生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1456-1464.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.019
吕贵方1,2( ), 吴颖欣2, 董长勋1,*(
), 吴颖欣2, 董长勋1,*( ), 卢阳2, 周玥2, 曾文军1,2, 吴文成2,*(
), 卢阳2, 周玥2, 曾文军1,2, 吴文成2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-12
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
吴文成,E-mail: wuwencheng@scies.org作者简介:吕贵方(1997年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境污染物控制。E-mail: 1362447284@qq.com
基金资助:
LÜ Guifang1,2( ), WU Yingxin2, DONG Changxun1,*(
), WU Yingxin2, DONG Changxun1,*( ), LU Yang2, ZHOU Yue2, ZENG Wenjun1,2, WU Wencheng2,*(
), LU Yang2, ZHOU Yue2, ZENG Wenjun1,2, WU Wencheng2,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-12
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
多氯联苯(PCBs)向铁基材料表面传输的过程(即传质过程)是铁基材料降解PCBs的关键途径。腐殖酸(HA)和表面活性剂吐温-80(Tween-80)能够通过改变传质过程来影响PCBs的降解而被广泛关注,但关于两者改变传质过程差异性及其机制的报道较少。通过制备微米镍铁(Ni/Fe)颗粒,探究不同质量浓度HA(10、50、100 mg∙L-1)和Tween-80[1、25、500倍临界胶束浓度 (CMC)]对Ni/Fe降解水溶液中2, 2′, 4′, 4′, 5-五氯联苯(PCB-99)的影响,通过体系中PCB-99、HA和Tween-80的固液分配来解析两者改变传质过程的机制与差异。结果表明,HA和Tween-80均抑制Ni/Fe降解PCB-99,降解过程符合准二级动力学模型,HA或Tween-80的质量浓度越高,抑制作用越显著,PCB-99的降解率越低。其中,HA吸附在Ni/Fe表面形成HA层,覆盖反应位点,阻碍PCB-99和水与Ni/Fe接触,导致留在固相上而未被降解的PCB-99占初始加入量的49.48%。相反,Tween-80主要通过增流和增溶作用影响传质过程,Tween-80吸附在Ni/Fe表面,能够降低界面张力,增加PCB-99的流动性,导致传质效率下降;当液相中的Tween-80质量浓度超过CMC时,PCB-99被困在胶束形成的疏水核中,占PCB-99初始加入量的56.01%,难以接触Ni/Fe。该研究可为持久性有机卤代烃的降解提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
吕贵方, 吴颖欣, 董长勋, 卢阳, 周玥, 曾文军, 吴文成. 腐殖酸和吐温-80对微米镍铁/多氯联苯体系的传质调控研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1456-1464.
LÜ Guifang, WU Yingxin, DONG Changxun, LU Yang, ZHOU Yue, ZENG Wenjun, WU Wencheng. Study on the Mass Transfer Regulation in Micro-scale Ni-Fe/PCBs System by Humic Acid and Tween-80[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1456-1464.
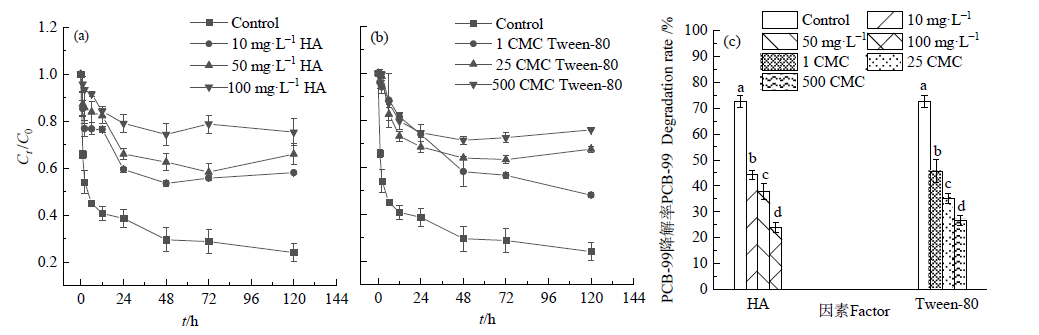
图2 不同质量浓度的HA(a)和Tween-80(b)影响下Ni/Fe降解PCB-99的动力学曲线及平衡降解率(c) 图中的误差线为标准差(n=3),下同;不同的字母表示不同处理间差异极显著(P<0.001),下同
Figure 2 Kinetic curves of the degradation of PCB-99 by Ni/Fe with different concentrations of HA (a) and Tween-(b), and the degradation rates of PCB-99 (c) The error bars in the figure are standard deviations (n=3), the same below; different letters indicate extremely significant differences among different treatments (P<0.001), the same below
| 因素 Factor | 质量浓度 C(Factor) | 准一级降解动力学 Pseudo-first-order degradation kinetics | 准二级降解动力学 Pseudo-second-order degradation kinetics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/h-1 | r12 | k2/[(mg∙L-1)-1∙h-1] | r22 | |||
| HA | 0 | 0.01389 | 0.81 | 0.03395 | 0.90 | |
| 10 mg∙L-1 | 0.00949 | 0.90 | 0.01446 | 0.92 | ||
| 50 mg∙L-1 | 0.00762 | 0.89 | 0.01039 | 0.90 | ||
| 100 mg∙L-1 | 0.00533 | 0.90 | 0.00638 | 0.92 | ||
| Tween-80 | 1 CMC | 0.01042 | 0.99 | 0.01413 | 0.99 | |
| 25 CMC | 0.00900 | 0.75 | 0.01154 | 0.80 | ||
| 500 CMC | 0.00691 | 0.75 | 0.00830 | 0.79 | ||
表1 HA和Tween-80影响下Ni/Fe降解PCB-99的动力学拟合结果
Table 1 Kinetic fitting results of Ni/Fe degradation of PCB-99 under the influence of HA and Tween-80
| 因素 Factor | 质量浓度 C(Factor) | 准一级降解动力学 Pseudo-first-order degradation kinetics | 准二级降解动力学 Pseudo-second-order degradation kinetics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/h-1 | r12 | k2/[(mg∙L-1)-1∙h-1] | r22 | |||
| HA | 0 | 0.01389 | 0.81 | 0.03395 | 0.90 | |
| 10 mg∙L-1 | 0.00949 | 0.90 | 0.01446 | 0.92 | ||
| 50 mg∙L-1 | 0.00762 | 0.89 | 0.01039 | 0.90 | ||
| 100 mg∙L-1 | 0.00533 | 0.90 | 0.00638 | 0.92 | ||
| Tween-80 | 1 CMC | 0.01042 | 0.99 | 0.01413 | 0.99 | |
| 25 CMC | 0.00900 | 0.75 | 0.01154 | 0.80 | ||
| 500 CMC | 0.00691 | 0.75 | 0.00830 | 0.79 | ||
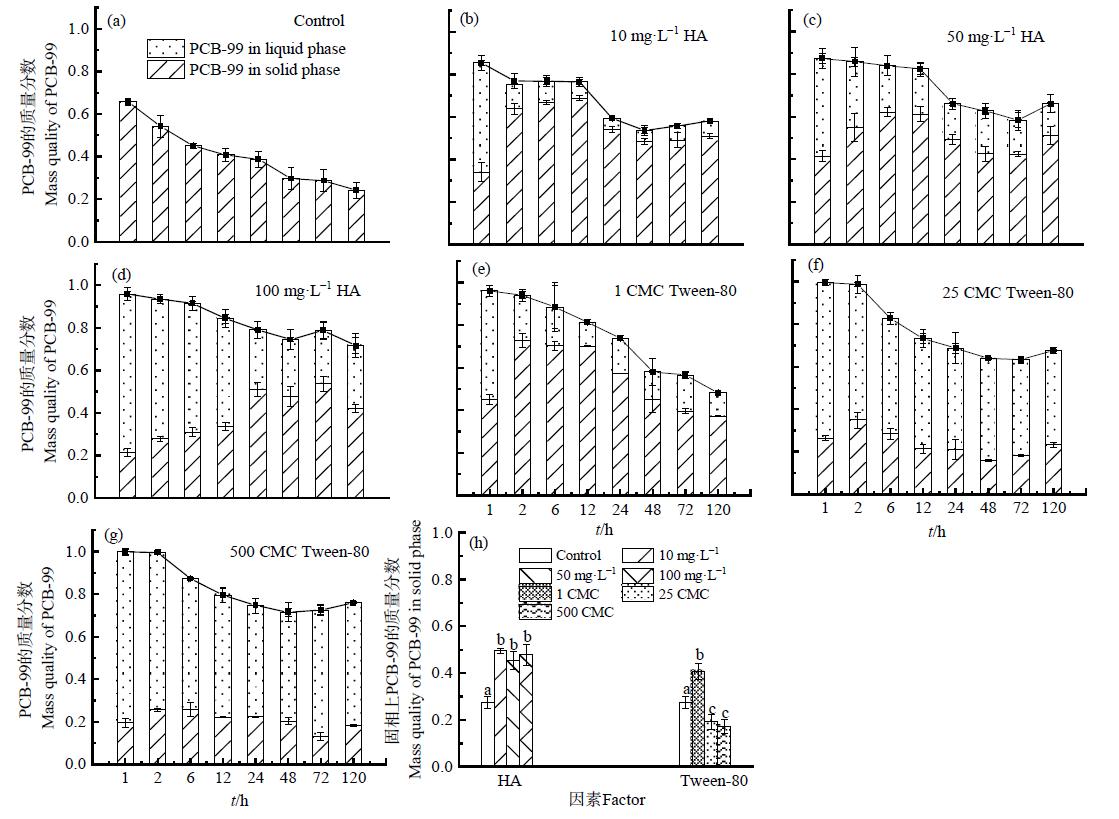
图3 不同质量浓度HA和Tween-80影响下PCB-99在固液两相中的分配
Figure 3 The partition of PCB-99 in solid and liquid phases under the influence of HA and Tween-80 at different concentrations
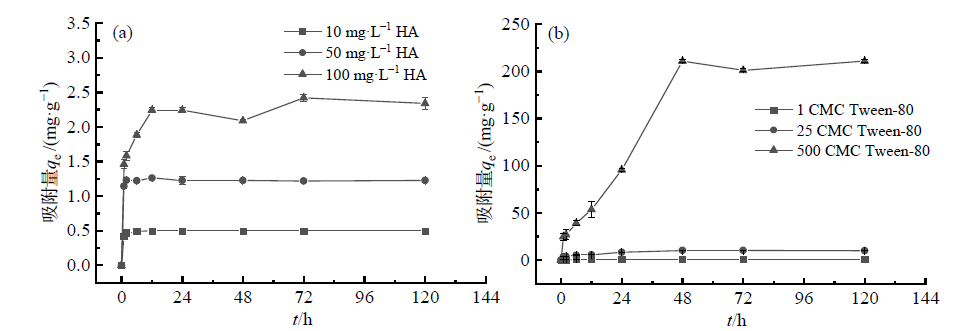
图4 不同质量浓度的HA(a)和Tween-80(b)在Ni/Fe降解PCB-99体系中的吸附动力学曲线
Figure 4 The adsorption kinetics curves of HA (a) and Tween-80 (b) at different concentrations in Ni/Fe degradation system
| 因素 Factor | 质量浓度 µ(factor) | qe/ (mg∙g-1) | 准一级吸附动力学 Pseudo-First-Order Adsorption Kinetics | 准二级吸附动力学 Pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qc/(mg∙g-1) | K1/h-1 | r12 | qc/(mg∙g-1) | K2/(g∙mg-1∙h-1) | r22 | ||||
| HA | 10 mg∙L-1 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 1.86497 | 0.96 | 0.50 | 12.87341 | 0.99 | |
| 50 mg∙L-1 | 1.23 | 1.23 | 2.64982 | 0.86 | 1.27 | 6.77221 | 0.99 | ||
| 100 mg∙L-1 | 2.27 | 2.20 | 0.84679 | 0.70 | 2.37 | 0.30022 | 0.99 | ||
| Tween-80 | 1 CMC | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.36033 | 0.85 | 0.49 | 3.58238 | 0.99 | |
| 25 CMC | 10.37 | 8.03 | 0.05684 | 0.92 | 10.71 | 0.01875 | 0.99 | ||
| 500 CMC | 210.83 | 198.34 | 0.02222 | 0.96 | 250 | 0.000176 | 0.95 | ||
表2 Ni/Fe吸附HA和Tween-80的动力学拟合结果
Table 2 Kinetic fitting results of HA and Tween-80 adsorption on Ni/Fe
| 因素 Factor | 质量浓度 µ(factor) | qe/ (mg∙g-1) | 准一级吸附动力学 Pseudo-First-Order Adsorption Kinetics | 准二级吸附动力学 Pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qc/(mg∙g-1) | K1/h-1 | r12 | qc/(mg∙g-1) | K2/(g∙mg-1∙h-1) | r22 | ||||
| HA | 10 mg∙L-1 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 1.86497 | 0.96 | 0.50 | 12.87341 | 0.99 | |
| 50 mg∙L-1 | 1.23 | 1.23 | 2.64982 | 0.86 | 1.27 | 6.77221 | 0.99 | ||
| 100 mg∙L-1 | 2.27 | 2.20 | 0.84679 | 0.70 | 2.37 | 0.30022 | 0.99 | ||
| Tween-80 | 1 CMC | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.36033 | 0.85 | 0.49 | 3.58238 | 0.99 | |
| 25 CMC | 10.37 | 8.03 | 0.05684 | 0.92 | 10.71 | 0.01875 | 0.99 | ||
| 500 CMC | 210.83 | 198.34 | 0.02222 | 0.96 | 250 | 0.000176 | 0.95 | ||
| [1] |
BOUZID I, MAIRE J, BRUNOL E, et al., 2017. Compatibility of surfactants with activated-persulfate for the selective oxidation of PAH in groundwater remediation[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(6): 6098-6106.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHENG M, ZENG G M, HUANG D L, et al., 2017. Advantages and challenges of Tween 80 surfactant-enhanced technologies for the remediation of soils contaminated with hydrophobic organic compounds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 314: 98-113.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DOONG R A, LAI Y L, 2006. Effect of metal ions and humic acid on the dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene by zerovalent iron[J]. Chemosphere, 64(3): 371-378.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FANG Z Q, CHEN J H, QIU X H, et al., 2011. Effective removal of antibiotic metronidazole from water by nanoscale zero-valent iron particles[J]. Desalination, 268(1-3): 60-67.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FU H Y, WEI C H, QU X L, et al., 2018. Strong binding of apolar hydrophobic organic contaminants by dissolved black carbon released from biochar: A mechanism of pseudomicelle partition and environmental implications[J]. Environmental Pollution, 232: 402-410.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HAN Y T, GHOSHAL S, LOWRY G V, et al., 2019. A comparison of the effects of natural organic matter on sulfidated and nonsulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron colloidal stability, toxicity, and reactivity to trichloroethylene[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 671: 254-261.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KIM M K, WON A Y, ZOH K D, 2017. Effects of molecular size fraction of DOM on photodegradation of aqueous methylmercury[J]. Chemosphere, 174: 739-746.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI Q, CHEN Z S, WANG H H, et al., 2021. Removal of organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148546.
DOI |
| [9] |
LI Y, LI X Q, XIAO Y, et al., 2016. Catalytic debromination of tetrabromobisphenol A by Ni/nZVI bimetallic particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 284: 1242-1250.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI Y R, ZHAO H P, ZHU L Z, 2021. Remediation of soil contaminated with organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143413.
DOI |
| [11] |
LIANG D W, YANG Y H, XU W W, et al., 2014. Nonionic surfactant greatly enhances the reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by nanoscale zero-valent iron: mechanism and kinetics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 278: 592-596.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIPPOLD H, GOTTSCHALCH U and KUPSCH H, 2008. Joint influence of surfactants and humic matter on PAH solubility. Are mixed micelles formed?[J]. Chemosphere, 70(11): 1979-1986.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MAO X H, JIANG R, XIAO W, et al., 2015. Use of surfactants for the remediation of contaminated soils: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 285: 419-435.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
PAJUREK M, PIETRON W, MASZEWSKI S, et al., 2019. Poultry eggs as a source of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, PBDEs and PBDD/Fs[J]. Chemosphere, 223: 651-658.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SCAGLIA B, BAGLIERI A, TAMBONE F, et al., 2016. Chlorpyrifos-methyl solubilisation by humic acids used as bio-surfactants extracted from lignocelluloses and kitchen wastes[J]. Chemosphere, 159: 208-213.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SHIN M C, CHOI H D, KIM D H, et al., 2008. Effect of surfactant on reductive dechlorination of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron[J]. Desalination, 223(1-3): 299-307.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SREDLOVA K, SKROB Z, FILIPOVA A, et al., 2020. Biodegradation of PCBs in contaminated water using spent oyster mushroom substrate and a trickle-bed bioreactor[J]. Water Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres. 2019.115274.
DOI |
| [18] |
SSEBUGERE P, SILLANPAA M, MATOVU H, et al., 2019. Human and environmental exposure to PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in Africa: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 223: 483-493.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TAN L, LIANG B, FANG Z Q, et al., 2014. Effect of humic acid and transition metal ions on the debromination of decabromodiphenyl by nano zero-valent iron: kinetics and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, DOI: 10.1007/s11051-014-2786-3.
DOI |
| [20] |
TRELLU C, PECHAUD Y, OTURAN N, et al., 2021. Remediation of soils contaminated by hydrophobic organic compounds: How to recover extracting agents from soil washing solutions?[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124137.
DOI |
| [21] |
WANG R, TANG T, LU G N, et al., 2019. Mechanisms and pathways of debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in various nano-zerovalent iron-based bimetallic systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 661: 18-26.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WU Y X, WU Z H, HUANG X F, et al., 2015. Synergistical enhancement by Ni2+ and Tween-80 of nanoscale zerovalent iron dechlorination of 2, 2′, 5, 5′-tetrachlorinated biphenyl in aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(1): 555-564.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WU Y X, WANG Y, HUANG X F, et al., 2018. Surfactant-facilitated dechlorination of 2, 2′, 5, 5′-tetrachlorinated biphenyl using zero-valent iron in soil/sediment solution: Integrated effects of plausible factors[J]. Chemosphere, 212: 845-852.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANG B, WANG C J, CHENG X, et al., 2021. Interactions between the antibiotic tetracycline and humic acid: Examination of the binding sites, and effects of complexation on the oxidation of tetracycline[J]. Water Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117379.
DOI |
| [25] |
YI Y Q, WU J, FANG Z Q, 2017. Identification Influence Mechanism of Humic Acid in the Degradation of Decabromodiphenyl Ether by the BC@Ni/Fe Nanoparticles[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 75(6): 629-636.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YI Y Q, WU J, TU G Q, et al., 2019. The humic acid influenced the behavior and reactivity of Ni/Fe nanoparticles in the removal of deca-brominated diphenyl ether from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(10): 10136-10147.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHANG Z, CISSOKO N, WO J J, et al., 2009. Factors influencing the dechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by Ni-Fe nanoparticles in the presence of humic acid[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165(1-3): 78-86.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHENG F, GAO B, SUN Y Y, et al., 2016. Removal of tetrachloroethylene from homogeneous and heterogeneous porous media: Combined effects of surfactant solubilization and oxidant degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 283: 595-603.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHENG Z H, YUAN S H, LIU Y, et al., 2009. Reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene by Cu/Fe bimetal in the presence of nonionic surfactant[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(2-3): 895-901.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHENG Z Q, LU G N, WANG R, et al., 2018. Effects of surfactant on the degradation of 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) by nanoscale Ag/Fe particles: Kinetics, mechanisms and intermediates[J]. Environmental Pollution, 245: 780-788.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHOU L, LI Z, YI Y Q, et al., 2021. Increasing the electron selectivity of nanoscale zero-valent iron in environmental remediation: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 421: 126709.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 陈少瑾, 梁贺升, 2009. 零价铁还原脱氯污染土壤中PCBs的实验研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 18(1): 193-196. |
| CHEN S J, LIANG H S, 2009. Experimental study of the dechlorination of PCBs in polluted soils by zero valent iron[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 18(1): 193-196. | |
| [33] | 丛鑫, 毕然, 孙思坤, 2020. 草炭土及其有机质组分对PCB138吸附动力学和热力学研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(2): 394-401. |
| CONG X, BI R, SUN S K, 2020. Adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics of PCB138 on peat soil and its different soil organic matter fractions[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(2): 394-401. | |
| [34] | 黄国富, 王淼, 王棉棉, 等, 2020. 表面活性剂强化PAC-Pd/Fe纳米颗粒降解四溴双酚A的研究[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 52(2): 53-59. |
| HUANG G F, WANG M, WANG M M, et al., 2020. Degradation of Tetrabromobisphenol A by Surfactant-Enhanced PAC-Pd/Fe Nanoparticles[J]. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 52(2): 53-59. | |
| [35] | 吕言臣, 李明, 章长松, 等, 2021. 纳米零价铁协同Fe(Ⅱ) 活化过碳酸钠降解含吐温-80水体中的三氯乙烯[J]. 环境工程学报, 15(2): 688-698. |
| LÜ Y C, LI M, ZHANG C S, et al., 2021. Degradation of trichloroethylene in water containing Tween-80 by nano-zero valent iron synergistically with Fe(Ⅱ) activation of sodium percarbonate[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 15(2): 688-698. | |
| [36] | 汪虹西, 廖兵, 卢涛, 等, 2020. 零价铁-生物炭复合材料对地下水中硝酸盐的去除[J]. 环境工程学报, 14(12): 3317-3328. |
| WANG H X, LIAO B, LU T, et al., 2020. Nitrate removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron-biochar composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 14(12): 3317-3328. | |
| [37] | 伍斌, 杨宾, 李慧颖, 等, 2014. 表面活性剂强化抽出处理含水层中DNAPL污染物的去除特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 8(5): 1956-1964. |
| WU B, YANG B, LI H Y, et al., 2014. Removal characteristics of DNAPL pollutants in aquifers by enhanced extraction of surfactants[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 8(5): 1956-1964. | |
| [38] | 姚梦东, 岳俊杰, 徐雪婧, 等, 2021. 球磨硫化零价铁活化过硫酸盐降解水体中有机氯农药[J]. 环境工程学报, 15(8): 2563-2575. |
| YAO M D, YUE J J, XU X J, et al., 2021. Degradation of organochlorine pesticides in water by ball-milled zerovalent iron sulfide activated persulfate[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 15(8): 2563-2575. | |
| [39] | 张羽, 高春阳, 陈昌照, 等, 2019. 零价铁活化过硫酸钠体系降解污染土壤中的多环芳烃[J]. 环境工程学报, 13(4): 955-962. |
| ZHANG Y, GAO C Y, CHEN C Z, et al., 2019. Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Contaminated Soil by Zero-valent Iron Activated Sodium Persulfate System[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 13(4): 955-962. |
| [1] | 阎洁, 余雪巍, 李鉴博, 顾海萍, 郭二辉. 一株菲降解细菌产生生物表面活性剂特性的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1683-1694. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
