生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1310-1320.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.023
徐志宇1( ), 薛颖昊1,2, 张军3, 孙仁华1, 石祖梁1, 赫天一4, 王久臣1,*(
), 薛颖昊1,2, 张军3, 孙仁华1, 石祖梁1, 赫天一4, 王久臣1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-28
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
* 王久臣(1966年生),男,主要从事农业生态环境保护工作。E-mail: moawjch@126.com作者简介:徐志宇(1975年生),男,副研究员,博士,主要从事农业生态环境保护工作。E-mail: xufanjin@126.com第一联系人:徐志宇与薛颖昊具有同等贡献,同为第一作者。
基金资助:
XU Zhiyu1( ), XUE Yinghao1,2, ZHANG Jun3, SUN Renhua1, SHI Zuliang1, HE Tianyi4, WANG Jiuchen1,*(
), XUE Yinghao1,2, ZHANG Jun3, SUN Renhua1, SHI Zuliang1, HE Tianyi4, WANG Jiuchen1,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-28
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
了解秸秆综合利用领域研究应用的热点和前沿,有助于制定并优化秸秆资源化的政策。文章以CSCD和SCI-E数据库为获取秸秆综合利用研究领域中英文文献的数据来源,比较分析1999—2003、2004—2008、2009—2013和2014—2019年4个时间段肥料化、燃料化、饲料化、原料化和基料化等5个应用方向的中英文文献的分布比例及发表论文的高频关键词,确定秸秆综合利用的研究热点与前沿。结果表明,近20年,国内外学者和机构为推动秸秆综合利用研究,做出了巨大贡献,发文量呈现不断增长的趋势。肥料化始终是秸秆综合利用领域中文文献最主要的研究方向,英文文献中肥料化和饲料化应用方向的发文量占比不断下降,而燃料化的发文量占比不断上升;原料化和基料化应用研究在中英文文献中始终关注度较低。2009年前,中文文献比较关注秸秆还田对土壤改良和培肥的影响,而英文文献的关注点聚焦于饲料化的可消化性和对牲畜生长性能等影响,以及对作物产量、土壤有机碳等影响的肥料化应用上;2009年后,中文文献更多研究保护性耕作和作物产量变化以及土壤微生物群落结构等,而英文文献转向制备生物乙醇、沼气、秸秆生物质热解等燃料化应用和土壤微生物、土壤养分管理等肥料化应用上。近年来,中文文献研究前沿主要集中于秸秆还田对土壤和作物的影响、秸秆热解和发酵以及秸秆复合材料应用等;而英文文献研究秸秆综合利用对环境(如土壤碳环境和温室气体排放等)的影响、秸秆生物质热解燃烧、秸秆发酵制备生物乙醇和沼气、还田对土壤微生物及氮磷养分等影响,点多面广。高频关键词聚类分析,对大数据进行可视化展示,可反映近20年秸秆综合利用的研发历程,为下一步更好发挥秸秆的耕地保育、种养循环、节能减排等功能提供借鉴意义。
中图分类号:
徐志宇, 薛颖昊, 张军, 孙仁华, 石祖梁, 赫天一, 王久臣. 基于文献计量的秸秆综合利用研究热点与前沿分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1310-1320.
XU Zhiyu, XUE Yinghao, ZHANG Jun, SUN Renhua, SHI Zuliang, HE Tianyi, WANG Jiuchen. Research Hotspots and Frontiers of Comprehensive Utilization of Straw on Bibliometric Analysis[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1310-1320.
| Sequence | Author | Institution | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ZHANG Renzhi | Gansu Agr Univ | 73 |
| 2 | CHANG Zhizhou | Jiangsu Acad Agr Sci | 70 |
| 3 | DOU Sen | Jilin Agr Univ | 53 |
| 4 | ZHAO Lixin | Acad Agr Planning & Engn, Minist Agr & Rural Affairs | 50 |
| 5 | PAN Genxing | Nanjing Agr Univ | 49 |
| 6 | CAI Liqun | Gansu Agr Univ | 48 |
| 7 | JIA Zhikuan | Northwest A&F Univ | 48 |
| 8 | HUANG Gaobao | Gansu Agr Univ | 48 |
| 9 | YANG Gaihe | Northwest A&F Univ | 47 |
| 10 | WU Jinshui | Inst Subtrop Agr, Chinese Acad Sci | 44 |
| 11 | MENG Haibo | Acad Agr Planning & Engn, Minist Agr & Rural Affairs | 42 |
| 12 | LI Huixin | Nanjing Agr Univ | 40 |
| 13 | LI Nianqing | Nanjing Agr Univ | 38 |
| 14 | ZHOU Dingguo | Nanjing Forestry Univ | 37 |
| 15 | SHEN Qirong | Nanjing Agr Univ | 37 |
表1 秸秆综合利用中文发文量前15的作者
Table 1 Top 15 authors with the number of Chinese publication articals on the comprehensive utilization of straw
| Sequence | Author | Institution | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ZHANG Renzhi | Gansu Agr Univ | 73 |
| 2 | CHANG Zhizhou | Jiangsu Acad Agr Sci | 70 |
| 3 | DOU Sen | Jilin Agr Univ | 53 |
| 4 | ZHAO Lixin | Acad Agr Planning & Engn, Minist Agr & Rural Affairs | 50 |
| 5 | PAN Genxing | Nanjing Agr Univ | 49 |
| 6 | CAI Liqun | Gansu Agr Univ | 48 |
| 7 | JIA Zhikuan | Northwest A&F Univ | 48 |
| 8 | HUANG Gaobao | Gansu Agr Univ | 48 |
| 9 | YANG Gaihe | Northwest A&F Univ | 47 |
| 10 | WU Jinshui | Inst Subtrop Agr, Chinese Acad Sci | 44 |
| 11 | MENG Haibo | Acad Agr Planning & Engn, Minist Agr & Rural Affairs | 42 |
| 12 | LI Huixin | Nanjing Agr Univ | 40 |
| 13 | LI Nianqing | Nanjing Agr Univ | 38 |
| 14 | ZHOU Dingguo | Nanjing Forestry Univ | 37 |
| 15 | SHEN Qirong | Nanjing Agr Univ | 37 |
| Sequence | Author | Institution | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WANAPAT M | Khon Kaen Univ | 126 |
| 2 | LAL R | Ohio State Univ | 92 |
| 3 | DALE B E | Michigan State Univ | 82 |
| 4 | CHEN Hongzhang | Chinese Acad Sci | 60 |
| 5 | BALAN V | Michigan State Univ | 59 |
| 6 | LIU Jianxin | Zhejiang Univ | 50 |
| 7 | MARSCHNER P | Univ Adelaide | 49 |
| 8 | TAN Zhiliang | Chinese Acad Sci | 47 |
| 9 | SUN Runcang | Beijing Forestry Univ | 44 |
| 10 | KARIMI K | Isfahan Univ Technol | 43 |
| 11 | HAN Lujia | China Agr Univ | 43 |
| 12 | YONG Qiang | Nanjing Forestry Univ | 41 |
| 13 | RECOUS S | INRA | 38 |
| 14 | LI Xiujin | Beijing Univ Chem Technol | 38 |
| 15 | JOERGENSEN R G | Univ Kassel | 38 |
表2 秸秆综合利用英文发文前15的作者
Table 2 Top 15 authors with the number of Chinese publication articals on the comprehensive utilization of straw
| Sequence | Author | Institution | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WANAPAT M | Khon Kaen Univ | 126 |
| 2 | LAL R | Ohio State Univ | 92 |
| 3 | DALE B E | Michigan State Univ | 82 |
| 4 | CHEN Hongzhang | Chinese Acad Sci | 60 |
| 5 | BALAN V | Michigan State Univ | 59 |
| 6 | LIU Jianxin | Zhejiang Univ | 50 |
| 7 | MARSCHNER P | Univ Adelaide | 49 |
| 8 | TAN Zhiliang | Chinese Acad Sci | 47 |
| 9 | SUN Runcang | Beijing Forestry Univ | 44 |
| 10 | KARIMI K | Isfahan Univ Technol | 43 |
| 11 | HAN Lujia | China Agr Univ | 43 |
| 12 | YONG Qiang | Nanjing Forestry Univ | 41 |
| 13 | RECOUS S | INRA | 38 |
| 14 | LI Xiujin | Beijing Univ Chem Technol | 38 |
| 15 | JOERGENSEN R G | Univ Kassel | 38 |
| Sequence | Title | First author | First institution | Citation frequency | Publication year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Straw resources and their utilization in China | HAN Lujia | China Agr Univ | 245 | 2002 |
| 2 | Effect of matching use of straw and chemical fertilizer on soil fertility | LAO Xiurong | Shandong Agr Univ | 172 | 2003 |
| 3 | The effect of stubble return on agro-ecological system and crop growth | JIANG Yonghong | China Agr Univ | 135 | 2001 |
| 4 | Estimation of nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its utilization situation in China | GAO Liwei | Hebei Agr Univ | 127 | 2009 |
| 5 | Review of research progress on the influence and mechanism of field straw residue incorporation on soil organic matter and nitrogen availability | PAN Jianling | Lanzhou Univ | 119 | 2013 |
| 6 | Effect of returning corn straw into soil on soil fertility | WU Zhijie | Inst Appl Ecol, Chinese Acad Sci | 109 | 2002 |
| 7 | Effects of different tillage methods and straw-returning on soil organic carbon content in a winter wheat field | TIAN Shenzhong | Shandong Agr Univ | 103 | 2010 |
| 8 | Effect of long-term returning straw to soil on soil fertility | LAO Xiurong | Shandong Agr Univ | 100 | 2002 |
| 9 | Effects of corn straw mulching on soil temperature and soil evaporation of winter wheat field | CHEN Suying | Chinese Acad Sci | 97 | 2005 |
| 10 | Analysis and comparison of the effects of plastic film mulching and straw mulching on soil fertility | BU Yushan | Shanxi Agr Univ | 96 | 2006 |
表3 秸秆综合利用被引频次前10的中文文献
Table 3 Top 10 Chinese publication articals cited for comprehensive utilization of straw
| Sequence | Title | First author | First institution | Citation frequency | Publication year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Straw resources and their utilization in China | HAN Lujia | China Agr Univ | 245 | 2002 |
| 2 | Effect of matching use of straw and chemical fertilizer on soil fertility | LAO Xiurong | Shandong Agr Univ | 172 | 2003 |
| 3 | The effect of stubble return on agro-ecological system and crop growth | JIANG Yonghong | China Agr Univ | 135 | 2001 |
| 4 | Estimation of nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its utilization situation in China | GAO Liwei | Hebei Agr Univ | 127 | 2009 |
| 5 | Review of research progress on the influence and mechanism of field straw residue incorporation on soil organic matter and nitrogen availability | PAN Jianling | Lanzhou Univ | 119 | 2013 |
| 6 | Effect of returning corn straw into soil on soil fertility | WU Zhijie | Inst Appl Ecol, Chinese Acad Sci | 109 | 2002 |
| 7 | Effects of different tillage methods and straw-returning on soil organic carbon content in a winter wheat field | TIAN Shenzhong | Shandong Agr Univ | 103 | 2010 |
| 8 | Effect of long-term returning straw to soil on soil fertility | LAO Xiurong | Shandong Agr Univ | 100 | 2002 |
| 9 | Effects of corn straw mulching on soil temperature and soil evaporation of winter wheat field | CHEN Suying | Chinese Acad Sci | 97 | 2005 |
| 10 | Analysis and comparison of the effects of plastic film mulching and straw mulching on soil fertility | BU Yushan | Shanxi Agr Univ | 96 | 2006 |
| Sequence | Title | First author | First institution | Citation frequency | Publication year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: A critical review | MOHAN D | Mississippi State Univ | 2941 | 2006 |
| 2 | Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production | KUMAR P | Univ Calif Davis | 1759 | 2009 |
| 3 | Biogas production: Current state and perspectives | WEILAND P | Johann Heinrich von Thunen Inst | 1177 | 2010 |
| 4 | Global potential bioethanol production from wasted crops and crop residues | KIM S | Michigan State Univ | 1012 | 2004 |
| 5 | Production of liquid biofuels from renewable resources | NIGAM P | Univ Ulster | 998 | 2011 |
| 6 | Progress and recent trends in biofuels | DEMIRBAS A | Selcuk Univ | 989 | 2007 |
| 7 | Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies | WYMAN C E | Dartmouth Coll | 849 | 2005 |
| 8 | Recent trends in global production and utilization of bio-ethanol fuel | BALAT M | Sila Sci & Energy Unltd Co | 744 | 2009 |
| 9 | A review of the production of ethanol from softwood | GALBE M | Lund Univ | 670 | 2002 |
| 10 | The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures | YUAN Jinhua | Chinese Acad Sci | 611 | 2011 |
表4 秸秆综合利用被引频次前10的英文文献
Table 4 Top 10 English publication articals cited for comprehensive utilization of straw
| Sequence | Title | First author | First institution | Citation frequency | Publication year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: A critical review | MOHAN D | Mississippi State Univ | 2941 | 2006 |
| 2 | Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production | KUMAR P | Univ Calif Davis | 1759 | 2009 |
| 3 | Biogas production: Current state and perspectives | WEILAND P | Johann Heinrich von Thunen Inst | 1177 | 2010 |
| 4 | Global potential bioethanol production from wasted crops and crop residues | KIM S | Michigan State Univ | 1012 | 2004 |
| 5 | Production of liquid biofuels from renewable resources | NIGAM P | Univ Ulster | 998 | 2011 |
| 6 | Progress and recent trends in biofuels | DEMIRBAS A | Selcuk Univ | 989 | 2007 |
| 7 | Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies | WYMAN C E | Dartmouth Coll | 849 | 2005 |
| 8 | Recent trends in global production and utilization of bio-ethanol fuel | BALAT M | Sila Sci & Energy Unltd Co | 744 | 2009 |
| 9 | A review of the production of ethanol from softwood | GALBE M | Lund Univ | 670 | 2002 |
| 10 | The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures | YUAN Jinhua | Chinese Acad Sci | 611 | 2011 |
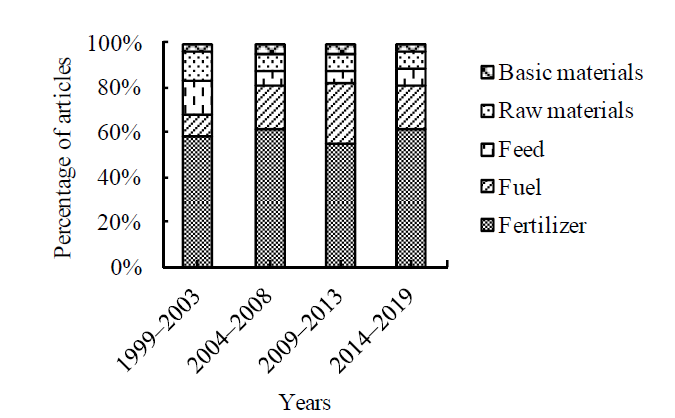
图4 秸秆综合利用中文发文5个应用方向的研究关注度演变
Fig. 4 Research attention evolution of five application of Chinese publication articals for comprehensive utilization of straw
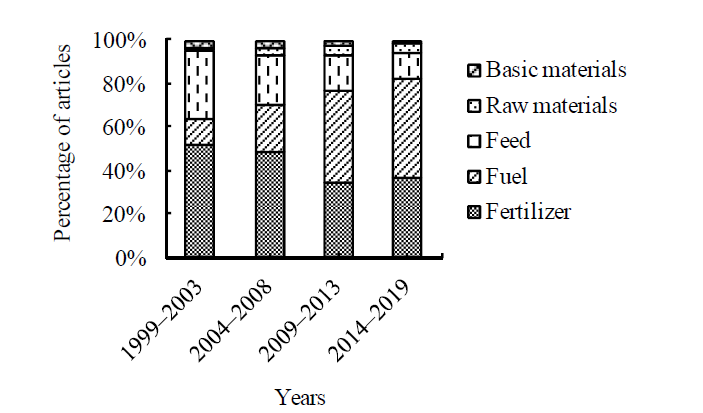
图5 秸秆综合利用英文发文5个应用方向的研究关注度演变
Fig. 5 Research attention evolution of five application of English publication articals for comprehensive utilization of straw
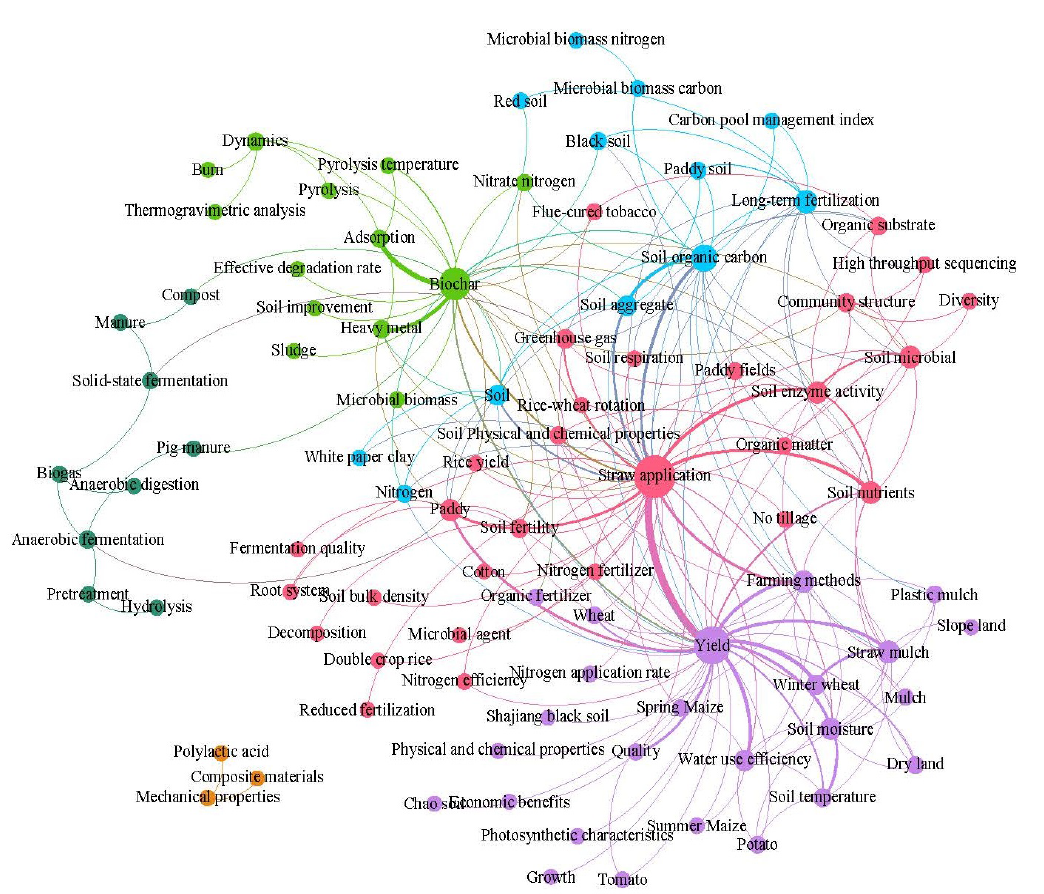
图8 秸秆综合利用中文文献研究前沿高频关键词聚类
Fig. 8 Clustering map of high frequency keywords on comprehensive utilization of straw collected from Chinese publication articals research frontiers
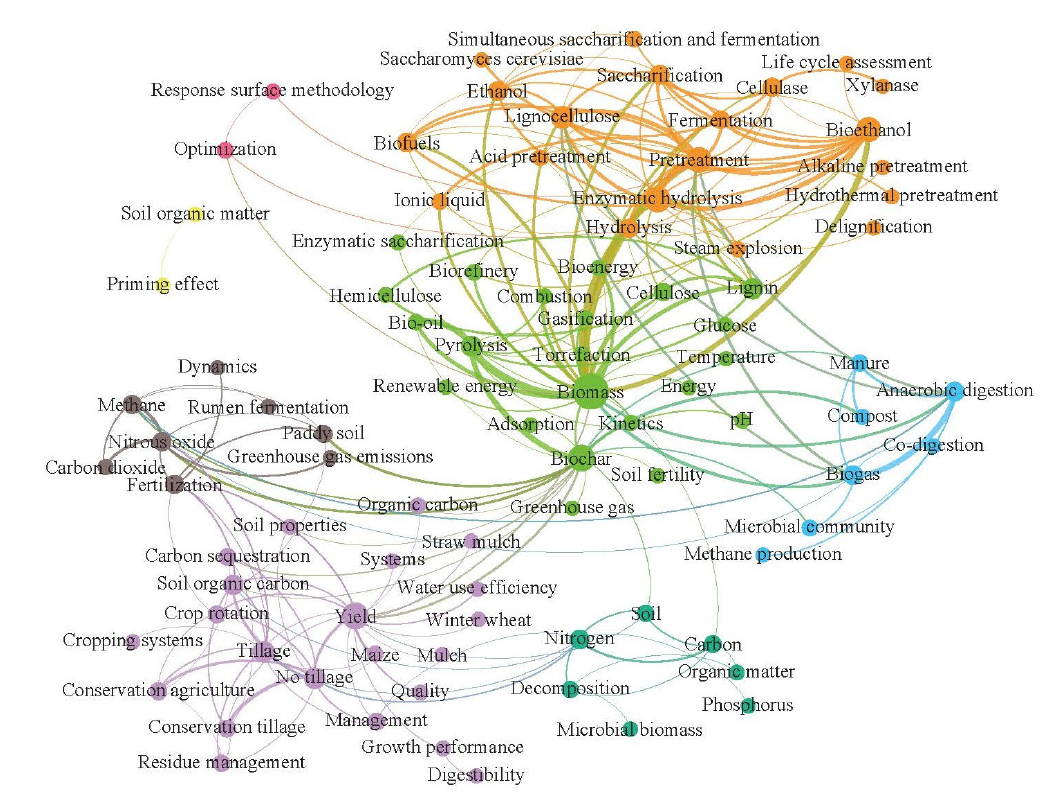
图9 秸秆综合利用英文文献研究前沿高频关键词聚类
Fig. 9 Clustering map of high frequency keywords on comprehensive utilization of straw collected from English publication articals research frontiers
| [1] |
AKHTAR K, WANG W, KHAN A, et al., 2019. Straw mulching with fertilizer nitrogen: An approach for improving crop yield, soil nutrients and enzyme activities[J]. Soil Use and Management, 35(3): 526-535.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BENBI D K, TOOR A S, KUMAR S, 2012. Management of organic amendments in rice-wheat cropping system determines the pool where carbon is sequestered[J]. Plant and Soil, 360(1): 145-162.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JAFARI M, RAHIMI M R, GHAEDI M, et al., 2017. Fixed-bed column performances of azure-II and auramine-O adsorption by Pinus eldarica stalks activated carbon and its composite with zno nanoparticles: Optimization by response surface methodology based on central composite design[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 507: 172-189.
DOI URL |
| [4] | KILIC U, KURT D, AYTAC S, et al., 2019. A study on the feed value, in vitro digestibility and methane production of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) field waste[J]. Progress in Nutrition, 21(2): 449-457. |
| [5] |
KUMAR P, BARRETT D M, DELWICHE M J, et al., 2009. Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 48(8): 3713-3729.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KUMAR T K, RANA D S, NAIN L, 2019. Legume residue and N management for improving productivity and N economy and soil fertility in wheat (Triticum aestivum)-based cropping systems[J]. National Academy Science Letters, 42(9): 297-307.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MEHMET S, REINHARD W, ROLAND B, et al., 2018. Interaction of straw amendment and soil NO3- content controls fungal denitrification and denitrification product stoichiometry in a sandy soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 126: 204-212.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MOHAN D, PITTMAN C U, STEELE P H, et al., 2006. Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: A critical review[J]. Energy & Fuels, 20(3):848-889.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
NAKHSHINIEV B, BIDDINIKA M K, GONZALES H B, et al., 2014. Evaluation of hydrothermal treatment in enhancing rice straw compost stability and maturity[J]. Bioresource Technology, 151: 306-313.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
OGURA T, DATE Y, KIKUCHI J, 2013. Differences in cellulosic supramolecular structure of compositionally similar rice straw affect biomass metabolism by paddy soil microbiota[J]. Plos One, 8(6): e66919.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PARITOSH K, VIVEKANAND V, 2019. Biochar enabled syntrophic action: Solid state anaerobic digestion of agricultural stubble for enhanced methane production[J]. Bioresour Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121712.
DOI |
| [12] |
PARUSHI N, VISHAL S, MAHAK G, et al., 2018. Application of ionic liquid and alkali pretreatment for enhancing saccharification of sunflower stalk biomass for potential biofuel-ethanol production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 267: 560-568.
DOI URL |
| [13] | PLAIMEIN A, ROTCHANAPHAN H, KITTIPONG R, et al., 2016. Enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis and biogas production from rice straw by pretreatment with organic acids[J]. Industrial Crops & Products, 87: 247-254. |
| [14] | PROCENTESE A, RAGANATI F, OLIVIERIl G, et al., 2019. Agro food wastes and innovative pretreatments to meet biofuel demand in Europe[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 42(5): 954-961. |
| [15] |
YUKESH K R, KAVITHA S, SIVASHANMUGHAM P, et al., 2019. Biohydrogen production from rice straw: Effect of combinative pretreatment, modelling assessment and energy balance consideration[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(4): 2203-2215.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SARKER J R, SINGH B P, FANG Y, et al., 2019. Tillage history and crop residue input enhanced native carbon mineralisation and nutrient supply in contrasting soils under long-term farming systems[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 193: 71-84.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SINGH A, BASAK P, 2018. Economic and environmental evaluation of rice straw processing technologies for energy generation: A case study of Punjab, India[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 212: 343-352.
DOI URL |
| [18] | TABAKAEV R B, ASTAFEV A V, DUBININ Y V, et al., 2018. Autothermal pyrolysis of biomass due to intrinsic thermal decomposition effects[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis & Calorimetry, 134(2): 1045-1057. |
| [19] |
TANTAYOTAI P, RATTANAPORN K, TEPAAMORNDECH S, et al., 2019. Analysis of an ionic liquid and salt tolerant microbial consortium which is useful for enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis and biogas production[J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 10(6): 1481-1491.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
TERESA M, MAHDI V, AMIT K, 2019. Assessment of energy production potential from agricultural residues in Bolivia[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 102: 14-23.
DOI URL |
| [21] | WEILAND P, 2010. Biogas production: current state and perspectives[J]. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 85(4): 849-860. |
| [22] | 敖金成, 罗华元, 张晓龙, 等, 2015. 玉米秸秆还田方式对初烤烟叶品质及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 27(8): 1456-1461. |
| AO J C, LUO H Y, ZHANG X L, et al., 2015. Effects of different corn straw returning modes on quality of flue-cured tobacco leaves and soil fertility[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 27(8): 1456-1461. | |
| [23] | 都华, 章雅馨, 张学勇, 等, 2017. 基于文献计量法分析中国秸秆利用研究现状及发展[J]. 辽宁大学学报(自然科学版), 44(2): 162-170. |
| DOU H, ZHANG Y X, ZHANG X Y, et al., 2017. Bibliometric analysis on the research status and development of straw utilization in China[J]. Journal of Liaoning University (Natural Science Edition), 44(2): 162-170. | |
| [24] | 丁绍兰, 张敏娜, 黄振侠, 等, 2018. 尿素氨化预处理对稻秆厌氧发酵产气特性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(1): 18-23. |
| DING S L, ZHANG M N, HUANG Z X, et al., 2018. Effect of urea ammoniation pretreatment on anaerobic fermentation characteristics of rice straw[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 27(1): 18-23. | |
| [25] | 苟丽琼, 姚恒, 王戈, 等, 2019. 稻草不同还田方式对土壤动物群落结构的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 31(3): 450-457. |
| GOU L Q, YAO H, WANG G, et al., 2019. Effects of different straw returning methods on cropland soil fauna community[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 31(3): 450-457. | |
| [26] | 何佳闻, 何春霞, 郭航言, 等, 2019. 5种秸秆生物炭吸附亚甲基蓝及其性能对比研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 42(2): 382-388. |
| HE J W, HE C X, GUO H Y, et al., 2019. Adsorption of methylene blue by five straw biochars and its performance comparison[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 42(2): 382-388. | |
| [27] | 韩鲁佳, 闫巧娟, 刘向阳, 等, 2002. 中国农作物秸秆资源及其利用现状[J]. 农业工程学报, 18(3): 87-91. |
| HAN L J, YAN Q J, LIU X Y, et al., 2002. Straw resources and their utilization in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 18(3): 87-91. | |
| [28] |
靳璇, 李赢, 李新, 等, 2016. 秸秆预处理工艺对秸秆基人造板性能的影响[J]. 应用化学, 33(4): 430-435.
DOI |
| JIN X, LI Y, LI X, et al., 2016. Effect of pretreatment methods of rice straw on straw board properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 33(4): 430-435. | |
| [29] | 劳秀荣, 孙伟红, 王真, 等, 2003. 秸秆还田与化肥配合施用对土壤肥力的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 40(4): 618-623. |
| LAO X R, SUN W H, WANG Z, et al., 2003. Effect of matching use of straw and chemical fertilizer on soil fertility[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 40(4): 618-623. | |
| [30] | 李栋宇, 靳辉勇, 屠乃美, 等, 2018. 等氮条件下有机无机配施对烤烟根际土壤微生物功能多样性的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 31(11): 2361-2365. |
| LI D Y, JIN H Y, TU N M, et al., 2018. Effects of combined application of organic and inorganic on metabolic functional diversity of rhizosphere soil microbial community of fuel-cured tobacco under same N condition[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(11): 2361-2365. | |
| [31] | 李昊昱, 孟兆良, 庞党伟, 等, 2019. 周年秸秆还田对农田土壤固碳及冬小麦-夏玉米产量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 45(6): 893-903. |
| LI H Y, MENG Z L, PANG D W, et al., 2019. Effect of annual straw return model on soil carbon sequestration and crop yields in winter wheat-summer maize rotation farmland[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 45(6): 893-903. | |
| [32] | 刘哲, 孙增慧, 张瑞庆, 2018. 秸秆添加对潮土团聚体及有机碳分布和稳定性的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 31(6): 1246-1252. |
| LIU Z, SUN Z H, ZHANG R Q, et al., 2018. Effects of application of rice straw on distribution and stability of aggregates and organic carbon in fluvo-aquic[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(6): 1246-1252. | |
| [33] | 罗熳丽, 段均华, 姚恒, 等, 2020. 稻草不同还田量对土壤动物群落结构的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 37(1): 85-92. |
| LUO M L, DUAN J H, YAO H, et al., 2020. Effects of different rice straw returning quantities on soil fauna community structure[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 37(1): 85-92. | |
| [34] | 马骁轩, 蔡红珍, 付鹏, 等, 2016. 中国农业固体废弃物秸秆的资源化处置途径分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(1): 168-174. |
| MA X X, CAI H Z, FU P, et al., 2016. Analysis of the reutilization methods for agricultural waste of straw in China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(1): 168-174. | |
| [35] | 任江波, 李钠钾, 秦平伟, 等, 2018. 不同覆盖材料对土壤理化性状和微生物量碳氮含量的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 31(10): 2140-2145. |
| REN J B, LI N J, QIN P W, et al., 2018. Effect of different mulching materials on physical and chemical characteristics of soil and microbial biomass[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(10): 2140-2145. | |
| [36] | 石祖梁, 王飞, 李想, 等, 2016. 秸秆“五料化”中基料化的概念和定义探讨[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (6): 152-155. |
| SHI Z L, WANG F, LI X, et al., 2016. The discussion on concept and definition of straw substrate utilization[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (6): 152-155. | |
| [37] | 王丹丹, 2020. 农作物秸秆的综合利用与可持续发展[J]. 农机化研究, 42(11): 264-268. |
| WANG D D, 2020. Comprehensive utilization and sustainable development of the straw of crops[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 42(11): 264-268. | |
| [38] | 王平, 宋振华, 常娟, 等, 2019. 农作物秸秆作为畜禽饲料的研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 42(3): 87-90. |
| WANG P, SONG Z H, CHANG J, et al., 2019. Research progress on corp straw as livestock feed[J]. Feed Research, 42(3): 87-90. | |
| [39] | 王秋菊, 焦峰, 刘峰, 等, 2019. 草甸白浆土稻秆氮利用效率及氮素调控对水稻产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(11): 86-94. |
| WANG Q J, JIAO F, LIU F, et al., 2019. Nitrogen utilization efficiency of rice straw and effect of nitrogen regulation technology on yield in meadow albic soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(11): 86-94. | |
| [40] | 叶新新, 王冰清, 刘少君, 等, 2019. 耕作方式和秸秆还田对砂姜黑土碳库及玉米小麦产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(14): 112-118. |
| YE X X, WANG B Q, LIU S J, et al., 2019. Influence of tillage and straw retention on soil carbon pool and maize-wheat yield in Shajiang black soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(14): 112-118. | |
| [41] | 曾哲, 刘保华, 张文俊, 等, 2019. 低掺量油菜秸秆纤维混凝土力学性能试验研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 21(6): 117-123. |
| ZENG Z, LIU B H, ZHANG W J, et al., 2019. Experimental study on mechanical properties of low-volume rape straw fiber concrete[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 21(6): 117-123. | |
| [42] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2020. 关于发布《第二次全国污染源普查公报》的公告[DB/OL]. [2020-06-09]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/2-02006/t20200610_783547.html. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment, PRC, 2020. Announcement on the issuance of the Bulletin of the Second National Census of Pollution Sources [DB/OL]. [2020-06-09]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/2-02006/t20200610_783547.html. | |
| [43] | 朱颢, 胡启春, 汤晓玉, 等, 2017. 我国农作物秸秆资源燃料化利用开发进展[J]. 中国沼气, 35(2): 115-120. |
| ZHU H, HU Q C, TANG X Y, et al., 2017. Current development and progress of fuelization of agricultural straw in China[J]. China Biogas, 35(2): 115-120. | |
| [44] | 朱士强, 陆祥安, 于春涵, 等, 2019. 热氧老化对麦秸秆/橡胶/PE仿藤条性能的影响[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 39(7): 32-38. |
| ZHU S Q, LU X A, YU C H, et al., 2019. Effects of thermal oxidative aging on wheat straw/rubber biomass imitation rattan[J]. China Biotechnology, 39(7): 32-38. | |
| [45] | 查良玉, 李毅念, 王兆烨, 等, 2015. 秸秆机械集中沟埋还田的经济效益分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 27(3): 467-476. |
| ZHA L Y, LI Y N, WANG Z Y, et al., 2015. Analysis on economic benefit of straw concentrated ditch-buried returning field using machine[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 27(3): 467-476. |
| [1] | 柯奇画, 张科利. 基于文献计量的中国水土流失尺度效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1489-1498. |
| [2] | 魏建兵, 郑泓, 程雨露, 王阳. 基于CiteSpace的生态安全格局研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 835-844. |
| [3] | 刘可慧, 李广娈, 李春明, 赵珂艺, 张宁宁, 薛洁怡, 李艺, 于方明, 段敏. 基于文献计量学和知识图谱分析的漓江生态环境40年研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 409-420. |
| [4] | 孙晓杰, 邹怡, 郭晨辉. 基于CNKI数据库的植物与昆虫关系研究文献计量分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 196-204. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
