichment on crops physiology[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 29(18): 11-15. | |
| [32] | 康红梅, 李花花, 徐当会, 等, 2020. 大气CO2浓度及温度升高对高山灌木鬼箭锦鸡儿 (Caragana jubata) 生长及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(1): 367-376. |
| KANG H M, LI H H, XU D H, et al., 2020. Effects of elevated CO2 and temperature on Caragana jubata (Alpine shrub) growth and antioxidant systems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(1): 367-376. | |
| [33] | 李洪娜, 许海港, 任饴华, 等, 2015. 不同施氮水平对矮化富士苹果幼树生长、氮素利用及内源激素含量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21(5): 1304-1311. |
| LI H N, XU H G, REN Y H, et al., 2015. Effect of different N application rates on plant growth, 15N-urea utilization and hormone content of dwarf apple trees[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 21(5): 1304-1311. | |
| [34] | 李庆余, 2010. 氮素形态调控番茄果实氮和有机酸代谢的分子生理机制[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学. |
| LI Q Y, 2010. Molecular and physiological regulation mechanism of the nitrogen and organic acid metabolism in tomato fruit by different nitrogen forms[D]. Degrees. PhD Thesis[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. | |
| [35] | 李文娆, 李永竞, 冯士珍, 2017. 不同施氮量和分施比例对棉花幼苗生长和水分利用效率的影响及其根源ABA调控效应[J]. 生态学报, 37(20): 6712-6723. |
| LI W R, LI Y J, FENG S Z, 2017. Regulation of root-sourced ABA to growth and water use efficiency of cotton seedlings and their response to different nitrogen levels and distribution ratios[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(20): 6712-6723. | |
| [36] | 李仪曼, 贺新蕊, 李清明, 等, 2019. CO2加富对干旱胁迫下黄瓜幼苗根系抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 55(7): 1011-1019. |
| LI Y M, HE X R, LI Q M, et al., 2019. Effect of CO2 enrichment on antioxidant system in cucumber seedling root system under drought stress[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 55(7): 1011-1019. | |
| [37] | 潘鸿, 曹吉鑫, 陈展, 等, 2022. CO2浓度升高对木荷幼苗光合特征的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(5): 865-872. |
| PANG H, CAO J X, CHEN Z, et al., 2022. Effects of elevated CO2concentrations on photosynthetic characteristics of Schima superba seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(5): 865-872. | |
| [38] | 乔枫, 史伟, 薛元杰, 2018. 模拟氮沉降对云杉人工林土壤有机碳组分及理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(5): 852-858. |
| QIAO F, SHI W, XUE Y J, 2018. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil organic carbon fractions and soil physico-chemical properties in Picea asperata plantation in Sichuan[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(5): 852-858. | |
| [39] | 阮亚男, 何兴元, 陈玮, 等, 2007. CO2浓度倍增对城市银杏 (Ginkgo biloba) 叶片膜脂过氧化与抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 27(3): 1106-1112. |
| RUAN Y N, HE X W, CHEN W, et al., 2007. Effects of elevated CO2 on lipid peroxidation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in Ginkgo biloba [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(3): 1106-1112. | |
| [40] | 圣倩倩, 高顺, 顾舒文, 等, 2021. CO2浓度升高对植物生理生化影响的研究进展[J]. 西部林业科学, 50(3): 171-176. |
| SHENG Q Q, GAO G, GU S W, et al., 2021. Research progress on physiological and biochemical effects of elevated CO2 concentration on plants[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 50(3): 171-176. | |
| [41] | 王精明, 李永华, 黄胜琴, 等, 2005. CO2浓度升高对红掌光合速率与生长发育的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 32(2): 335-338. |
| WANG J M, LI Y H, HUANG S H, et al., 2005. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on photosynthetic rate, growth and development in Anthurium andraeanum Lind. Leaves[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 32(2): 335-338. | |
| [42] | 王满莲, 王香英, 韦霄, 等, 2017. 施氮对三个南方珍稀树种幼苗生长和生物量分配的影响[J]. 广西植物, 37(1): 127-133. |
| WANG M L, WEN X Y, WEI X, et al., 2017. Effects of nitrogen addition on seedling growth and biomass allocation of three rare tree species in the south of China[J]. Guihaia, 37(1): 127-133. | |
| [43] | 王星, 刘肖飞, 周宜君, 等, 2014. 植物SOD基因表达调控的分子机制[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 36(2): 275-280. |
| WANG X, LIU X F, ZHOU Y J, et al., 2014. Molecular mechanism of expression and regulation of SOD gene in plant[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 36(2): 275-280. | |
| [44] | 吴志丹, 尤志明, 王峰, 等, 2014. 施氮量对茶树生长及叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 茶叶科学技术 (4): 16-20. |
| WU Z D, YOU Z M, WANG F, et al., 2014. Effect of nitrogen application rate on the growth and leaf photosynthetic characteristics of tea[J]. Tea Science and Technology (4): 16-20. | |
| [45] | 熊露露, 邓小红, 王健健, 2021. 增温与施氮对薄荷幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 40(7): 19-23. |
| XIONG L L, DENG X H, WANG J J, 2021. Effects of warming and nitrogen application on growth and physiological characteristics of Mentha haplocalyx (M. haplocalyx) Briq. Seedling[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 40(7): 19-23. | |
| [46] | 徐国伟, 陆大克, 刘聪杰, 等, 2018. 干湿交替灌溉和施氮量对水稻内源激素及氮素利用的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 34(7): 137-146. |
| XU G W, LU D K, LIU C J, et al., 2018. Effect of alternate wetting and drying irrigation and nitrogen coupling on endogenous hormones, nitrogen utilization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 34(7): 137-146. | |
| [47] | 叶思源, 2019. CO2浓度升高和N沉降对马尾松和木荷幼苗气体交换参数及单萜烯释放的影响[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| YE S Y, 2019. Effects of elevated CO2 and nitrogen deposition on gas exchange parameters and monoterpenes emission of Pinus massoniana Lamb and Schima superba seedlings[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry. | |
| [48] | 于浩, 2017. 近地层 O3浓度升高对亚热带树木幼苗的影响[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| YU H, 2017. Effects of elevated O3 level on seedlings of tree species in subtropical China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry. | |
| [49] | 袁昌洪, 韩冬, 杨菲, 等, 2016. 氮肥对茶树春季光合, 抗衰老特性及内源激素含量的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报: 自然科学版, 44(6): 67-73. |
| YUAN C H, HAN D, YANG F, et al., 2016. Effects of nitrogen fertilization level in soil on physiological characteristics and quality of tea leaves[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University Natural Science Edition, 44(6): 67-73. | |
| [50] | 曾贞, 郇慧慧, 刘刚, 等, 2016. 增温和升高CO2浓度对桑树幼苗的生长和叶片品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(8): 2445-2451. |
| ZENG Z, XUN H H, LIU G, et al., 2016. Effects of elevated temperature and CO2 concentration on growth and leaf quality of Morusalba seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(8): 2445-2451. | |
| [51] |
翟开恩, 潘伟槐, 叶晓帆, 等, 2015. 高等植物局部生长素合成的生物学功能及其调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 50(2): 149-158.
DOI |
|
ZHAI K N, PAN W H, YE X F, et al., 2015. Biological functions and regulatory mechanisms of local auxin biosynthesis in higher plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 50(2): 149-158.
DOI URL |
|
| [52] | 翟晓朦, 2015. CO2浓度升高对不同秋眠类型苜蓿生理生化影响研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学. |
| ZHAI X M, 2015. Effect of physiclogical and biochemical mechanism of different fall dromancay alfalfa under high CO2 concentration[D]. Haikou: Hainan University. | |
| [53] | 翟晓朦, 臧春鑫, 王敏, 等, 2016. CO2浓度升高对不同秋眠型苜蓿内源激素含量的影响[J]. 草业科学, 33(3): 442-449. |
| ZHAI X M, ZANG C X, WANG M, et al., 2016. Effect of CO2 enrichment on hormone content of different types fall dormancy alfalfa[J]. Pratacultural Science, 33(3): 442-449. | |
| [54] | 张雪, 李强, 余宏军, 等, 2016. 氮胁迫对黄瓜幼苗抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 32(S2): 142-147. |
| ZHANG X, LI Q, YU H J, et al., 2016. Response of antioxidant enzyme system to nitrogen deficiency in cucumber seedling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 32(S2): 142-147. | |
| [55] | 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋, 等, 2021. 植物响应镉胁迫的生理与分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 57(7): 1437-1450. |
| ZHANG X Y, YE Z B, ZHANG Y Y, et al., 2021. Advances in physiological and molecular mechanism of plant response to cadmium stress[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 57(7): 1437-1450. | |
| [56] |
张翼飞, 于崧, 李彩凤, 等, 2013. 甜菜幼苗生长及叶片光化学活性对氮素的响应特征[J]. 核农学报, 27(9): 1391-1400.
DOI |
| ZHANG Y F, YU S, LI C F, et al, 2013. Response characteristics of plant growth and leaf photochemical activity of sugar beet seedlings to different nitrogen application levels[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 27(9): 1391-1400. | |
| [57] | 张振花, 孙胜, 刘洋, 等, 2018a. 增施CO2对温室番茄结果期叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(5): 1398-1402. |
| ZHANG Z H, SUN S, LIU Y, et al., 2018. Effects of CO2 enrichment on photosynthetic characteristics of greenhouse tomato during fruiting stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(5): 1398-1402. | |
| [58] | 张振花, 袁宏霞, 刘洋, 等, 2018b. 温室番茄对增施不同浓度CO2的光合响应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(4): 1010-1018. |
| ZHANG Z H, YUAN H X, LIU Y, et al., 2018. Photosynthetic responses of tomato to different concentrations of CO2 enrichment in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 24(4): 1010-1018. | |
| [59] | 赵平, 林克惠, 郑毅, 2005. 氮钾营养对烟叶衰老过程中内源激素与叶绿素含量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 11(3): 379-384. |
| ZHAO P, LIN K H, ZHENG Y, 2005. Effect of N and K nutrition on chlorophyll content and endogenous hormones in the process of tobacco senescence[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 11(3): 379-384. | |
| [60] | 庄明浩, 陈双林, 李迎春, 等, 2013. CO2浓度升高对三种地被类观赏竹生理特性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(9): 2408-2414. |
| ZHUANG M H, CHEN S L, LI Y C, et al., 2013. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on physiological characters of three dwarf ornamental bamboo species[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(9): 2408-2414. |
| [1] | 杨凯, 杨靖睿, 曹培培, 吕春华, 孙文娟, 于凌飞, 邓希. CO2浓度升高下水稻株高、茎蘖与SPAD动态响应及其模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [2] | 朱勇勇, 宋秉羲, 杨王敏, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻生长、产量与经济收益的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2150-2156. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
