生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1370-1382.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.009
收稿日期:2022-03-28
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
*张诗函(1993年生),女,助教,硕士,主要从事教育学相关研究。E-mail: zsh1993@cxtc.edu.cn作者简介:姜倪皓(1990年生),男(彝族),讲师,博士,主要从事种群生态及农业生态相关研究。E-mail: jnhskip@cxtc.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIANG Nihao1( ), ZHANG Shihao2, ZHANG Shihan3,*(
), ZHANG Shihao2, ZHANG Shihan3,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-28
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
探索哀牢山紫茎泽兰(Ageratina adenophora)入侵群落主要物种种间联结和物种分布与环境因子的关系,为该区域紫茎泽兰入侵后植物群落的管理以及本土生物多样性保护提供理论依据。在野外调查的基础上,采用χ2检验、方差比率法、联结系数和Spearman相关分析研究物种的种间联结,采用冗余分析、方差分解、多元逐步回归分析、随机森林模型和结构方程模型探索环境因子对主要物种分布和紫茎泽兰入侵的影响。结果表明,(1)紫茎泽兰的重要值和生态位宽度最大,占显著优势地位,伴生种中里白(Diplopterygium glaucum)和虎杖(Reynoutria japonica)的重要值较大,同时二者与紫茎泽兰的生态位重叠指数均大于0.5。(2)入侵群落总体呈现显著负关联,群落处于非稳定状态,而紫茎泽兰与里白和虎杖均具有极显著的负联结关系。(3)对紫茎泽兰入侵群落主要物种组成影响显著的环境因子为有效钾、土壤温度、土壤pH值,土壤因子是影响群落物种组成变异的最主要因素。(4)土壤全磷与入侵植物入侵强度指数及群落可入侵性指数呈显著负相关,有效钾与群落稳定性指数呈显著负相关。基于生态效益和经济效益的整体性原则,未来或可考虑利用里白和虎杖对哀牢山地区的紫茎泽兰进行替代控制。
中图分类号:
姜倪皓, 张世浩, 张诗函. 哀牢山紫茎泽兰入侵群落主要物种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382.
JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Associations and Environmental Interpretation of the Dominant Species of the Communities Invaded by Ageratina adenophora in Ailao Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1370-1382.
| 编号 No. | 物种 Species | 重要值 Important value/% | 变异系数 Coefficient of Variation/% | 生态位宽度 Niche breadth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 土蜜树 Bridelia tomentosa | 3.01 | 24.51 | 0.41 |
| S2 | 羊耳菊 Inula cappa | 2.10 | 15.47 | 0.40 |
| S3 | 石海椒 Reinwardtia indica | 5.71 | 17.32 | 0.34 |
| S4 | 里白 Diplopterygium glaucum | 22.31 | 14.50 | 0.76 |
| S5 | 虎杖 Reynoutria japonica | 7.89 | 15.38 | 0.47 |
| S6 | 紫茎泽兰 Ageratina adenophora | 28.90 | 10.50 | 0.79 |
| S7 | 白蒿 Herba artimisiae | 2.30 | 17.76 | 0.52 |
| S8 | 芒萁 Dicranopteris dichotoma | 1.3 | 28.65 | 0.59 |
| S9 | 白茅 Imperata cylindrica | 2.33 | 13.27 | 0.58 |
| S10 | 野豌豆 Vicia sepium | 2.52 | 14.43 | 0.35 |
表1 草本层优势种重要值及其生态位宽度
Table 1 Importance value and niche breadth of dominant species in herbaceous layer
| 编号 No. | 物种 Species | 重要值 Important value/% | 变异系数 Coefficient of Variation/% | 生态位宽度 Niche breadth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 土蜜树 Bridelia tomentosa | 3.01 | 24.51 | 0.41 |
| S2 | 羊耳菊 Inula cappa | 2.10 | 15.47 | 0.40 |
| S3 | 石海椒 Reinwardtia indica | 5.71 | 17.32 | 0.34 |
| S4 | 里白 Diplopterygium glaucum | 22.31 | 14.50 | 0.76 |
| S5 | 虎杖 Reynoutria japonica | 7.89 | 15.38 | 0.47 |
| S6 | 紫茎泽兰 Ageratina adenophora | 28.90 | 10.50 | 0.79 |
| S7 | 白蒿 Herba artimisiae | 2.30 | 17.76 | 0.52 |
| S8 | 芒萁 Dicranopteris dichotoma | 1.3 | 28.65 | 0.59 |
| S9 | 白茅 Imperata cylindrica | 2.33 | 13.27 | 0.58 |
| S10 | 野豌豆 Vicia sepium | 2.52 | 14.43 | 0.35 |
| 编号 No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.513 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.065 | 0.356 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.955 | 0.000 | |
| S2 | 0.718 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.045 | 0.185 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.558 | 0.000 | |
| S3 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.348 | 0.000 | 0.347 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S4 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.471 | 0.652 | 0.642 | 0.652 | 0.652 | 0.000 | 0.652 | |
| S5 | 0.070 | 0.053 | 0.000 | 0.880 | 0.362 | 0.935 | 0.935 | 0.065 | 0.924 | |
| S6 | 0.614 | 0.432 | 0.599 | 0.735 | 0.554 | 0.297 | 0.297 | 0.356 | 0.297 | |
| S7 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.882 | 0.997 | 0.512 | 0.981 | 0.000 | 0.968 | |
| S8 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.881 | 0.996 | 0.511 | 0.999 | 0.000 | 0.987 | |
| S9 | 0.996 | 0.778 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.611 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S10 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.879 | 0.994 | 0.509 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
表2 紫茎泽兰群落主要优势种间的生态位相似性比例(对角线上)和生态位重叠指数(对角线下)
Table 2 Niche similarity (above the diagonal) and niche overlap (below the diagonal) of dominant plant species in Ageratina adenophora community
| 编号 No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.513 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.065 | 0.356 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.955 | 0.000 | |
| S2 | 0.718 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.045 | 0.185 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.558 | 0.000 | |
| S3 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.348 | 0.000 | 0.347 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S4 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.471 | 0.652 | 0.642 | 0.652 | 0.652 | 0.000 | 0.652 | |
| S5 | 0.070 | 0.053 | 0.000 | 0.880 | 0.362 | 0.935 | 0.935 | 0.065 | 0.924 | |
| S6 | 0.614 | 0.432 | 0.599 | 0.735 | 0.554 | 0.297 | 0.297 | 0.356 | 0.297 | |
| S7 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.882 | 0.997 | 0.512 | 0.981 | 0.000 | 0.968 | |
| S8 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.881 | 0.996 | 0.511 | 0.999 | 0.000 | 0.987 | |
| S9 | 0.996 | 0.778 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.611 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S10 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.879 | 0.994 | 0.509 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| 方差比率 Variance ratio (Rv) | 检验统计量 Test statistics (W) | χ2临界值 χ2 thershold (χ20.95, χ20.05) | 测度结果 Measurement results |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.181 | 16.25 | (69.13, 113.14) | 显著负关联 Significantly negative correlation |
表3 主要物种间的总体联结性
Table 3 Overall interspecific associations among dominant species
| 方差比率 Variance ratio (Rv) | 检验统计量 Test statistics (W) | χ2临界值 χ2 thershold (χ20.95, χ20.05) | 测度结果 Measurement results |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.181 | 16.25 | (69.13, 113.14) | 显著负关联 Significantly negative correlation |
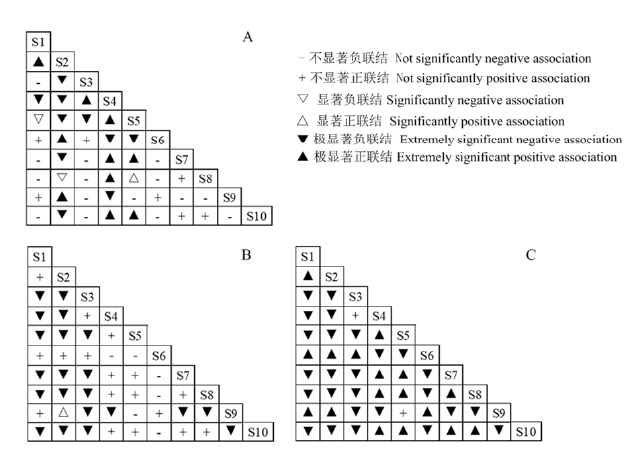
图2 主要物种的χ2检验(A)、联结系数(Cr)(B)和Spearman秩相关分析(C)半矩阵图 编号对应物种见表1
Figure 2 Semi-matrix diagram of χ2-test coefficient (a), association coefficient (b) and Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients of interspecific association among main species Species numbers are shown in Table 1
| 曲线类型 Type of curve | 决定系数 Determination coefficient (r2) | 交点坐标 Nodal corrdinate | 测度结果 Measurement results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | |||
| y= -0.0065x2+ 1.5437x+8.1539 | 0.802 | 40.25 | 59.75 | 不稳定 Unstable |
表4 群落稳定性分析结果(M. Godron法)
Table 4 Results of community stability (M. Godron’s method)
| 曲线类型 Type of curve | 决定系数 Determination coefficient (r2) | 交点坐标 Nodal corrdinate | 测度结果 Measurement results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | |||
| y= -0.0065x2+ 1.5437x+8.1539 | 0.802 | 40.25 | 59.75 | 不稳定 Unstable |
| 项目 Item | 物种分布 Species distribution | 入侵相关指数 Invasion-related index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | ||
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 0.764 | 0.022 | 0.791 | 0.015 | |
| 物种-环境相关系数 Species-environment correlation coefficient | 0.886 | 0.948 | 0.898 | 0.903 | |
| 物种环境关系的累积解释 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relation/% | 76.40 | 78.65 | 79.18 | 80.69 | |
表5 物种分布与入侵相关指数沿环境因子的RDA排序结果
Table 5 RDA calculation of species distribution and invasion-related indexes along environmental gradients
| 项目 Item | 物种分布 Species distribution | 入侵相关指数 Invasion-related index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | ||
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 0.764 | 0.022 | 0.791 | 0.015 | |
| 物种-环境相关系数 Species-environment correlation coefficient | 0.886 | 0.948 | 0.898 | 0.903 | |
| 物种环境关系的累积解释 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relation/% | 76.40 | 78.65 | 79.18 | 80.69 | |
| 环境因子 Environment factors | 物种分布 Species distribution | 入侵相关指数 Invasion-related index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 解释率 Contribution/% | F | P | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 解释率 Contribution/% | F | P | |
| AN | 0.091 | -0.125 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0.52 | 0.192 | -0.436 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.806 |
| AK | 0.781** | -0.385 | 47 | 11.5 | 0.008** | 0.848 | -0.377 | 12.8 | 2.3 | 0.306 |
| AP | 0.289 | -0.363 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.672 | 0.451 | -0.096 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.804 |
| pH | -0.144 | -0.821** | 13.7 | 4.2 | 0.007** | 0.334 | -0.061 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.97 |
| SWC | 0.355 | 0.182 | 3.6 | 1 | 0.35 | 0.442 | 0.454 | 4.6 | 1.9 | 0.166 |
| ST | -0.032 | 0.238* | 19.5 | 7.5 | 0.024* | -0.269 | -0.107 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.884 |
| EC | -0.209 | -0.083 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.628 | -0.317 | -0.386 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.274 |
| CC | 0.257 | 0.241 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.618 | 0.103 | 0.368 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.666 |
| A | -0.379 | -0.628 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.682 | -0.136 | 0.015 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.468 |
| TN | -0.364 | -0.646 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.796 | -0.119 | -0.042 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.808 |
| TK | -0.774 | 0.411 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.498 | -0.901 | 0.162 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.704 |
| TP | -0.759 | 0.550 | 6.4 | 2.1 | 0.166 | -0.911** | 0.253 | 65.7 | 24.9 | 0.002** |
| SOM | -0.334 | -0.604 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 0.654 | -0.111 | -0.012 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 0.458 |
| SA | 0.125 | -0.162 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.468 | 0.251 | -0.046 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 0.369 |
表6 环境因子与RDA排序轴之间的相关系数
Table 6 Correlation coefficients between RDA axis and environment factors
| 环境因子 Environment factors | 物种分布 Species distribution | 入侵相关指数 Invasion-related index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 解释率 Contribution/% | F | P | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 解释率 Contribution/% | F | P | |
| AN | 0.091 | -0.125 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0.52 | 0.192 | -0.436 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.806 |
| AK | 0.781** | -0.385 | 47 | 11.5 | 0.008** | 0.848 | -0.377 | 12.8 | 2.3 | 0.306 |
| AP | 0.289 | -0.363 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.672 | 0.451 | -0.096 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.804 |
| pH | -0.144 | -0.821** | 13.7 | 4.2 | 0.007** | 0.334 | -0.061 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.97 |
| SWC | 0.355 | 0.182 | 3.6 | 1 | 0.35 | 0.442 | 0.454 | 4.6 | 1.9 | 0.166 |
| ST | -0.032 | 0.238* | 19.5 | 7.5 | 0.024* | -0.269 | -0.107 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.884 |
| EC | -0.209 | -0.083 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.628 | -0.317 | -0.386 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.274 |
| CC | 0.257 | 0.241 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.618 | 0.103 | 0.368 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.666 |
| A | -0.379 | -0.628 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.682 | -0.136 | 0.015 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.468 |
| TN | -0.364 | -0.646 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.796 | -0.119 | -0.042 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.808 |
| TK | -0.774 | 0.411 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.498 | -0.901 | 0.162 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.704 |
| TP | -0.759 | 0.550 | 6.4 | 2.1 | 0.166 | -0.911** | 0.253 | 65.7 | 24.9 | 0.002** |
| SOM | -0.334 | -0.604 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 0.654 | -0.111 | -0.012 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 0.458 |
| SA | 0.125 | -0.162 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.468 | 0.251 | -0.046 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 0.369 |
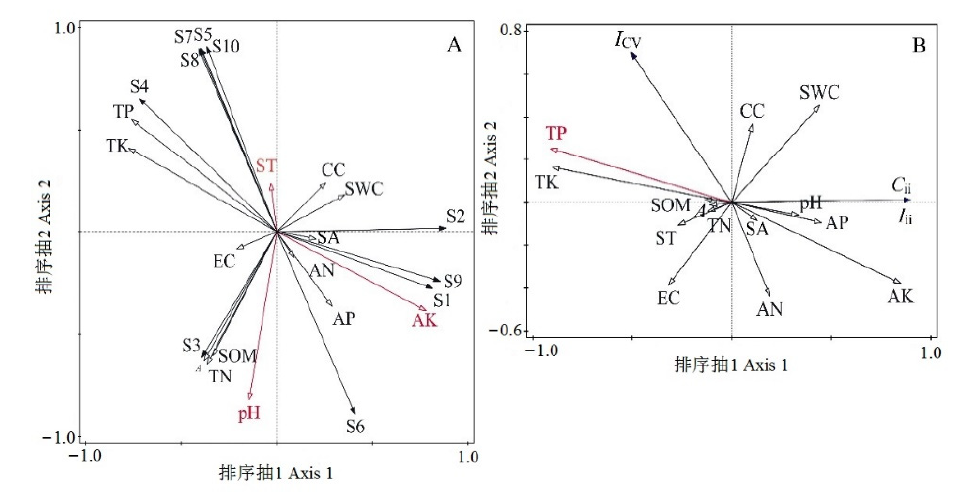
图3 物种分布(A)和入侵相关指数(B)沿环境因子的RDA二维排序图 红色箭头线段表示具有显著影响的环境因子;编号对应物种见表1;pH:土壤pH;SA:坡向;EC:电导率;SOM:土壤有机质;TN:全氮;CC:郁闭度;AN:有效氮;SWC:土壤含水量;AK:有效钾;A:海拔;TP:全磷;TK:全钾;AP:有效磷;Iii:入侵植物入侵强度指数;Cii:群落可入侵性指数;ICV:群落稳定性指数
Figure 3 Two-dimensional RDA ordination diagram of species (A) and invasion-related indexes (B) along environmental gradients The red arrows lines represent the factors with significant effects. Species numbers are shown in Table 1; pH: soil pH; SA: slope aspect; EC: Electric conductivity; SOM: Soil organic matter; TN: Total nitrogen; CC: Canopy closure; AN: available nitrogen; SWC: Soil water content; AK: available potassium: A: Altitude; TP: Total phosphorus; TK: Total potassium; AP: Available phosphorus; Iii: Invasion intensity index of alien invasive plants; Cii: Community invasibility index; ICV: Community stability index
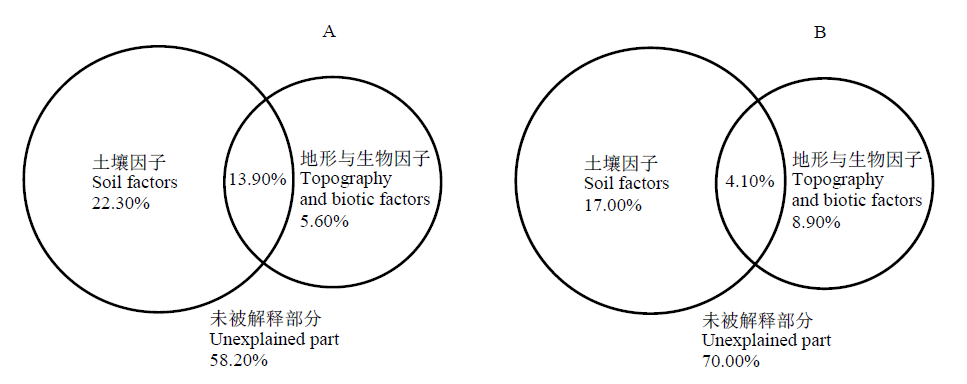
图4 环境因子对物种分布(A)和入侵相关指数(B)的解释率
Figure 4 Explanatory power of different environmental factors for species distribution (A) and invasion-related indexes (B)
| 入侵相关指数 Intrusion-related index | 逐步回归方程 Stepwise regression equation | 调整后决定系数 Adjusted R square (R2adj) | F | P | 容忍度 Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入侵植物入侵强度指数 Invasion intensity index of alien invasive plants (Iii) | Iii=1.125-0.029w(TP) | 0.639 | 25.82 | 0.001** | 1.000 |
| 群落可入侵性指数 Community invasibility index (Cii) | Cii=1.084-0.130w(TP) | 0.665 | 25.82 | 0.002** | 1.000 |
| 群落稳定性指数 Community stability index (ICV) | ICV=0.661-0.006w(AK) | 0.442 | 12.10 | 0.004** | 1.000 |
表7 入侵相关指数与环境因子的逐步回归分析
Table 7 Stepwise regression analysis of intrusion-related indexes and environmental factors
| 入侵相关指数 Intrusion-related index | 逐步回归方程 Stepwise regression equation | 调整后决定系数 Adjusted R square (R2adj) | F | P | 容忍度 Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入侵植物入侵强度指数 Invasion intensity index of alien invasive plants (Iii) | Iii=1.125-0.029w(TP) | 0.639 | 25.82 | 0.001** | 1.000 |
| 群落可入侵性指数 Community invasibility index (Cii) | Cii=1.084-0.130w(TP) | 0.665 | 25.82 | 0.002** | 1.000 |
| 群落稳定性指数 Community stability index (ICV) | ICV=0.661-0.006w(AK) | 0.442 | 12.10 | 0.004** | 1.000 |
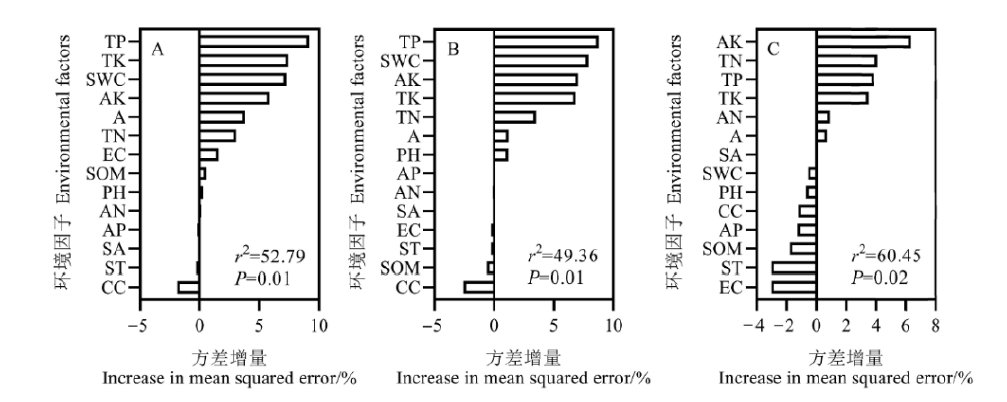
图5 环境因子对入侵植物入侵强度指数(A)、群落可入侵性指数(B)、群落稳定性指数(C)的重要性 环境因子简写详见图3。下同
Figure 5 Importance of environmental factors to invasion intensity index of alien invasive plants (A), community invasibility index (B) and community stability index (C), respectively Abbreviation of environmental factors are the same as in Fig. 3. The same below
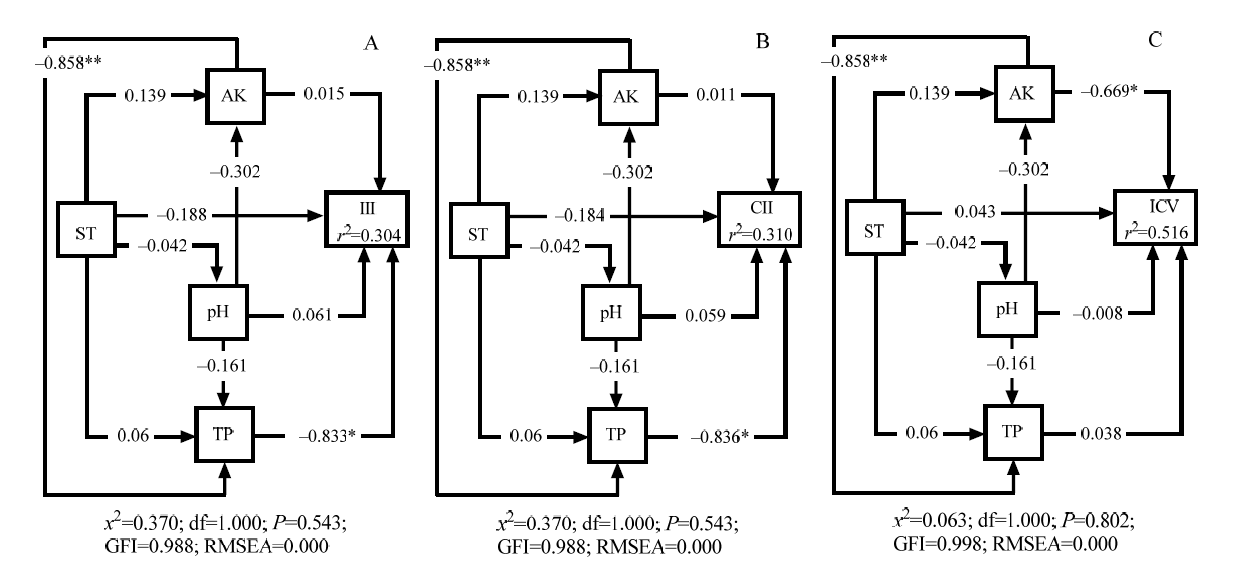
图6 入侵植物入侵强度指数(A)、群落可入侵性指数(B)、群落稳定性指数(C)与环境因子结构方程模型 箭头上的数字是标准化路径系数;R2表示解释率;*P<0.05;**P<0.01
Figure 6 Structural equation model for invasion intensity index of alien invasive plants (A), community invasibility index (B), community stability index (C) and environmental factors The standard path coefficients were shown on arrows; R2 means the rate of explanation; * P<0.05;** P<0.01
| [1] |
CYBILL S, SORAYA R, JEAN-NICOLAS B, et al., 2020. Ecological implications of the replacement of native plant species in riparian systems: unexpected effects of Reynoutria japonica Houtt. leaf litter[J]. Biological Invasions, 22(6): 1917-1930.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DASSONVILLE N, GUILLAUMAUD N, PIOLA F, et al., 2011. Niche construction by the invasive Asian knotweeds (species complex Fallopia): Impact on activity, abundance and community structure of denitrifiers and nitrifiers[J]. Biological Invasions, 13(5): 1115-1133.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FABIAN A, MELINZ L, FLADERER J P, et al., 2021. UHPLC analysis of reynoutria japonica houtt. rhizome preparations regarding stilbene and anthranoid composition and their antimycobacterial activity evaluation[J]. Plants, 10(9): 1809.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GONG W N, XIE B Y, WAN F H, et al., 2010. Molecular cloning, characterization, and heterologous expression analysis of heat shock protein genes (hsp70 and hsp90) of the invasive alien weed, Ageratina adenophora (Asteraceae)[J]. Weed Biology and Management, 10(2): 91-101.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GUI F R, WAN F H, GUO J Y, 2008. Population genetics of Agemtina adenophom using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) molecular markers in China[J]. Plant Biosystems, 142(2): 255-263.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HAUKISALMI V, HENTTONEN H, 1998. Analysing interspecific associations in parasites: Alternative methods and effects of sampling heterogeneity[J]. Oecologia, 116(4): 565-574.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HOLMGREM M, SCHEFFER M, HUSTON M A, 1997. The interplay of facilitation of and competition in plant communities[J]. Ecology, 78(7): 1966-1975.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HU C C, LEI Y B, TAN Y H, et al., 2019. Plant nitrogen and phosphorus utilization under invasive pressure in a montane ecosystem of tropical China[J]. Journal of Ecology, 107(1): 372-386.
DOI URL |
| [9] | LI W H, LUO J N, TIAN X S, et al., 2015. A new strategy for controlling invasive weeds: selecting valuable native plants to defeat them[J]. Scientific Reports, 5(10): 1-11. |
| [10] |
MCCOLL J G, FIRESTONE M K, 1991. Soil chemical and microbial effect of simulated acid rain on clover and soft chess[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 60(3-4): 301-313.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
NAEEM S, KNOPS J M H, TILMAN D, et al., 2000. Plant diversity increases resistance to invasion in the absence of covarying extrinsic factors[J]. Oikos, 91(1): 97-108.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SCHLUTER D, 1984. A variance test for detecting species associations, with some example applications[J]. Ecology, 65(3): 998-1005.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
STEFANOWICZ A M, STANEK M, NOBIS M, et al., 2017. Few effects of invasive plants Reynoutria japonica, Rudbeckia laciniata and Solidago gigantea on soil physical and chemical properties[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 574(1): 938-946.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SUN X, GAO C, GUO L D, 2013. Changes in soil microbial community and enzyme activity along an exotic plant Eupatorium adenophorum invasion in a Chinese secondary forest[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(33): 4101-4108.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TIAN H Q, CHEN G S, ZHANG C, et al., 2010. Pattern and variation of C꞉N꞉P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data[J]. Biogeochemistry, 98: 139-151.
DOI URL |
| [16] | WANG C Y, WEI M, WANG S, et al., 2020. Erigeron annuus (L.) Pers. and Solidago canadensis L antagonistically affect community stability and community invasibility under the co-invasion condition[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 716(10): 137128.1-137128.10. |
| [17] |
WANG R, WANG Y Z, 2006. Invasion dynamics and potential spread of the invasive alien plant species Agemtina adenophom (Asteraceae) in China[J]. Diversity and Distributions, 12(4): 397-408.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG W B, WANG R F, LEI Y B, et al., 2013. High resource capture and use efficiency and prolonged growth season contribute to invasiveness of Eupatorium adenophorum [J]. Plant Ecology, 214(6): 857-868.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YAN X J, YANG W H, CHEN X H, et al., 2020. Soil phosphorus pools, bioavailability and environmental risk in response to the phosphorus supply in the red soil of southern China[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 17(20): 7384.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 陈佳卉, 卜元坤, 苏少峰, 等, 2021. 油松飞播林灌木层主要物种种间联结及其环境解释[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(11): 3512-3522. |
| CHEN J H, BU Y K, SU S F, et al., 2021. Interspecific association of main species in shrub layer of Pinus tabuliformis aerial seeding forest and the environmental interpretation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(11): 3512-3522. | |
| [21] | 陈旭, 2008. 长白山哈泥泥炭地七种苔藓植物种间联结和生态位研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学:24. |
| CHEN X, 2008. Study on interspecific association and niche characteristics of seven bryophyte species in Hani Peatland in Changbai Mountains[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University:24. | |
| [22] |
陈旭, 王国严, 彭培好, 等, 2021. 四川攀西地区云南松群落物种多样性和谱系多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 29(7): 865-874.
DOI |
|
CHEN X, WANG G Y, PENG P H, et al., 2021. Effects of taxonomic and phylogenetic diversity of resident Pinus yunnanensis communities on Ageratina adenophora invasion in the Panxi region, Sichuan Province[J]. Biodiversity Science, 29(7): 865-874.
DOI URL |
|
| [23] | 戴开结, 沈有信, 周文君, 等, 2005. 云南松根际pH与不同磷水平下云南松幼苗根际pH变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 25(12): 2490-2494. |
| DAI K J, SHEN Y X, ZHOU W J, et al., 2005. Rhizosphere pH of Pinus yunnanensis Franch. and rhizosphere pH of P. yunnanensis seedlings at different phosphorous rates[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 25(12): 2490-2494. | |
| [24] | 邓丹丹, 刘棋, 蒋智林, 等, 2015. 紫茎泽兰与不同植物群落土壤养分及酶活性差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(9): 1466-1471. |
| DENG D D, LIU Q, JIANG Z L, et al., 2015. Differences in soil enzymatic activities and soil nutrients of Ageratina adenophora and different plant communities[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(9): 1466-1471. | |
| [25] | 郭佳琦, 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 等, 2021. 喜旱莲子草入侵群落主要物种生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(8): 1607-1616. |
| GUO J Q, CHEN J C, HUANG X, et al., 2021. Niche characteristics and interspecific associations of the dominant species of the communities invaded by Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(8): 1607-1616. | |
| [26] | 郭连金, 王涛, 2009. 空心莲子草入侵对乡土植物群落种间联结性及稳定性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 17(5): 851-856. |
|
GUO L J, WANG T, 2009. Impact of invasion of exotic plant Alternanthera philoxeroides on interspecies association and stability of native plant community[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 17(5): 851-856.
DOI URL |
|
| [27] | 郭忠玲, 马元丹, 郑金萍, 等, 2004. 长白山落叶阔叶混交林的物种多样性、种群空间分布格局及种间关联性研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 15(11): 2013-2018. |
| GUO Z L, MA Y D, ZHENG J P, et al., 2004. Biodiversity of tree species, their populations’ spatial distribution pattern and interspecific association in mixed deciduous broadleaved forest in Changbai Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15(11): 2013-2018. | |
| [28] | 何永福, 聂莉, 陆德清, 等, 2005. 紫茎泽兰的防治研究现状[J]. 贵州农业科学, 33(S1): 50-52. |
| HE Y F, NIE L, LU D Q, et al., 2005. Research status of controlling eupatorium Adenophorum sprengel [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 33(S1): 50-52. | |
| [29] |
黄庆阳, 曹宏杰, 谢立红, 等, 2020. 五大连池火山熔岩台地草本层物种多样性及环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 28(6): 658-667.
DOI |
|
HUANG Q Y, CAO H J, XIE L H, et al., 2020. Species diversity and environmental interpretation of herb layer in lava platform of Wudalianchi, China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 28(6): 658-667.
DOI URL |
|
| [30] |
江焕, 张辉, 龙文兴, 等, 2019. 金钟藤入侵群落的种间联结及生态位特征[J]. 生物多样性, 27(4): 388-399.
DOI |
|
JIANG H, ZHANG H, LONG W X, et al., 2019. Interspecific associations and niche characteristics of communities invaded by Decalobanthus boisianus[J]. Biodiversity Science, 27(4): 388-399.
DOI URL |
|
| [31] | 姜倪皓, 张诗函, 2021. 楚雄市西郊云南松林下草本优势种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2109-2120. |
| JIANG N H, ZHANG S H, 2021. Interspecific association and environmental interpretation of dominant herbaceous species in Pinus yunnanensis forest in the western suburbs of Chuxiong city[J]. Ecology and Environment, 30(11): 2109-2120. | |
| [32] | 李杰, 石元亮, 陈智文, 2011. 我国南方红壤磷素研究概况[J]. 土壤通报, 42(3): 763-768. |
| LI J, SHI Y L, CHEN Z W, 2011. Research on phosphorus in southern red soils of in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 42(3): 763-768. | |
| [33] | 刘润红, 陈乐, 涂洪润, 等, 2020. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落灌木层主要物种生态位与种间联结[J]. 生态学报, 40(6): 2057-2071. |
| LIU R H, CHEN L, XU H R, 2020. Niche and interspecific association of main species in shrub layer of Cyclobalanopsis glauca community in karst hills of Guilin, southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(6): 2057-2071. | |
| [34] | 李小飞, 陈志彪, 陈志强, 等, 2013. 南方红壤侵蚀区芒萁生长特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 水土保持通报, 33(3): 33-37. |
| LI X F, CHEN Z B, CHEN Z Q, et al., 2013. Responses of Disranopteris dichotoma growth to environmental factors in eroded red-soil region of southern china[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(3): 33-37. | |
| [35] | 李霞霞, 张钦弟, 朱珣之, 2017. 近十年入侵植物紫茎泽兰研究进展[J]. 草业科学, 11(2): 283-292. |
| [ LI X X, ZHANG Q D, ZHU X Z, 2017. Progress of the research on invasive plant species Eupatorium adenophorum over the last decade [J]. Pratacultural Science, 11(2): 283-292. | |
| [36] | 刘潮, 冯玉龙, 田耀华, 2007. 紫茎泽兰入侵对土壤酶活性和理化因子的影响[J]. 植物研究, 27(6): 729-735. |
| LIU C, FENG Y L, TIAN Y H, 2007. Effects of eupatorium adenophorum Sprengel invasion on soil enzyme activities and physical and chemical factors[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 27(6): 729-735. | |
| [37] | 刘海, 杜如万, 王勇, 等, 2017. 紫茎泽兰对四川省凉山州共生植物种间联结性及稳定性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(15): 5031-5038. |
| LIU H, DU R W, WANG Y, et al., 2017. Effects of Eupatorium adenophorum on interspecific association and the stability of companion species in Liangshan Prefecture of Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(15): 5031-5038. | |
| [38] | 牛红榜, 刘万学, 万方浩, 2007. 紫茎泽兰 (Ageratina adenophora) 入侵对土壤微生物群落和理化性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 27(7): 3051-3066. |
| NIU H B, LIU W X, WAN F H, 2007. Invasive effects of Ageratina adenophora Sprengel (Asteraceae) on soil microbial community and physical and chemical properties[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(7): 3051-3066. | |
| [39] | 宋紫玲, 彭明俊, 王崇云, 等, 2019. 紫茎泽兰入侵滇中不同森林群落的特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(9): 2630-2637. |
| SONG Z L, PENG M J, WANG C Y, et al., 2019. Characteristics of different forest communities invaded by Ageratina adenophora in central Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(9): 2630-2637. | |
| [40] | 万方浩, 刘万学, 郭建英, 等, 2011. 外来植物紫茎泽兰的入侵机理与控制策略研究进展[J]. 中国科学 (生命科学), 41(1): 13-21. |
| WAN F H, LIU W X, GUO J Y, et al., 2010. Invasive mechanism and control strategy of Ageratina adenophora (Sprengel)[J]. Science in China (Series C), 41(1): 13-21. | |
| [41] | 王高升, 刘文耀, 付昀, 等, 2008. 哀牢山湿性常绿阔叶林林冠和林地腐殖质理化特性、微生物量及酶活性比较[J]. 生态学报, 28(3): 1328-1336. |
| WANG G S, LIU W Y, FU Y, et al., 2008. Comparison of physical and chemical properties and microbial biomass and enzyme activities of humus from canopy and forest floor in a montane moist evergreen broad-leaved forest in Ailao Mts. Yunnan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(3): 1328-1336. | |
| [42] |
王酉石, 储诚进, 2011. 结构方程模型及其在生态学中的应用[J]. 植物生态学报, 35(3): 337-344.
DOI |
|
WANG Y S, CHU C J, 2011. A brief introduction of structural equation model and its application in ecology[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35(3): 337-344.
DOI URL |
|
| [43] | 吴昊, 2015. 秦岭山地松栎混交林土壤养分空间变异及其与地形因子的关系[J]. 自然资源学报, 30(5): 858-869. |
| WU H, 2015. The relationship between terrain factors and spatial variability of soil nutrients for Pine-Oak mixed forest in Qinling Mountains[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 30(5): 858-869. | |
| [44] | 吴佳梦, 徐娜娜, 张文珺, 等, 2019. 浙江舟山定海护城河浮游植物优势种生态位与种间联结性季节性分析[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(2): 429-439. |
|
WU J M, XU N N, ZHANG W J, et al., 2019. Seasonal analysis of the niche and interspecific association of dominant species of phytoplankton in the Dinghai Moat, Zhoushan City[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(2): 429-439.
DOI URL |
|
| [45] | 吴天马, 丁晖, 刘志磊, 等, 2007. 外来入侵植物紫茎泽兰对土壤养分的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 23(2): 94-96. |
| WU T M, DING H, LIU Z L, et al., 2007. Effects of alien invasive plant Eupatorium adenophorum on soil nutrients[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 23(2): 94-96. | |
| [46] | 文亦芾, 艾有群, 2005. 南方红壤磷素化学研究进展和展望[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 20(4): 534-538. |
| WEN Y F, AI Y Q, 2005. Research and expectation on phosphorus transformation in southern red soils[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 20(4): 534-538. | |
| [47] |
谢玉彬, 马遵平, 杨庆松, 等, 2012. 基于地形因子的天童地区常绿树种和落叶树种共存机制研究[J]. 生物多样性, 20(2): 159-167.
DOI |
|
XIE Y B, MA Z P, YANG Q S, et al., 2012. Coexistence mechanisms of evergreen and deciduous trees based on topographic factors in Tiantong region, Zhejiang Province, eastern China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 20(2): 159-167.
DOI URL |
|
| [48] | 熊平生, 李东江, 2012. 中国南方丘陵区不同母岩型红土表土孢粉组合特征研究--以赣南地区为例[J]. 衡阳师范学院学报, 33(6): 77-83. |
| XIONG P S, LI D H, 2012. Research on topsoil pollen assemblages of different parent rock pattern in hilly area of southern China: Example as Gannan region[J]. Journal of Hengyang Normal University, 33(6): 77-83. | |
| [49] | 张峰, 张金屯, 2003. 历山自然保护区猪尾沟森林群落植被格局及环境解释[J]. 生态学报, 23(3): 421-427. |
| ZHANG F, ZHANG J T, 2003. Pattern of forest vegetation and its environmental interpretation in Zhuweigou, Lishan Mountain Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23(3): 421-427. | |
| [50] | 张丽坤, 王朔, 冯玉龙, 2014. 紫茎泽兰种子形态特征和萌发特性与其入侵性的关系[J]. 生态学报, 34(13): 3584-3591. |
| ZHANG L K, WANG S, FENG Y L, 2014. Effects of seed characteristics and germination oil invasiveness of Ageratina Adenophora[J]. Aeta Ecologica Sinica, 34(13): 3584-3591. | |
| [51] | 张金屯, 2018. 数量生态学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 科学出版社: 147-162. |
| ZHANG J T, 2018. Quantitative Ecology[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: Science Press: 147-162. | |
| [52] | 张修玉, 许振成, 宋巍巍, 等, 2010. 紫茎泽兰 (Eupatorium adenophorum) 入侵地的生物多样性[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(7): 1525-1531. |
| ZHANG X Y, XU Z C, SONG WW, et al., 2010. Biodiversity of invaded area of Eupatorium adenophorum [J]. Ecology and Environment, 19(7): 1525-1531. | |
| [53] | 郑晓阳, 赵冲, 刘青青, 等, 2018. 成熟杉木人工林林下草本层生态位特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(2): 332-338. |
| ZHENG X Y, ZHAO C, LIU Q Q, et al., 2018. Niche characteristics of understory herb layer in a mature Chinese fir plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(2): 332-338. | |
| [54] | 郑元润, 2000. 森林群落稳定性研究方法初探[J]. 林业科学, 36(5): 28-32. |
| ZHENG Y R, 2000. Comparison of methods for studying stability of forest community[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 36(5): 28-32. | |
| [55] | 郑昭佩, 宋德香, 刘作新, 2004. 长期灌溉施肥对半干旱区褐土氮、磷和钾库的影响Ⅱ. 对褐土农田土壤钾库的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 23(5): 19-23. |
| ZHENG Z P, SONG D X, LIU Z X, 2004. Effect of long-term irrigation and fertilization on nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium pools of cinnamon soil in semi-arid area Ⅱ. Effect on potassium pool of cinnamon soil farmland[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 23(5): 19-23. | |
| [56] | 朱文达, 曹坳程, 颜冬冬, 等, 2013. 不同林木种群对紫茎泽兰营养生长和生殖生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(11): 1790-1794. |
| ZHU W D, CAO A C, YAN D D, et al., 2013. Vegetative and reproductive growth of Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng in different forest communities[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(11): 1790-1794. |
| [1] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [2] | 寇祝, 卿纯, 袁昌果, 李平. 西藏东北部热泉水中硫氧化菌的多样性及分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [3] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [4] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [5] | 薛文凯, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳. 纳木措水体可培养丝状真菌优势种的时空特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [6] | 李聪, 吕晶花, 陆梅, 杨志东, 刘攀, 任玉连, 杜凡. 滇东南亚热带土壤细菌群落对植被垂直带变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| [7] | 何瑞, 蒋然, 杨芳, 张心凤, 林键銮, 朱小平, 彭松耀. 茂名近岸海域中、小型浮游动物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 142-150. |
| [8] | 刘小菊, 褚江涛, 张越, 单奇. 环境因子和火干扰因子对喀纳斯泰加林柳兰分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 37-43. |
| [9] | 蔡锡安, 黄娟, 吴彤, 刘菊秀, 蒋芬, 王森浩. 植物叶片排放甲烷的初步研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1842-1847. |
| [10] | 郭佳琦, 陈俊辰, 黄旬, 黄佳乐, 赵丽娅, 李兆华. 喜旱莲子草入侵群落主要物种生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1607-1616. |
| [11] | 姚世庭, 芦光新, 邓晔, 党宁, 王英成, 张海娟, 颜珲璘. 模拟增温对土壤真菌群落组成及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1404-1411. |
| [12] | 薛力园, 刘志亮, 宋伟, 安颖, 袁晓博, 陈晓. 秦皇岛海域春季海月水母碟状幼体空间分布及其与海洋环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1240-1248. |
| [13] | 郑诗禹, 张绿水, 郭晓敏, 黄子峻, 肖以华. 不同森林郁闭度环境内空气负氧离子的时空变化及环境影响要素研究——以广州帽峰山为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2204-2212. |
| [14] | 王琪, 张峰, 赵萌莉, 张新宇, 张军. 放牧强度对短花针茅荒漠草原植物群落组成及种间关系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1961-1967. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
