生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 757-770.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.05.009
收稿日期:2023-12-20
出版日期:2024-05-18
发布日期:2024-06-27
通讯作者:
* 朱雪强。E-mail: zhuxq0615@163.com作者简介:赵乐依(1999年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤与地下水修复。E-mail: zhaoleyi1999@163.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Leyi1( ), ZHU Xueqiang1,*(
), ZHU Xueqiang1,*( ), LIU Jian1,2, LU Ping1
), LIU Jian1,2, LU Ping1
Received:2023-12-20
Online:2024-05-18
Published:2024-06-27
摘要:
恩诺沙星(ENR)属于氟喹诺酮类抗生素,具有稳定性强、难分解、易富集等特性,常用于水产养殖、畜禽养殖等,其在环境中总体浓度较低,但长期低剂量暴露可能对人体健康和生态环境带来极大风险。采用碳球(CS)负载纳米零价铁(nZVI)活化过硫酸盐(PS)去除水体中的ENR。应用两步碳热还原法制备了碳球负载纳米零价铁(Fe@C),采用单因素实验研究了Fe@C投加量、PS浓度、ENR初始浓度和pH值对ENR降解的影响及降解动力学,通过自由基及降解产物分析推测了Fe@C活化PS降解ENR的反应机制与降解路径。结果表明,ENR的降解符合准一级动力学,在温度为25 ℃、Fe@C投加量为0.3 g∙L−1、PS浓度为1 mmol∙L−1、ENR初始质量浓度为10 mg∙L−1、pH值为3的条件下,ENR降解率最高达98.6%。ENR降解率随着腐植酸(HA)、氨氮(NH3-N)、碳酸氢根离子(HCO3−)浓度的升高而降低。氯离子(Cl−)在低浓度时对ENR的降解有微弱的促进作用,高浓度时有抑制作用。自由基淬灭实验表明SO4−∙是ENR降解的主要自由基。根据ENR的降解产物,推测哌嗪环的裂解、喹诺酮环的分解及脱氟为ENR主要降解途径。碳球负载纳米零价铁活化PS高级氧化工艺可作为一种高效去除水中ENR的工艺。
中图分类号:
赵乐依, 朱雪强, 刘健, 路平. 碳球负载纳米零价铁活化过硫酸盐降解水中恩诺沙星的性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 757-770.
ZHAO Leyi, ZHU Xueqiang, LIU Jian, LU Ping. Study on the Performance of Carbon Sphere-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Activated Persulfate for Degradation of Enrofloxacin in Water[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(5): 757-770.
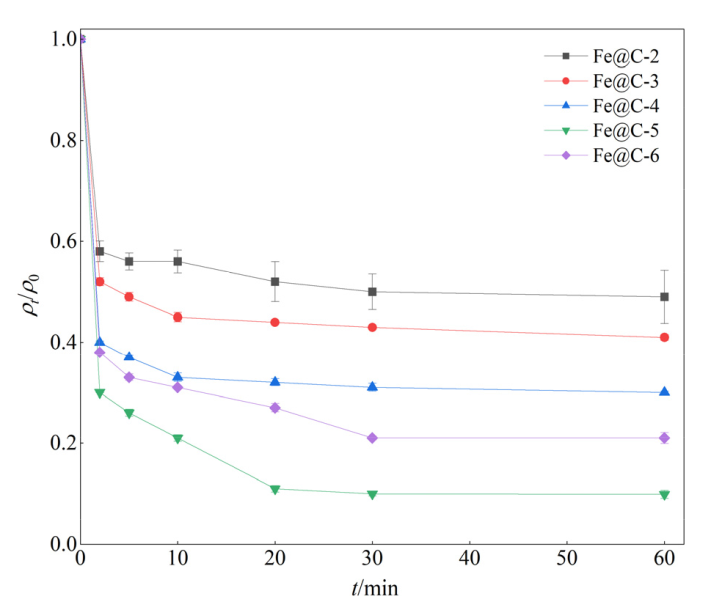
图4 不同铁碳比对ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10 mg?L?1,[PS]=0.5 mmol?L?1,[Fe@C]=0.2 g?L?1,θ=25 ℃,pH未调节
Figure 4 Effect of Fe@C with different CS ratio on the degradation of ENR

图5 Fe@C投加量对 ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10 mg?L?1,[PS]=0.5 mmol?L?1,[Fe@C-5]=0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4和0.5 g?L?1,θ=25 ℃,pH未调节
Figure 5 Effect of Fe@C dosages on the degradation of ENR
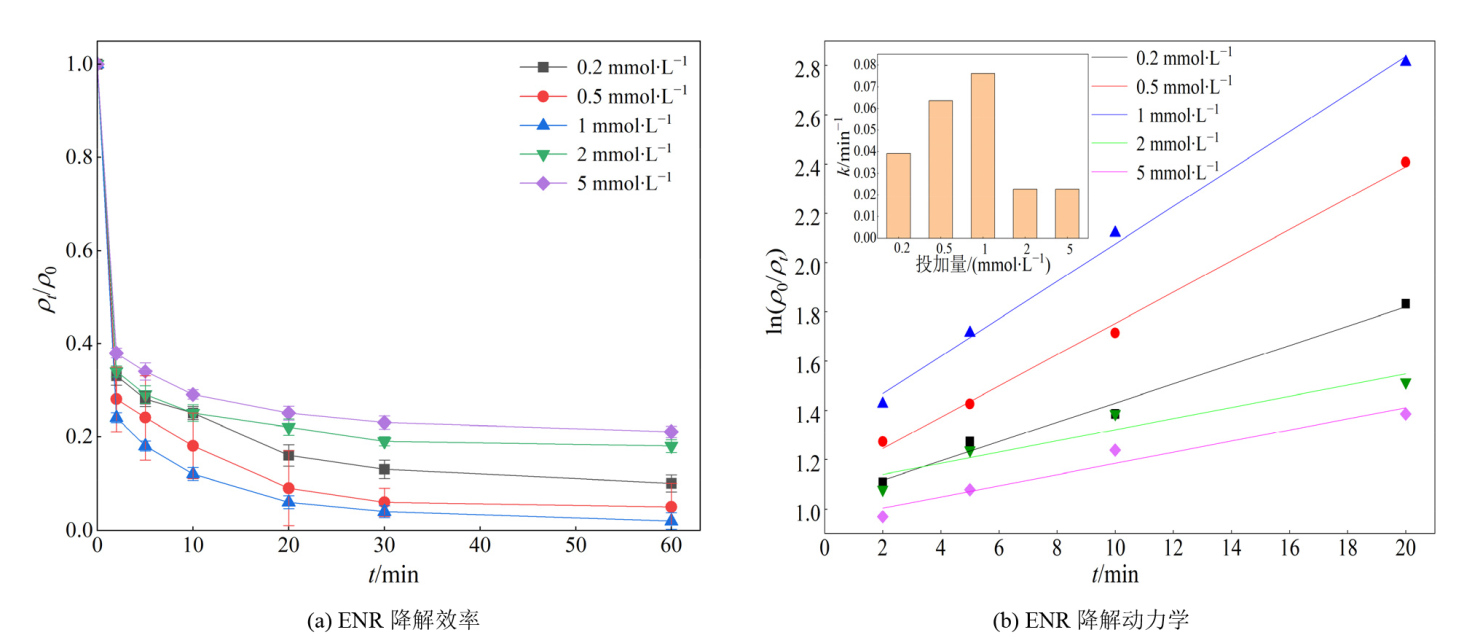
图6 PS浓度对ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10 mg?L?1;[PS]=0.2-5 mmol?L?1;[Fe@C]=0.3 g?L?1;θ=25 ℃;pH未调节
Figure 6 Effect of PS concentrations on the degradation of ENR
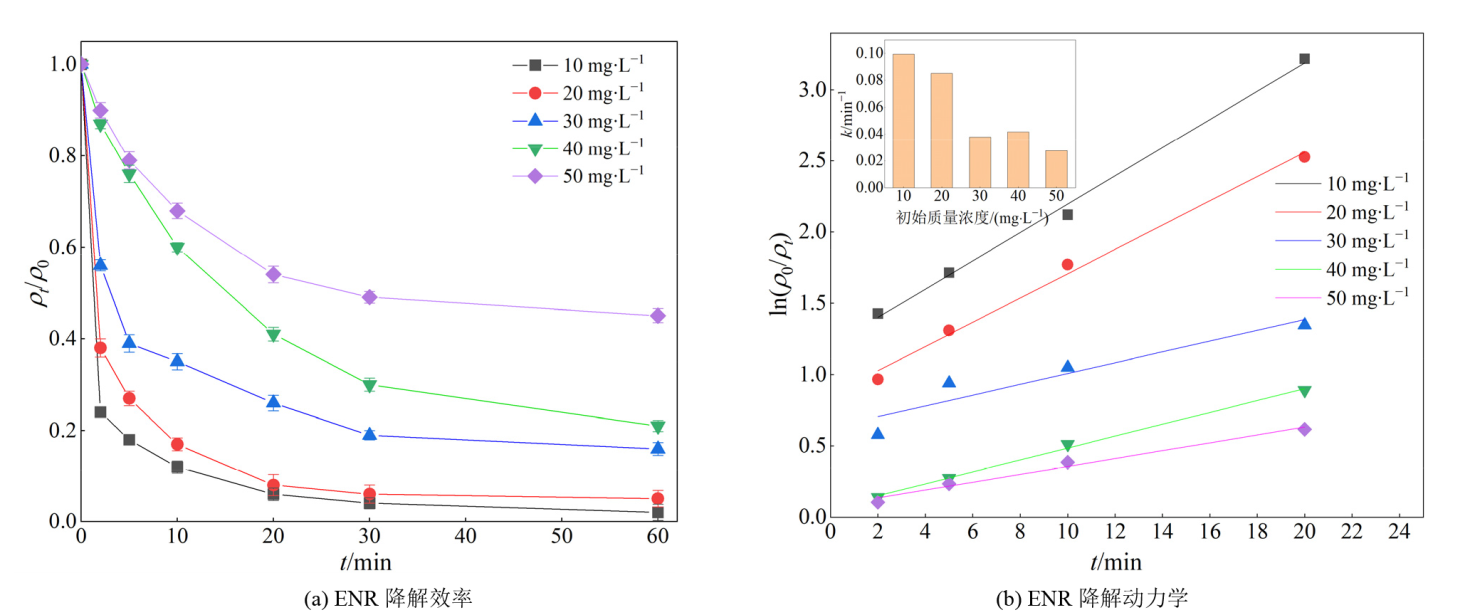
图7 ENR初始质量浓度对ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10-50 mg?L?1,[PS]=1 mmol?L?1,[Fe@C]=0.3 g?L?1,θ=25 ℃,pH未调节
Figure 7 The impact of initial ENR mass concentration on the degradation effect of ENR
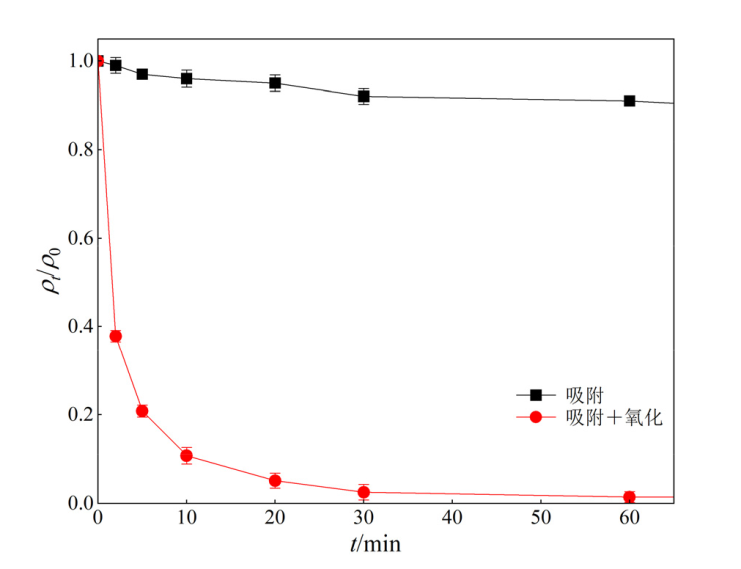
图9 吸附和氧化对ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10 mg?L?1,[PS]=1 mmol?L?1,[Fe@C]=0.3 g?L?1,θ=25 ℃,pH=3
Figure 9 Effect of adsorption and oxidation on the degradation of ENR
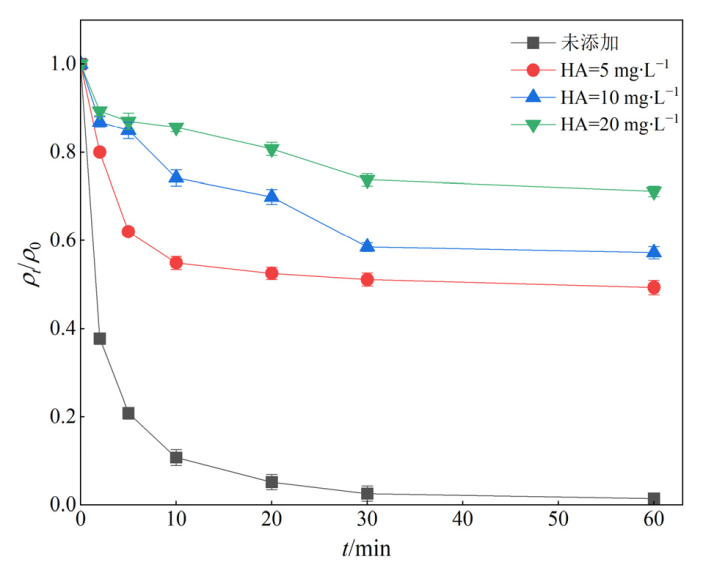
图10 不同质量浓度腐植酸对ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10 mg?L?1,[PS]=1 mmol?L?1,[Fe@C]=0.3 g?L?1,θ=25 ℃,pH=3
Figure 10 Effect of different mass concentrations of HA on the degradation of ENR
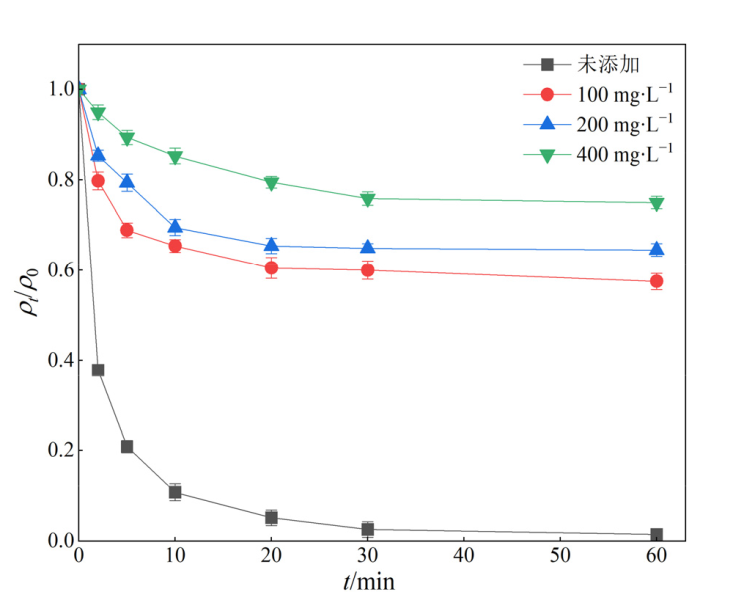
图11 不同质量浓度NH3-N对ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10 mg?L?1,[PS]=1 mmol?L?1,[Fe@C]=0.3 g?L?1,θ=25 ℃,pH=3
Figure 11 Effect of different mass concentrations of NH3-N on the degradation of ENR
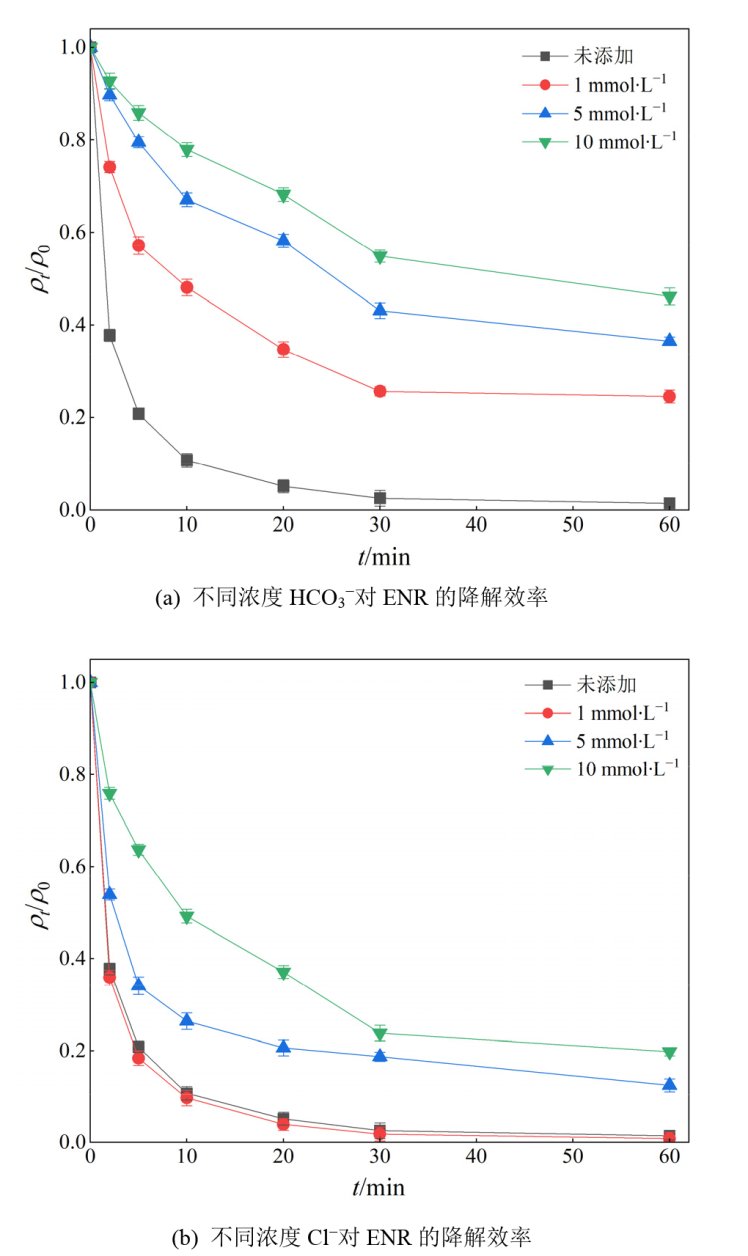
图12 不同无机阴离子对ENR降解效果的影响 实验条件:[ENR]=10 mg?L?1,[PS]=1 mmol?L?1,[Fe@C]=0.3 g?L?1,θ=25 ℃,pH=3
Figure 12 Effect of different inorganic anions on the degradation of ENR
| 名称 | 化学式 | LCMS质荷比 | m/z | 保留时间/min | 结构式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C19H23FN3O4 | 376.16562 | 376.16 | 8.06 | 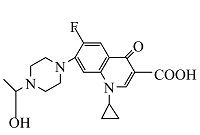 |
| 2 | C19H21FN3O4 | 374.00037 | 374.15 | 9.07 | 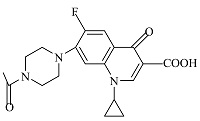 |
| 3 | C17H19FN3O4 | 348.12372 | 348.14 | 9.18 | 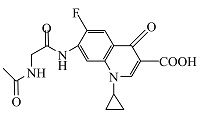 |
| 4 | C17H19FN3O3 | 331.99915 | 332.14 | 4.71 | 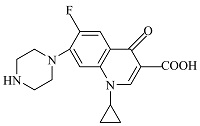 |
| 5 | C13H12FN2O3 | 263.00095 | 263.08 | 5.98 | 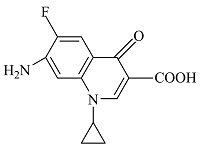 |
| 6 | C19H23FN3O4 | 376.16696 | 376.17 | 10.14 | 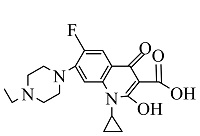 |
| 7 | C19H25FN3O4 | 378.18158 | 378.18 | 10.42 | 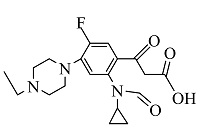 |
| 8 | C17H25FN3O3 | 338.18842 | 338.18 | 11.70 | 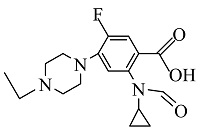 |
| 9 | C17H18N3O4 | 328.12994 | 328.13 | 3.25 | 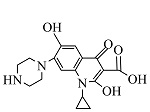 |
| 10 | C14H10N2O5 | 286.05911 | 286.06 | 8.33 | 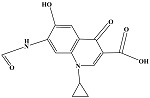 |
| 11 | C13H11N2O4 | 258.82837 | 259.07 | 9.72 | 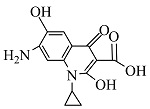 |
表1 ENR降解产物
Table 1 Products of ENR degradation
| 名称 | 化学式 | LCMS质荷比 | m/z | 保留时间/min | 结构式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C19H23FN3O4 | 376.16562 | 376.16 | 8.06 |  |
| 2 | C19H21FN3O4 | 374.00037 | 374.15 | 9.07 |  |
| 3 | C17H19FN3O4 | 348.12372 | 348.14 | 9.18 |  |
| 4 | C17H19FN3O3 | 331.99915 | 332.14 | 4.71 |  |
| 5 | C13H12FN2O3 | 263.00095 | 263.08 | 5.98 |  |
| 6 | C19H23FN3O4 | 376.16696 | 376.17 | 10.14 |  |
| 7 | C19H25FN3O4 | 378.18158 | 378.18 | 10.42 |  |
| 8 | C17H25FN3O3 | 338.18842 | 338.18 | 11.70 |  |
| 9 | C17H18N3O4 | 328.12994 | 328.13 | 3.25 |  |
| 10 | C14H10N2O5 | 286.05911 | 286.06 | 8.33 |  |
| 11 | C13H11N2O4 | 258.82837 | 259.07 | 9.72 |  |
| [1] |
AZHAR M R, ABID H R, SUN H Q, et al., 2016. Excellent performance of copper based metal organic framework in adsorptive removal of toxic sulfonamide antibiotics from wastewater[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 478: 344-352.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | CERQUEIRA F, MATAMOROS V, BAYONA J, et al., 2019. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in soils and crops. A field study in legume plants (Vicia faba L.) grown under different watering regimes[J]. Environmental Research, 170: 16-25. |
| [3] | CHEN L W, ZUO X, YANG S J, et al., 2019. Rational design and synthesis of hollow Co3O4@Fe2O3 core-shell nanostructure for the catalytic degradation of norfloxacin by coupling with peroxymonosulfate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 359: 373-384. |
| [4] | CHENG D L, NGO H H, GUO W S, et al., 2018a. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors for antibiotic wastewater treatment: Performance and membrane fouling issues[J]. Bioresource Technology, 267: 714-724. |
| [5] | CHENG D L, NGO H H, GUO W S, et al., 2018b. Bioprocessing for elimination antibiotics and hormones from swine wastewater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 621: 1664-1682. |
| [6] | DANNER M C, ROBERTSON A, BEHRENDS V, et al., 2019. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 664: 793-804. |
| [7] | GUO H G, GAO N Y, YANG Y, et al., 2016. Kinetics and transformation pathways on oxidation of fluoroquinolones with thermally activated persulfate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 292: 82-91. |
| [8] | GUO W Q, ZHAO Q, DU J S, et al., 2020. Enhanced removal of sulfadiazine by sulfidated ZVI activated persulfate process: Performance, mechanisms and degradation pathways[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 388: 124303. |
| [9] | KOVALAKOVA P, CIZMAS L, MCDONALD T J, et al., 2020. Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 251: 126351. |
| [10] | LI S, TANG J C, LIU Q L, et al., 2020. A novel stabilized carbon-coated nZVI as heterogeneous persulfate catalyst for enhanced degradation of 4-chlorophenol[J]. Environment International, 138: 105639. |
| [11] | LI S, TANG J C, YU C, et al., 2022. Efficient degradation of anthracene in soil by carbon-coated nZVI activated persulfate[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 431: 128581. |
| [12] |
MARTINEZ J L, 2009. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants[J]. Environmental Pollution, 157(11): 2893-2902.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | RASHEED A, HOWE J Y, DADMUN M D, et al., 2007. The efficiency of the oxidation of carbon nanofibers with various oxidizing agents[J]. Carbon, 45(5): 1072-1080. |
| [14] | SUN C J, QU L L, WU L, et al., 2020. Advances in analysis of nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in various matrices[J]. Trac-trends in Analytical Chemistry, 127: 115878. |
| [15] |
SZEKERES E, CHIRIAC C M, BARICZ A, et al., 2018. Investigating antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and microbial contaminants in groundwater in relation to the proximity of urban areas[J]. Environmental Pollution, 236: 734-744.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | WANG J L, ZHUAN R, 2020. Degradation of antibiotics by advanced oxidation processes: An overview[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 701: 135023. |
| [17] | WANG S Z, WANG J L, 2019. Oxidative removal of carbamazepine by peroxymonosulfate (PMS) combined to ionizing radiation: Degradation, mineralization and biological toxicity[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 658: 1367-1374. |
| [18] | WANG X Y, DU Y, MA J, 2016. Novel synthesis of carbon spheres supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of metronidazole[J]. Applied Surface Science, 390: 50-59. |
| [19] | WANG Y F, WANG L F, LIU R M, et al., 2022. Source-specific risk apportionment and critical risk source identification of antibiotic resistance in Fenhe River basin, China[J]. Chemosphere, 287(Part 1): 131997. |
| [20] | XU J, ZHANG X L, SUN C, et al., 2018. Catalytic degradation of diatrizoate by persulfate activation with peanut shell biochar-supported nano zero-valent iron in aqueous solution[J]. International Journal of Environment Research and Public Health, 15(9): 1937. |
| [21] |
YU F, LI Y, HAN S, et al., 2016. Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from aqueous solution using carbon materials[J]. Chemosphere, 153: 365-385.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | ZHANG J K, CHEN L, ZHANG X Y, 2022. Removal of p-nitrophenol by nano zero valent iron-cobalt and activated persulfate supported onto activated carbon[J]. Water, 14(9): 1387. |
| [23] | ZHANG R H, CHEN Y D, LI S D, et al., 2022. Remediation and optimisation of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation in contaminated water by persulfate activated with bagasse biochar-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron[J]. Sustainability, 14(15): 9324. |
| [24] | ZHI S L, SHEN S Z, ZHOU J, et al., 2020. Systematic analysis of occurrence, density and ecological risks of 45 veterinary antibiotics: Focused on family livestock farms in Erhai Lake basin, Yunnan, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 267(Part 1): 115539. |
| [25] | ZHOU M D, LI C X, ZHAO L X, et al., 2021. Synergetic effect of nano zero-valent iron and activated carbon on high-level ciprofloxacin removal in hydrolysis-acidogenesis of anaerobic digestion[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 752: 142261. |
| [26] | ZHOU Y Z, WANG T, ZHI D, et al., 2019. Applications of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites to the removal of antibiotics: A review[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 54(19): 12171-12188. |
| [27] | ZHU T T, SU Z X, LAI W X, et al., 2021. Insights into the fate and removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes using biological wastewater treatment technology[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 776: 145906. |
| [28] | ZOU J, MA J, CHEN L W, et al., 2013. Rapid acceleration of ferrous iron/peroxymonosulfate oxidation of organic pollutants by promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle with hydroxylamine[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(20): 11685-11691. |
| [29] | 陈涛, 沈梦楠, 蔡航, 等, 2024. 环境中抗生素修复技术研究进展[J]. 化工设计通讯, 50(1): 141-143. |
| CHEN T, SHEN M N, CAI H, et al., 2024. Research progress in antibiotic remediation technology in the environment[J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 50(1): 141-143. | |
| [30] | 仇思, 李小明, 罗琨, 等, 2022. g-C3N4/Ag3PO4/CNT对亚甲基蓝和四环素光催化的降解[J]. 环境化学, 41(7): 2414-2424. |
| CHOU S, LI X M, LUO K, et al., 2022. Study on the photocatalytic degradation performance of g-C3N4/Ag3PO4/CNT on methylene blue and tetracycline[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 41(7): 2414-2424. | |
| [31] | 杜毅, 2018. 新型碳球负载纳米铁的制备及其去除水中抗生素研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学. |
| DU Y, 2018. Novel synthesis of carbon spheres-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of metronidazole[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology. | |
| [32] | 胡锋平, 龙兰兰, 占鹏, 等, 2023. 过渡金属负载碳基复合材料活化过硫酸盐降解有机废水研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 52(3): 885-891. |
| HU F P, LONG L L, ZHAN P, et al., 2023. Research progress of activated persulfate degradation of organic wastewater by transition metal supported carbon matrix composites[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 52(3): 885-891. | |
| [33] | 廖晓数, 朱成煜, 仇玥, 等, 2022. 纳米零价铁基生物炭活化过硫酸盐降解土霉素[J]. 环境工程, 40(8): 118-124, 195. |
| LIAO X S, ZHU C Y, QIU Y, et al., 2022. Persulfate activation via nanoscale zero-valent iron based biochar for oxytetracycline degradation[J]. Environmental Engineering, 40(8): 118-124, 195. | |
| [34] | 鲁涛涛, 2023. 炭载纳米零价铁的制备及其在污染场地原位修复中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京石油化工学院. |
| LU T T, 2023. Preparation of carbon-supported nano zero-valent iron and its application in in-situ remediation of contaminated sites[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology. | |
| [35] | 唐亚鑫, 黄雯, 张建强, 等, 2022. Fe0/Fe3C羊粪生物炭复合材料的制备及其活化过一硫酸盐降解磺胺嘧啶[J]. 环境化学, 41(12): 3991-4005. |
| TANG Y X, HUANG W, ZHANG J Q, et al., 2022. Preparation of Fe0/ Fe3C sheep manure biochar composites foractivating peroxymonosulfate to degrade sulfadiazine[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 41(12): 3991-4005. | |
| [36] | 杨颖, 郭洪光, 邓钦祖, 等, 2016. Fe2+激活过氧单硫酸盐去除水中氨氮分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 47(8): 2900-2906. |
| YANG Y, GUO H G, DENG Q Z, et al., 2016. Analysis on removal of ammonia nitrogen using peroxymonosulfate activated by Fe2+[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 47(8): 2900-2906. | |
| [37] | 殷凯, 2019. Mn(Ⅶ)及基于UV的氧化降解水中新兴微污染物的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学. |
| YIN K, 2019. Degradation of emerging micropollutants in water by permanganate and UV-based oxidations[D]. Changsha: Hunan University. | |
| [38] |
于江波, 于婧, 刘杰, 等, 2024. 光催化去除水体中的抗生素[J]. 化学进展, 36(1): 95-105.
DOI |
|
YU J B, YU J, LIU J, et al., 2024. Photocatalytic removal of antibiotics from water[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 36(1): 95-105.
DOI |
|
| [39] | 张宏玲, 李森, 张杨, 等, 2016. 过渡金属离子活化过硫酸盐去除土壤中的芘[J]. 环境工程学报, 10(10): 6009-6014. |
| ZHANG H L, LI S, ZHANG Y, et al., 2016. Removal of pyrene in contaminated soil by transition metal ions activated persulfate[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 10(10): 6009-6014. |
| [1] | 丛鑫, 曹平, 王晓博. 生物炭负载纳米铁活化过硫酸盐去除土壤中的五氯联苯[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 282-290. |
| [2] | 周椿富, 于锐, 王翔, 闯绍闯, 杨洪杏, 谢越. 抗生素对不同土壤中酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2234-2241. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
