生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1321-1332.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.024
• 综述 •
上一篇
收稿日期:2021-02-24
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
作者简介:王薇(1975年生),女,教授,博士,硕士研究生导师,国家一级注册建筑师,研究方向建筑技术和人居环境。E-mail: vivi.gan@126.com
基金资助:Received:2021-02-24
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
细颗粒物(PM2.5)在城市发展进程中,对城市环境空气质量和居民健康的影响程度日益上升。文章数据来源于1971—2020年WOS和CNKI数据库中城市环境中细颗粒物相关研究主题的文献样本数据,利用CiteSpace软件,通过区域分布特征分析、关键词共现分析、突现词探测、文献共被引分析和多维尺度分析等,系统梳理了城市环境中细颗粒物研究领域的前沿、知识基础、热点现状与发展趋势,得出以下结论:(1)在研究趋势方面,中国学者近年来在国际上发表论文的占比逐年递增,国内外研究内容稍有差异,但总体趋同;(2)在研究性质方面,国内研究侧重于描述细颗粒物的产生原因及表现特征方面,国外则多运用动力学和沉积原理对场域中的细颗粒物运动规律做出解析;(3)在研究对象方面,国内的源解析案例较多,而国外则推进交通排放空间格局的研究;(4)在研究前沿方面,国内研究主要关注主成分分析的细化和室内空气质量的优化,国外研究则更倾向于从可持续发展、人类健康及改善人居环境角度研究细颗粒对人体的影响。最后,文章认为应加强多学科交叉与合作,拓展人居环境视角下细颗粒物的系统性研究,综合关注其在不同城市和功能区的水平运动和垂直扩散规律,有效优化绿色基础设施的空间配置,准确地从源头控制环境污染,从而改善城市的空气质量,维护城市生态平衡。
中图分类号:
王薇, 张蕾. 基于CiteSpace的城市环境中细颗粒物研究进展的可视化分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1321-1332.
WANG Wei, ZHANG Lei. Visual Analysis of Research Progress of Fine Particles in Urban Environment Based on CiteSpace[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1321-1332.
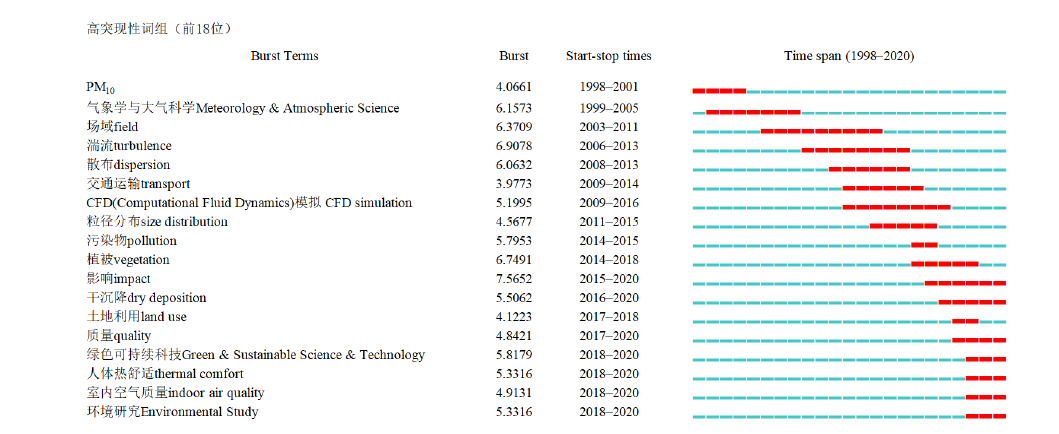
图6 基于WOS的城市环境中颗粒物研究中的突现词图谱 引文年份始自1971年,但至1998年才出现满足突现条件的词汇,因此以1998—2020年作为分析的时间跨度
Fig. 6 Burst terms in the study of the particulate matter in urban environment based on Web of Science
| 年份 Year | 关键词 Keyword | 中心度 Centre | 年份 Year | 关键词 Keyword | 中心度 Centre |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | PM10 | 0.77 | 2015 | 滞尘能力 Dust detaining abilities | 0.05 |
| 2004 | PM2.5 | 0.36 | 2016 | 大气污染 Atmospheric pollution | 0.23 |
| 2005 | 源解析 Source analysis | 0.37 | 2016 | 水溶性离子 Soluble ions | 0.14 |
| 2005 | 可吸入颗粒物 Inhalable particles | 0.19 | 2016 | 因子分析 Factor analysis | 0.1 |
| 2011 | 粒径分布 Particle size distribution | 0.22 | 2016 | PM2.5浓度 Concentration of PM2.5 | 0.05 |
| 2014 | 分布 Distribution | 0.3 | 2016 | 城市森林 Prban forest | 0.02 |
| 2014 | 空气污染 Air pollution | 0.26 | 2017 | 污染特征 Pollution characteristics | 0.22 |
| 2014 | 相关性 Correlation | 0.22 | 2017 | 主成分分析 Principal component analysis | 0.2 |
| 2014 | 功能区 Functional zone | 0.1 | 2017 | 无机元素 Inorganic elements | 0.2 |
| 2015 | 城市绿地 Urban green space | 0.27 | 2017 | 春季 Springtime | 0.06 |
| 2015 | 园林植物 Ornamental plants | 0.1 | 2017 | 影响因素 Influence factor | 0.05 |
| 2015 | 雾霾 Haze | 0.14 | 2017 | 穿透系数 Penetration factor | 0.05 |
表1 城市环境中细颗粒物研究关键词共现网络的关键词中心性排序列表
Table 1 The keyword centre index rank of study on fine particulate matter in urban environment co-occurrence network
| 年份 Year | 关键词 Keyword | 中心度 Centre | 年份 Year | 关键词 Keyword | 中心度 Centre |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | PM10 | 0.77 | 2015 | 滞尘能力 Dust detaining abilities | 0.05 |
| 2004 | PM2.5 | 0.36 | 2016 | 大气污染 Atmospheric pollution | 0.23 |
| 2005 | 源解析 Source analysis | 0.37 | 2016 | 水溶性离子 Soluble ions | 0.14 |
| 2005 | 可吸入颗粒物 Inhalable particles | 0.19 | 2016 | 因子分析 Factor analysis | 0.1 |
| 2011 | 粒径分布 Particle size distribution | 0.22 | 2016 | PM2.5浓度 Concentration of PM2.5 | 0.05 |
| 2014 | 分布 Distribution | 0.3 | 2016 | 城市森林 Prban forest | 0.02 |
| 2014 | 空气污染 Air pollution | 0.26 | 2017 | 污染特征 Pollution characteristics | 0.22 |
| 2014 | 相关性 Correlation | 0.22 | 2017 | 主成分分析 Principal component analysis | 0.2 |
| 2014 | 功能区 Functional zone | 0.1 | 2017 | 无机元素 Inorganic elements | 0.2 |
| 2015 | 城市绿地 Urban green space | 0.27 | 2017 | 春季 Springtime | 0.06 |
| 2015 | 园林植物 Ornamental plants | 0.1 | 2017 | 影响因素 Influence factor | 0.05 |
| 2015 | 雾霾 Haze | 0.14 | 2017 | 穿透系数 Penetration factor | 0.05 |
| [1] |
ASSIMAKOPOULOS V D, APSIMON H M, MOUSSIOPOULOS N, 2003. A numerical study of atmospheric pollutant dispersion in different two-dimensional street canyon configurations[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 37(29): 4037-4049.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BADACH J, DYMNICKA M, BARANOWSKI A, 2020. Urban Vegetation in Air Quality Management: A Review and Policy Framework[J]. Sustainability, 12(3): 1258.
DOI URL |
| [3] | BAIK J J, KIM J J, 1999. A numerical study of flow and pollutant dispersion characteristics in urban street canyons[J]. Clarivate Analytics Web of Science, 38(11):1576-1589 |
| [4] |
BRITTER R E, HANNA S R, 2003. Flow and dispersion in urban areas[J]. Annual REVIEW of Fluid Mechanics, 35(1): 469-496.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BUCCOLIERI R, SANDBERG M, SABATINO S D, 2010. City breathability and its link to pollutant concentration distribution within urban-like geometries[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 44(15): 1894-1903.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHAN C K, YAOX H, 2007. Air pollution in mega cities in China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 42(1): 1-42.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHEN C M, IBEKWE-SANJUAN F, HOU J H, 2010. The structure and dynamics of co-citation clusters: A multiple-perspective co-citation analysis[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 61(7): 1386-1409.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN C M, 2006. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 57(3): 359-377.
DOI URL |
| [9] | DUAN G, BRIMBLECOMBE P, CHU Y L, et al., 2020. Turbulent flow and dispersion inside and around elevated walkways[J]. Building and Environment, 173: 1-14. |
| [10] | FENG H H, ZOU B, TANG Y M, 2017. Scale- and Region-Dependence in Landscape-PM2.5 Correlation: Implications for Urban Planning[J]. Remote Sensing, 9(9): 1-20. |
| [11] |
GHAFFARIANHOSEINI A, ALWAER H, OMRANY H, et al., 2018. Sick building syndrome: are we doing enough?[J]. Architectural Science Review, 61(3): 99-121.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
GROMKE C, BUCCOLIERI R, SABATINO S, et al., 2008. Dispersion study in a street canyon with tree planting by means of wind tunnel and numerical investigations—Evaluation of CFD data with experimental data[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 42(37): 8640-8650.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GROMKE C, RUCK B, 2009. On the Impact of Trees on Dispersion Processes of Traffic Emissions in Street Canyons[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 131(1): 19-34.
DOI URL |
| [14] | HANG J, CHEN X Y, CHEN G W, et al., 2019. The influence of aspect ratios and wall heating conditions on flow and passive pollutant exposure in 2D typical street canyons[J]. Building and Environment, 168: 1-20. |
| [15] |
HANG J, LI Y G, SANDBERG M, et al., 2012. The influence of building height variability on pollutant dispersion and pedestrian ventilation in idealized high-rise urban areas[J]. Building and Environment, 56: 346-360.
DOI URL |
| [16] | HE L J, HANG J, WANG X M, et al., 2017. Numerical investigations of flow and passive pollutant exposure in high-rise deep street canyons with various street aspect ratios and viaduct settings[J]. The Science of the total environment, 584-585: 189-206. |
| [17] | JANHALL S, 2015. Review on urban vegetation and particle air pollution-Deposition and dispersion[J]. Clarivate Analytics Web of Science, 105: 130-137. |
| [18] |
JONES A M, HARRISON R M, 2004. The effects of meteorological factors on atmospheric bioaerosol concentrations——a review[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 326(1-3): 151-180.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KETZEL M, WÅHLIN P, BERKOWICZ R, et al., 2003. Particle and trace gas emission factors under urban driving conditions in Copenhagen based on street and roof-level observations[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 37(20): 2735-2749.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
KIM J J, BAIK J J, 2004. A numerical study of the effects of ambient wind direction on flow and dispersion in urban street canyons using the RNG k-ε turbulence model[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 38(19): 3039-3048.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
KUMAR P, KETZEL M, VARDOULAKIS S, et al., 2011. Dynamics and dispersion modelling of nanoparticles from road traffic in the urban atmospheric environment——A review[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 42(9): 580-603.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LI X X, LIU C H, DENNIS Y C, et al., 2006. Recent progress in CFD modelling of wind field and pollutant transport in street canyons[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 40(29): 5640-5658.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LONGLEY I D, GALLAGHER M W, DORSEY J R, et al., 2003. Inglis. A case study of aerosol (4.6 nm<Dp<10 μm) number and mass size distribution measurements in a busy street canyon in Manchester, UK[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 37(12): 1563-1571.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
MA Z W, HU X W, HUANG L, et al., 2014. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 in China using satellite remote sensing[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(13): 7436-44.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MANFRED N, HANNS M, DANIEL R, 2013. Acute and subacute effects of urban air pollution on cardiopulmonary emergencies and mortality: time series studies in austrian cities[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(10): 4728-4751.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MAZZEO N A, VENEGAS L E, 2011. Study of natural and traffic-producing turbulences analysing full-scale data from four street canyons[J]. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 47(1-4): 290-301.
DOI URL |
| [27] | MONN C, 2001. Exposure assessment of air pollutants: a review on spatial heterogeneity and indoor/outdoor/personal exposure to suspended particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide and ozone[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 35(1): 1-32. |
| [28] | OKE T R, 1988. Street design and urban canopy layer climate[J]. Elsevier, 11(1-3): 103-113. |
| [29] |
PETTIT T, IRGA P J, TORPY F R, 2018. Towards practical indoor air phytoremediation: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 208: 960-974.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
PUTAUD J P, DINGENEN R, ALASTUEY A, et al., 2009. A European aerosol phenomenology-3: Physical and chemical characteristics of particulate matter from 60 rural, urban, and kerbside sites across Europe[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 44(10): 1308-1320.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
RAMPONI R, BLOCKEN B, COO L D, et al., 2015. CFD simulation of outdoor ventilation of generic urban configurations with different urban densities and equal and unequal street widths[J]. Building and Environment, 92: 152-166.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
REQUIA W, ROIG H, KOUTRAKIS P, et al., 2017. Modeling spatial patterns of traffic emissions across 5570 municipal districts in Brazil[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 148: 845-853.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
SABATINO S D, BUCCOLIERI R, PULVIRENTI B, et al., 2007. Simulations of pollutant dispersion within idealised urban-type geometries with CFD and integral models[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 41(37): 8316-8329.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
SALIM S M, CHEAH S C, CHAN A, 2011. Numerical simulation of dispersion in urban street canyons with avenue-like tree plantings: Comparison between RANS and LES[J]. Building and Environment, 46(9): 1735-1746.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
SALMOND J A, PAUSCHER L, PIGEON G, et al., 2010. Vertical transport of accumulation mode particles between two street canyons and the urban boundary layer[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 44(39): 5139-5147.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
SINI J F, ANQUETIN S, MESTAYER P G, 1996. Pollutant dispersion and thermal effects in urban street canyons[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 30(15): 2659-2677.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
TAY B K, MCFIGGANS G B, JONES D P, et al., 2010. Linking urban aerosol fluxes in street canyons to larger scale emissions[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10(5): 2475-2490.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
TOMINAGA Y, STATHOPOULOS T, 2013. CFD simulation of near-field pollutant dispersion in the urban environment: A review of current modeling techniques[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 79: 716-730.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
VARDOULAKIS S, FISHER B, PERICLEOUS K, et al., 2003. Modelling air quality in street canyons: A review[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 37(2): 155-182.
DOI URL |
| [40] | WALLACE L, 2012. Indoor Particles: A Review[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 46(2): 98-126. |
| [41] |
WEERASURIYA A U, ZHANG X L, GAN V J L, et al., 2019. A holistic framework to utilize natural ventilation to optimize energy performance of residential high-rise buildings[J]. Building and Environment, 153: 218-232.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WEHNER B, BIRMILI W, GNAUK T, et al., 2002. Particle number size distributions in a street canyon and their transformation into the urban-air background: measurements and a simple model study[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 36(13): 2215-2223.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
XUE F, LI X F, 2017. The impact of roadside trees on traffic released PM10 in urban street canyon: Aerodynamic and deposition effects[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 30: 195-204.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ZHANG H L, WANG Y G, HU J L, et al., 2015. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China[J]. Environmental Research, 140: 242-254.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHAO P S, DONG F, HE D, et al., 2013. Characteristics of concentrations and chemical compositions for PM2.5 in the region of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 13(9): 4631-4644.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 包贞, 冯银厂, 焦荔, 等, 2010. 杭州市大气PM2.5和PM10污染特征及来源解析[J]. 中国环境监测, 26(2): 44-48. |
| BAO Z, FENG Y C, JIAO L, et al., 2010. Characteristics and source analysis of atmospheric PM2.5 and PM2.5 pollution in Hangzhou[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 26(2): 44-48. | |
| [47] | 柴一新, 祝宁, 韩焕金, 2002. 城市绿化树种的滞尘效应——以哈尔滨市为例[J]. 应用生态学报, 13(9): 1121-1126. |
| CHAI Y X, ZHU N, HAN H J, 2002. Dust Catching Effect of Urban Greening Tree Species: A Case Study of Harbin City[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 13(9): 1121-1126. | |
| [48] | 陈波, 李少宁, 鲁绍伟, 等, 2016. 北京大兴南海子公园PM2.5和PM10质量浓度变化特征[J]. 生态科学, 35(2): 104-110. |
| CHEN B, LI S N, LU S W, et al., 2016. Variation characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 mass concentrations in Nanhaizi Park, Daxing, Beijing[J]. Ecological Science, 35(2): 104-110. | |
| [49] | 陈波, 刘海龙, 赵东波, 等, 2016. 北京西山绿化树种秋季滞纳PM2.5能力及其与叶表面AFM特征的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(3): 777-784. |
| CHEN B, LIU H L, ZHAO D B, et al., 2016. Relationship between PM2.5 capacity and leaf surface AFM characteristics of green tree species in the Western Hills of Beijing in autumn[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(3): 777-784. | |
| [50] | 陈波, 鲁绍伟, 李少宁, 2016. 北京城市森林不同天气状况下PM2.5浓度变化[J]. 生态学报, 36(5): 1391-1399. |
| CHEN B, LU S W, LI S N, 2016. Variation of PM2.5 concentration in urban forest under different weather conditions in Beijing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(5): 1391-1399. | |
| [51] | 陈超, 王平, 陈紫光, 等, 2016. 不同结构型式建筑外窗缝隙通风对建筑室内细颗粒物 (PM2.5) 浓度的影响[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 42(4): 601-608. |
| CHEN C, WANG P, CHEN Z G, et al., 2016. Effect of gap ventilation on indoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentration in buildings with different structural types[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 42(4): 601-608. | |
| [52] | 陈金媛, 唐凯杰, 朱莹, 等, 2016. 杭州市PM2.5中水溶性离子的污染特征研究[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 44(4): 410-416. |
| CHEN J Y, TANG K J, ZHU Y, et al., 2016. Study on pollution characteristics of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 in Hangzhou[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 44(4): 410-416. | |
| [53] | 戴菲, 陈明, 傅凡, 等, 2019. 基于城市空间规划设计视角的颗粒物空气污染控制策略研究综述[J]. 中国园林, 35(2): 75-80. |
| DAI F, CHEN M, FU F, et al., 2019. A review of particulate air pollution control strategies from the perspective of urban spatial planning and design[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 35(2): 75-80. | |
| [54] | 戴昭鑫, 张云芝, 胡云锋, 等, 2016. 基于地面监测数据的2013—2015年长三角地区PM2.5时空特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 25(5): 813-821. |
| DAI Z X, ZHANG Y Z, HU Y F, et al., 2016. Temporal and spatial characteristics of PM2.5 in the Yangtze River Delta from 2013 to 2015 based on surface monitoring data[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 25(5): 813-821. | |
| [55] | 董雪玲, 刘大锰, 袁杨森, 等, 2009. 北京市大气PM10和PM2.5中有机物的时空变化[J]. 环境科学, 30(2): 328-334. |
| DONG X L, LIU D M, YUAN Y S, et al., 2009. Temporal and spatial variation of organic compounds in atmospheric PM10 and PM2.5 in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 30(2): 328-334. | |
| [56] | 杜万光, 王成, 王茜, 等, 2017. 春季旗山福建柏林内外空气颗粒物变化特征[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(10): 176-184. |
| DU W G, WANG C, WANG Q, et al., 2017. Characteristics of airborne particulate matter in spring in Qishan, Fujian and Berlin[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(10): 176-184. | |
| [57] | 段文军, 王成, 张昶, 等, 2017. 夏季3种生境森林内空气颗粒物变化特征[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 39(5): 73-81. |
| DUAN W J, WANG C, ZHANG C, et al., 2017. Characteristics of airborne particulate matter in three habitats in summer[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 39(5): 73-81. | |
| [58] | 冯银厂, 彭林, 吴建会, 等, 2005. 乌鲁木齐市环境空气中TSP和PM10来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 25(Z1): 30-33. |
| FENG Y C, PENG L, WU J H, et al., 2005. Sources of TSP and PM10 in ambient air of Urumqi[J]. China Environmental Science, 25(S1): 30-33. | |
| [59] | 冯银厂, 吴建会, 朱坦, 等, 2004. 济南市环境空气中TSP和PM10来源解析研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 17(2): 1-5. |
| FENG Y C, WU J H, ZHU T, et al., 2004. Analysis of sources of TSP and PM10 in ambient air in Ji'nan[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 17(2): 1-5. | |
| [60] | 郭飞, 2017. 基于WRF的城市热岛效应高分辨率评估方法[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 39(1): 13-19. |
| GUO F, 2017. High-resolution evaluation method of urban heat island effect based on WRF[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering, 39(1): 13-19. | |
| [61] | 郭琳琳, 李保峰, 陈宏, 2017. 我国在街区尺度的城市微气候研究进展[J]. 城市发展研究, 24(1): 75-81. |
| GUO L L, LI B F, CHEN H, 2017. Research progress of urban microclimate at block scale in China[J]. Urban Development Research, 24(1): 75-81. | |
| [62] |
韩晔, 周忠学, 2015. 西安市绿地景观吸收雾霾生态系统服务测算及空间格局[J]. 地理研究, 34(7): 1247-1258.
DOI |
|
HAN Y, ZHOU Z X, 2015. Estimation and spatial pattern of haze absorption ecosystem services of green space landscape in Xi'an City[J]. Geographical Research, 34(7): 1247-1258.
DOI |
|
| [63] | 胡元洁, 2018. 室内外大气颗粒物和典型有机污染物的环境行为及人体呼吸暴露风险[D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所): 175-176. |
| HU Y J, 2018. Environmental behavior of indoor and outdoor atmospheric particulate matter and typical organic pollutants and human respiratory exposure risk[D]. Guangzhou: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences): 175-176. | |
| [64] | 华蕾, 郭婧, 徐子优, 等, 2006. 北京市主要PM10排放源成分谱分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 22(6): 64-71. |
| HUA L, GUO J, XU Z Y, et al., 2006. Composition spectrum analysis of main PM10 emission sources in Beijing[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 22(6): 64-71. | |
| [65] | 金嘉恒, 张根茂, 李倩, 2017. PM2.5的综述与进展[J]. 科技创新导报, 14(3): 74-75, 139. |
| JIN J H, ZHANG G M, LI Q, 2017. Review and progress of PM2.5[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Review, 14(3): 74-75, 139. | |
| [66] | 李景广, 黄衍, 李旻雯, 2017. 建筑室内细颗粒物(PM2.5)防控设计研究[J]. 暖通空调, 47(1): 109-112, 73. |
| LI J G, HUANG Y, LI M W, 2017. Control design of indoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in buildings[J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 47(1): 109-112, 73. | |
| [67] | 李绥, 杨二东, 石铁矛, 等, 2014. 商业街区可吸入颗粒物空间分布及其气象要素的相关性[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 30(5): 923-930. |
| LI S, YANG E D, SHI T M, et al., 2014. Spatial distribution of inhalable particulate matter and its correlation with meteorological factors in commercial districts[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science Edition), 30(5): 923-930. | |
| [68] | 刘彩霞, 2006. 天津市开放源可吸入颗粒物污染问题分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 22(4): 80-83. |
| LIU C X, 2006. Analysis of open source inhalable particulate pollution in Tianjin[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 22(4): 80-83. | |
| [69] | 刘建峰, 王宝庆, 牛宏宏, 等, 2017. 计算流体力学模拟街道峡谷特征和风向对细颗粒物污染扩散的影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 39(4): 367-374. |
| LIU J F, WANG B Q, NIU H H, et al., 2017. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of the effects of street canyon characteristics and wind direction on the diffusion of fine particulate matter pollution[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 39(4): 367-374. | |
| [70] | 刘晴, 高鹏, 李成, 等, 2019. 泰安市典型生态功能区空气负离子的时空分布及影响因素分析[J]. 环境化学, 38(1): 169-176. |
| LIU Q, GAO P, LI C, et al., 2019. Spatial and temporal distribution and influencing factors of air anions in Tai'an City typical ecological function area[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 38(1): 169-176. | |
| [71] | 鲁绍伟, 蒋燕, 陈波, 等, 2017. 北京城市植被区PM2.5浓度时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(1): 180-187. |
| LU S W, JIANG Y, CHEN B, et al., 2017. Spatiotemporal variation and influencing factors of PM2.5 concentration in urban vegetation areas of Beijing[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(1): 180-187. | |
| [72] | 毛慧伦, 何红弟, 2019. 上海黄浦江轮渡颗粒物污染状况的分布特征[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 45(2): 113-122. |
| MAO H L, HE H D, 2019. Distribution characteristics of particulate matter pollution in Shanghai Huangpu River ferry[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 45(2): 113-122. | |
| [73] | 秦晓楠, 卢小丽, 武春友, 2014. 国内生态安全研究知识图谱——基于Citespace的计量分析[J]. 生态学报, 34(13): 3693-3703. |
| QIN X N, LU X L, WU C Y, 2014. Knowledge map of ecological security research in China: A quantitative analysis based on CiteSpace[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(13): 3693-3703. | |
| [74] | 任思佳, 2018. 城市街谷绿化形式对机动车尾气扩散影响的数值模拟研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学: 37-39. |
| REN S J, 2018. Numerical simulation study on the influence of greening forms on vehicle exhaust diffusion in urban street canyons[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University: 37-39. | |
| [75] | 孙晓丹, 李海梅, 周春玲, 等, 2015. 园林植物消减大气颗粒物研究进展[J]. 北方园艺 (24): 184-188. |
| SUN X D, LI H M, ZHOU C L, et al., 2015. Research progress on reduction of atmospheric particulate matter by garden plants[J]. Northern Horticulture, (24): 184-188. | |
| [76] | 王的, 冯海艳, 景慧敏, 2017. 北京市冬季、春季PM10和PM2.5中元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学进展, 32(8): 850-858. |
| WANG D, FENG H Y, JING H M, 2017. Geochemical characteristics of PM10 and PM2.5 in winter and spring in Beijing[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 32(8): 850-858. | |
| [77] | 王敬, 毕晓辉, 冯银厂, 等, 2014. 乌鲁木齐市重污染期间PM2.5污染特征与来源解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 27(2): 113-119. |
| WANG J, BI X H, FENG Y C, et al., 2014. Characteristics and source analysis of PM2.5 pollution during heavy pollution period in Urumqi[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 27(2): 113-119. | |
| [78] | 王申博, 余飞, 燕启社, 等, 2017. 典型背景区大气颗粒物中元素粒径分布特征[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(6): 133-140. |
| WANG S B, YU F, YAN Q S, et al., 2017. Element size distribution characteristics of atmospheric particulate matter in typical background area[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(6): 133-140. | |
| [79] | 王越, 2018. 英国空气污染防治演变研究(1921—1997)[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学: 1-7. |
| WANG Y, 2018. Evolution of air pollution control in UK (1921-1997)[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University: 1-7. | |
| [80] |
吴健生, 许娜, 张曦文, 2016. 中国低碳城市评价与空间格局分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 35(2): 204-213.
DOI |
| WU J S, XU N, ZHANG X W, 2016. Evaluation and spatial pattern analysis of low-carbon cities in China[J]. Progress in Geography, 35(2): 204-213. | |
| [81] | 吴琳, 冯银厂, 戴莉, 等, 2009. 天津市大气中PM10、PM2.5及其碳组分污染特征分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 29(11): 1134-1139. |
| WU L, FENG Y C, DAI L, et al., 2009. Characteristics of atmospheric PM10, PM2.5 and its carbon component pollution in Tianjin[J]. China Environmental Science, 29(11): 1134-1139. | |
| [82] | 吴正旺, 王岩慧, 单海楠, 2014. 北京市PM2.5分布的不均匀现象[J]. 环境科学与技术, 37(S1): 87-91, 95. |
|
WU Z W, WANG Y H, SHAN H N, 2014. Unevenness of PM2.5 distribution in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(S1): 87-91, 95.
DOI URL |
|
| [83] | 肖玉, 王硕, 李娜, 等, 2015. 北京城市绿地对大气PM2.5的削减作用[J]. 资源科学, 37(6): 1149-1155. |
| XIAO Y, WANG S, LI N, et al., 2015. Effects of urban green space on atmospheric PM2.5 reduction in Beijing[J]. Resources Science, 37(6):1149-1155. | |
| [84] | 肖致美, 毕晓辉, 冯银厂, 等, 2012. 宁波市环境空气中PM10和PM2.5来源解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 25(5): 549-555. |
| XIAO Z M, BI X H, FENG Y C, et al., 2012. Sources of PM10 and PM2.5 in ambient air in Ningbo City[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 25(5): 549-555. | |
| [85] | 谢心庆, 郑薇, 2015. 国内外PM2.5研究进展综述[J]. 电力科技与环保, 31(4): 17-20. |
| XIE X Q, ZHENG W, 2015. Research progress of PM2.5 at home and abroad[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 31(4): 17-20. | |
| [86] | 阳海鸥, 陈文波, 梁照凤, 2017. LUR模型模拟的南昌市PM2.5浓度与土地利用类型的关系[J]. 农业工程学报, 33(6): 232-239. |
| YANG H L, CHEN W B, LIANG Z F, 2017. Relationship between PM2.5 concentration and land use types simulated by LUR model in Nanchang City[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 33(6): 232-239. | |
| [87] | 杨帆, 周亮, 林蔚, 等, 2016. 2001—2010年非洲大气PM2.5污染浓度空间格局演化[J]. 世界地理研究, 25(3): 30-39. |
| YANG F, ZHOU L, LIN W, et al., 2016. Evolution of spatial pattern of PM2.5 pollution concentration in Africa during 2001-2010 [J]. World Regional Studies, 25(3): 30-39. | |
| [88] | 张辉辉, 王芳, 王砚玲, 等, 2017. 可吸入颗粒物围护结构渗透机理研究进展[J]. 建筑科学, 33(4): 134-141. |
| ZHANG H H, WANG F, WANG Y L, et al., 2017. Research progress on permeation mechanism of respirable particulate matter envelope[J]. Building Science, 33(4): 134-141. | |
| [89] | 张灵艺, 秦华, 2015. 城市园林绿地滞尘研究进展及发展方向[J]. 中国园林, 31(1): 64-68. |
| ZHANG L Y, QIN H, 2015. Research on Progress of Dust-Retention for Urban Green Space[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 31(1): 64-68. | |
| [90] | 张桐, 洪秀玲, 孙立炜, 等, 2017. 6种植物叶片的滞尘能力与其叶面结构的关系[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 39(6): 70-77. |
| ZHANG T, HONG X L, SUN L W, et al., 2017. Particle-retaining characteristics of six tree species and their relations with micro- configurations of leaf epidermis[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 39(6): 70-77. | |
| [91] | 赵晨曦, 王玉杰, 王云琦, 等, 2013. 细颗粒物(PM2.5)与植被关系的研究综述[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(8): 2203-2210. |
| ZHAO C X, WANG Y J, WANG Y Q, et al., 2013. Research review on the relationship between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and vegetation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32(8): 2203-2210. | |
| [92] | 赵晨曦, 王云琦, 王玉杰, 等, 2014. 北京地区冬春PM2.5和PM10污染水平时空分布及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 环境科学, 35(2): 418-427. |
| ZHAO C X, WANG Y Q, WANG Y J, et al., 2014. Spatial and temporal distribution of PM2.5 and PM10 pollution levels in winter and spring in Beijing and their relationship with meteorological conditions[J]. Environmental Science, 35(2): 418-427. | |
| [93] | 赵力, 陈超, 王平, 等, 2015. 北京市某办公建筑夏冬季室内外PM2.5浓度变化特征[J]. 建筑科学, 31(4): 32-39. |
| ZHAO L, CHEN C, WANG P, et al., 2015. Variation characteristics of indoor and outdoor PM2.5 concentration in an office building in Beijing in summer and winter[J]. Architectural Science, 31(4): 32-39. | |
| [94] | 郑玫, 张延君, 闫才青, 等, 2014. 中国PM2.5来源解析方法综述[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 50(6): 1141-1154. |
| ZHENG M, ZHANG Y J, YAN C Q, et al., 2014. A review of PM2.5 source analysis methods in China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitae Pekinensis, 50(6): 1141-1154. | |
| [95] | 周姝雯, 唐荣莉, 张育新, 等, 2017. 城市街道空气污染物扩散模型综述[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(3): 1039-1048. |
| ZHOU S W, TANG R L, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2017. Review on diffusion models of urban street air pollutants[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(3): 1039-1048. | |
| [96] | 朱易, 胡衡生, 张新英, 等, 2004. 南宁市大气颗粒物TSP、PM10、PM2.5污染水平研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 26(3): 176-178, 242. |
| ZHU Y, HU H S, ZHANG X Y, et al., 2004. Study on atmospheric particulate matter TSP, PM10, PM2.5 pollution levels in Nanning City[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 26(3): 176-178, 242. | |
| [97] | 邹佳乐, 林尧林, 杨薇, 2019. 中国近年PM2.5污染研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治, 41(3): 357-361, 366. |
| ZOU J L, LIN Y L, YANG W, 2019. Research progress of PM2.5 pollution in China in recent years[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 41(3): 357-361, 366. |
| [1] | 魏建兵, 郑泓, 程雨露, 王阳. 基于CiteSpace的生态安全格局研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 835-844. |
| [2] | 刘可慧, 李广娈, 李春明, 赵珂艺, 张宁宁, 薛洁怡, 李艺, 于方明, 段敏. 基于文献计量学和知识图谱分析的漓江生态环境40年研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 409-420. |
| [3] | 孙晓杰, 邹怡, 郭晨辉. 基于CNKI数据库的植物与昆虫关系研究文献计量分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 196-204. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

